Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Skorobogatko V, Umphress B. Plexiform neurofibroma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissueneurofibromaplexiform.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign, peripheral nerve sheath tumor that arises from Schwann cells; generally surrounds multiple nerve fascicles
- Demonstrates irregularly thickened and distorted, tortuous configurations
- Plexiform: complex; in the form of a plexus or network
Essential features
- Benign tumor arising from nerve sheath cells
- Most likely congenital and strongly associated with neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1)
- May be locally aggressive and infiltrate into surrounding tissue causing symptoms
- Immunohistochemistry shows scattered S100 reactivity and EMA can highlight perineurial cells
- Carries risk of developing into malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST)
- Surgical excision can be curative; however, recurrence rate is high
- Medications such as MEK inhibitors have also shown promising results in NF1 patients
Terminology
- Plexiform neurofibroma (PN, PNF)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: D36.10 - benign neoplasm of peripheral nerves and autonomic nervous system, unspecified
Epidemiology
- M = F
- Age of onset: birth
- Grows larger with age, not associated with hormonal changes in puberty or pregnancy (J Pediatr 2014;164:620, PLoS One 2020;15:e0232031)
- NF1 patients have an estimated 30 - 50% chance of developing PN, although sporadic development has been documented (Lancet Neurol 2014;13:834, Acta Dermatovenerol Croat 2020;28:245)
Sites
- Most common: craniofacial (35%), limb (19%) (Am J Med Genet A 2022;188:1723)
- Other sites: neck, back, inguinal
Pathophysiology
- Neural crest stem cell (variable NF1) → neuro / glial lineage or Schwann cell lineage (variable NF1) → plexiform neurofibroma (negative NF1)
- Cell of origin: Schwann cell precursors (Neurooncol Adv 2019;2:i13)
- Normally, activated Ras (GTP) is dephosphorylated by neurofibromin to inactivated Ras (GDP)
- Loss of heterozygosity → inactive neurofibromin
- Inactive neurofibromin → activated Ras stays constitutively on to activate signaling pathways downstream → tumor development (Nat Rev Cancer 2015;15:290)
- PN formation involves tumor cells and immune cells, such as mast cells and macrophages, to participate in growth through inflammation (Neurooncol Adv 2019;2:i23, J Clin Invest 2018;128:2848)
- Mast cells are recruited by chemoattractant stem cell factors within tumors (Stem Cell Res 2020;49:102068)
- Inhibition of JAK / STAT3 pathway was shown to reduce inflammatory cytokine expression and number of macrophages within tumor → reduced tumor growth (Oncogene 2019;38:2876)
Etiology
- NF1 gene loss of heterozygosity (Oncogene 2017;36:3168)
- Germline and somatic non-NF1 mutation variants, such as GNAZ and LZTR1 genes (Exp Dermatol 2022;31:775)
Clinical features
- Congenital but may not become apparent for years
- Most pediatric PNs grow slowly if at all; majority of PNs that grow will grow most rapidly during first decade of life (Orphanet J Rare Dis 2012;7:75, Cancer Cell 2014;26:596)
- Large tumors are attached to major nerve trunks in neck or extremities
- Often associated with pain, dysfunction, skeletal deformities and changes in appearance
- Can be associated with hyperpigmentation and hypertrichosis; pigmentation may follow Blaschko lines (JAAD Case Rep 2019;5:670, J Am Acad Dermatol 2007;56:862, Cutan Aesthet Surg 2021;14:381)
- Part of diagnostic criteria for NF1 (Genet Med 2021;23:1506)
- Solitary PNs may be due to NF1 mosaicism or loss of heterozygosity
- 38% of childhood NF1 patients had plexiform neurofibromas in one study; > 50% were symptomatic (Brain Behav 2022;12:e2599)
Diagnosis
- Typically a clinical diagnosis with biopsy demonstrating classic histologic characteristics
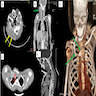
- MRI or PET / CT may be utilized based on the size and location of the lesion
- F-FDG PET / CT may be used to discriminate between benign and malignant PN and monitor tumor progression (Medicine (Baltimore) 2018;97:e10648)
Laboratory
- Soluble AXL levels significantly increased in serum of PN patients compared with only dermal neurofibromas (PloS One 2014;9:e115916)
- Midkine and fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) levels increased in NF1 patients with PNs (Am J Transl Res 2022;14:3180)
Radiology description
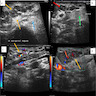
- Sonography: multilobulated, hypoechoic nodules on a hyperechoic background with significant vascularity; largely located in the cutaneous and subcutaneous planes with vascular portion showing a pattern of peripherally attenuating vessels (J Med Ultrasound 2002;10:141, Radiol Case Rep 2021;16:2824)
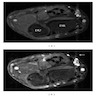
- CT: low attenuation due to myelin lipid content, fat entrapment and high water content in endoneurium myxoid tissue, important modality to assess bony involvement (Case Rep Radiol 2013;2013:493752)
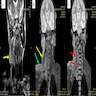
- MRI: lobulated, serpiginous morphology with central low signal intensity surrounded by rim of high intensity signal on T2W
- Target sign with each target depicting involved nerve fascicle (Radiol Case Rep 2021;16:2824, J Comput Assist Tomogr 2020;44:928)
- Reverse target sign on contrast enhanced scans (AJR Am J Roentgenol 2014;203:W697)
- PET / CT: to detect transformation to MPNST (PLoS One 2015;10:e0143305)
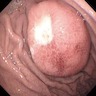
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Increased mortality risk in pediatric NF1 populations (J Pediatr 2012;160:461)
- Recurrence following surgery is common (Neurol Sci 2022;43:1281)
- Partial resection (< 50% excision): 55 - 68% recurrence
- Subtotal resection (50 - 90% excision): 29 - 45% recurrence
- Near total resection (> 90% excision): 40% recurrence
- Greatest risk of recurrence postsurgery is in children < 10 years old with head and neck PN (Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2005;131:712)
- PNs are 20x more likely to have malignant transformation into MPNST compared to cutaneous neurofibromas (Neurology 2005;65:205)
Case reports
- 2 year old girl with neck mass (Turk Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2021;59:297)
- 7 year old girl with mass in the perineum and pelvic cavity (Ann Dermatol 2019;31:331)
- 17 year old girl with shoulder pain (J Clin Imaging Sci 2018;8:3)
- 55 year old man with lower extremity weakness and bladder dysfunction (World J Clin Cases 2022;10:4519)
Treatment
- Excision for symptomatic relief is the gold standard; often cannot completely excise the tumor (Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2022;31:31, Neurol Sci 2022;43:1281)
- Recurrence may occur even if completely excised
- Selumetinib, an oral selective MEK inhibitor, FDA approved in 2020 for pediatric patients with NF1 and inoperable symptomatic PNs (Clin Cancer Res 2021;27:4142, N Engl J Med 2020;382:1430, Pediatr Dermatol 2022;39:764, Neurology 2022;98:e938)
- Under investigation (phase II trials):
- Trametinib, a MEK inhibitor, in those with MAPK / ERK activation (TRAM-01) (BMC Cancer 2019;19:1250, Childs Nerv Syst 2021;37:1909)
- Mirdametinib, a MEK inhibitor, in patients with NF1 (J Clin Oncol 2021;39:797)
- Cabozantinib, a multi-RTK inhibitor, for patients > 15 years old with NF1 (Nat Med 2021;27:165)
- In vitro studies: propranolol provided dose dependent suppression of viability in tumorous Schwann cells that were cultured from unrelated patients with NF1 (In Vivo 2020;34:1031)
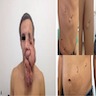
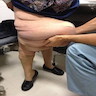
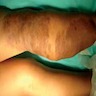
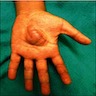
Clinical images
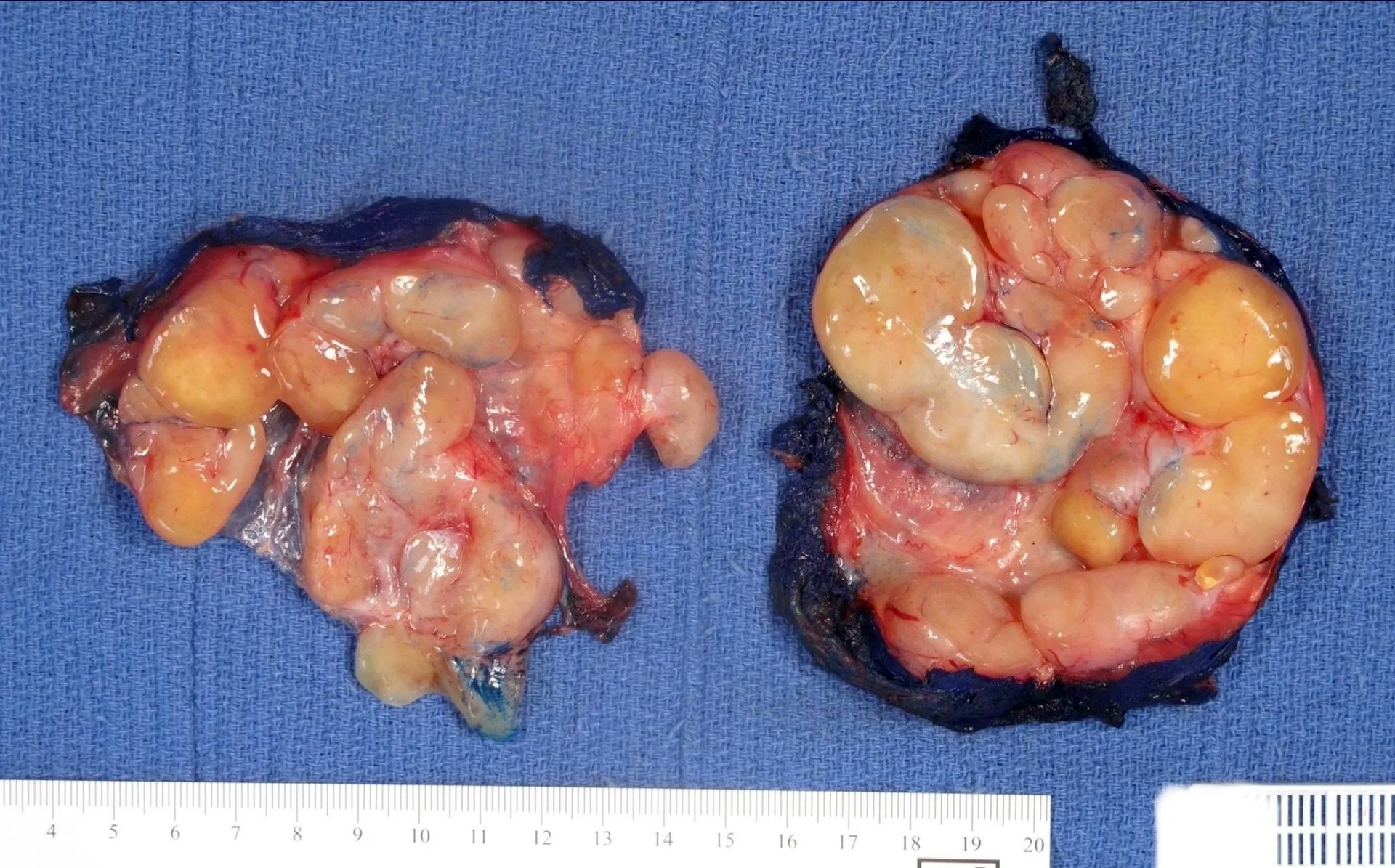
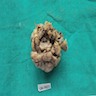
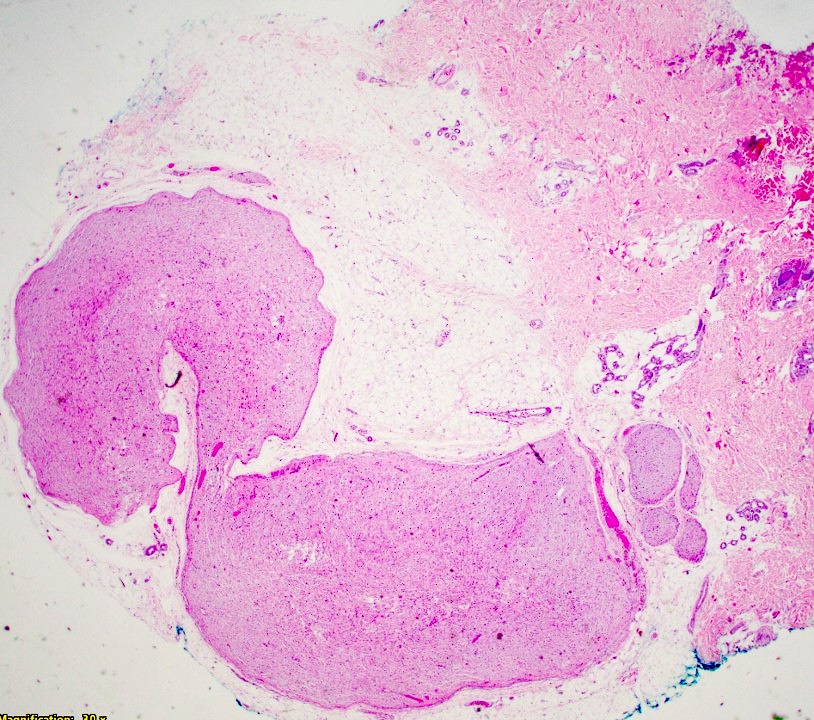
Gross description
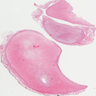
- Associated with grossly enlarged and tortuous nerves
- Deeper tumors may be larger
- Often is characterized as having a bag of worms appearance
- Vascularized and locally invasive
- Involvement of an entire extremity may also be known as elephantiasis neuromatosa
- References: StatPearls: Neurofibroma [Accessed 30 August 2022], Oncol Lett 2016;11:3709
Gross images
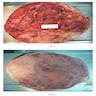
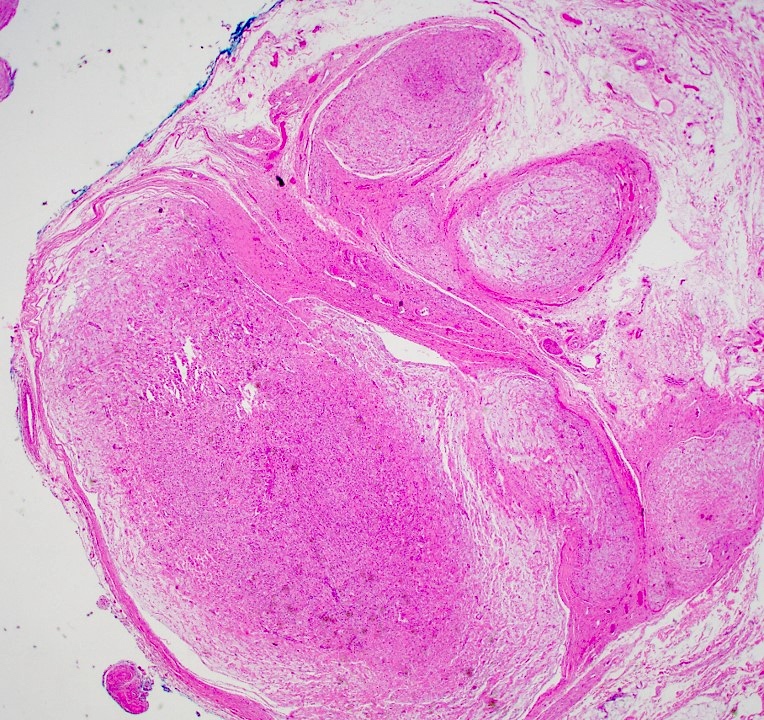
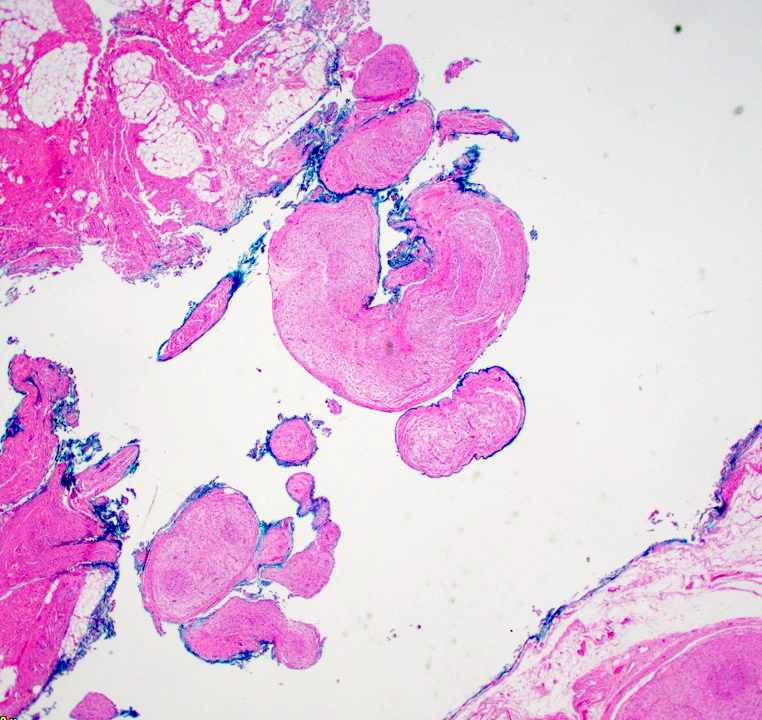
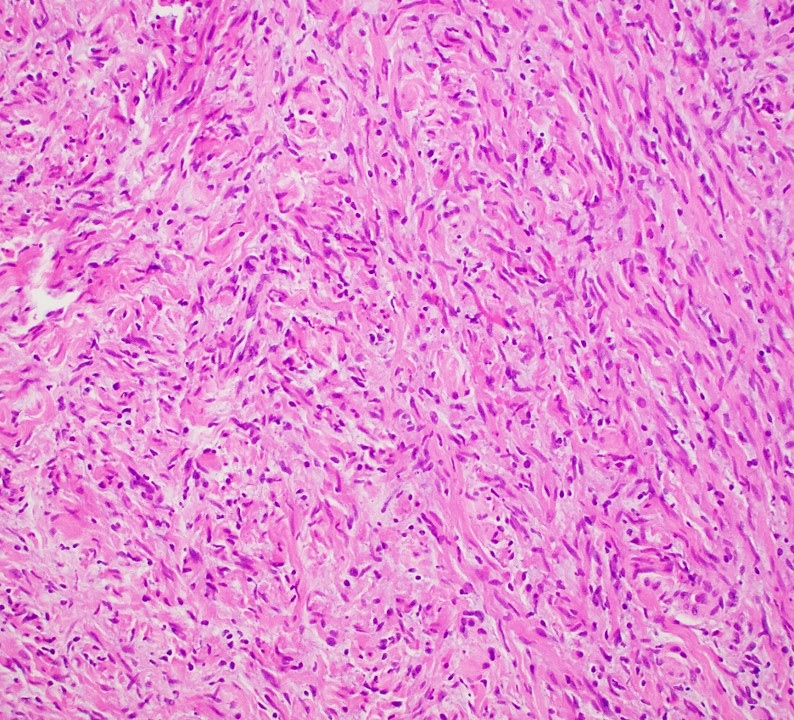
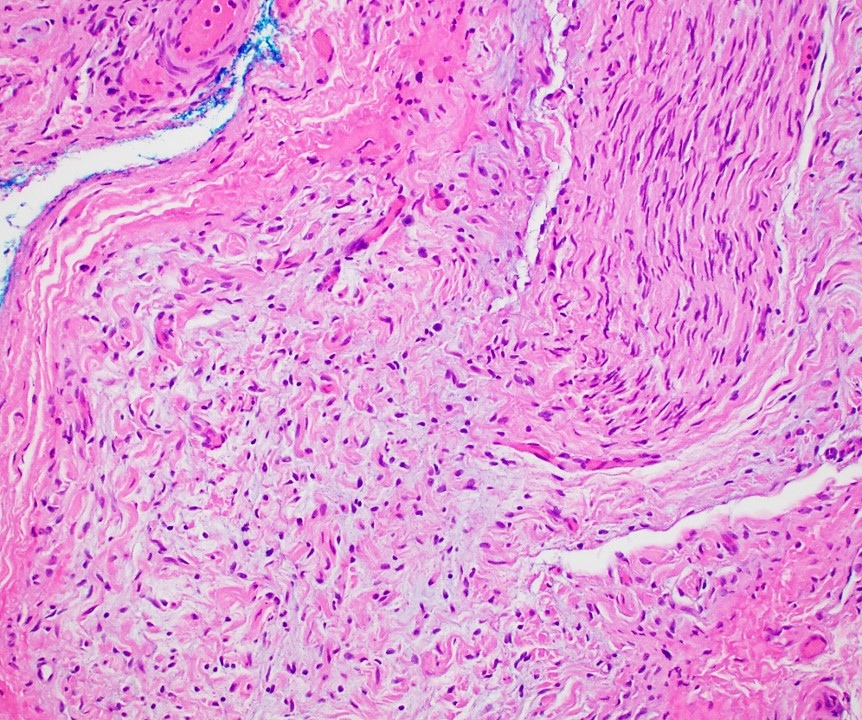
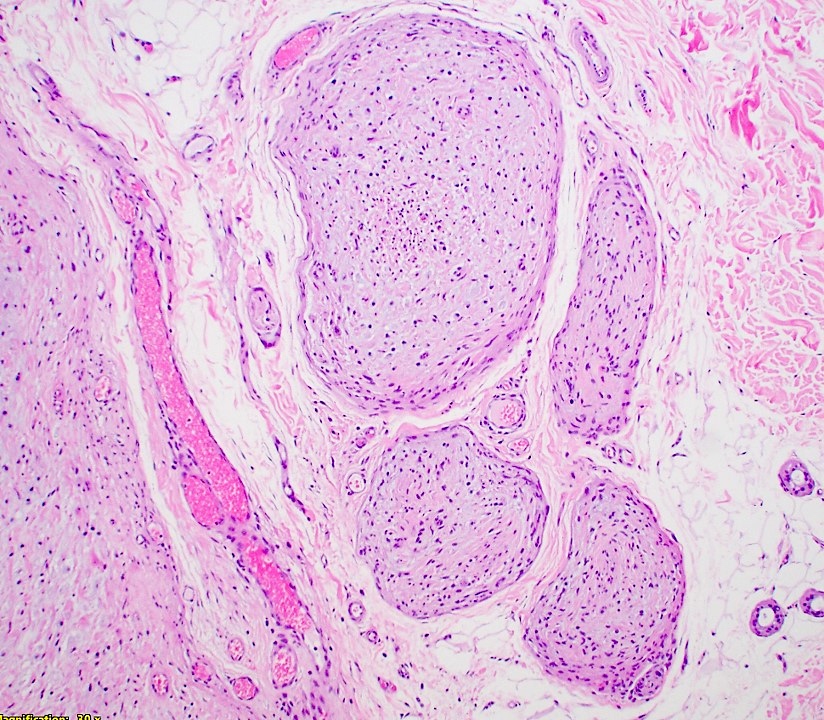
Microscopic (histologic) description
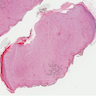
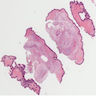
- Multinodular, plexiform or tortuous bundles of bland spindle cells consistent with expanded nerve branches
- On high power, cytologic characteristics are often analogous to those of conventional neurofibromas
- Can be relatively hypocellular with myxoid type changes, comprised of Schwann cells, fibroblasts and mast cells
- Outer area of the proliferation is lined by perineurium
- Rarely is pigmented due to melanocytes (J Am Acad Dermatol 2007;56:862)
- Can display nuclear atypia; care should be exercised when viewing lesions with increased cellularity and increased atypia as these lesions can undergo malignant transformation
- Small cutaneous lesions showing a microscopic plexiform pattern may not necessarily be associated with NF1
Microscopic (histologic) images
Virtual slides
Positive stains
- S100 in scattered cells (unlike strong staining in schwannoma)
- CD34 (usually) (J Pathol Transl Med 2011;45:30)
- Perineurial cells are EMA+ in plexiform but not in ordinary neurofibromas (Ann Diagn Pathol 2014;18:95)
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Tumor contains neuronal axons, Schwann cells, fibroblasts
- Peripheral nerves with mucinous degeneration (Eur J Med Res 2010;15:84)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- NF1 loss appears to frequently be the driver of plexiform neurofibroma tumorigenesis in NF1 patients (Oncogene 2017;36:3168)
- Epidermal growth factor receptor erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase 2 (ERBB2) and ERBB3 were significantly upregulated in PN (Anticancer Res 2022;42:2327)
- MicroRNA-155 has demonstrated a role in PN growth and Schwann cell proliferation; microRNA-155 deletion in vivo significantly decreased tumor number and volume in mouse models (Oncogene 2021;40:951)
- Deletion of chemokine Cxcl10 receptor Cxcr3 prevents PN formation in mouse models, demonstrating T cell and dendritic cell role; Cxcr3 expression in both of those cells is required to maintain elevated macrophages and the inflammatory microenvironment (JCI Insight 2019;4:e98601)
- CXCR4 gene expression is increased 3 - 120 fold and CXCL12 gene expression is increased 33 - 512 fold (Childs Nerv Syst 2018;34:877)
- IL8, GRO1 / CXCL1, IL1B, IL6, TNF and leukemia inhibitory factor are overexpressed (Clin Cancer Res 2004;10:3763)
- Upregulation of AP1 transcription factor family including FOS, FOSB, JUN and JUNB are implicated in cell transformation, invasive growth, angiogenesis and metastasis (Clin Cancer Res 2004;10:3763)
- Upregulation of apoptotic genes including TNFRSF10A / TRAILR1 and TNFRSF10B / TRAILR2 (Clin Cancer Res 2004;10:3763)
- KIS gene is overexpressed in PN and MPNSTs compared to dermal neurofibromas (Brain Res Mol Brain Res 2003;114:55)
Videos
Plexiform neurofibroma
Sample pathology report
- Left thigh, subcutaneous tissue, excision:
- Plexiform neurofibroma (see comment)
- Comment: The findings are those of an expansile proliferation within the subcutaneous fat, which demonstrates tortuous bundles of bland cells with wavy and elongated nuclei. Subtle background features of myxoid change are appreciated. Furthermore, overt evidence of malignancy (atypia, necrosis and mitoses) is not appreciated. In the context of the patient's reported history of neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), the histologic findings would be most consistent with those of a plexiform neurofibroma. In this regard, clinicopathologic correlation is recommended.
Differential diagnosis
- Plexiform schwannoma:
- S100+ (strong and diffuse)
- Histologically demonstrates multiple nodules of varying sizes with a very thin capsule and otherwise typical features of schwannoma (hypercellular and hypocellular areas, Verocay bodies)
- MPNST:
- Perineurioma:
- Dermatofibroma:
- Plexiform fibrohistiocytic tumor:
- Can exhibit plexiform growth, however, demonstrates nodular fibrous tissue with associated histiocytes and possibly osteoclast-like giant cells
- S100-
Board review style question #1
A 16 year old boy presents with a mass on his neck. Physical exam reveals multiple café au lait macules on the trunk and axillary freckling. Biopsy of the mass demonstrates multiple torturous nodules with cylindrical enlargement of nerves, scattered mast cells and variable S100 reactivity. When did the patient likely develop the mass?
- Birth
- 1 - 5 years of age
- 6 - 10 years of age
- 11 - 16 years of age
Board review style answer #1
A. Birth. A is the correct answer because the diagnosis is plexiform neurofibroma. Diagnosis is supported with clinical features of NF1 and histological findings. PNs are congenital tumors that may take several years to manifest clinically due to slow growth. B, C and D are not the correct answers because the tumor was more than likely present at birth.
Comment Here
Reference: Plexiform neurofibroma
Comment Here
Reference: Plexiform neurofibroma
Board review style question #2
Which of the following stains is positive in plexiform neurofibroma?
- Cytokeratin AE1 / AE3
- Mucicarmine
- SMA
- S100
Board review style answer #2
D. S100. Plexiform neurofibromas stain with S100 in scattered cells. Answers A - C are incorrect because PN does not demonstrate cytokeratin AE1 / AE3, mucicarmine or SMA positivity.
Comment Here
Reference: Plexiform neurofibroma
Comment Here
Reference: Plexiform neurofibroma