Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Frazzette N, Mantilla JG. Intramuscular myxoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissuemyxoma.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign, hypocellular soft tissue tumor composed of bland spindle cells in an abundant myxoid stroma
Essential features
- Benign hypocellular intramuscular lesion composed of bland spindle cells without nuclear atypia in abundant myxoid stroma
- Mostly commonly seen in middle aged females
- GNAS1 point mutations in > 90% of cases
- May display focal, nondestructive infiltration of surrounding tissue
- Surgical resection is curative
Terminology
- Cellular myxoma
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8840/0 - myxoma, NOS
- ICD-11: 2E84.Z & XH6Q84 - benign fibrogenic or myofibrogenic tumor, site unknown & myxoma, NOS
Epidemiology
- Most common in middle age (40 - 70 years of age)
- Female predominance (M:F = 0.3:1)
- Most cases are sporadic
- Multiple lesions may occur in association with fibrous dysplasia in the context of germline GNAS1 mutation (Mazabraud syndrome)
- References: Am J Clin Pathol 1965;43:104, Mayo Clin Proc 1973;48:401, Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:1222, Histopathology 2001;39:287, Bone Rep 2023;18:101685
Sites
- Typically presents in the large muscles of extremities (e.g., quadriceps, hamstrings, biceps, triceps) though can occur in any soft tissue site (Am J Clin Pathol 1965;43:104, Mayo Clin Proc 1973;48:401, Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:1222, Histopathology 2001;39:287, Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 2021;131:e52)
Pathophysiology
- GNAS1 activating point mutations are detected in > 90% of sporadic cases and in Mazabraud syndrome associated cases (Mod Pathol 2009;22:718, Diagn Pathol 2018;13:52, Virchows Arch 2002;440:12)
- GNAS1 activation leads to downstream FOS activation (J Cell Mol Med 2009;13:1291)
Etiology
- Exact etiology of sporadic cases is unknown
Clinical features
- Slow growing, painless, intramuscular mass
- May be multiple, especially when associated with Mazabraud syndrome
Diagnosis
- Intramuscular mass in middle aged adults
- Hypocellular myxoid tumor with bland spindle cells, hypovascularity, nondestructive infiltration of surrounding tissue
- Detection of GNAS mutation can support the diagnosis; however, these are not routinely evaluated
- Reference: Orthopedics 2002;25:1297
Radiology description
- Typically seen as a well circumscribed intramuscular mass; some may have partially ill defined borders
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Intramuscular myxoma does not typically recur after complete excision
- Cellular variants may have a small risk of local recurrence; however, they are benign, indolent lesions
- References: Histopathology 2001;39:287, J Bone Joint Surg Am 2019;101:160
Case reports
- 47 year old woman with right quadriceps intramuscular myxoma (Cureus 2024;16:e63144)
- 58 year old man with pterygoid and masseteric intramuscular myxoma (Cureus 2023;15:e49772)
- 63 year old man with right adductor compartment intramuscular myxoma (Int J Surg Case Rep 2024;116:109402)
- 67 year old woman with flexor carpi ulnaris intramuscular myxoma (J Orthop Case Rep 2024;14:135)
Treatment
- Surgical resection is curative
Gross description
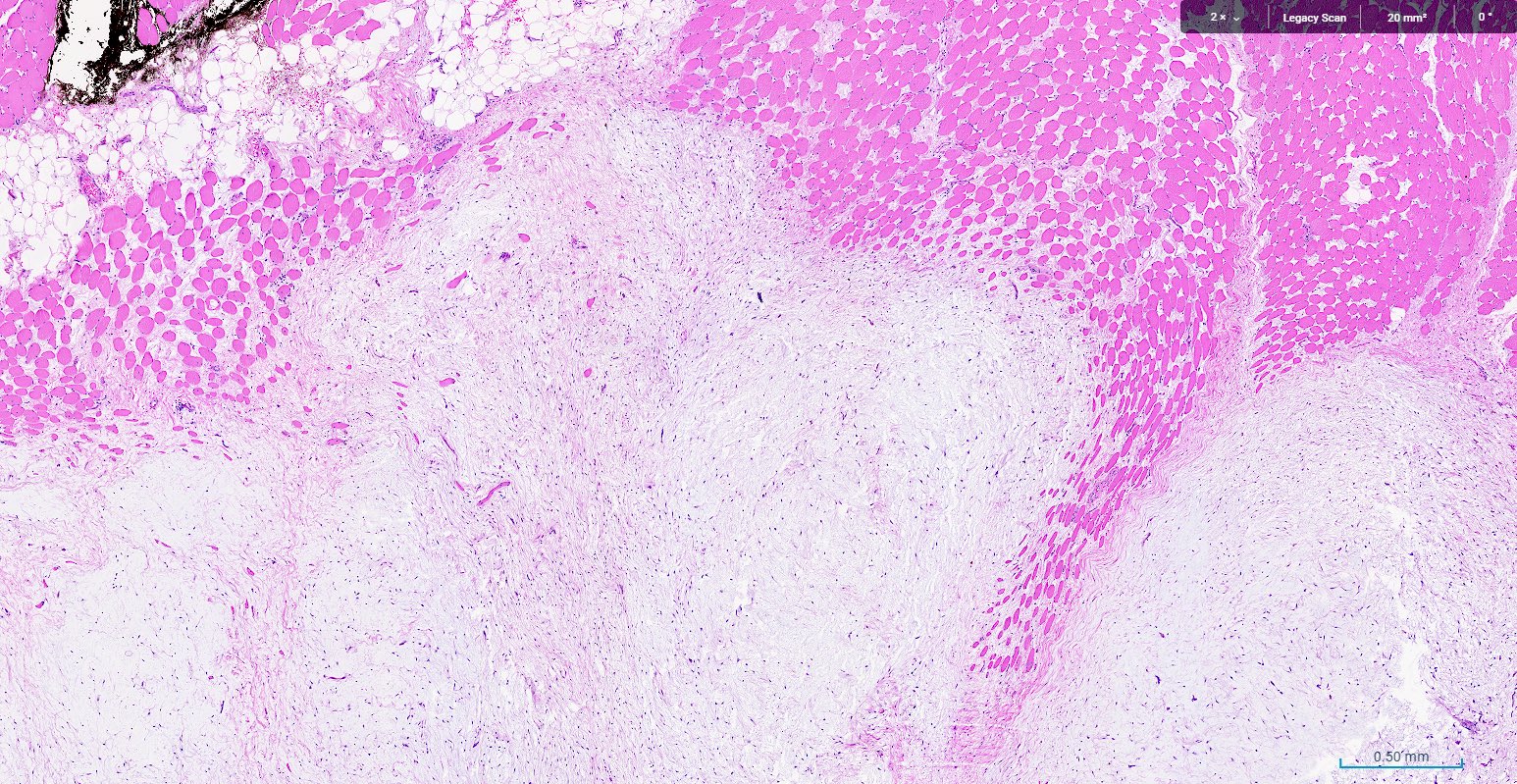
- Typically well circumscribed with occasional focally ill defined borders with infiltration into surrounding skeletal muscle
- Cut surface is gelatinous and may have fluid filled cystic spaces
- References: Am J Clin Pathol 1965;43:104, Mayo Clin Proc 1973;48:401, Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:1222, Histopathology 2001;39:287
Microscopic (histologic) description
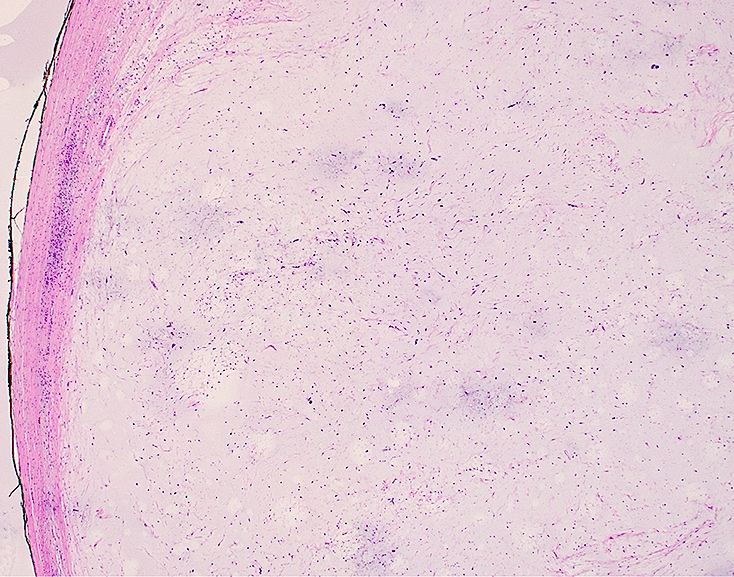
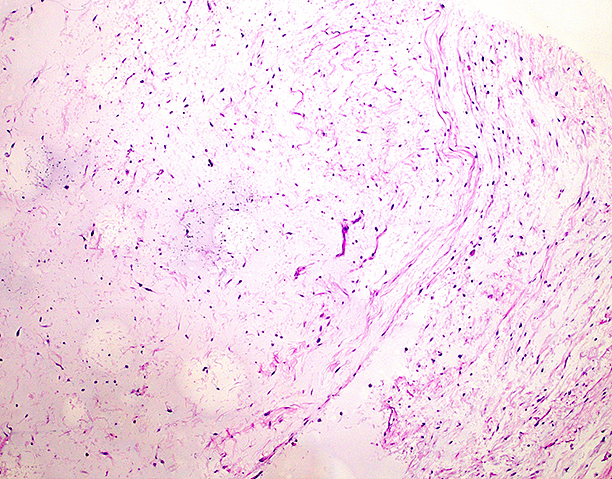
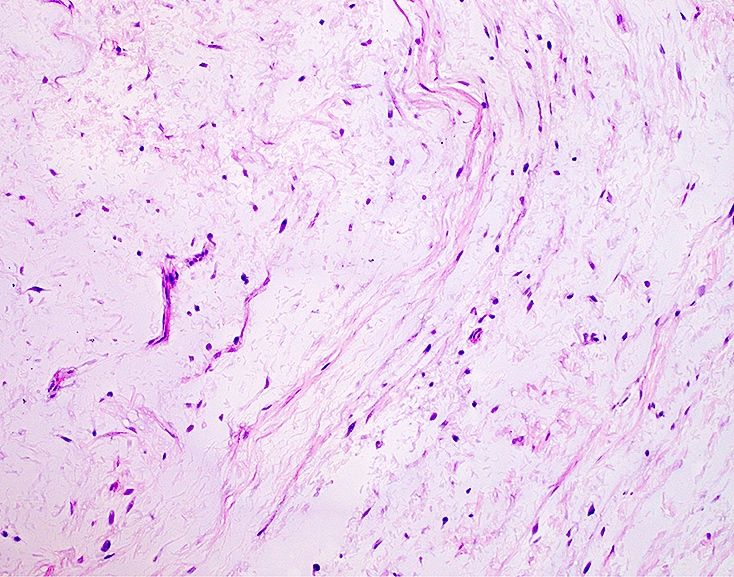
- Cytologically bland / uniform and hypocellular lesion with spindle cells in an abundant extracellular myxoid stroma
- Nuclei are small and ovoid; atypia is minimal to absent
- Sparse, small capillaries may be seen
- Necrosis and mitosis are absent
- Cellularity may be increased at the periphery and focal nondestructive infiltration of surrounding tissue may be seen
- Cellular variant may have an increased number of similarly bland, uniform cells with more prominent vascularity; however, nuclei atypia remains minimal; prominent mitotic activity and tumor necrosis should not be identified
- References: Am J Clin Pathol 1965;43:104, Mayo Clin Proc 1973;48:401, Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:1222, Histopathology 2001;39:287
Microscopic (histologic) images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Up to 90% of cases harbor GNAS1 activating point mutations (Mod Pathol 2009;22:718, Diagn Pathol 2018;13:52, Virchows Arch 2002;440:12)
Videos
Intramuscular myxoma: 5 minute pathology pearl series
by Jerad Gardner, M.D.
Sample pathology report
- Left gluteus mass, excision:
- Intramuscular myxoma, completely excised
- Tumor size: 2.5 cm in greatest dimension
Differential diagnosis
- Low grade myxofibrosarcoma:
- Has characteristic curvilinear vessels with perivascular condensation of cells around vessels
- Distinction may be very challenging in small biopsy specimens
- Variable nonspecific cytogenetic aberrations (83%), no GNAS1 activating mutations
- Nerve sheath myxoma:
Board review style question #1
A 45 year old woman presents with a painless, slowly growing mass in her thigh. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) demonstrates a well defined lesion within the muscle with high T2 signal intensity and low T1 signal intensity. On resection, the histology above is seen. Immunohistochemical studies are negative for S100, SOX10 and CD34. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- Intramuscular myxoma
- Low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma
- Myxoid liposarcoma
- Neurofibroma
- Schwannoma
Board review style answer #1
A. Intramuscular myxoma. Intramuscular myxoma is a benign, soft tissue tumor typically presenting in middle aged adults, often in the thigh or upper arm. On MRI, it characteristically appears as a well circumscribed lesion with high T2 and low T1 signal intensities. Histologically, it is composed of sparse, bland spindle cells in a myxoid stroma with a paucity of blood vessels. Immunohistochemical staining for markers like S100 and SOX10 is generally negative in intramuscular myxomas; while CD34 is often positive, this is not always the case.
Answer C is incorrect because, while myxoid liposarcomas can also present as well circumscribed lesions on MRI with high T2 signal, histologically they generally show lipoblasts and a more vascular pattern, including chicken wire capillaries, which are absent in this case. Answer B is incorrect because low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma has a more cellular and less myxoid appearance than intramuscular myxoma and often contains alternating areas of collagenous and myxoid stroma. It typically stains positive for MUC4, which is a helpful distinguishing marker, whereas intramuscular myxomas are MUC4 negative. Answer D is incorrect because neurofibromas are often positive for S100 and SOX10 due to their neural origin. They usually contain wavy, spindle shaped cells within a collagenous or myxoid background. Answer E is incorrect because, like neurofibromas, schwannomas typically show positive staining for S100 and SOX10. Histologically, they have cellular Antoni A areas and less cellular Antoni B areas, which are not described in this case.
Comment Here
Reference: Intramuscular myxoma
Answer C is incorrect because, while myxoid liposarcomas can also present as well circumscribed lesions on MRI with high T2 signal, histologically they generally show lipoblasts and a more vascular pattern, including chicken wire capillaries, which are absent in this case. Answer B is incorrect because low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma has a more cellular and less myxoid appearance than intramuscular myxoma and often contains alternating areas of collagenous and myxoid stroma. It typically stains positive for MUC4, which is a helpful distinguishing marker, whereas intramuscular myxomas are MUC4 negative. Answer D is incorrect because neurofibromas are often positive for S100 and SOX10 due to their neural origin. They usually contain wavy, spindle shaped cells within a collagenous or myxoid background. Answer E is incorrect because, like neurofibromas, schwannomas typically show positive staining for S100 and SOX10. Histologically, they have cellular Antoni A areas and less cellular Antoni B areas, which are not described in this case.
Comment Here
Reference: Intramuscular myxoma
Board review style question #2
A 47 year old woman presents with a slow growing mass in her left thigh. Magnetic resonance imaging demonstrates a well circumscribed, T2 hyperintense, intramuscular lesion. A biopsy of the lesion contains a paucicellular neoplasm composed of cytologically bland spindle shaped cells within a myxoid matrix with scant thin walled blood vessels, lacking perivascular condensation of the tumor cells. Which of the following genetic alterations is typically present in this tumor?
- AMACR amplification
- GNAS1 point mutation
- NF1 deletion
- NTRK1 amplification
- TP53 point mutation
Board review style answer #2
B. GNAS1 point mutation. GNAS1 activating mutations are seen in > 90% of intramuscular myxomas. Answer A is incorrect because this aberration is not seen in intramuscular myxoma and, while not specific, may be present in myxofibrosarcoma. Answer E is incorrect because this aberration is not seen in intramuscular myxoma. TP53 mutations are characteristic of many malignancies and are rarely seen in benign neoplasms.
Answer D is incorrect because this aberration is not seen in intramuscular myxoma and while not specific is commonly seen in a variety of soft tissue sarcomas. Answer C is incorrect because somatic alterations in NF1 may be present in a variety of malignant neoplasms (up to 5% of cancers). Germline NF1 mutations are associated with type I neurofibromatosis and present in nerve sheath neoplasms associated with this condition.
Comment Here
Reference: Intramuscular myxoma
Comment Here
Reference: Intramuscular myxoma