Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Epidemiology | Clinical features | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Shankar V. Lymphangioendothelioma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissuelymphangioendothelioma.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
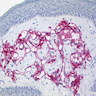
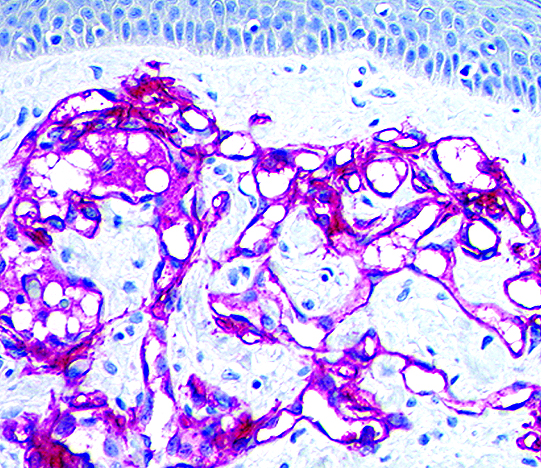
- Proliferation of D2-40+ endothelial cells
- Uncommon benign vascular lesion that may mimic well differentiated angiosarcoma or patch stage Kaposi's sarcoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:1047)
Terminology
- Also called acquired progressive lymphangioma
Epidemiology
- Rare
- No gender preference, median age 54 years, range 17 - 90 years
- Usually not associated with other vascular anomalies or HIV infection
Clinical features
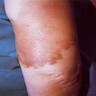
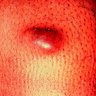
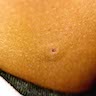
- Solitary red or bruise-like slow growing plaque present for median 5.5 years
- Often in head and neck, but variable sites
- May resemble actinic keratosis (Cutis 2001;67:29)
Prognostic factors
- Benign
- Occasional local recurrence
Case reports
- 26 year old woman with right upper anterior thigh lesion (University of Pittsburg)
- 32 year old man with acquired progressive lymphangioma (benign lymphangioendothelioma) (Actas Dermosifiliogr 2010;101:792)
- 75 year old man with giant benign lymphangioendothelioma (J Cutan Pathol 2012;39:950)
Clinical images
Gross description
- Median 1.5 cm, range 0.3 cm to 10 cm
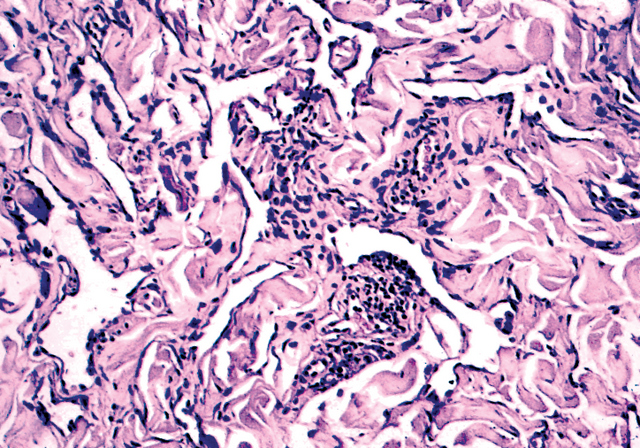
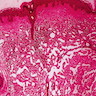
Microscopic (histologic) description
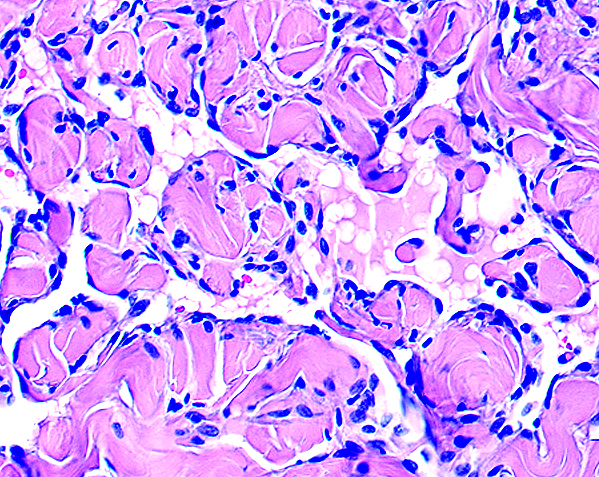
- Delicate, thin walled, endothelium lined dilated vascular spaces involving the superficial dermis
- Intravascular papillary stromal projections resembles papillary endothelial hyperplasia
- Deeper portion of lesions have vascular space collapse and dissect collagen bundles, mimicking patch stage Kaposi's sarcoma
- Preexisting vessels and adnexal structures of the dermis also appear dissected by newly formed vascular channels
- Smooth muscle often focally present around vascular spaces
- Endothelial cells may hobnail, may form morula resembling giant cells
- Crowding of endothelial cells present, but no endothelial atypia
- Vascular spaces lack erythrocytes and hemosiderin deposits
- No mitotic figures
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
Negative stains
Differential diagnosis
- Atypical or benign vascular proliferations of breast: history of radiation therapy
- Kaposi sarcoma: patch stage usually has widespread multiple lesions in HIV+ patients or extensive lesion of lower extremities in elderly patients of Jewish or Mediterranean origin; usually lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate, with inflammatory cells aggregating around vessels, commonly extravasated red blood cells, often other forms of Kaposi’s sarcoma present
- Lymphangioma circumscriptum
- Angiosarcoma - well differentiated: elderly patients, reddish blue plaques or nodules, more endothelial atypia, multilayering and micropapillary tufting, often epithelioid or spindle cell component, inflammatory response common (Am J Dermatopathol 2000;22:151)
Additional references





.jpg)