Table of Contents
Definition / general | Epidemiology | Clinical features | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Arora K. Focal myositis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissuefocalmyositis.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Inflammatory condition of skeletal muscle with degeneration and regeneration, inflammatory cells and fibrosis
- Not a WHO diagnosis
Epidemiology
- Mean age 41 years, range 7 - 94 years
Clinical features
- Usually healthy patients with no history of trauma
- Evolves over weeks to a localized, painful soft tissue swelling, usually of lower extremity
- Solitary, self limited, may be related to denervation
- May be due to statins (Int J Cardiol 2009;133:e33, Cleve Clin J Med 2011;78:393)
Case reports
- 16 year old girl (J R Coll Surg Edinb 2000;45:339)
- 27 year old man post bCG vaccination (Rheumatology (Oxford) 2002;41:1074)
- 32 year old pregnant woman (Rheumatology (Oxford) 2000;39:211)
- 36 year old man with recurrent disease of peroneal muscles (Rheumatology (Oxford) 2002;41:1318)
- 43 year old man with Lyme disease (Arthritis Rheum 2006;54:2697)
Treatment
- Usually none; spontaneously regresses
Gross description
- Pale, ill defined
- Mean 4 cm, range 1 - 20 cm
Microscopic (histologic) description
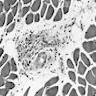
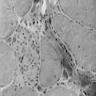
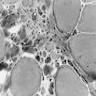
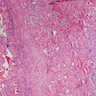
- Degeneration and regeneration of muscle fibers associated with interstitial inflammation and fibrosis
- Also focal neurogenic changes
- Occasionally prominent eosinophils
- Markedly inflamed cases have B cells or CD123+ dendritic plasma cells
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Inflammatory cells, skeletal muscle fibers with degenerative and regenerative changes, fibrous tissue (Acta Cytol 2005;49:653)
Negative stains
- Macrophages are S100- and CD1a-
- Lymphocytes are negative for TIA1, granzyme B, EBV and ALK1 (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1016)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- No B or T cell rearrangement
Differential diagnosis
- Poliomyelitis