Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Electron microscopy images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Akinsanya AO, Dehner C. Phosphaturic mesenchymal tumor. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissuephosphaturic.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Mesenchymal neoplasm involving the bone and soft tissue associated with hyperphosphaturia
- Predominant cause of oncogenic tumor induced osteomalacia (TIO)
Essential features
- Rare spindle cell neoplasm associated with tumor induced osteomalacia
- FN1::FGFR1 fusions lead to overproduction of FGF23 and hyperphosphaturia
- Bland spindle cell lesion with grungy or smudgy calcifications and vascularized stroma
- Predominantly benign lesion with good prognosis when completely excised
Terminology
- Abbreviation: phosphaturic mesenchymal tumor (PMT)
- Other name: phosphaturic mesenchymal tumor, mixed connective tissue type
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8990/0 - phosphaturic mesenchymal tumor, NOS
- ICD-11
- 2F7C & XH9T96 - neoplasms of uncertain behavior of connective or other soft tissue & phosphaturic mesenchymal tumor, benign
- 2F7C & XH3B27 - neoplasms of uncertain behavior of connective or other soft tissue & phosphaturic mesenchymal tumor, malignant
Epidemiology
- Exceedingly rare tumor (Semin Diagn Pathol 2019;36:260)
- Predominantly middle aged adults
- No significant gender predilection (Endocr J 2017;64:675)
- Strong association with chronic hypophosphatemia and osteomalacia
- Rare, nonphosphaturic cases exist
Sites
- Can occur in any soft tissue location
- Mostly involves extremities and acral sites (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:1371)
- Rare in visceral and retroperitoneal locations
- May present multifocal (BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2017;18:79)
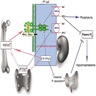
Pathophysiology
- FN1::FGFR1 gene fusions occur in about half of PMT cases (J Pathol 2015;235:539, Virchows Arch 2021;478:757)
- Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) overproduction inhibits phosphate reabsorption in renal tubules and suppresses synthesis of 1,2 dihydroxyvitamin D3 (Endocrinology 2004;145:3087)
- FGF binds predominantly to FGFR1, leading to the activation of proteins involved in cellular proliferation, survival and differentiation
Etiology
- Unknown; osteomalacia has numerous etiologies (i.e., advanced age, vitamin D deficiency secondary to inadequate sun exposure, intestinal malabsorption, parathyroid or renal disease, drugs and toxins, rare inherited genetic disorders including X linked hypophosphatemic rickets or autosomal dominant hypophosphatemic rickets) (Semin Diagn Pathol 2019;36:260)
- Rare reports of chromosomal translocation resulting in α Klotho regulation may predispose to PMTs (Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008;105:3455)
Clinical features
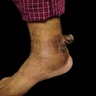
- Bone pain, muscle pain and progressive weakness are common
- Pathologic fractures can occur
- Epistaxis and breathing difficulties with sinonasal lesions
- Lesions arise in superficial and deep soft tissue, ranging from 2 to 14 cm in size (median: 5.6 cm) (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1)
Diagnosis
- Distinctive clinical symptoms guide diagnosis
- Occult tumors can be detected using 68Ga-DOTATATE positron emission tomography (PET) / CT imaging
Laboratory
- Low serum phosphorus
- Low serum 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3
- Elevated serum alkaline phosphatase
- Reference: Endocr Rev 2023;44:323
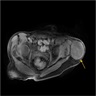
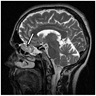
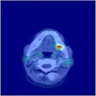
Radiology description
- Computed tomography (CT) scan
- Osteolytic bone lesions
- Narrow zone of transition
- Internal matrix
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Solidly enhancing
- T1 isointense and T2 hyperintense lesions
- Metabolically active lesions can be identified by radionuclide scan, 68Ga-DOTATATE PET / CT imaging, 99mTc sestamibi scintigraphy (Skeletal Radiol 2019;48:119, Semin Diagn Pathol 2019;36:260)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Mostly benign course
Case reports
- 30 year old woman with phosphaturic mesenchymal tumor and de novo liver metastasis (Ther Adv Med Oncol 2024;16:17588359241232092)
- 37 year old man with a 5 cm hip mass (Radiol Case Rep 2019;14:1518)
- 50 year old woman with an ethmoid sinus mass (Medicina (Kaunas) 2020;56:34)
- 52 year old man with a lumbar spine mass and tumor induced osteomalacia (TIO) (Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99:e18603)
- 66 year old woman with 4.5 cm nodule on left thigh (JAAD Case Rep 2021;19:34)
- 70 year old man with tumor induced osteomalacia and a 2.5 cm right foot lesion (Radiol Case Rep 2021;16:1355)
Treatment
- Complete resection is curative in benign lesions
- FGFR inhibitors reduce tumor burdens in PMT patients
Gross description
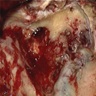
- Well circumscribed lesion
- Focal cystic and hemorrhagic areas (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:1371)
- May have a component of fat
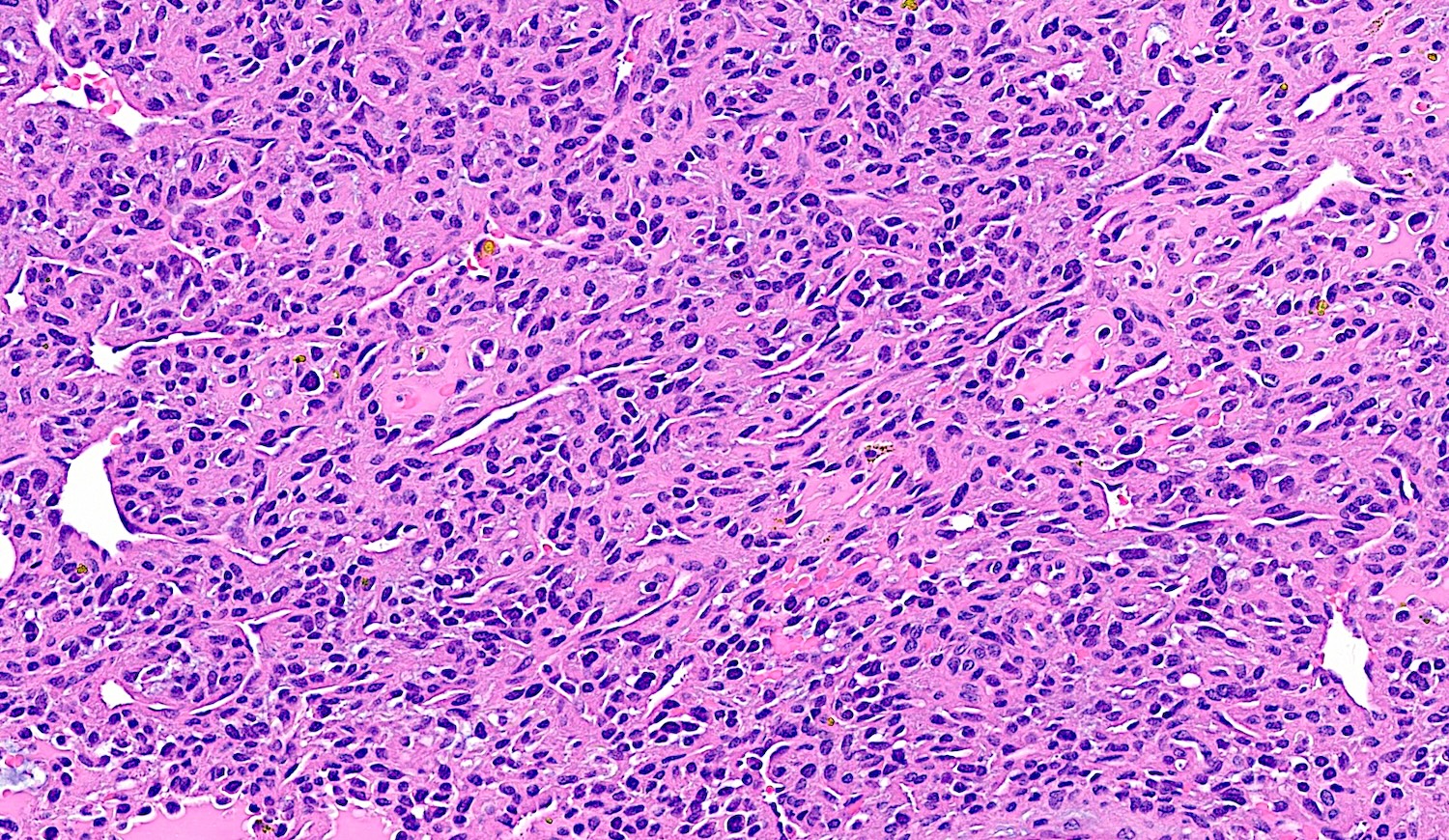
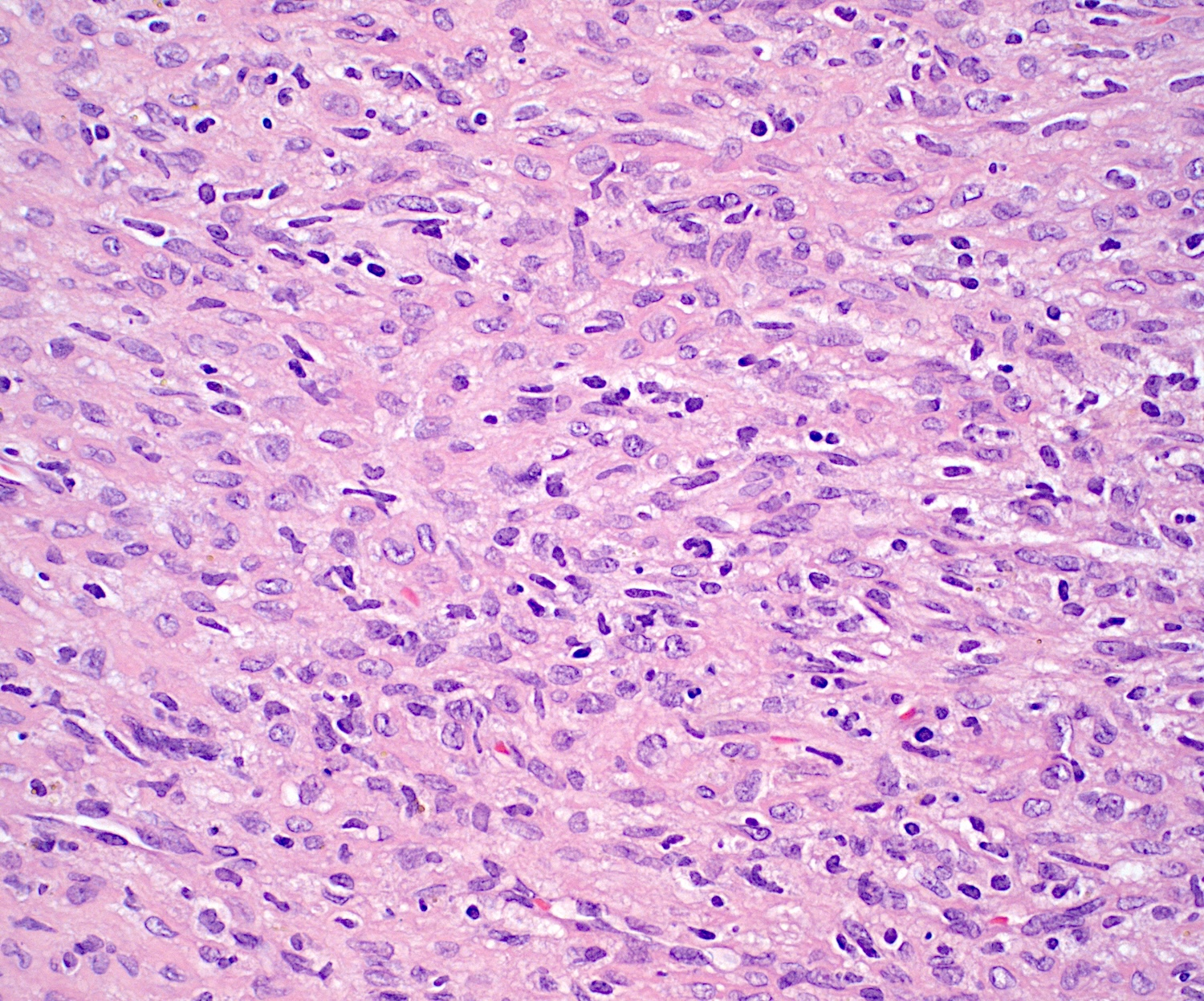
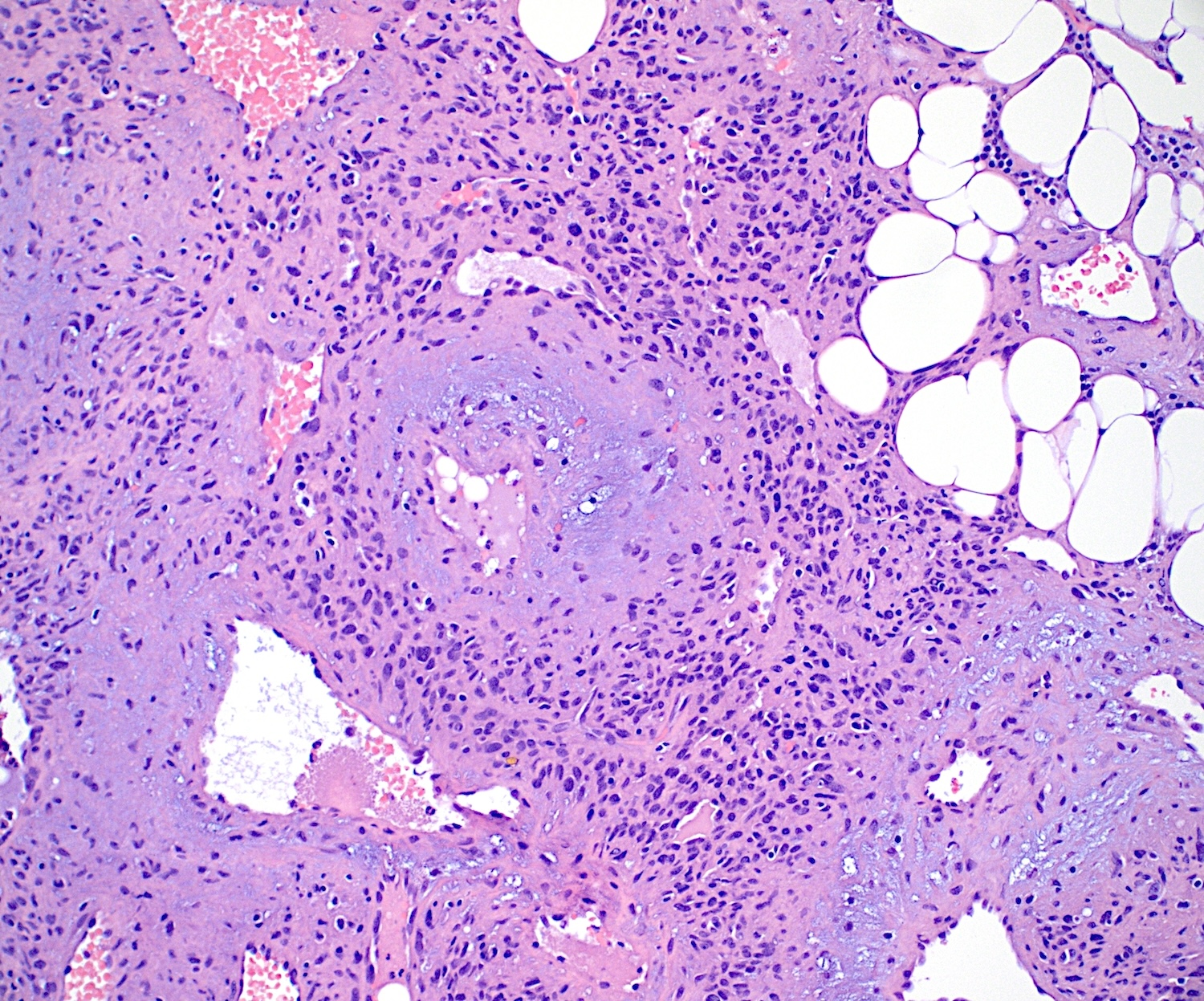
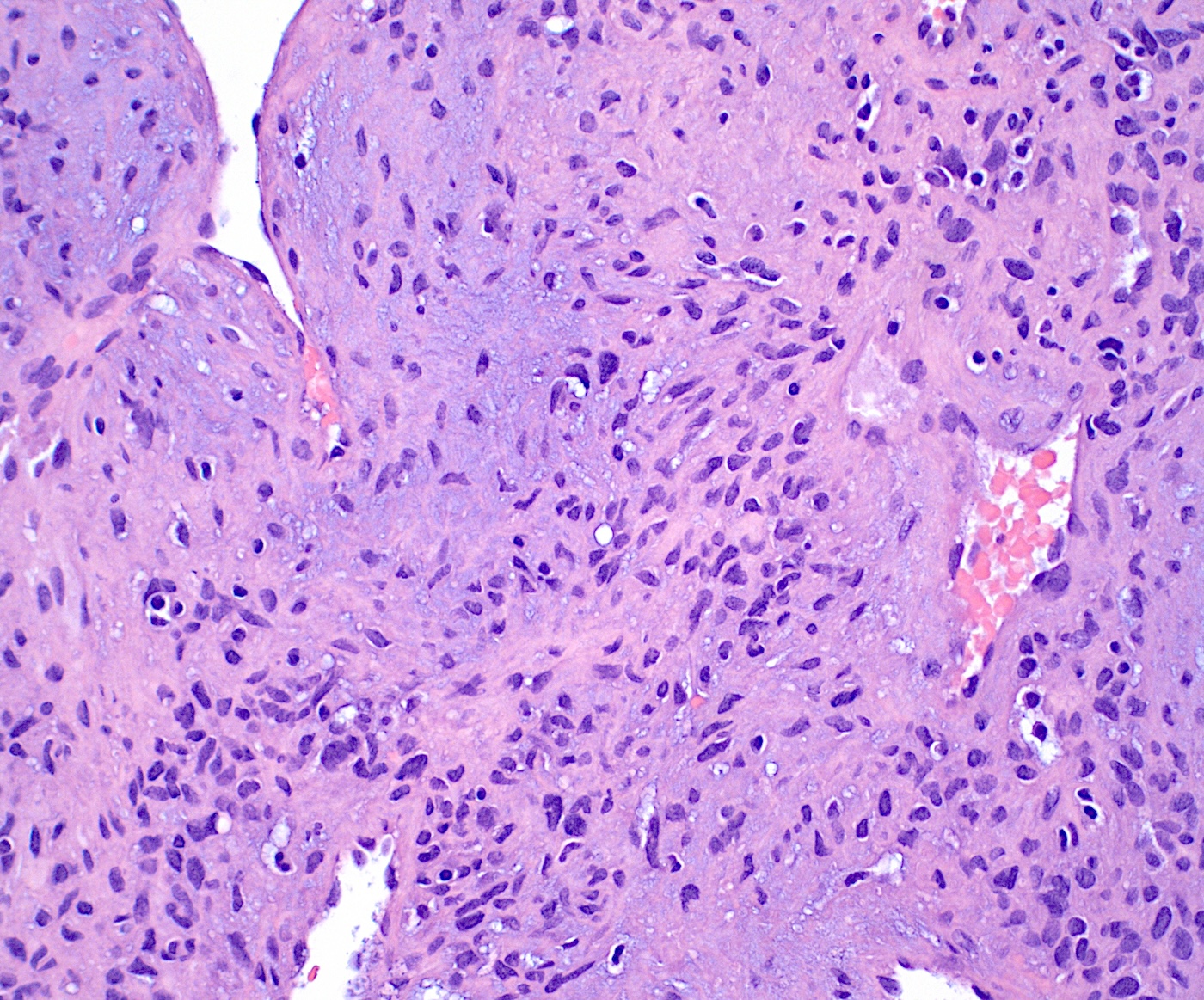
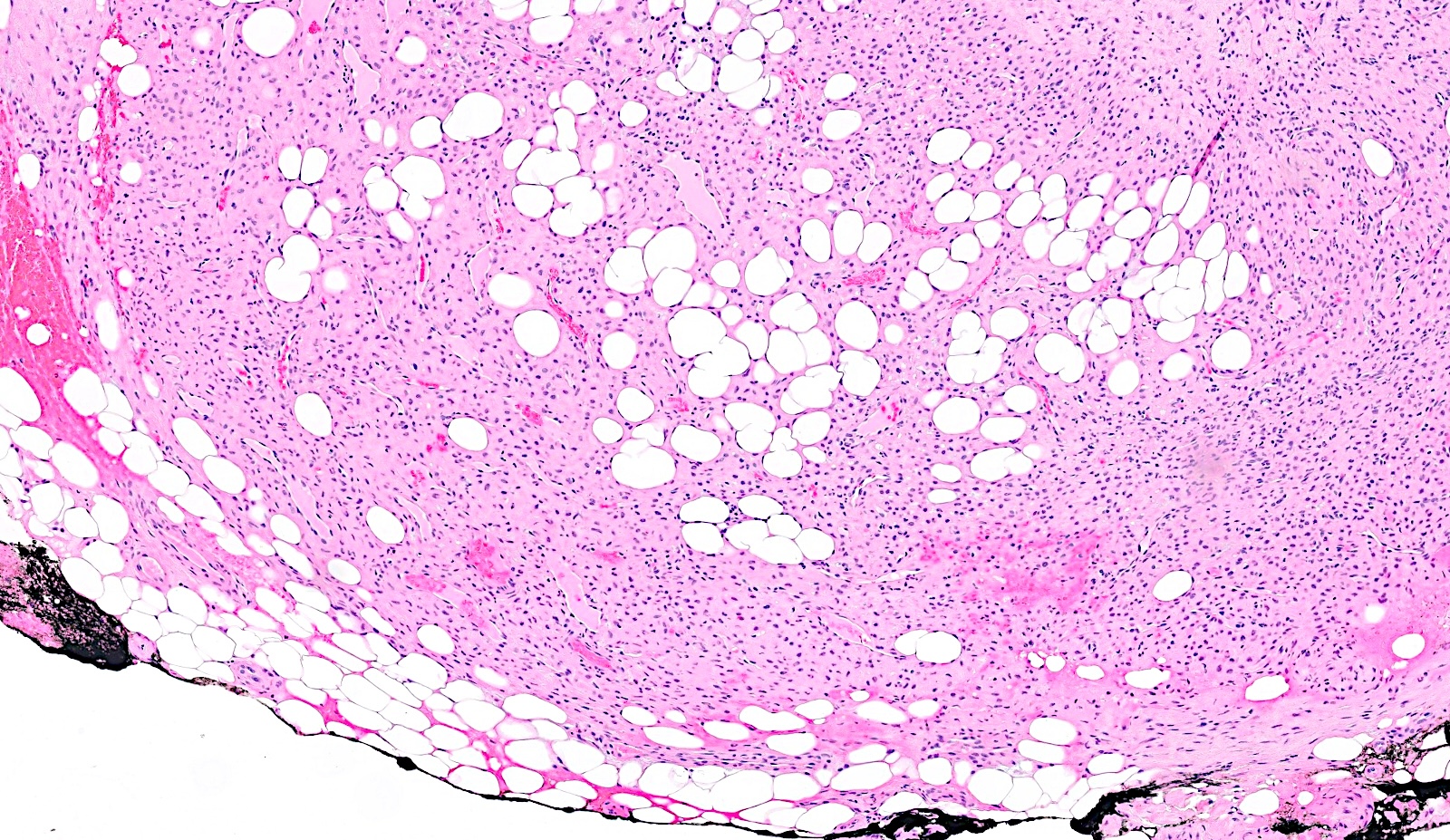
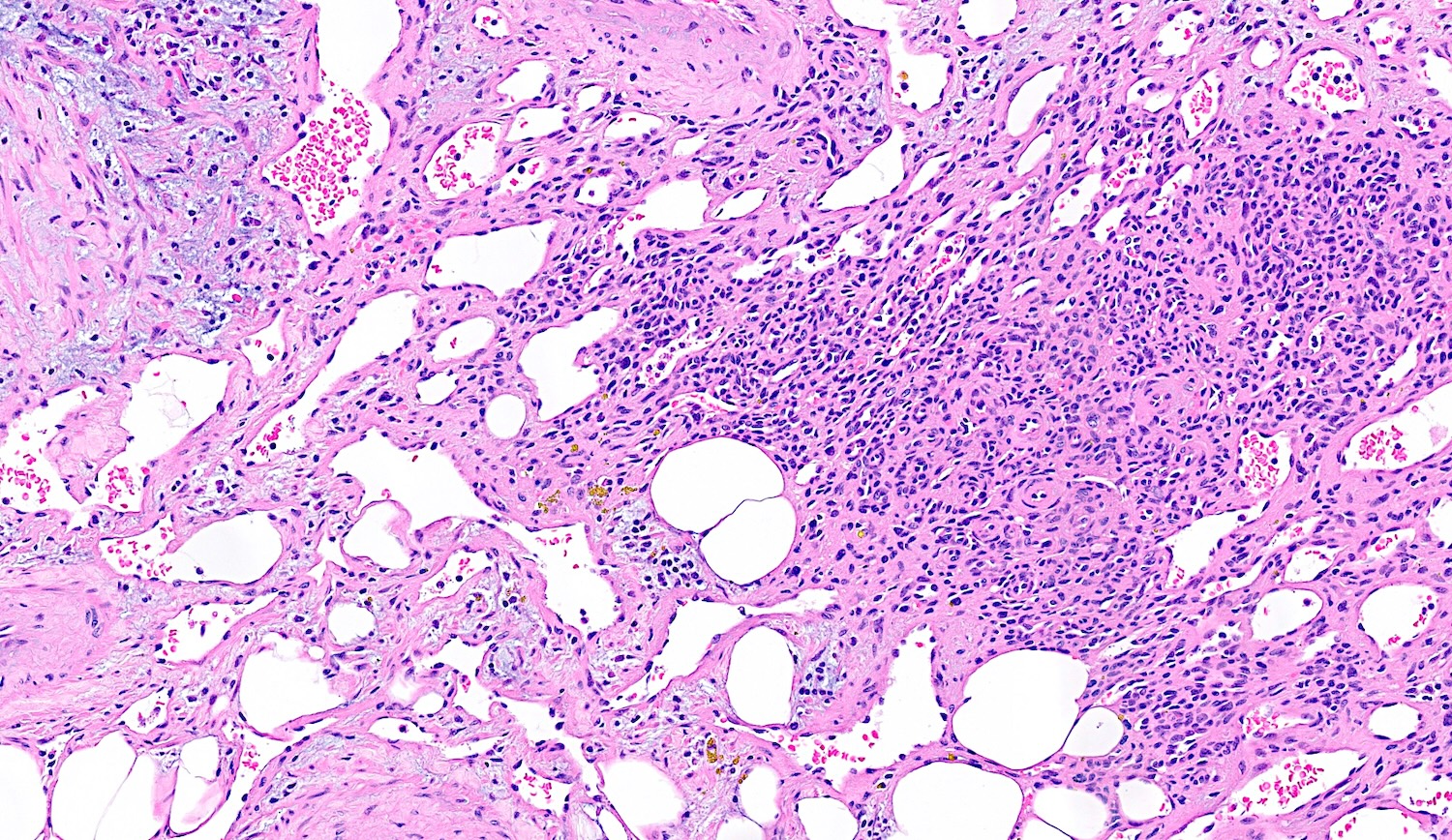
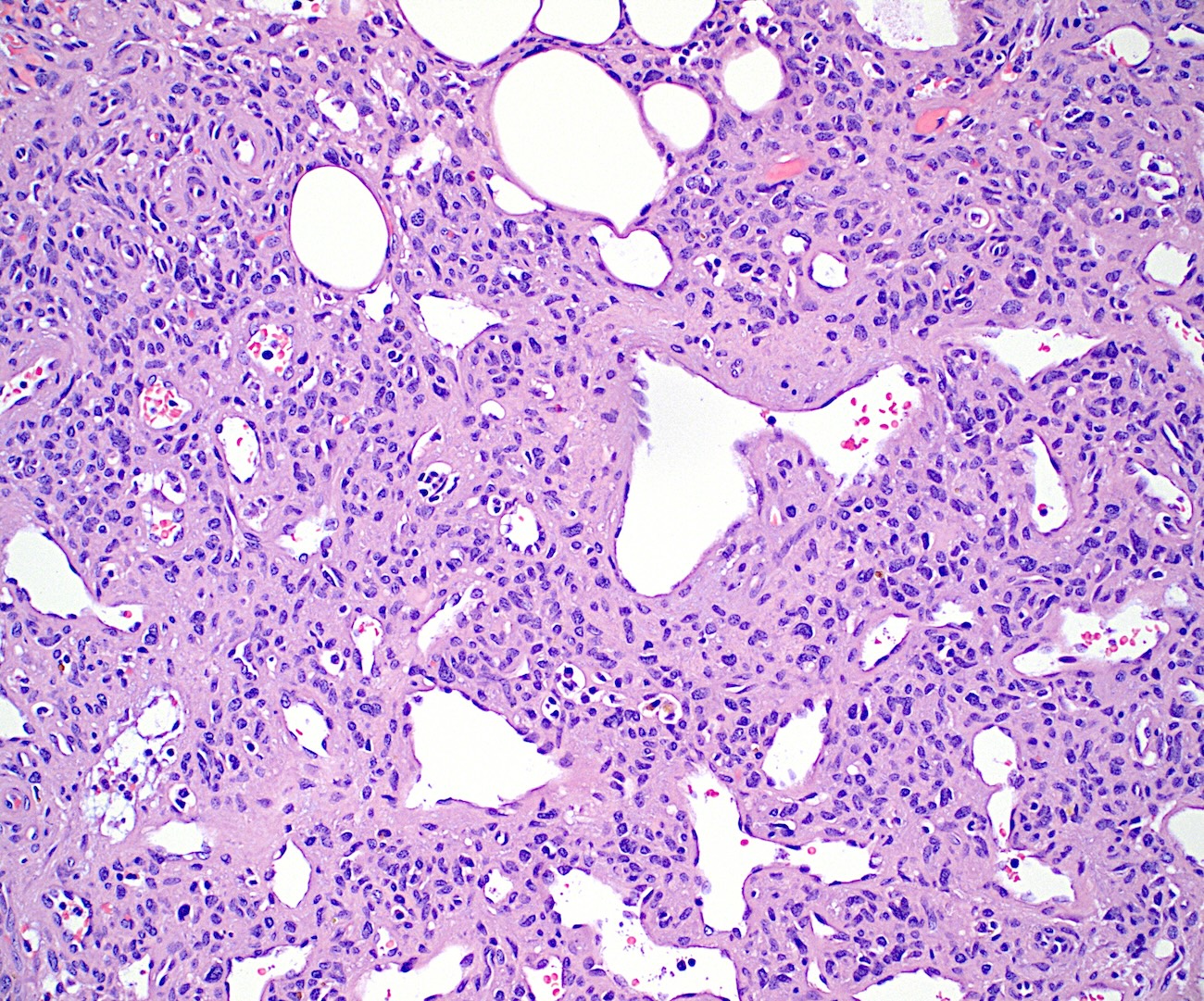
Microscopic (histologic) description
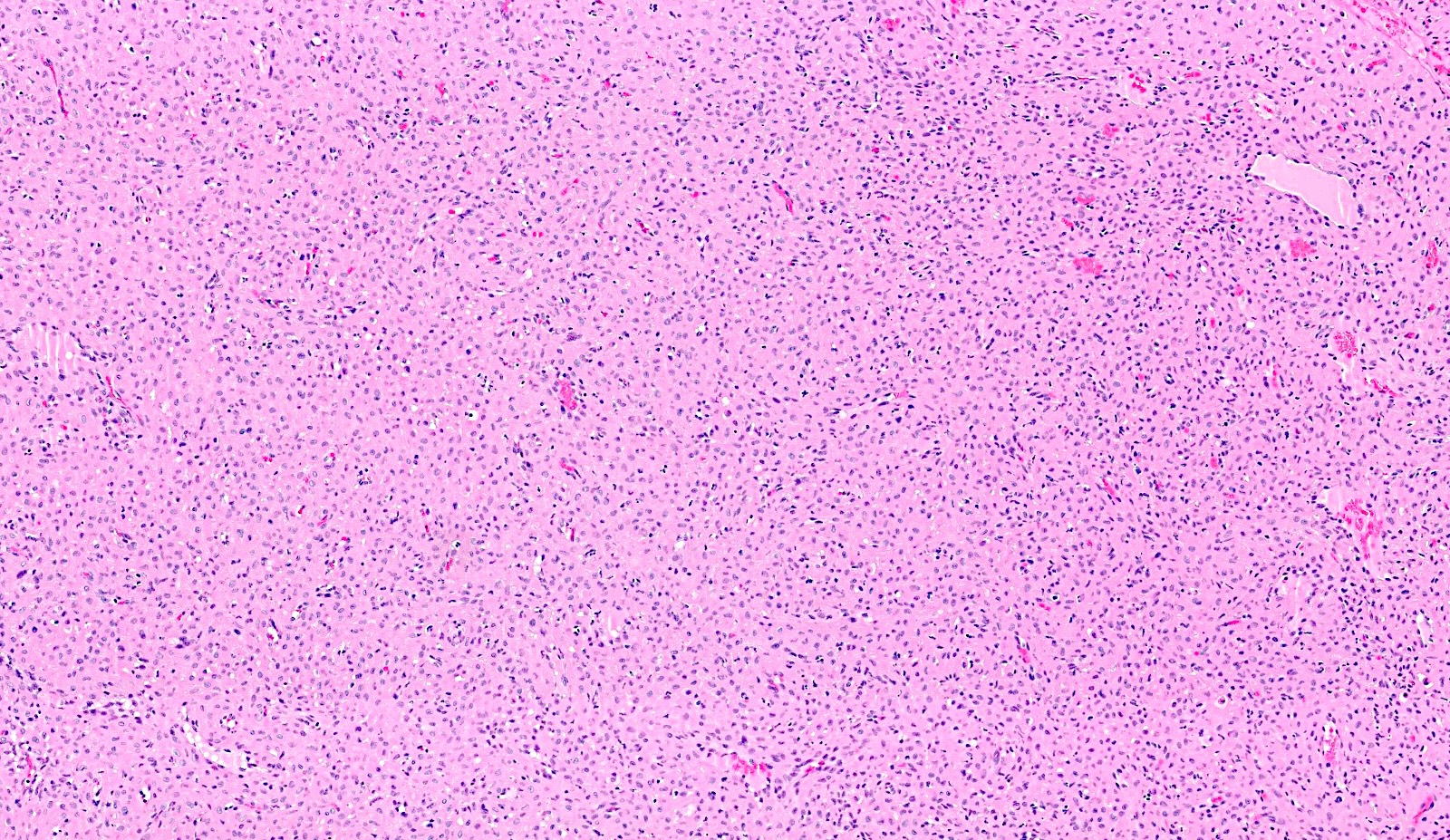
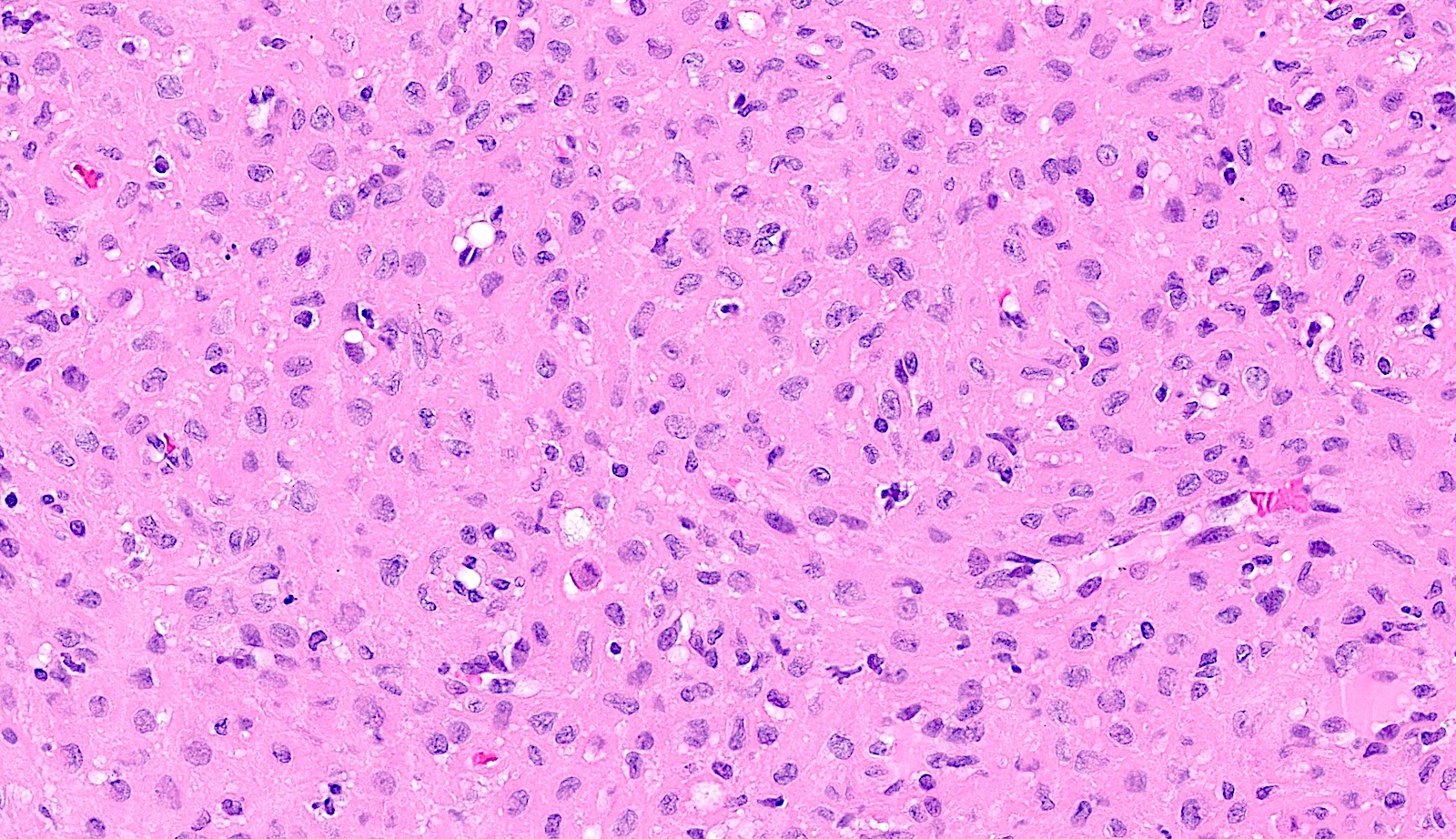
- Bland spindle to stellate cells with low to moderate cellularity
- Hyalinized to smudgy basophilic surrounding matrix
- Grungy calcified matrix, occasionally forming flower-like crystals
- Scattered areas with osteoid morphology and areas resembling primitive cartilage
- Tumor vasculature can be branching in a pericytoma-like pattern
- Microcystic pattern is also common
- Osteoclast-like giant cells may be present
- Can have areas of aneurysmal bone cyst-like changes
- May infiltrate the surrounding fat
- Mitotic activity is low
- Necrosis is usually absent
- In bone, abundant osteoid production has been reported
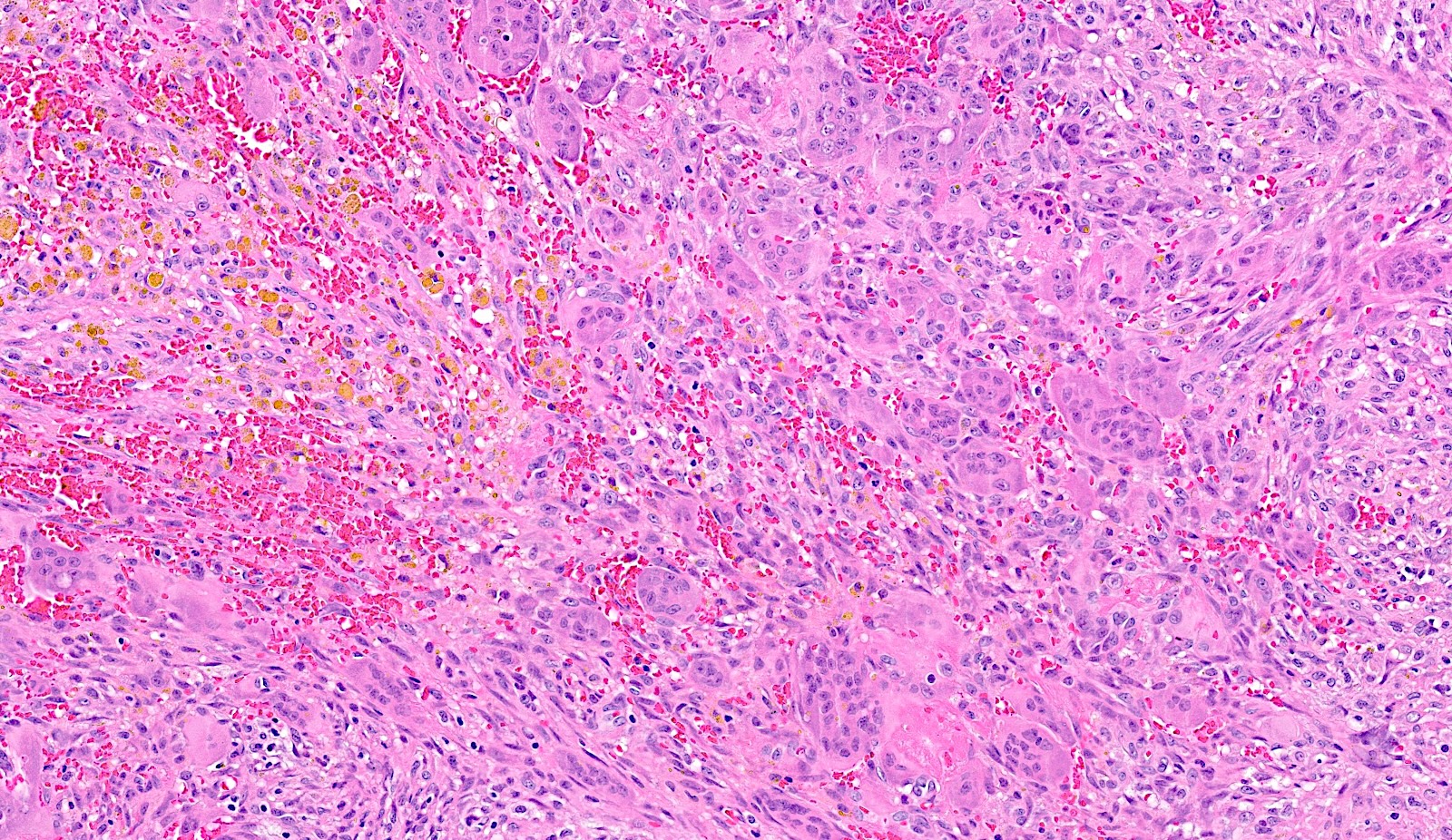
- Malignant PMT
- High nuclear grade and nuclear pleomorphism
- Elevated mitotic activity, high cellularity and necrosis
- May metastasize (Medicine (Baltimore) 2017;96:e6750)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Bland spindle cells with fine chromatin and scant cytoplasm
- Surrounding stromal matrix present
- Rare osteoclast type giant cells
- No significant atypia or mitoses (Diagn Cytopathol 2008;36:115, Diagn Cytopathol 2012;40:E109)
Positive stains
Electron microscopy description
- Tumor cells are oval to spindle shaped with irregular nuclei
- Cytoplasm may demonstrate abundant intermediate filaments
- Intercellular matrix shows collagen fibers and numerous matrix granules (Cancer 1987;59:1442)
Electron microscopy images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Chromogenic in situ hybridization (CISH) can detect FGF23 mRNA in > 95% of cases (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:75)
- Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) detects FGF23 in ~94% of PMTs with TIO and 75% of PMTs without TIO (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1348)
- Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) can detect FN1::FGFR1 fusions in 41% of PMT cases (J Pathol 2015;235:539)
Sample pathology report
- Soft tissue, left big toe, excision:
- Phosphaturic mesenchymal tumor (see comment)
- Comment: Histologic sections show a bland spindle cell proliferation with scattered stellate cells in a hyalinized background. Focal areas of grungy calcification are identified with associated osteoclast-like giant cells. Abundant background vasculature is present with occasional staghorn vessels. There is no increased mitotic activity or necrosis. Immunohistochemical stains for SATB2, CD56 and SSTR2A are positive in the lesional cells, while CD34, S100 and STAT6 are negative. All controls stain appropriately. Chromogenic in situ hybridization for FGF23 mRNA performed on additional formalin fixed sections is expressed in tumor cells. These findings, with the history of chronic osteomalacia and elevated FGF levels, are consistent with a diagnosis of phosphaturic mesenchymal tumor.
Differential diagnosis
- Solitary fibrous tumor:
- Giant cell tumor (GCT) of bone and soft tissue:
- More prominent osteoclast-like giant cells
- GCT of bone expresses H3G34W
- Osteosarcoma:
- Younger age group
- Predominantly involves bone
- More prominent osteoid deposition
- Increased nuclear atypia
- Mesenchymal chondrosarcoma:
- More mature areas of cartilage or bone
- Malignant appearing lesional cells
- HEY1::NCOA2 gene rearrangement
- Sinonasal glomangiopericytoma:
- Solid and fascicular growth pattern
- SMA, desmin positive
- Aberrant nuclear beta catenin expression
- Calcifying chondroid mesenchymal neoplasms:
- Predilection for temporomandibular joint and extremities
- Lobular architecture
- Can be associated with calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition
- Translocations involving FN1 and other fusion partners besides FGFR
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
C. Phosphaturic mesenchymal tumor (PMT). The image shows abundant bland spindle cells in a collagenized stroma and characteristic grungy calcifications. There are background blood vessels with occasional branching and focal fat trapping. There is minimal atypia and mitotic activity, with no necrosis. These histologic features, clinical history, age and location support the diagnosis of PMT. Answer A is incorrect because schwannoma has spindle cells with hypercellular Antoni A areas, occasional Verocay bodies and hypocellular Antoni B areas. Answer B is incorrect because osteosarcoma has more atypical cells with osteoid deposition and occurs in the metaphyses of long bones in younger patients. Answer D is incorrect because solitary fibrous tumor has more staghorn shaped vessels and does not have the grungy calcifications seen in PMT.
Comment Here
Reference: Phosphaturic mesenchymal tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Phosphaturic mesenchymal tumor
Board review style question #2
Malignant phosphaturic mesenchymal tumors are characterized by which of the following?
- Infiltration of surrounding fat
- Presence of immature cartilage
- Presence of necrosis
- Size > 5 cm
Board review style answer #2
C. Presence of necrosis. Significant cellularity, nuclear pleomorphism, mitosis and nuclear atypia are present in malignant phosphaturic mesenchymal tumors (PMTs). Answer D is incorrect because there are no reported size criteria for PMT. Answers A and B are incorrect because the presence of immature cartilage or osteoid and fat trapping can be seen in the benign tumors.
Comment Here
Reference: Phosphaturic mesenchymal tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Phosphaturic mesenchymal tumor