Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Stålhammar G. BAP1. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsBAP1.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- BAP1: BRCA1 Associated Protein-1, located on chromosome 3p21.1
- Loss of BAP1 expression in tumor nuclei is associated with poor patient prognosis in several cancers
- Loss of BAP1 expression can be used to differentiate certain malignant lesions from benign proliferations
Essential features
- BAP1 is functionally a tumor suppressor (Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2014;111:285)
- BAP1 is a deubiquitinase that associates with multiprotein complexes that regulate key cellular pathways, including the cell cycle, cellular differentiation, cell death, gluconeogenesis and the DNA damage response (Nat Rev Cancer 2013;13:153)
- Used by pathologists for:
- Prognostication of uveal melanoma
- Differentiation of metastatic uveal melanoma (at least 77% negative) from metastatic skin melanoma (5% negative) (Br J Cancer 2014;111:1373, Nat Genet 2011;43:1018)
- Differentiation of mesothelioma from benign mesothelial proliferation
Terminology
- BAP1
- UCHL2
- Hucep-6
- HUCEP-13
Pathophysiology
- Ubiquitin tag promotes breakdown of certain proteins
- BAP1 removes ubiquitin tags, thereby inhibiting protein breakdown, which affects diverse cellular processes
- BAP1 is thought to help inhibit cell proliferation and promote apoptosis of damaged cells
- BAP1 protein is normally localized in the cell nucleus due to the presence of a nuclear localization sequence (NLS)
- In the presence of a ubiquitin conjugating enzyme (UBE20), NLS will be covered with ubiquitin localizing the BAP1 protein in the cytoplasm
- Wild type BAP1 protein has the capability to remove the ubiquitin and hence is able to enter back into the nucleus
- Mutated BAP1 protein loses its autodeubiquitination property and remains in the cytoplasm (Ocul Oncol Pathol 2020;6:129)
- BAP1 cytogenetic location: 3p21.1
- Molecular location: base pairs 52,401,004 to 52,410,030 on chromosome 3
Clinical features
- Lack of nuclear BAP1 expression has been associated with aggressive disease and worse survival in uveal melanoma and breast cancer (Transl Vis Sci Technol 2019;8:11, Br J Ophthalmol 2021;105:582, PLoS ONE 2019;14:e0211507)
- Loss of nuclear BAP1 expression can be used to differentiate mesothelioma from reactive mesothelial proliferations (Mod Pathol 2015;28:1043)
- Germline BAP1 mutations have been associated with:
- Familial melanoma (J Natl Cancer Inst 2018;110:1328)
- Meningioma (Neuro Oncol 2017;19:1447)
- Lung adenocarcinoma (J Med Genet 2011;48:856)
- Renal cell carcinoma (Am J Hum Genet 2013;92:974)
- Basal cell carcinoma (Clin Genet 2015;88:273)
- Squamous cell carcinoma (Pathology 2017;49:539)
- A cancer syndrome characterized by early onset of benign melanocytic skin tumors and later in life by a high incidence of mesothelioma, uveal melanoma, cutaneous melanoma and possibly additional cancers (Nat Rev Cancer 2013;13:153)
Interpretation
- Nuclear staining: any visible nuclear staining above background is sufficient for positive classification
- Degree of cytoplasmic staining is prognostically irrelevant but has shown some correlation with gene expression class 2 in uveal melanoma (associated with poor prognosis) (Ocul Oncol Pathol 2020;6:129)
Uses by pathologists
- For prognostication of uveal melanoma: lack of BAP1 expression in tumor nuclei associated with significantly shorter metastasis free survival (Ophthalmology 2018;125:203)
- For differentiation of metastatic uveal melanoma (at least 77% negative) from metastatic skin melanoma (5% negative) (Br J Cancer 2014;111:1373, Nat Genet 2011;43:1018)
- For differentiation of mesothelioma from benign mesothelial proliferation: in biopsies initially interpreted as reactive mesothelial proliferation, BAP1 loss was 100% predictive of malignancy (Mod Pathol 2015;28:1043)
Prognostic factors
- Nuclear staining in < 33% of tumor cell nuclei associated with significantly shorter metastasis free survival and a hazard ratio of > 20 for uveal melanoma metastasis (Transl Vis Sci Technol 2019;8:11, Ocul Oncol Pathol 2020;6:129)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Recommended method for BAP1 scoring of uveal melanoma:
- Make sure the stain works in both external controls (e.g. skin or BAP1 positive uveal melanoma tissue from previous cases) and internal controls (e.g. ganglion layer of retina, normal melanocytes in choroid or iris or optic nerve nuclei)
- Under low magnification (40x), select the tumor area with most intense BAP1 staining
- Within this area, use higher magnification to assess the percentage of tumor cells with nuclear stain
- Count at least 100 cells in each of 3 high power fields (200x - 400x)
- Use the mean score for classification:
- If < 33% of tumor nuclei are positive, classify as BAP1 low
- If ≥ 33% are positive, classify as BAP1 high
- Some pathologists would argue that uveal melanomas usually have either complete absence of staining (0% positive tumor nuclei) or fully retained expression (100% positive tumor nuclei) and that mixed tumors (1 - 99% positive tumor nuclei) are exceptions (J Pathol Clin Res 2018;4:26)
- Regarding melanocytic nevi:
- Benign melanocytic nevi associated with BAP1 germline mutations are often spitzoid or epitheliod
- These melanocytic tumors may have overlapping features with melanoma
- Spitzoid tumors often lack epidermal hyperplasia, Kamino bodies, clefting
- Many lesions are highly cellular, pleomorphic and can contain molecular aberrations occasionally identified in melanoma (Nat Genet 2011;43:1018)
- Benign melanocytic nevi associated with BAP1 germline mutations are often spitzoid or epitheliod
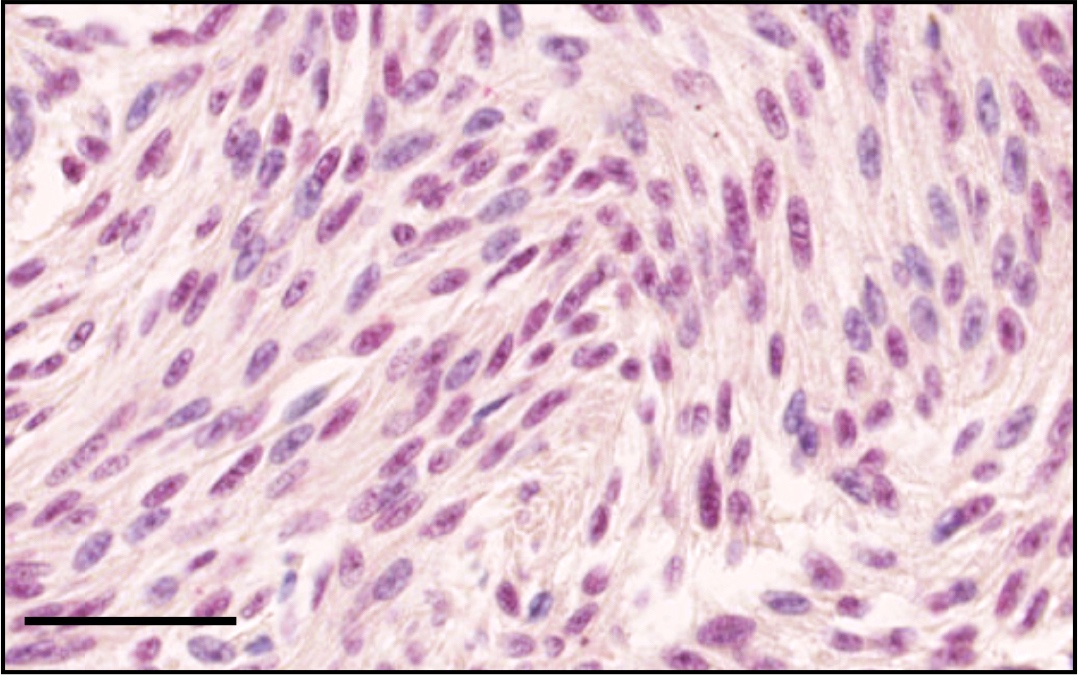
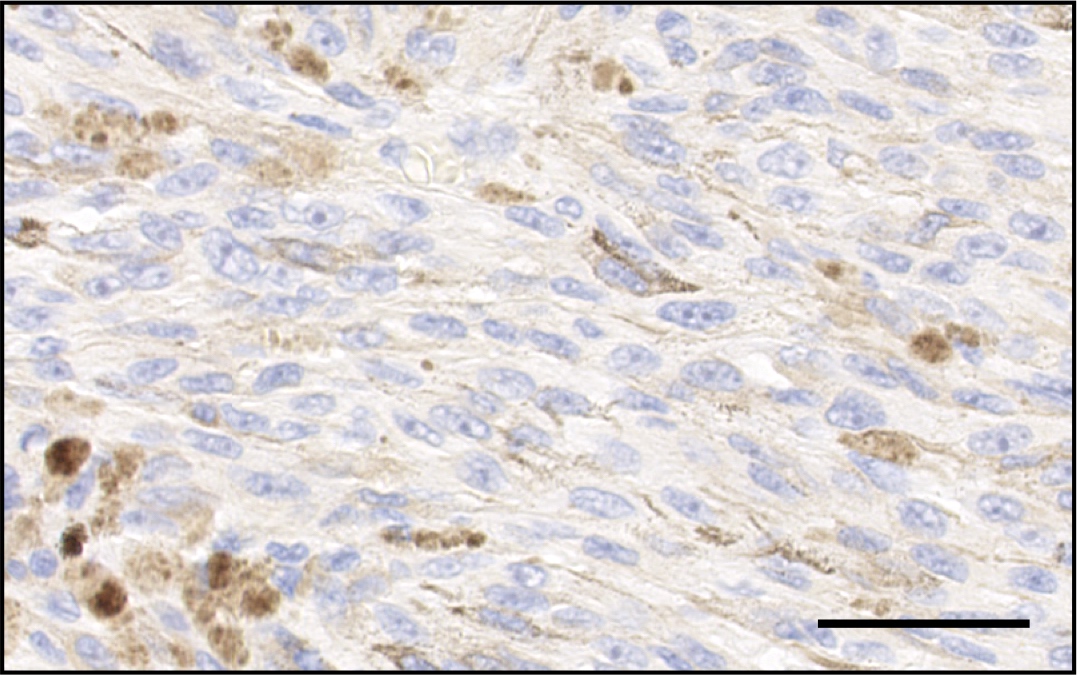
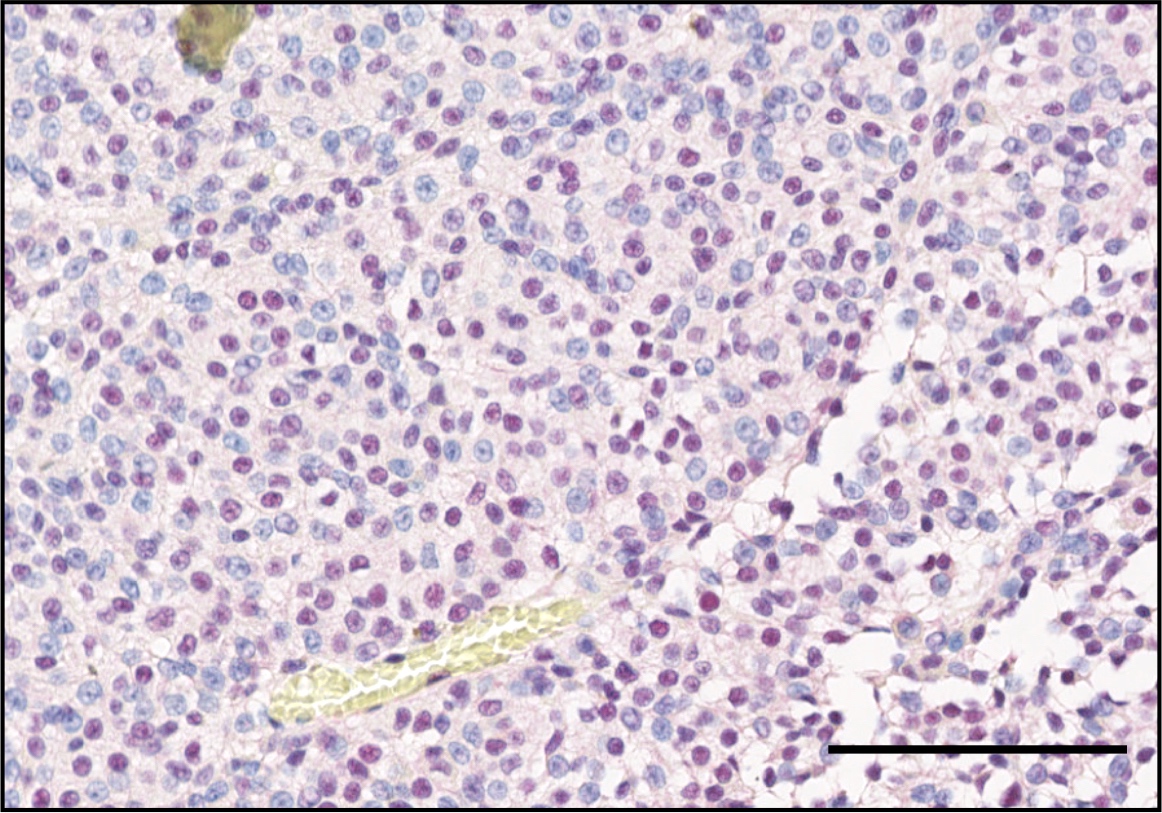
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
- BAP1 is expressed in most normal tissues
- Recommendable positive controls are pancreas, skin, ganglion layer of retina, normal melanocytes or optic nerve nuclei (J Pathol Clin Res 2018;4:26, Br J Ophthalmol 2021;105:582)
Positive staining - disease
- Metastatic skin melanoma (95% positive) (Br J Cancer 2014;111:1373, Nat Genet 2011;43:1018)
Negative staining
- Uveal melanoma: 37 - 63% of tumors negative (Br J Ophthalmol 2021;105:582, Ocul Oncol Pathol 2020;6:129)
- Mesothelioma: 66% of tumors negative (Mod Pathol 2015;28:1043)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Multiplatform analysis has identified 4 molecularly distinct subtypes of uveal melanoma, of which 2 are associated with poor prognosis monosomy 3 and 2 with disomy 3 (Cancer Cell 2017;32:204)
- Disomy 3 is associated with mutations in EIF1AX and SF3B1 (Cancer Cell 2017;32:204)
- Monosomy 3 is associated with aberrant BAP1 (Cancer Cell 2017;32:204)
- In a quarter of BAP1 negative uveal melanomas, no BAP1 mutation is identified (J Pathol Clin Res 2018;4:26)
Sample pathology report
- Eye with uveal melanoma, enucleation:
- BAP1 IHC: low expression (tumor proportion score 10%)
- BAP1 IHC is a prognostic test in uveal melanoma. Classification is as follows: if < 33% of tumor nuclei are positive, classify as low. If ≥ 33% are positive, classify as high. The tumor proportion score is estimated by manual quantification or digital image analysis.
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
C. Loss of nuclear expression of BAP1 is associated with a poor prognosis
Comment Here
Reference: BAP1
Comment Here
Reference: BAP1