Table of Contents
Definition / general | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) imagesCite this page: Shankar V. Metastases. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/spleenmetastases.html. Accessed December 22nd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Splenic metastasis is usually associated with extensive metastases - isolated splenic metastasis is rare
Sites
- Usually from lung, breast, melanoma, colon, ovary (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2000;124:526)
- Rarely from endometrium, brain, liver or salivary glands
Pathophysiology
- Metastasis may be rare due to spleen's immunological function
- Metastases developed by hematogenous, lymphatic or abdominal cavity implantation routes; also direct invasion from lesions in adjacent organs
- Hematogenous or direct seeding is more common
Clinical features
- No specific clinical presentation
- Rarely present with splenic rupture
Diagnosis
- By radiological examination followed by histopathological confirmation
Radiology description
- In ultrasonographic examination, the metastatic foci in the spleen may be hyperechoic, hypoechoic or nonechoic
- In CT, hypodense lesions are seen
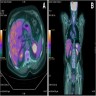
Radiology images
Case reports
- 47 year old woman with metastatic glioblastoma (Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 2003;43:452)
- 54 year old woman with solitary spleen metastasis of endometrial carcinoma (Chin J Cancer 2010;29:30)
- 61 year old man with atraumatic splenic rupture secondary to metastatic non small cell lung cancer (J Surg Case Rep 2013;2013:rjt051)
- 66 year old man with splenic metastasis from carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma of parotid gland (World J Surg Oncol 2014;12:18)
Treatment
- Splenectomy and chemotherapy depending on the primary tumor
Gross description
- Splenic metastasis can be seen as solitary nodule, multiple nodules or diffuse infiltration or cyst
- Rarely resembles follicular lymphoma grossly with multiple nodules
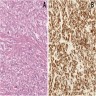
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Histology is similar to primary tumor
- Red pulp may show nodular transformation similar to sclerosing angiomatoid nodular transformation