Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Jiang J, Chung M, Huang YY. Solitary circumscribed neuroma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissuesolitarycircneuroma.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Solitary circumscribed neuroma (SCN) is a benign, slow growing proliferation of Schwann cells and nerve axons within the perineurium
Essential features
- Benign, slow growing proliferation of peripheral nerve cells
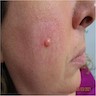
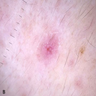
- Small (< 1 cm), solitary, skin colored papulonodule on the face of a middle aged adult
- Surgical excision is usually curative and SCNs rarely recur (even with incomplete excision) (Int J Surg Pathol 2019;27:506)
Terminology
- Also known as palisaded encapsulated neuroma (PEN)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: D36.10 - benign neoplasm of peripheral nerves and autonomic nervous system, unspecified
Epidemiology
- Typically found in middle aged adults
- No difference in incidence between men and women
- Rarely, multiple SCNs can be associated with MEN2B syndrome (Am J Dermatopathol 2014;36:562)
- Rarely, multiple acral SCNs can be associated with PTEN mutations (Am J Dermatopathol 2014;36:562, Pediatr Dermatol 2017;34:e219)
Sites
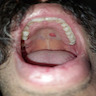
- Commonly found on the head and neck (especially near mucocutaneous junctions) and oral cavity (Int J Surg Pathol 2019;27:506, J Yeungnam Med Sci 2022;39:168)
- Less often found on trunk, extremities and genitalia (Cureus 2016;8:e726, J Dent Sci 2021;16:1041, Dermatol Online J 2020;26:13030/qt3b10r3zk)
- Multiple acral PENs can be associated with PTEN mutations (Pediatr Dermatol 2017;34:e219, J Cutan Pathol 2022;49:82)
Pathophysiology
- Poorly understood at this time
- Thought to be reactive but are often reported without any history of inciting trauma (Cutis 2013;92:167)
- Has not been found to be associated with malignancies
Etiology
- Largely unknown
- Benign neoplasm that is thought to be idiopathic or reactive in nature (Cutis 2013;92:167, J Yeungnam Med Sci 2022;39:168)
- Rarely, multiple SCNs can be associated with MEN2B (Am J Dermatopathol 2014;36:562)
- Rarely, multiple acral SCNs can be associated with PTEN mutations (Pediatr Dermatol 2017;34:e219, J Cutan Pathol 2022;49:82)
Clinical features
- Usually solitary
- Small (< 1 cm), firm, rubbery, skin colored papulonodules, often near mucocutaneous junctions
- Generally asymptomatic
- Reference: VisualDx: Palisaded Encapsulated Neuroma [Accessed 21 August 2024]
Diagnosis
- Definitive diagnosis requires skin biopsy with histopathologic evaluation
Prognostic factors
- Benign tumor but can be cosmetically bothersome
- Surgical excision is curative
- Rarely recurs, even with incomplete excision (J Yeungnam Med Sci 2022;39:168)
- Acral plexiform lesions and multiple lesions can rarely be associated with underlying genetic mutations (Am J Dermatopathol 2014;36:562, Pediatr Dermatol 2017;34:e219, J Cutan Pathol 2022;49:82)
Case reports
- 30 year old woman with painful nodule on the right cheek (Dermatol Online J 2020;26:13030/qt11r6714r)
- 30 year old man with exophytic mass on the hard palate (Clin Case Rep 2023;11:e8212)
- 50 year old man with dome shaped papule on the upper lip (JAAD Case Rep 2024;49:1)
- 52 year old man with solitary papule on the glans penis (Dermatol Online J 2020;26:13030/qt3b10r3zk)
- 63 year old woman with painless cystic nodule on the lower lip (J Yeungnam Med Sci 2022;39:168)
Treatment
- Surgical excision is curative and recurrence is rare (even with incomplete excision) (J Yeungnam Med Sci 2022;39:168)
Clinical images
Gross description
- Firm, well circumscribed, gray-white, sphere to ovoid papule (Am J Surg Pathol 1989;13:574)
Microscopic (histologic) description
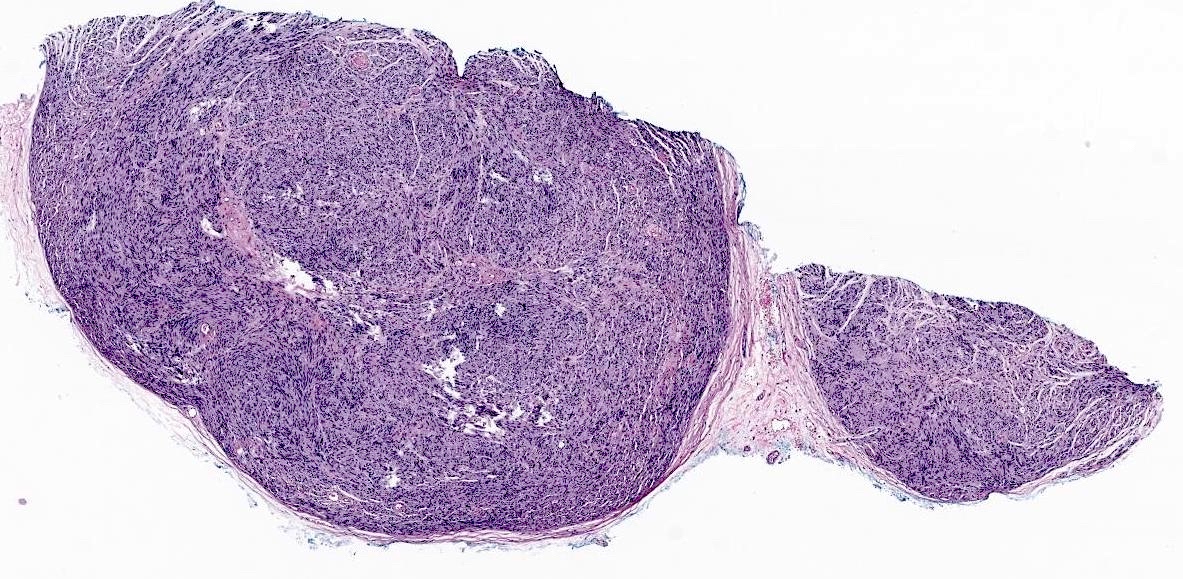
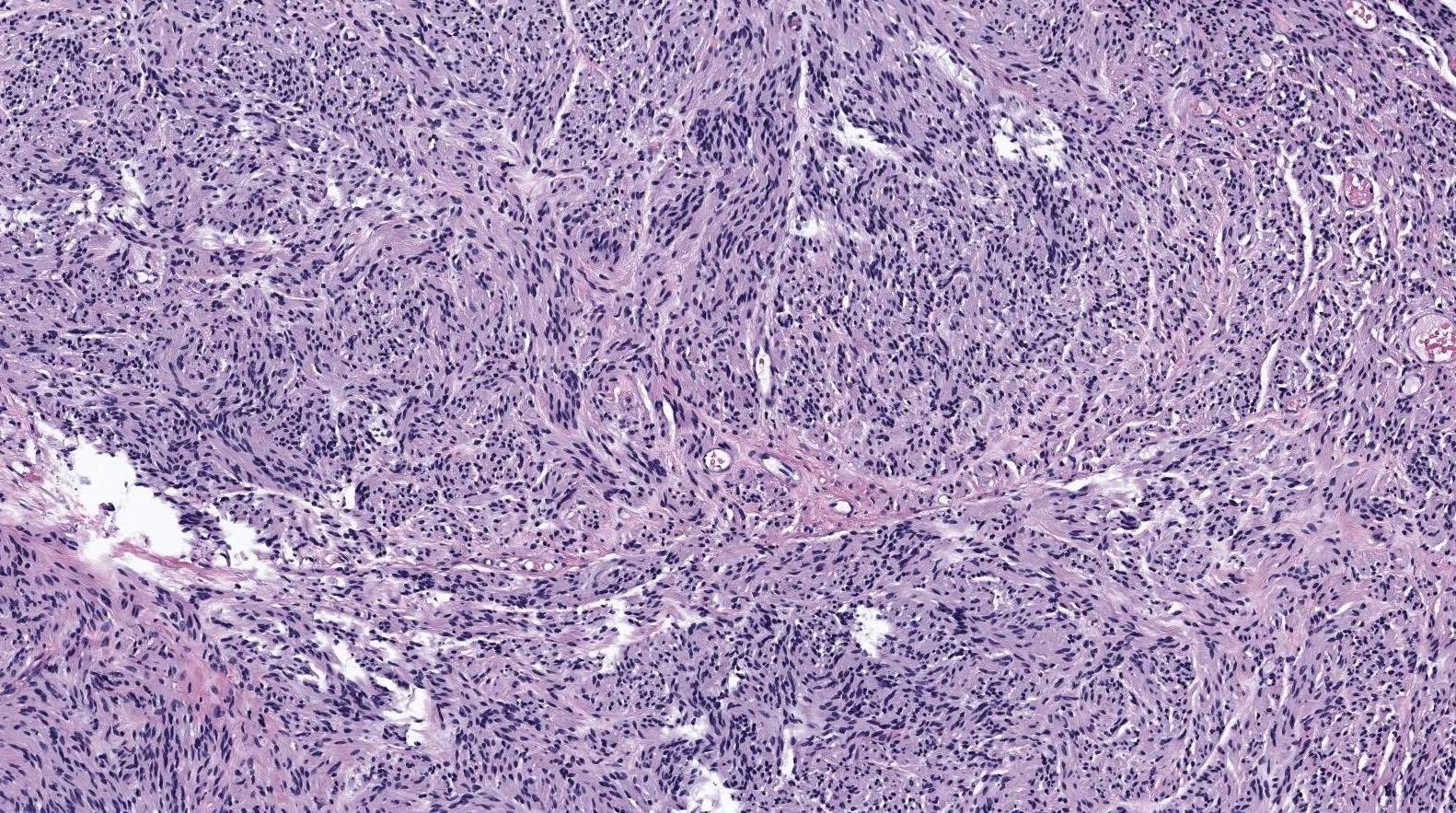
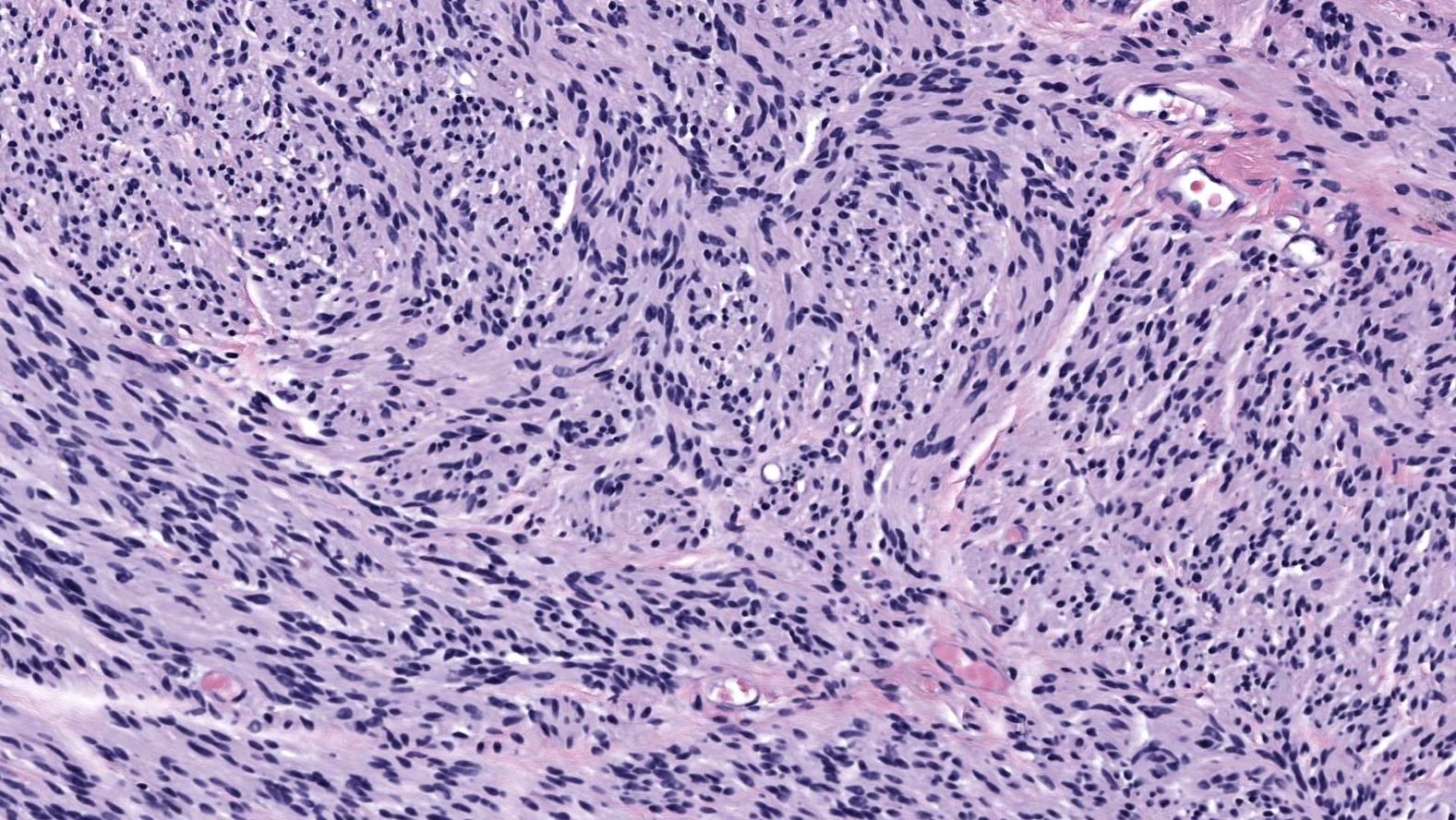
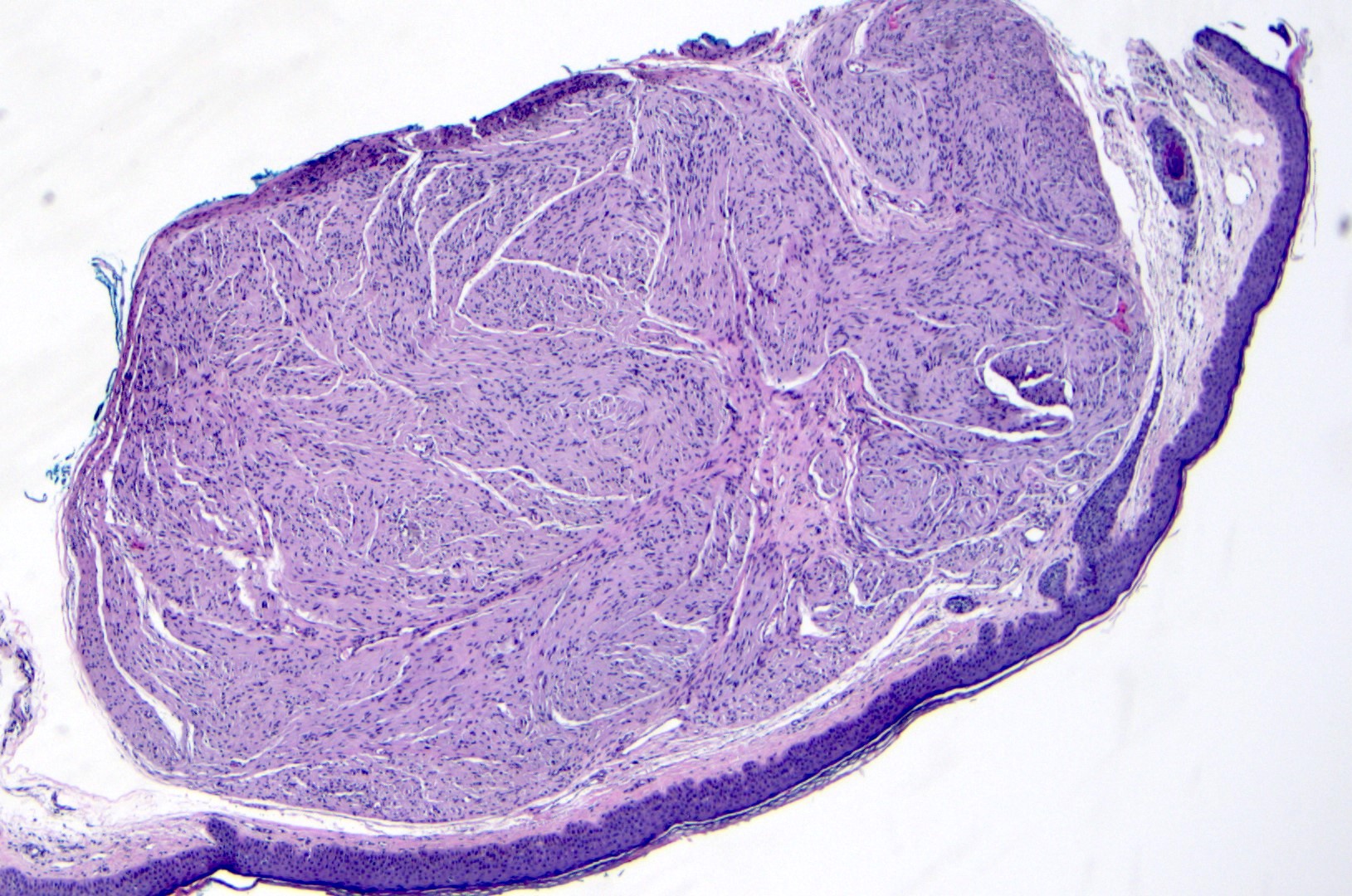
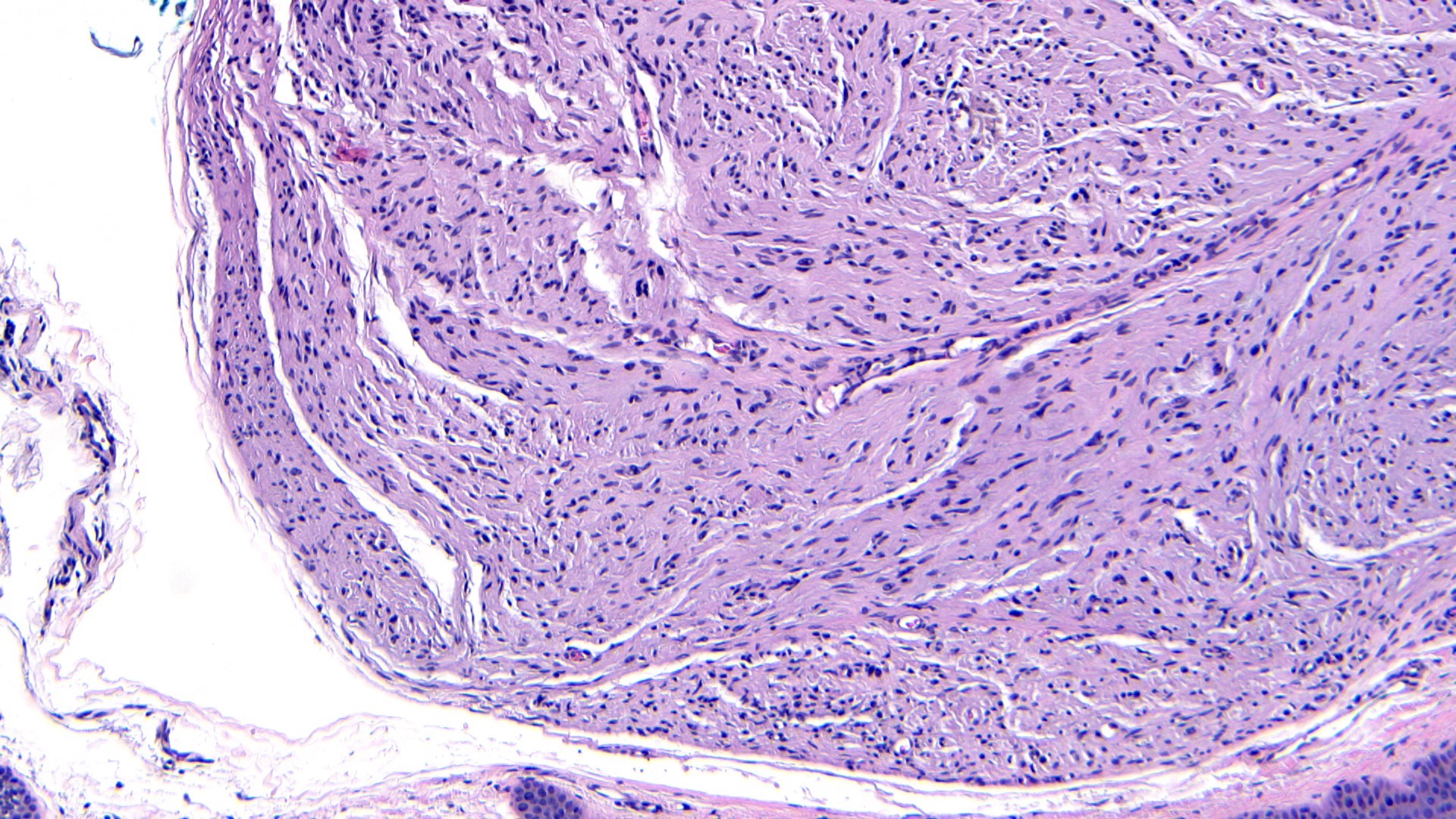
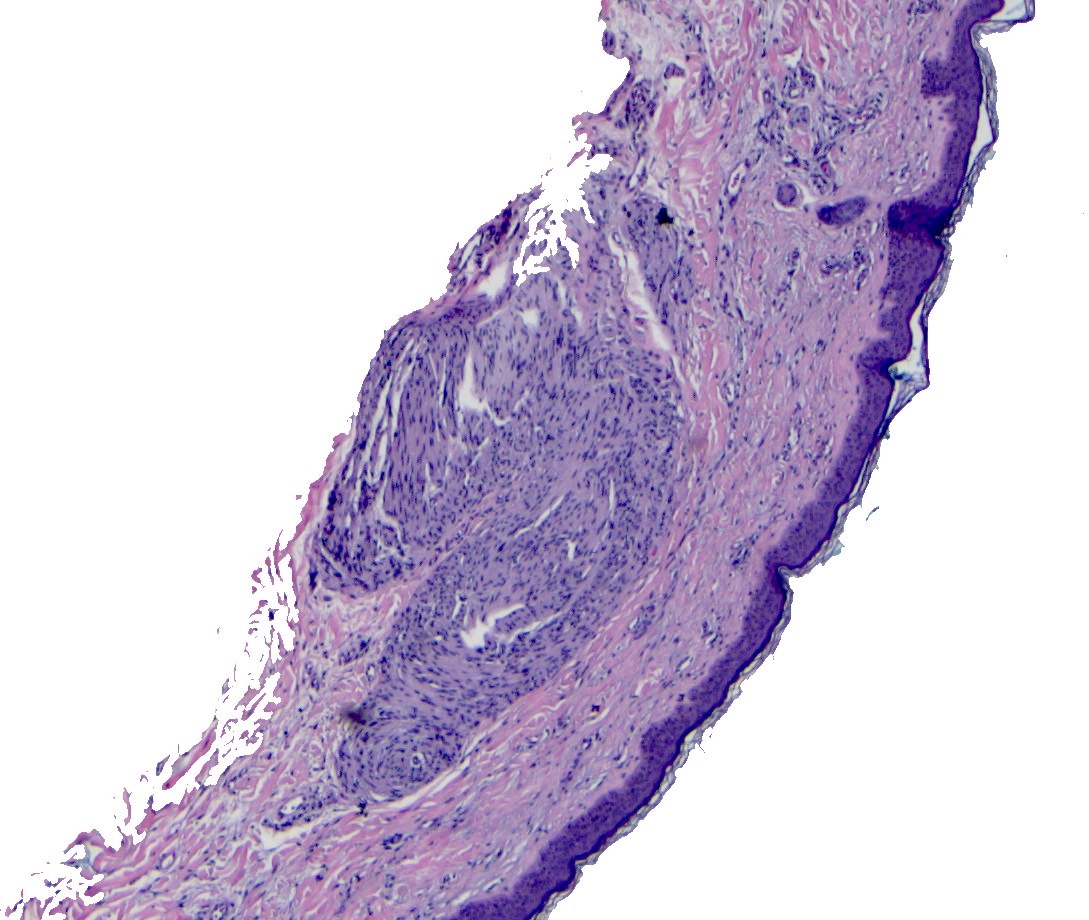
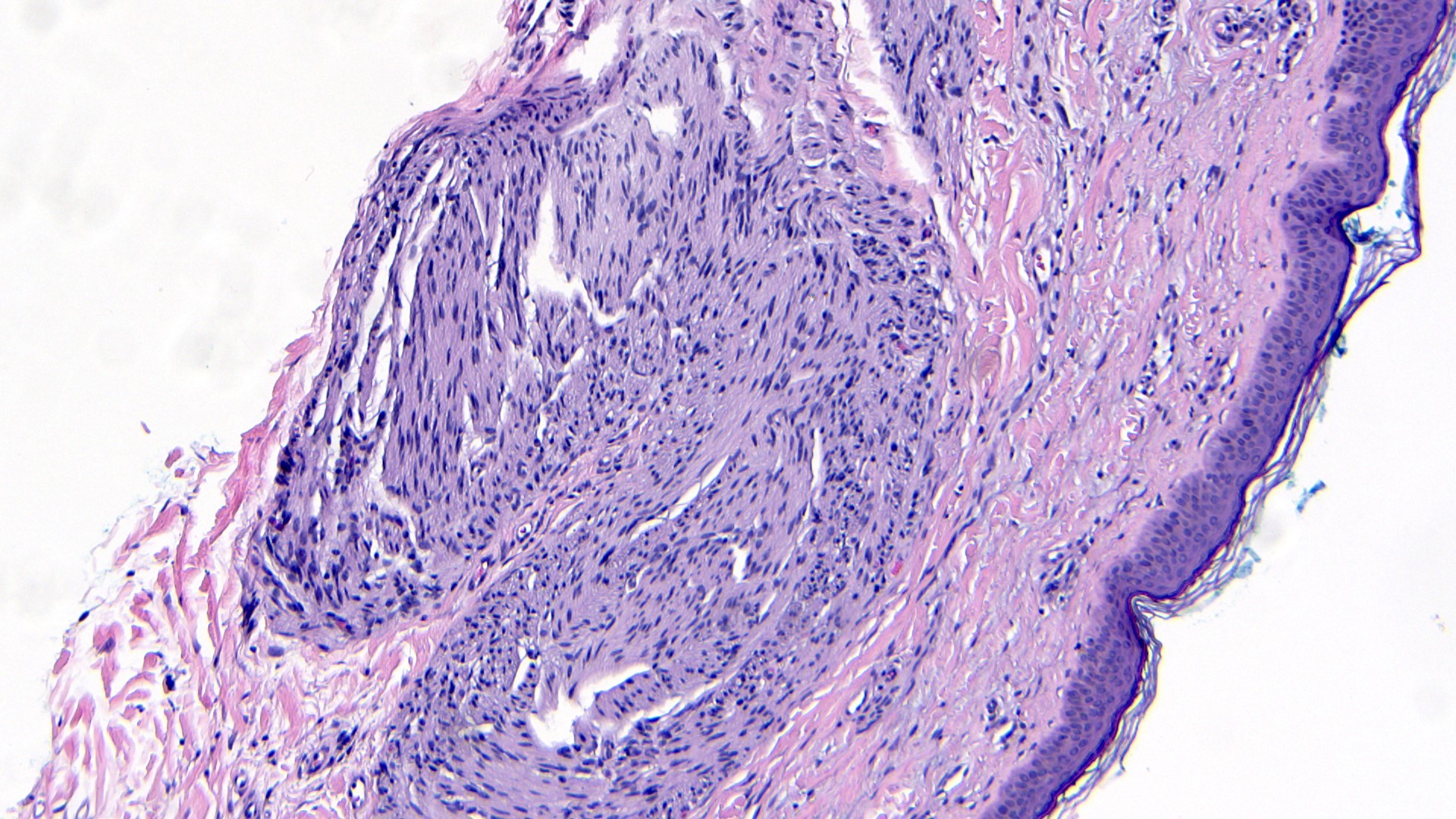
- Well circumscribed dermal tumor
- Thin to incomplete perineural connective tissue capsule surrounding the tumor
- Cells are arranged in fascicles or small nodules
- Distinct artificial cleft and cracks between the fascicles
- Compositional cells are narrow, elongated and wavy with tapered ends
- Multinodular or plexiform growth pattern is uncommon (J Cutan Pathol 1993;20:34)
- Rarely, epithelioid cells are present (Histopathology 1992;20:439)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
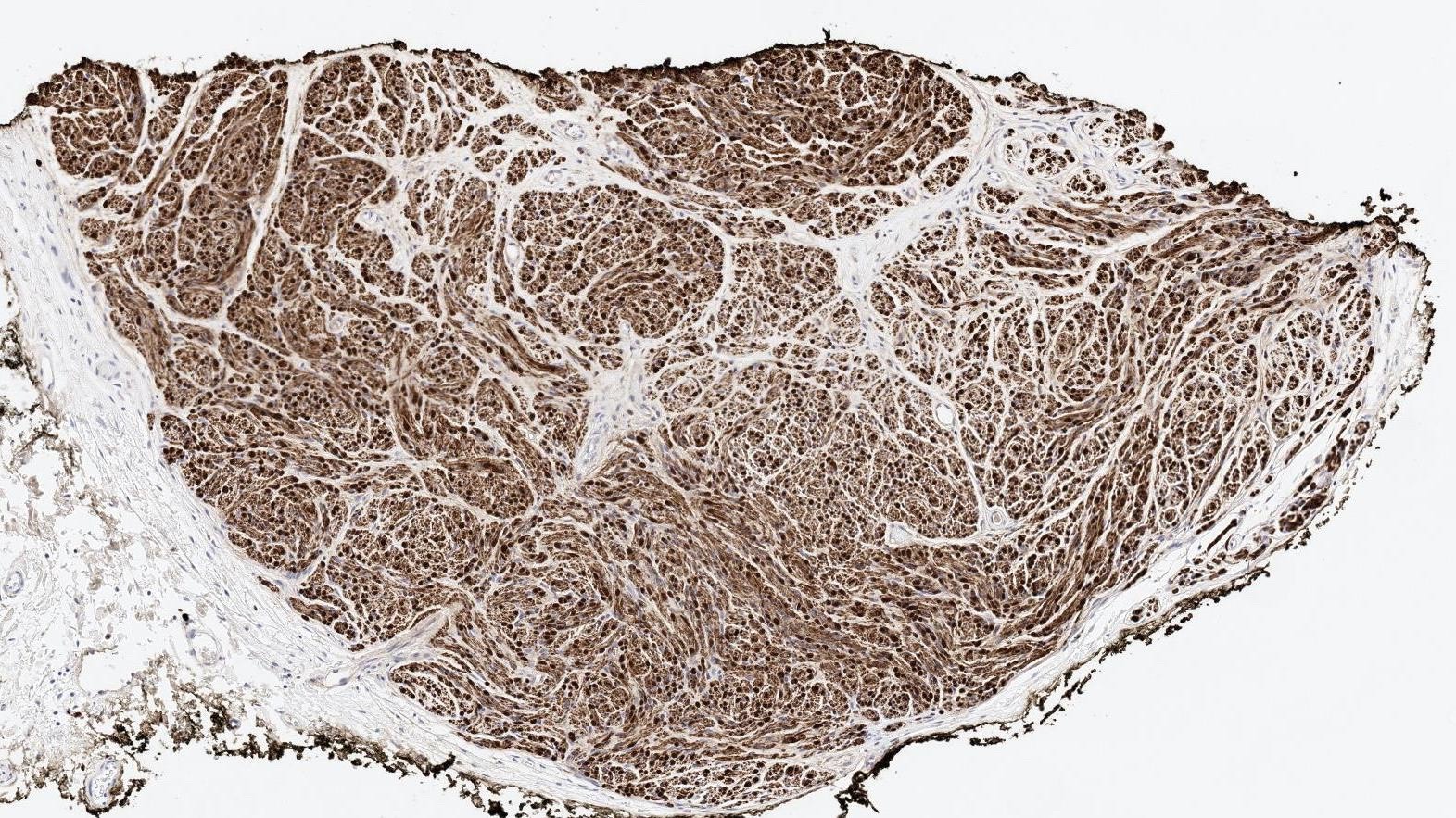
- S100 (strong and diffuse staining) (Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 2011;27:e35)
- EMA (positive only in the perineurial cells of the peripheral capsule) (Am J Surg Pathol 1989;13:574)
- Neurofilament (focal positivity in intermingling axons) (Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 2011;27:e35)
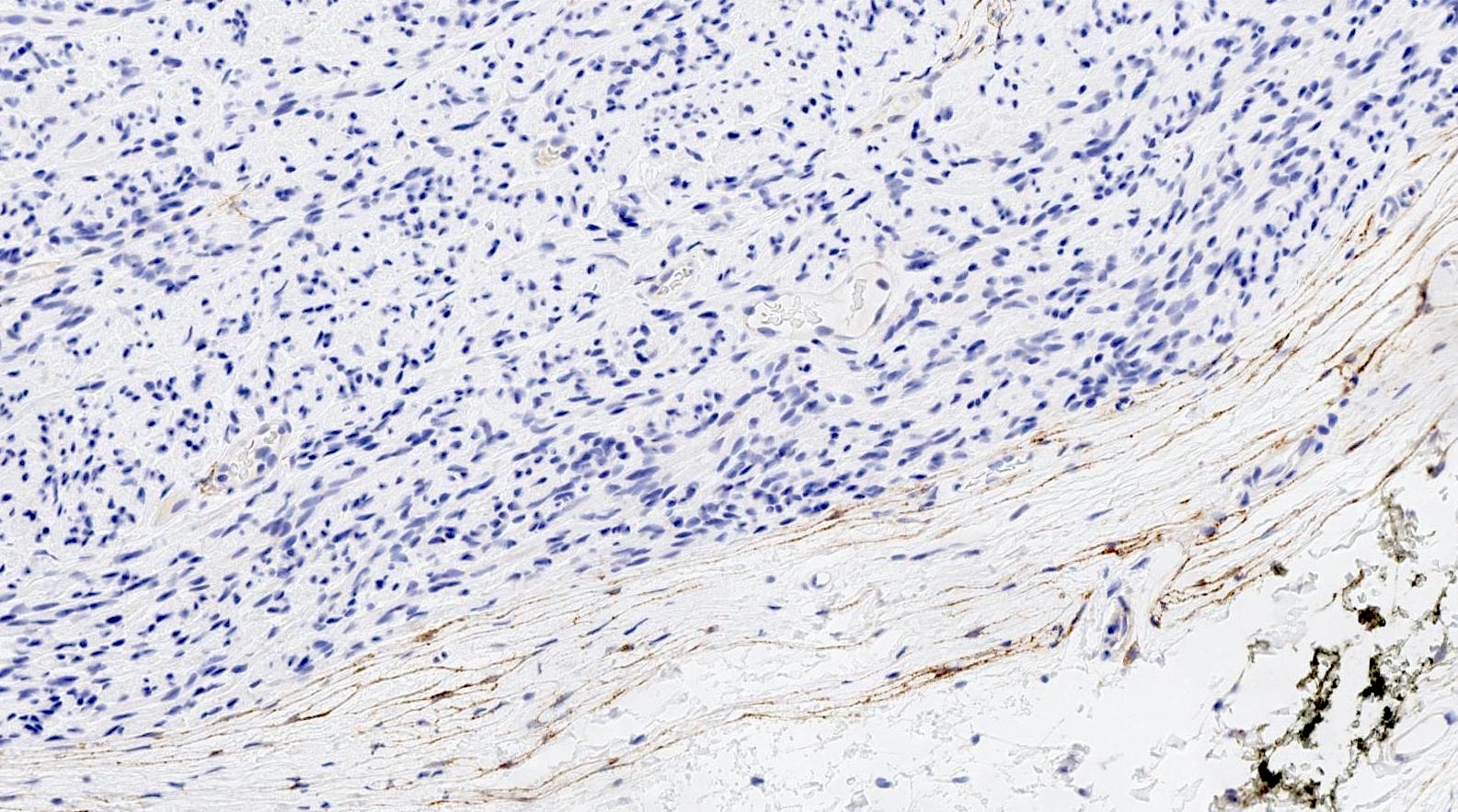
Negative stains
Videos
Palisaded encapsulated neuroma (solitary circumscribed neuroma)
Sample pathology report
- Skin, left cheek, shave biopsy:
- Solitary circumscribed neuroma (palisaded encapsulated neuroma) (see comment)
- Comment: Sections show a well circumscribed dermal nodule with peripheral thin connective tissue capsule. The proliferation is composed of wavy spindle cells in nests and fascicles with intermittent cleft-like spaces.
Differential diagnosis
- Schwannoma:
- More defined and developed capsule
- Displays a varied cell density (Antoni A and Antoni B)
- Lacks the clefting artifact of solitary circumscribed neuroma
- Neurofibroma:
- Lacks capsule
- Heterogeneous appearance due to mixed composition of Schwann cells, fibroblasts, collagen fibers and mast cells
- Weaker S100 staining
- Traumatic neuroma:
- Occurs at site of previous trauma or surgery
- Disorganized organization of nerve bundles
- Also has clefting artifacts
- Has a background fibrotic stroma
- Leiomyoma:
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
B. It is commonly seen in the oral cavity. The image above shows a solitary circumscribed neuroma (palisaded encapsulated neuroma). They are commonly seen on the head and neck and oral cavity. Answer A is incorrect because this is a well circumscribed proliferation composed of wavy spindled Schwannian cells (cigar shaped spindle cells would refer to smooth muscle cells). Answer D is incorrect because they are benign neoplasms and excision is curative, with low risk of recurrence. Answer C is incorrect because rarely, multiple solitary circumscribed neuromas are associated with underlying neurofibromatosis.
Comment Here
Reference: Solitary circumscribed neuroma
Comment Here
Reference: Solitary circumscribed neuroma
Board review style question #2
Which of the following stains is diffusely positive in solitary circumscribed neuroma (SCN)?
- Cytokeratin
- EMA
- S100
- SMA
Board review style answer #2
C. S100. Solitary circumscribed neuroma is diffusely positive for S100. Answer B is incorrect because there is only focal positivity in the peripheral perineural cells of the thin capsule. Answers A and D are incorrect because SCN is negative for cytokeratin and SMA.
Comment Here
Reference: Solitary circumscribed neuroma
Comment Here
Reference: Solitary circumscribed neuroma