Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Ashfaq Z, Anjum S, Ud Din N. Fibroma of tendon sheath. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissuefibromatendon.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign fibroblastic / myofibroblastic nodular proliferation usually attached to a tendon / tendon sheath
Essential features
- Benign nodular, paucicellular spindle cell lesion with slit-like spaces mostly on finger tendon sheath
- Cellularity may be higher at the periphery
- Has the propensity to recur in 5 - 10% cases
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- M > F
- 20 - 50 years
- Young individuals; see Case reports (BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2020;21:732)
Sites
- Mostly on finger tendons
- Intra-articular, rarely
Etiology
- Not known at this time
Clinical features
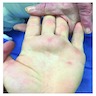
- Slow growing, painless and firm mass
- Usually ≤ 3 cm
- Overlying skin is usually unremarkable
- Reference: Geschickter: Tumors of Bone, 1949
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis requires correlation of site with typical histological features
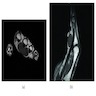
Radiology description
- Plain Xrays show a soft tissue shadow without calcification or bone involvement
- Ultrasound: well circumscribed hypoechoic mass
- MRI: iso signal intensity to muscle on T1 weighted images, low signal intensity to muscle on T2 weighted images (BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2020;21:732)
Prognostic factors
- Benign lesion
- Can recur in 5 - 10% cases
Case reports
- 3 year old boy with fibroma of tendon sheath of hand (BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2020;21:732)
- 14 year old boy with fibroma of tendon sheath of the hand with novel chromosomal translocation 4;10 (Case Rep Orthop 2019;2019:3514013)
- 35 year old Japanese man with fibroma of tendon sheath presenting limited flexion of the fingers (Case Rep Orthop 2017;2017:4129714)
- 42 year old woman, 54 year old woman and 63 year old man with fibroma of tendon sheath around large joints (BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2017;18:376)
- 54 year old man with fibroma of tendon sheath on medial side of knee (J Med Invest 2017;64:173)
Treatment
- Surgical excision (marginal excision) is warranted in all cases
Clinical images
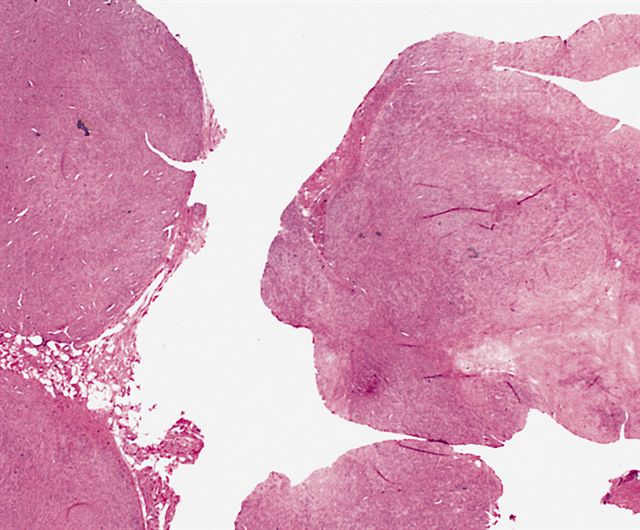
Gross description
- Lobulated, firm
- Usually well circumscribed
- Usually ≤ 3 cm
- Reference: Geschickter: Tumors of Bone, 1949
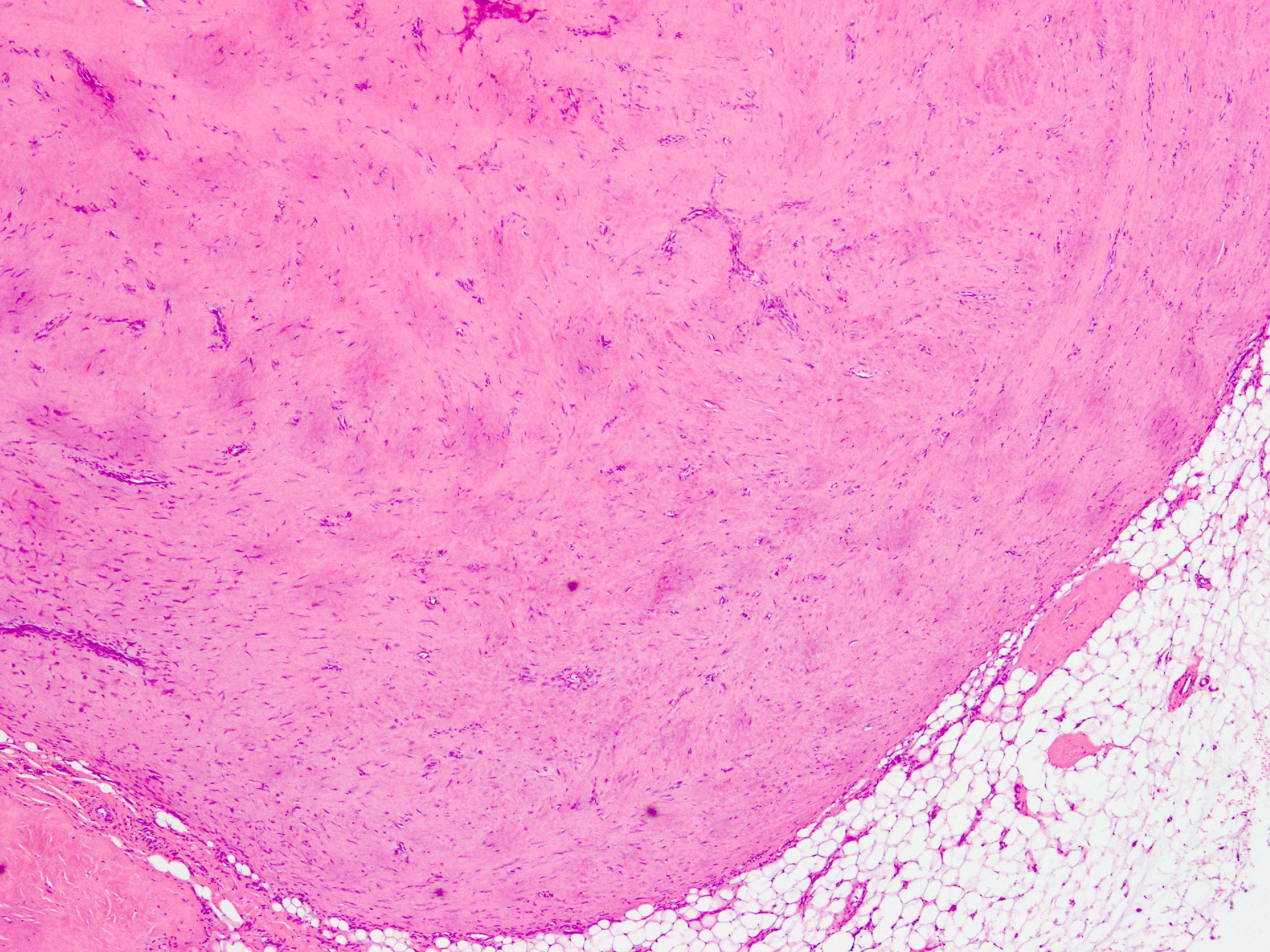
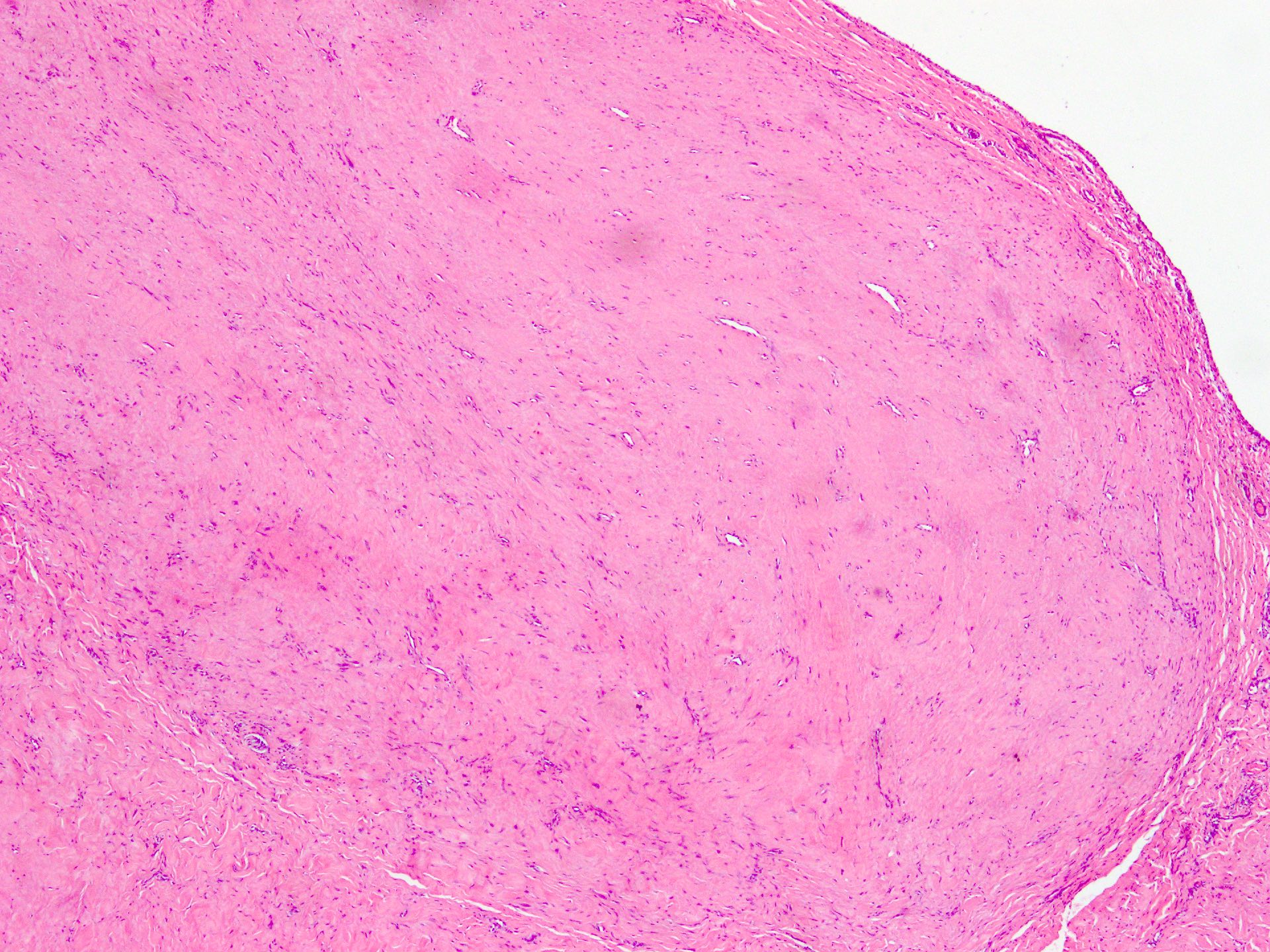
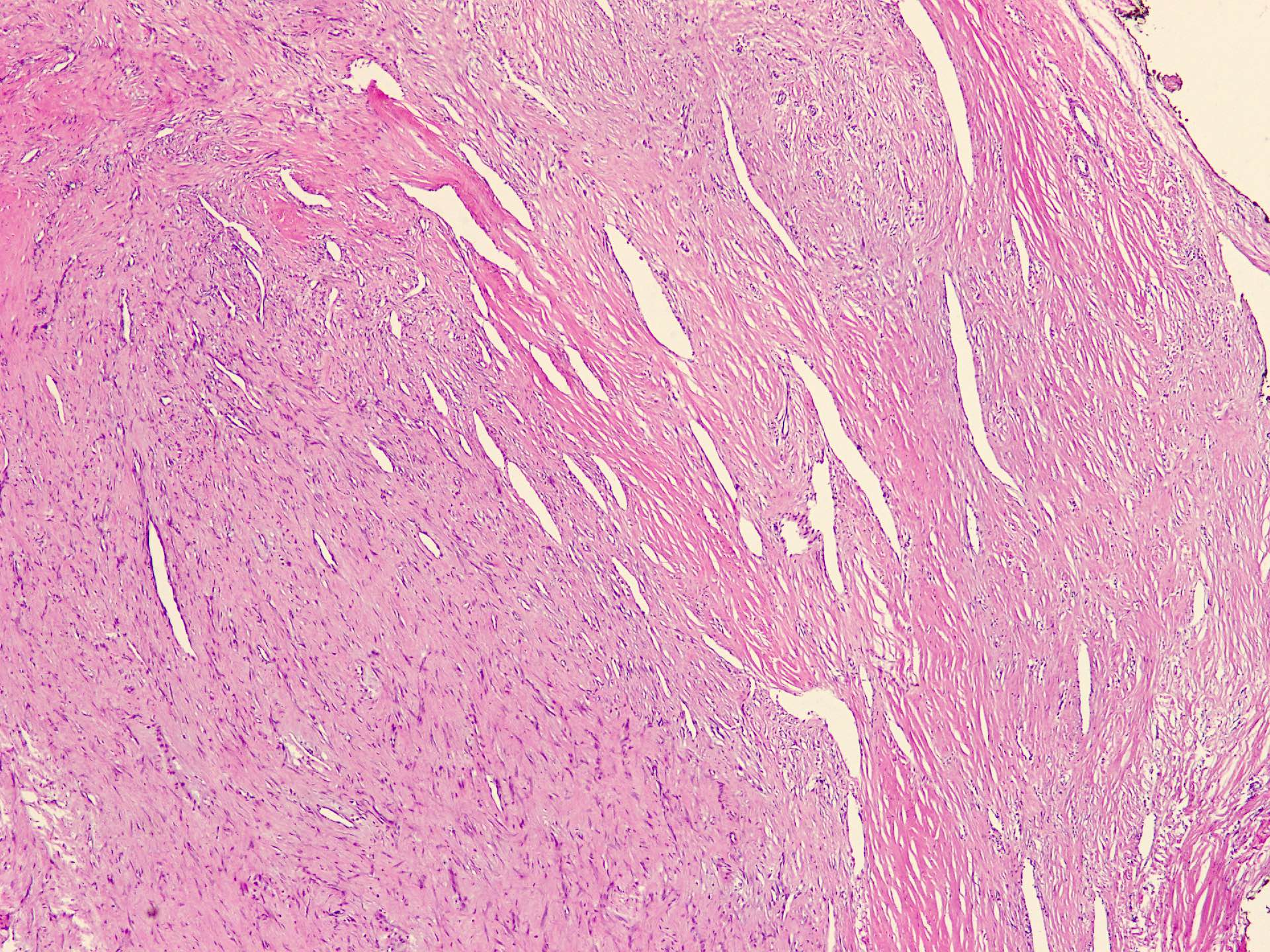
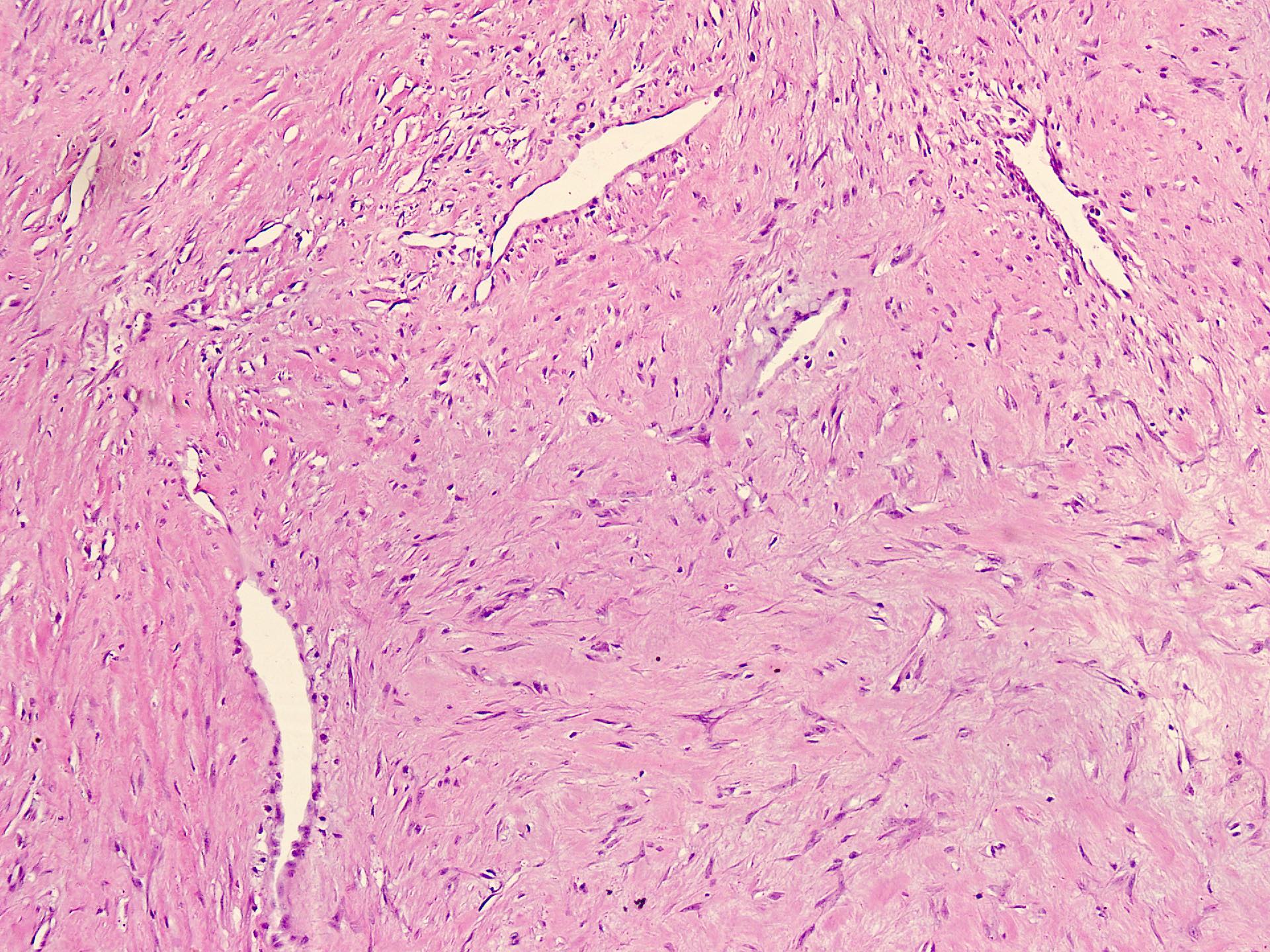
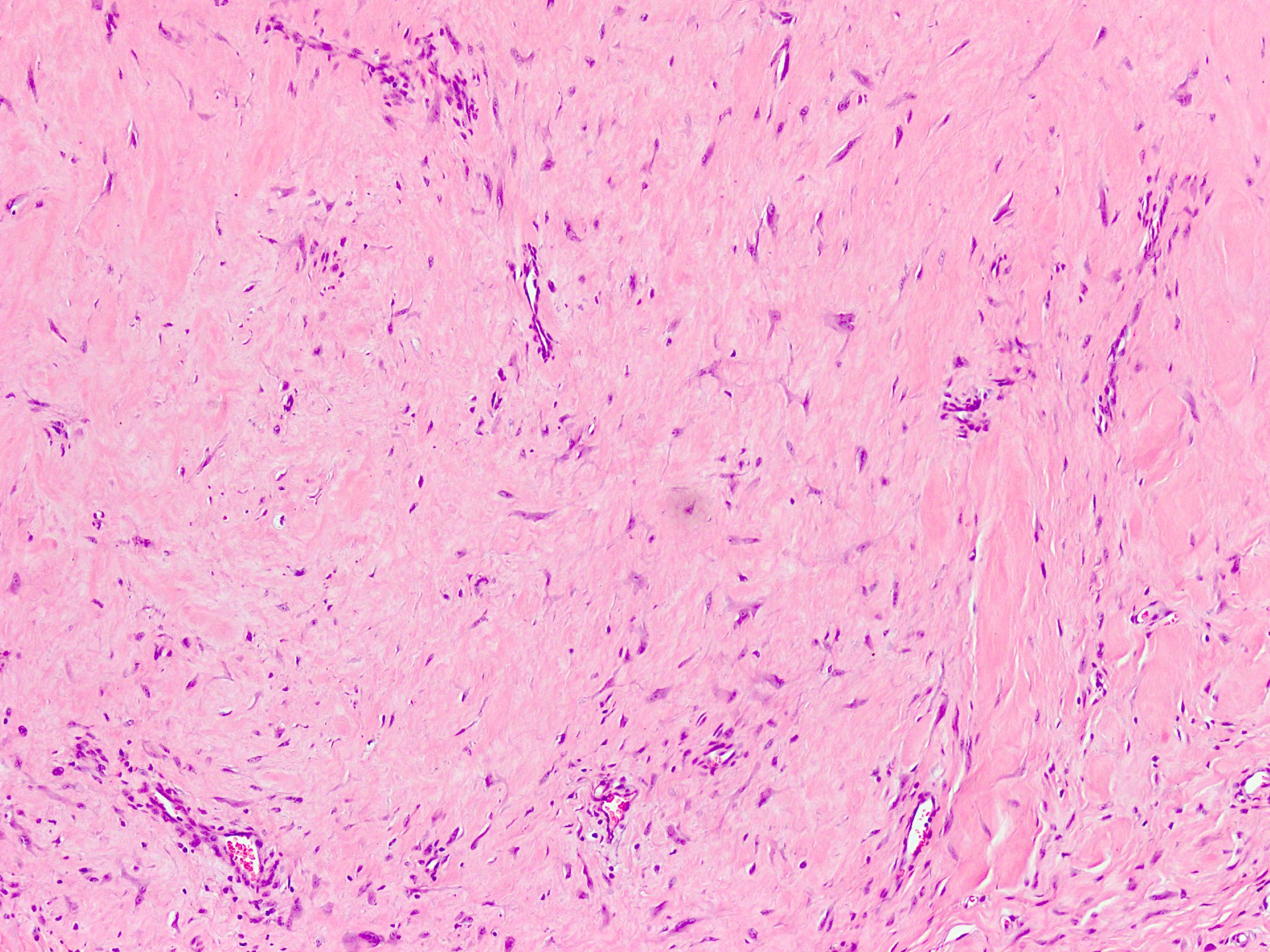
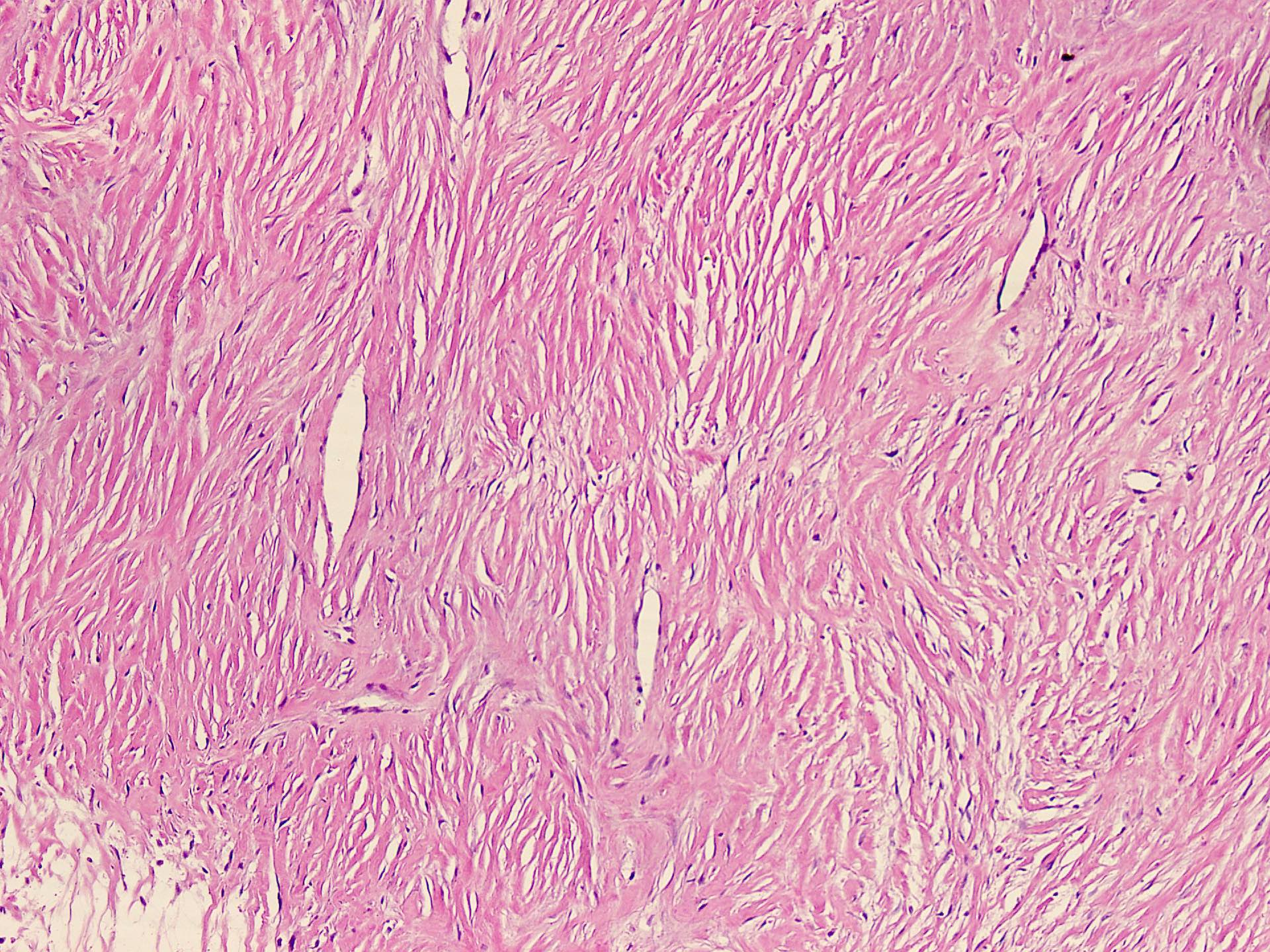
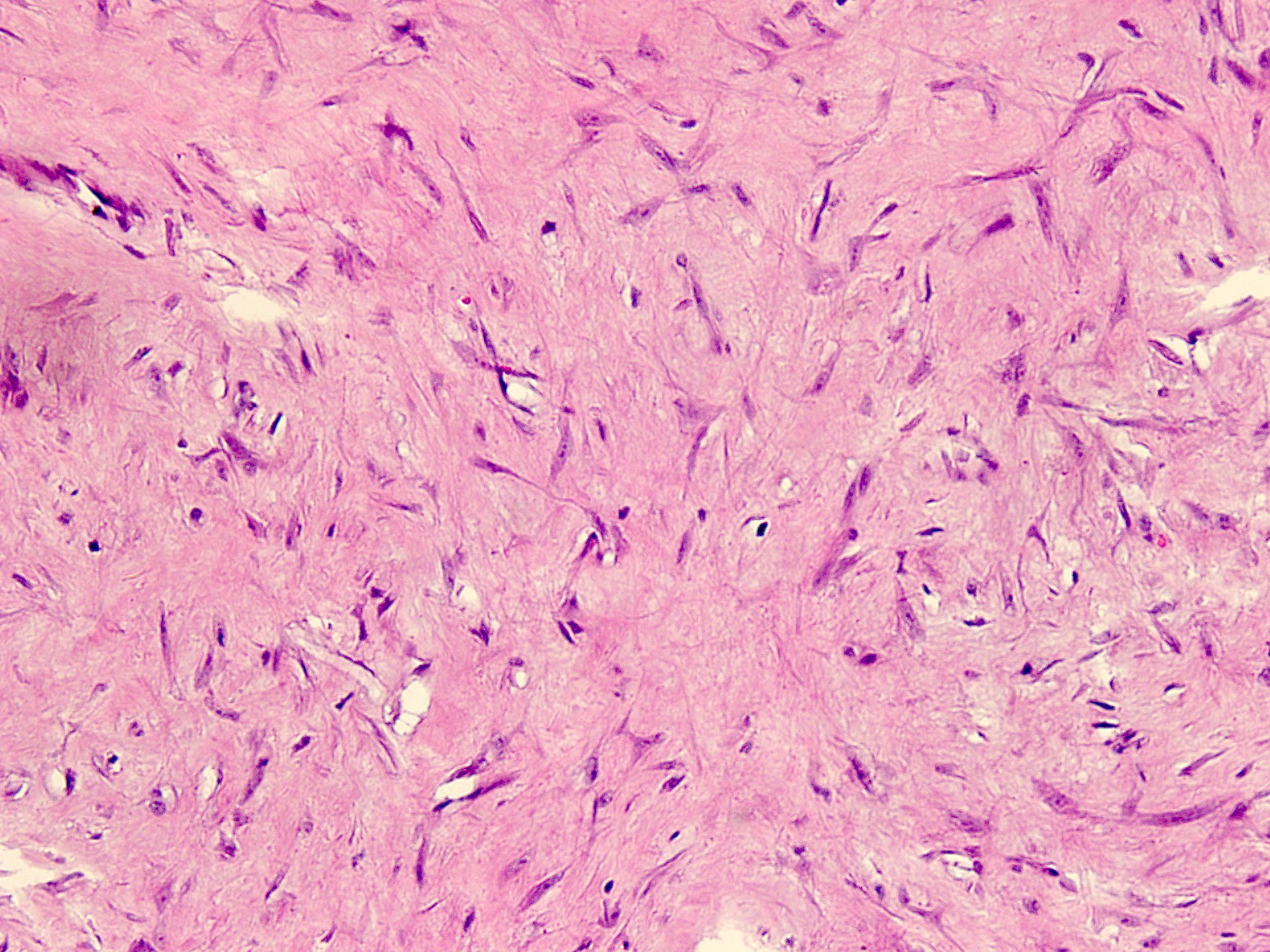
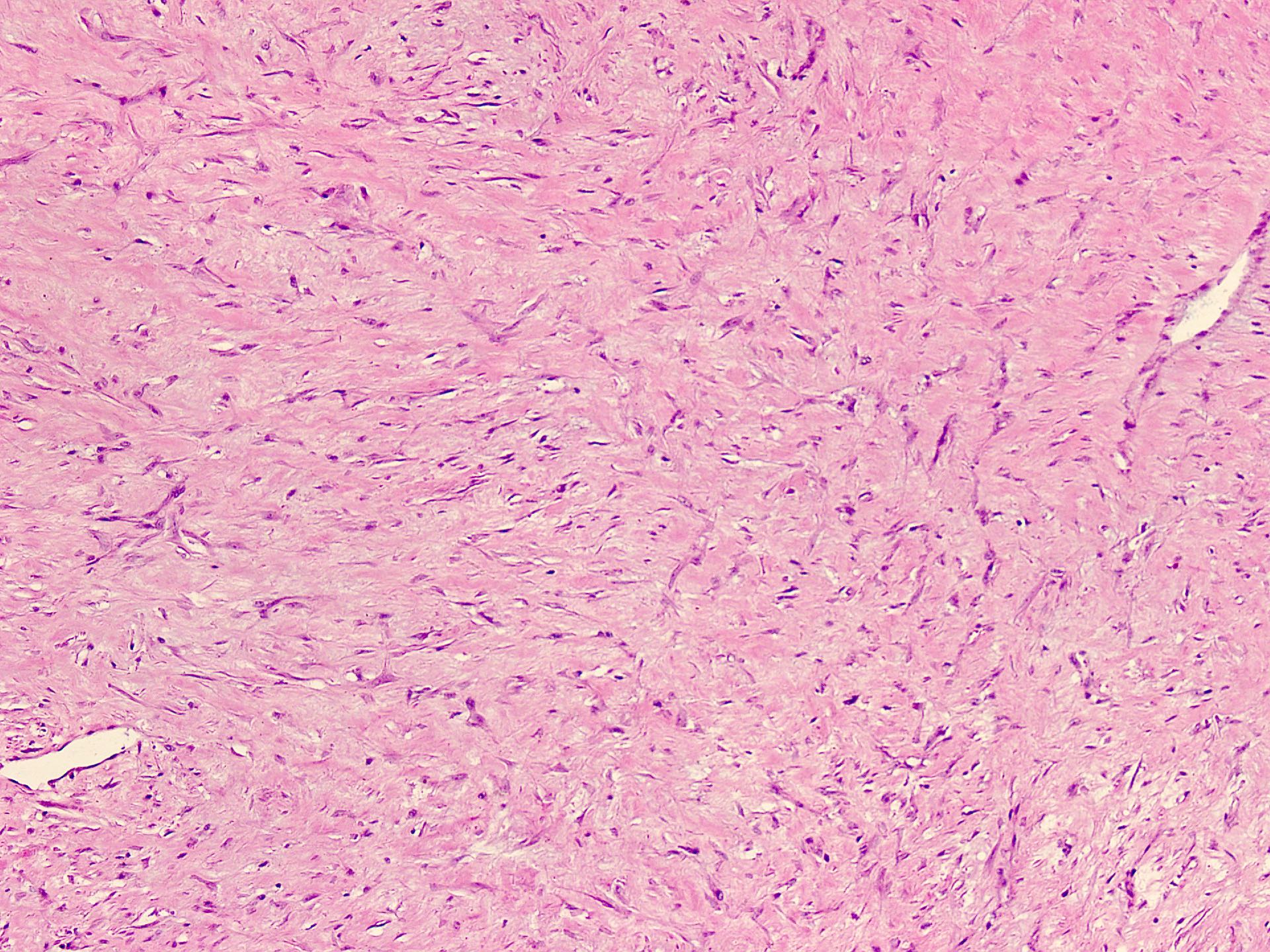
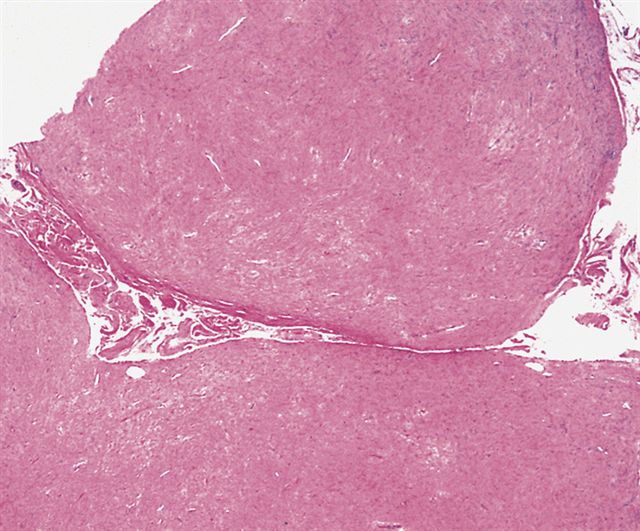
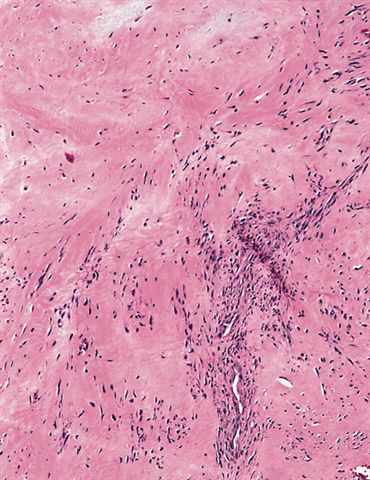
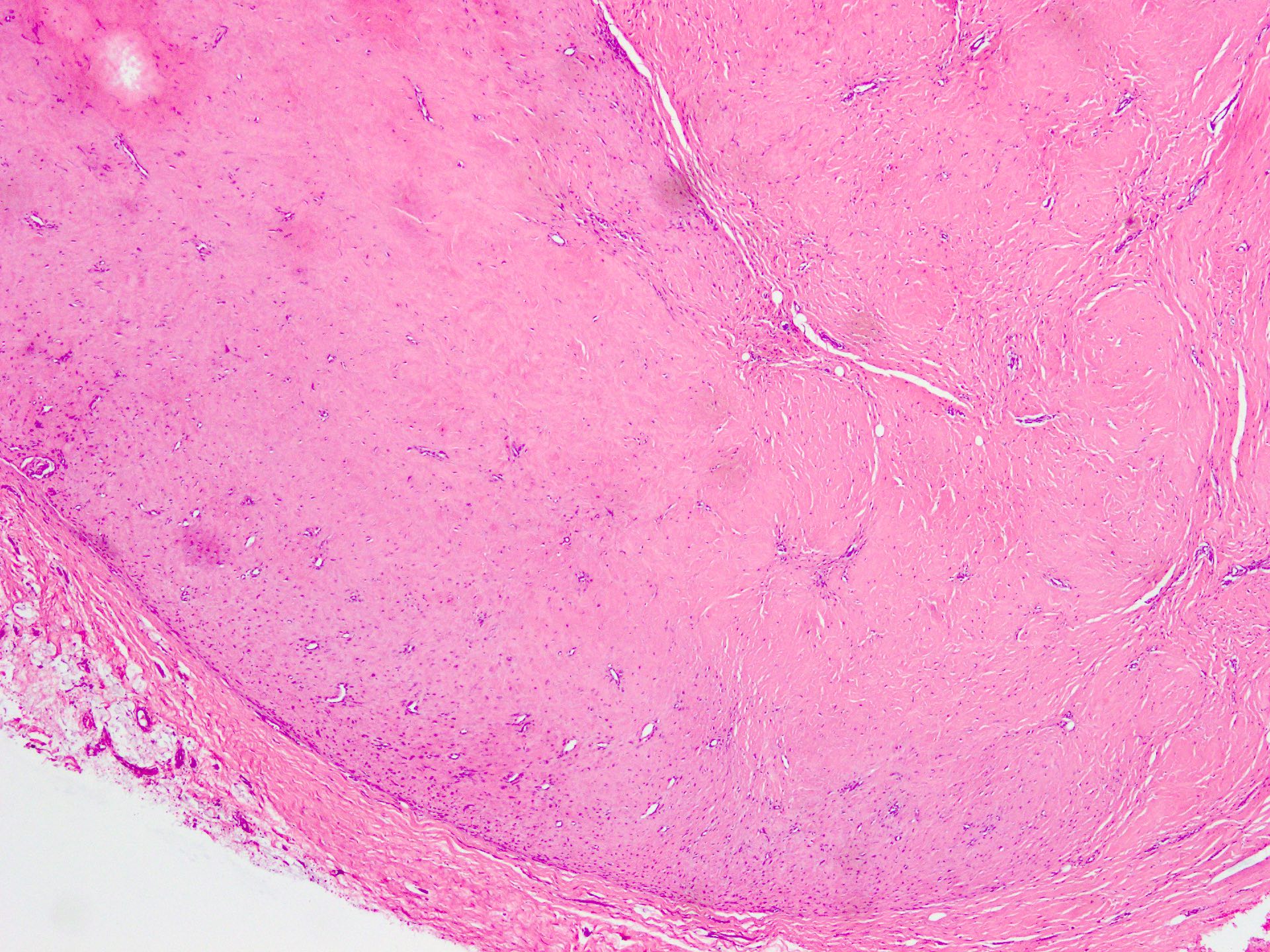
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Well circumscribed tumor of variable cellularity
- Cellularity mostly higher at tumor edges
- Bland spindle cells in a collagenous background
- Tumor has characteristic thin walled slit-like vessels
- Degenerative changes like myxoid / cystic change, osseous / chondroid metaplasia can be seen
- Bizarre pleomorphic cells can also be present
- Mitotically inactive
- Necrosis not present
- Cellular variant of fibroma of tendon sheath also exists; it overlaps morphologically with nodular fasciitis and fibrous histiocytoma (Cancer 1979;44:1945)
- Reference: Geschickter: Tumors of Bone, 1949
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Nasir Ud Din, M.B.B.S.
AFIP images
Cytology description
- H&E stained slides (J Cytol 2015;32:207):
- Low cellularity
- Few loose clusters and singly dispersed bland appearing fibrotic spindle cells and stellate cells admixed with hyalinized fibrocollagenous matrix
- Necrosis and atypical mitoses not seen
Positive stains
- May be focally positive for CD34, SMA, vimentin
- Rare cells can demonstrate calponin
- Special stain Masson trichrome highlights collagen
- References: Ann Dermatol 2019;31:110, Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 2013;29:e1, Anticancer Res 2014;34:5159
Negative stains
- CD31, CD34, CD117, beta catenin, FLI1, CD68, muscle specific actin (HHF35) and desmin
- < 1% of the cells demonstrated proliferation via Ki67
- References: Ann Dermatol 2019;31:110, Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 2013;29:e1, Anticancer Res 2014;34:5159
Electron microscopy images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- t(9;11)(p24;q13-14) (Case Rep Orthop 2019;2019:3514013, Anticancer Res 2014;34:5159)
- t(4;10)(p16;q24) (Case Rep Orthop 2019;2019:3514013)
- t(2;11)(q31-32;q12) (Case Rep Orthop 2019;2019:3514013)
- USP6 gene rearrangement (Mod Pathol 1999;12:565)
- Cellular variant of fibroma of tendon sheath harbors gene rearrangements in USP6 with different partners (Mod Pathol 2021;34:13)
Sample pathology report
- Finger nodule, excision:
- Fibroma of tendon sheath (see comment)
- Comment: Histology showed a well circumscribed, variably cellular lesion composed of bland spindle cells having regular nuclei arranged in sheets and fascicles. Thin walled vessels are present. The background is collagenous.
- It is a benign condition with recurrence in 5 - 10% cases.
Differential diagnosis
- Deep benign fibrous histiocytoma:
- Involves extremities and head and neck region
- Affects wide age range (i.e. 6 - 84 years)
- Slight male predominance
- Histologically well circumscribed and cellular lesion, prominent histiocyte-like cells, foam cells, giant cells and hemosiderin
- IHC: CD34 positive
- Tenosynovial cell tumor, localized type:
- Present in hands; located in close proximity to synovium of tendon sheath or interphalangeal joint
- Age range of 30 - 35 years
- Female predominance
- Histologically cellular tumor exhibiting variable composition of mononuclear cells, multinucleated giant cells, foamy macrophages, inflammatory cells and hemosiderin
- IHC: positive for CD68, CD163 and CD45
- Inclusion body fibromatosis:
- Affects toes of children < 5 years of age
- Ill defined, paucicellular, plump spindle cells exhibiting intracytoplasmic inclusion and bland nucleus with low mitotic activity
- IHC: expresses SMA
- Recurrence rate is high
Additional references
Board review style question #1
What is the most common location for fibroma of tendon sheath?
- Face
- Fingers
- Oral cavity
- Pelvis
- Toes
Board review style answer #1
B. Fingers. The most common location for fibroma of tendon sheath is finger tendons (i.e. thumb, index finger and middle finger).
Comment Here
Reference: Fibroma of tendon sheath
Comment Here
Reference: Fibroma of tendon sheath
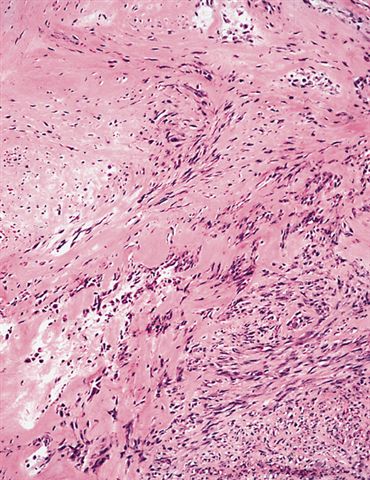
Board review style question #2
A 32 year old man has had painless swelling in the palm of his hand for 6 months. It was excised and the histology is shown in the above image. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Benign fibrous histiocytoma
- Fibroma of tendon sheath
- Nodular fasciitis
- Palmar fibromatosis
- Tenosynovial giant cell tumor, localized type
Board review style answer #2