Table of Contents
Definition / general | Major updates | WHO (2020) | Microscopic (histologic) images | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Alexiev BA. WHO classification. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissuewhoclassification.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- WHO classification of soft tissue tumors serves as a guide to clarify diagnoses among a multidisciplinary team composed of pathologists, radiologists and clinicians (Adv Anat Pathol 2021;28:44)
Major updates
- Adipocytic tumors
- 2 new entities are considered in the new classification: atypical spindle cell / pleomorphic lipomatous tumor and myxoid pleomorphic liposarcoma
- Benign
- Atypical spindle cell / pleomorphic lipomatous tumor (ASPLT) (Adv Anat Pathol 2021;28:44, Pathologica 2021;113:70)
- Malignant
- Myxoid pleomorphic liposarcoma (Adv Anat Pathol 2021;28:44, Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:645)
- Extrarenal angiomyolipoma was deleted in this category and reclassified in the category of tumors of uncertain differentiation and is now referred to as angiomyolipoma (Adv Anat Pathol 2021;28:44)
- Extra-adrenal myelolipoma was removed in this edition
- Fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors
- 3 new benign entities are considered in the new classification
- Benign
- Angiofibroma of soft tissue (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:500)
- EWSR1-SMAD3 fibroblastic tumor (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:522)
- Superficial CD34 positive fibroblastic tumor (Mod Pathol 2014;27:294)
- So called fibrohistiocytic tumors
- Most relevant entity that has disappeared since 2013 is represented by the family of so called malignant fibrous histiocytoma (MFH) (Pathologica 2021;113:70)
- Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma currently represents the correct designation for the storiform and pleomorphic variant of MFH
- Giant cell MFH is currently replaced by 3 distinct tumor types: giant cell tumor of soft tissues, extraskeletal osteosarcoma and giant cell rich osteosarcoma (Pathologica 2021;113:70)
- Myxoid MFH is currently recognized as a purely fibroblastic tumor, identified with the original name myxofibrosarcoma (Pathologica 2021;113:70)
- Inflammatory MFH overlaps entirely with the inflammatory variant of dedifferentiated liposarcomas (Pathologica 2021;113:70)
- Angiomatoid MFH (an indolent lesion most often harboring a EWSR1-CREB1 fusion gene and more rarely a EWSR1-ATF1 or FUS-ATF1 fusion gene) is currently listed within the group of soft tissue lesion of unknown differentiation (Pathologica 2021;113:70, Clin Cancer Res 2007;13:7322)
- Most relevant entity that has disappeared since 2013 is represented by the family of so called malignant fibrous histiocytoma (MFH) (Pathologica 2021;113:70)
- Vascular tumors
- Benign
- Single new entity appearing among vascular lesions is named anastomosing hemangioma (Pathologica 2021;113:70, Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1364)
- Benign
- Smooth muscle tumors
- 2 new entities are considered in the new classification: EBV associated smooth muscle tumors and inflammatory leiomyosarcoma (Pathologica 2021;113:70)
- Intermediate
- EBV associated smooth muscle tumor / smooth muscle tumor of uncertain malignant potential (Front Immunol 2018;9:368)
- Malignant
- Inflammatory leiomyosarcoma (Mod Pathol 2018;31:93)
- Peripheral nerve sheath tumors
- Single major change introduced by the 2020 WHO classification is the recognition that so called melanotic schwannoma actually represents a clinically aggressive neoplasm (no longer belonging to the intermediate category) and is consequently relabeled as malignant melanotic nerve sheath tumor (Pathologica 2021;113:70)
- Malignant
- Malignant melanotic nerve sheath tumor (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:94)
- Tumors of uncertain differentiation
- NTRK rearranged spindle cell neoplasms (excluding infantile fibrosarcoma that represent a distinct clinicopathologic entity defined molecularly by the presence of NTRK3-ETV6 fusion gene) represent an emerging group of molecularly defined rare soft tissue tumors (Pathologica 2021;113:70)
- Prognosis of NTRK rearranged adult tumors appear to be related to histological grade
- NTRK rearranged spindle cell neoplasm
- This provisional category includes the recently described lipofibromatosis-like neural tumor and NTRK rearranged neoplasm resembling peripheral nerve sheath tumors (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1407, Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2018;57:611, Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:435, J Pathol 2016;238:700)
- Undifferentiated small round cell sarcoma of bone and soft tissue
- This new section contains not only the prototypical round cell sarcoma named Ewing sarcoma but also 3 distinct subsets that differs from Ewing sarcoma clinically, pathologically and molecularly (Pathologica 2021;113:70):
- Round cell sarcomas with EWSR1 gene fusion with non-ETS family members (Virchows Arch 2020;476:109, Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1112, Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:220, Mod Pathol 2019;32:1593)
- CIC rearranged sarcomas (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2012;51:207, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:941)
- BCOR rearranged sarcomas (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:604)
- This new section contains not only the prototypical round cell sarcoma named Ewing sarcoma but also 3 distinct subsets that differs from Ewing sarcoma clinically, pathologically and molecularly (Pathologica 2021;113:70):
WHO (2020)
-
Adipocytic tumors ICD-O
- Benign
- Lipoma, NOS8850/0
- Intramuscular lipoma8856/0
- Chondrolipoma
- Lipomatosis
- Diffuse lipomatosis
- Multiple symmetrical lipomatosis
- Pelvic lipomatosis
- Steroid lipomatosis
- HIV lipodystrophy
- Lipomatosis of nerve
- Lipoblastomatosis8881/0
- Angiolipoma, NOS8861/0
- Cellular angiolipoma
- Myolipoma8890/0
- Chondroid lipoma8862/0
- Spindle cell lipoma8857/0
- Atypical spindle cell / pleomorphic lipomatous tumor 8857/0
- Hibernoma8880/0
- Lipoma, NOS8850/0
- Intermediate (locally aggressive)
- Malignant
- Liposarcoma, well differentiated, NOS8851/3
- Lipoma-like liposarcoma8851/3
- Inflammatory liposarcoma8851/3
- Sclerosing liposarcoma8851/3
- Dedifferentiated liposarcoma8858/3
- Myxoid liposarcoma8852/3
- Pleomorphic liposarcoma8854/3
- Myxoid pleomorphic liposarcoma8859/3
- Liposarcoma, well differentiated, NOS8851/3
-
Fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors ICD-O
- Benign
- Nodular fasciitis8828/0
- Intravascular fasciitis
- Cranial fasciitis
- Proliferative fasciitis8828/0
- Proliferative myositis8828/0
- Elastofibroma8820/0
- Fibrous hamartoma of infancy8992/0
- Fibromatosis colli
- Juvenile hyaline fibromatosis
- Inclusion body fibromatosis
- Fibroma of tendon sheath8813/0
- Demoplastic fibroblastoma8810/0
- Myofibroblastoma8825/0
- Calcifying aponeurotic fibroma8816/0
- EWSR1-SMAD3 positive fibroblastic tumor (emerging)
- Angiomyofibroblastoma8826/0
- Cellular angiofibroma9160/0
- Angiofibroma, NOS9160/0
- Nuchal fibroma8810/0
- Acral fibromyxoma8811/0
- Gardner fibroma8810/0
- Nodular fasciitis8828/0
- Intermediate (locally aggressive)
- Solitary fibrous tumor, benign8815/0
- Palmar / plantar type fibromatosis8813/1
- Desmoid type fibromatosis8821/1
- Extra-abdominal desmoid8821/1
- Abdominal fibromatosis8822/1
- Lipofibromatosis8851/1
- Giant cell fibroblastoma8834/1
- Intermediate (rarely metastasizing)
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, NOS8832/1
- Pigmented dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans8833/1
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, fibrosarcomatous8832/3
- Myxoid dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans with myoid differentiation
- Plaque-like dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
- Solitary fibrous tumor, NOS8815/1
- Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor8825/1
- Myofibroblastic sarcoma8825/3
- Superficial CD34 positive fibroblastic tumor8810/1
- Myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcoma8811/1
- Infantile fibrosarcoma8814/3
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, NOS8832/1
- Malignant
- Solitary fibrous tumor, malignant8815/3
- Fibrosarcoma, NOS8810/3
- Myxofibrosarcoma8811/3
- Low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma8840/3
- Sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma8840/3
-
So called fibrohistiocytic tumors ICD-O
- Benign
- Intermediate (rarely metastasizing)
- Malignant
-
Vascular tumors ICD-O
- Benign
- Hemangioma, NOS9120/0
- Intramuscular hemangioma9132/0
- Arteriovenous hemangioma9123/0
- Venous hemangioma9122/0
- Anastomosing hemangioma9120/0
- Epithelioid hemangioma9125/0
- Cellular epithelioid hemangioma
- Atypical epithelioid hemangioma
- Lymphangioma, NOS9170/0
- Cystic lymphangioma9173/0
- Acquired tufted hemangioma9161/0
- Intermediate (locally aggressive)
- Intermediate (rarely metastasizing)
- Retiform hemangioendothelioma9136/1
- Papillary intralymphatic angioendothelioma9135/1
- Composite hemangioendothelioma9136/1
- Neuroendocrine composite hemangioendothelioma
- Kaposi sarcoma9140/3
- Pseudomyogenic (epithelioid sarcoma-like) hemangioendothelioma9138/1
- Malignant
-
Pericytic (perivascular) tumors ICD-O
- Benign and intermediate
- Glomus tumor, NOS8711/0
- Glomangioma8712/0
- Glomangiomyoma8713/0
- Glomangiomatosis8711/1
- Glomus tumor of uncertain malignant potential8711/1
- Myopericytoma8824/0
- Myofibromatosis8824/1
- Myofibroma8824/0
- Infantile myofibromatosis8824/1
- Angioleiomyoma8894/0
- Glomus tumor, NOS8711/0
- Malignant
- Glomus tumor, malignant8711/3
-
Smooth muscle tumors ICD-O
- Benign and intermediate
- Malignant
- Leiomyosarcoma, NOS8890/3
- Inflammatory leiomyosarcoma8890/3
-
Skeletal muscle tumors ICD-O
- Benign
- Rhabdomyoma, NOS 8900/0
- Fetal rhabdomyoma8903/0
- Adult rhabdomyoma8904/0
- Genital rhabdomyoma8905/0
- Rhabdomyoma, NOS 8900/0
- Malignant
- Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma, NOS8910/3
- Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma, pleomorphic8920/3
- Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma8910/3
- Pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma, NOS8901/3
- Spindle cell rhabdomyosarcoma, NOS8912/3
- Ectomesenchymoma8921/3
- Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma, NOS8910/3
-
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors ICD-O
-
Chondro-osseous tumors ICD-O
- Benign
- Chondroma, NOS8922/0
- Chondroblastoma-like soft tissue chondroma
- Chondroma, NOS8922/0
- Malignant
-
Peripheral nerve sheath tumors ICD-O
- Benign
- Schwannoma, NOS9560/0
- Ancient schwannoma9560/0
- Cellular schwannoma9560/0
- Plexiform schwannoma9560/0
- Epithelioid schwannoma
- Microcystic / reticular schwannoma
- Neurofibroma, NOS9540/0
- Ancient neurofibroma
- Cellular neurofibroma
- Atypical neurofibroma
- Plexiform neurofibroma9550/0
- Perineurioma, NOS9571/0
- Reticular perineurioma
- Sclerosing perineurioma
- Granular cell tumor, NOS9580/0
- Nerve sheath myxoma9562/0
- Solitary circumscribed neuroma9570/0
- Plexiform solitary circumscribed neuroma
- Meningioma, NOS9530/0
- Benign triton tumor / neuromuscular choristoma
- Hybrid nerve sheath tumor9563/0
- Perineurioma / schwannoma
- Schwannoma / neurofibroma
- Perineurioma / neurofibroma
- Schwannoma, NOS9560/0
- Malignant
- Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor, NOS9540/3
- Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor, epithelioid9542/3
- Melanotic malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor9540/3
- Granular cell tumor, malignant9580/3
- Perineurioma, malignant9571/3
- Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor, NOS9540/3
-
Tumors of uncertain differentiation ICD-O
- Benign
- Myxoma, NOS8840/0
- Cellular myxoma
- Aggressive angiomyxoma8841/0
- Pleomorphic hyalinizing angiectatic tumor8802/1
- Phosphaturic mesenchymal tumor, NOS8990/0
- Perivascular epithelioid tumor, benign8714/0
- Angiomyolipoma8860/0
- Myxoma, NOS8840/0
- Intermediate (locally aggressive)
- Hemosiderotic fibrolipomatous tumor8811/1
- Angiomyolipoma, epithelioid8860/1
- Intermediate (rarely metastasizing)
- Atypical fibroxanthoma8830/1
- Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma8836/1
- Ossifying fibromyxoid tumor, NOS8842/0
- Mixed tumor, NOS8940/0
- Mixed tumor, malignant, NOS8940/3
- Myoepithelioma, NOS8982/0
- Malignant
- Phosphaturic mesenchymal tumor, malignant8990/3
- NTRK rearranged spindle cell neoplasm (emerging)
- Synovial sarcoma, NOS9040/3
- Epithelioid sarcoma8804/3
- Alveolar soft part sarcoma9581/3
- Clear cell sarcoma, NOS9044/3
- Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma9231/3
- Desmoplastic small round cell tumor8806/3
- Rhabdoid tumor, NOS8963/3
- Perivascular epithelioid tumor, malignant8714/3
- Intimal sarcoma9137/3
- Ossifying fibromyxoid tumor, malignant8842/3
- Myoepithelial carcinoma8982/3
- Undifferentiated sarcoma8805/3
- Spindle cell sarcoma, undifferentiated8801/3
- Pleomorphic sarcoma, undifferentiated8802/3
- Round cell sarcoma, undifferentiated8803/3
- Phosphaturic mesenchymal tumor, malignant8990/3
-
Undifferentiated small round cell sarcoma of bone and soft tissue ICD-O
- Ewing sarcoma9364/3
- Round cell sarcoma with EWSR1 non-ETS fusions9366/3
- CIC rearranged sarcoma9367/3
- Sarcoma with BCOR genetic alterations9368/3
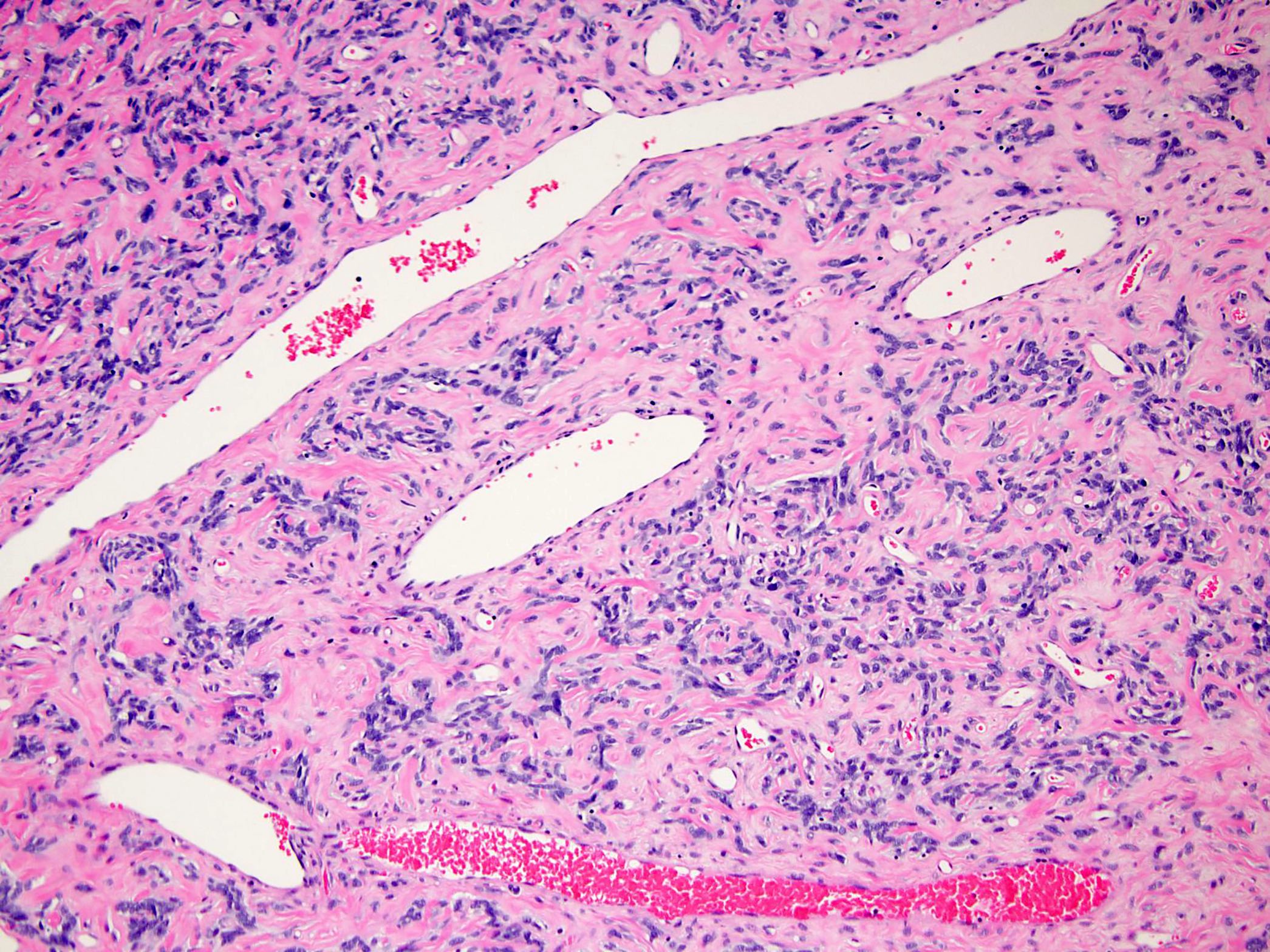
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Borislav A. Alexiev, M.D.
Additional references
Board review style question #1
The single new entity appearing among vascular lesions in the WHO 2020 classification is named anastomosing hemangioma. What is the most common site of anastomosing hemangioma?
- Head and neck
- Intestinal tract
- Kidney and retroperitoneal adipose tissue
- Limbs
- Lungs and uterus
Board review style answer #1
C. Kidney and retroperitoneal adipose tissue
Comment Here
Reference: WHO classification of soft tissue tumors
Comment Here
Reference: WHO classification of soft tissue tumors
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2
E. Solitary fibrous tumor. Solitary fibrous tumor is characterized by haphazardly arranged spindled to ovoid cells with indistinct, pale eosinophilic cytoplasm within a variably collagenous stroma and branching staghorn vascular pattern (hemangiopericytomatous vessels).
Comment Here
Reference: WHO classification of soft tissue tumors
Comment Here
Reference: WHO classification of soft tissue tumors