Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Alexiev BA. Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissueeskchondrosarcomamyxoid.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma (EMC) is a malignant mesenchymal neoplasm of uncertain differentiation with abundant myxoid matrix, multilobular architecture, uniform cells arranged in cords, clusters and reticular networks and NR4A3 rearrangement
Essential features
- Bland cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and round to oval nuclei with evenly distributed chromatin and inconspicuous nucleolus
- Tumor cells are characteristically interconnected with one another to form cords and small clusters and complex trabecular or cribriform arrays
- Despite the name, there is no evidence of cartilaginous differentiation
- NR4A3 rearrangement
Terminology
- NR4A3 rearranged myxoid sarcoma (provisional)
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 9231/3 - Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma
- ICD-11: 2B5F.2 & XH9344 - Sarcoma, not elsewhere classified of other specific sites and myxoid chondrosarcoma
Epidemiology
- Rare, accounting for < 1% of soft tissue sarcomas
- Usually occurs in adults, mainly in the fourth to seventh decades (Mod Pathol 2018;31:744)
- M:F = ~2:1 (Mod Pathol 2018;31:744)
Sites
- Most arise in the deep soft tissues of the proximal extremities and limb girdles, with the thigh being the most common site (Hum Pathol 1972;3:421, Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:636)
- Less common sites include
- Pelvis (Tunis Med 2018;96:84)
- Masticator space (J Clin Exp Dent 2017;9:e825)
- Bone (Pathol Res Pract 2017;213:461, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:752)
- Lung (Int J Surg Case Rep 2016;27:96)
- Dura (Rare Tumors 2014;6:5586)
- Retroperitoneum (Am J Clin Pathol 1986;85:514)
- Pleura (Am J Clin Pathol 1992;97:498)
Pathophysiology
- Majority of cases are driven by gene fusions (see Molecular / cytogenetics description)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Slowly enlarging, minimally painful soft tissue mass (JBJS Case Connect 2020;10:e0614)
- Approximately 87% of patients present with primary localized disease and 13% with metastases (Cancer 2008;113:3364)
- First site of metastasis is the lung in 80% of cases (Cancer 2008;113:3364)
Diagnosis
- Tissue sampling is the gold standard for a definitive diagnosis
- Characterized by the rearrangements of the NR4A3 gene (World J Surg 1978;2:719, Cancer Genet 2014;207:276, Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2017;56:582)
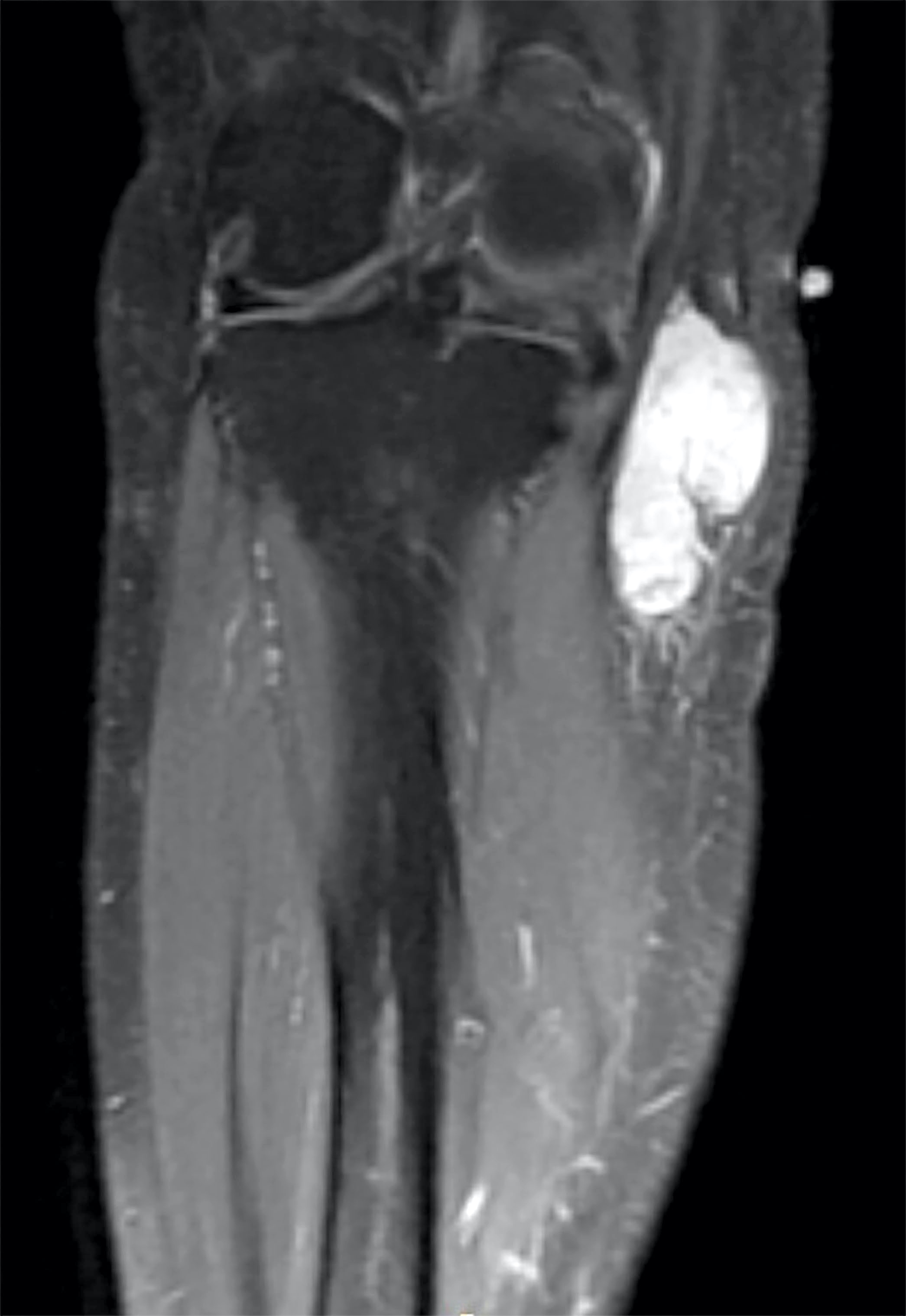
Radiology description
- CT and MRI images demonstrate lobulated mass with hyposignal intensity on T1 weighted sequences and hypersignal intensity on T2 weighted sequences (Biomed Res Int 2018;2018:9684268)
- Shows enhancing internal septation after injection of gadolinium (Biomed Res Int 2018;2018:9684268)
Prognostic factors
- Prolonged clinical course (Cancer 2008;113:3364, Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:636, Cancer 1992;70:2827)
- 5 year, 10 year and 15 year survival rates of 82 - 90%, 65 - 70% and 58 - 60%, respectively (Cancer 2008;113:3364, Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:636)
- Older age, larger tumor size (> 10 cm) and proximal location are adverse prognostic factors (Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:636, Mod Pathol 2000;13:900)
- Some studies suggest that high cellularity, presence of anaplasia or rhabdoid features, mitotic activity more than 2 per 10 high power fields, Ki67 ≥ 10% and Ki67 hot spot ≥ 25% were associated with decreased metastasis free or overall survival (Mod Pathol 2000;13:900)
- Tumors with variant non-EWSR1 gene fusions tend to show a higher incidence of rhabdoid cells, high grade morphology and aggressive outcome than the EWSR1-NR4A3 positive EMCs (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1407)
Case reports
- 24 year old woman with mass of the vulva (J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2011;37:1706)
- 41 year old woman presented with a mass in the left cerebellum (Medicine (Baltimore) 2017;96:e8684)
- 43 year old man presented with a soft tissue mass in his right thigh (J Med Case Rep 2016;10:321)
- 58 year old man with a right midfoot mass (JBJS Case Connect 2019;9:e0458)
- 62 year old man presented with a slowly enlarging, minimally painful soft tissue mass over the right lateral distal knee (JBJS Case Connect 2020;10:e0614)
Treatment
- Standard treatment for localized disease is surgery, plus or minus radiation therapy with an expected prolonged survival, even though the risk of relapse is about 50% (Cancers (Basel) 2020;12:2703)
- In advanced cases, besides the standard chemotherapy currently used for soft tissue sarcoma, antiangiogenic agents have recently shown promising activity (Cancers (Basel) 2020;12:2703)
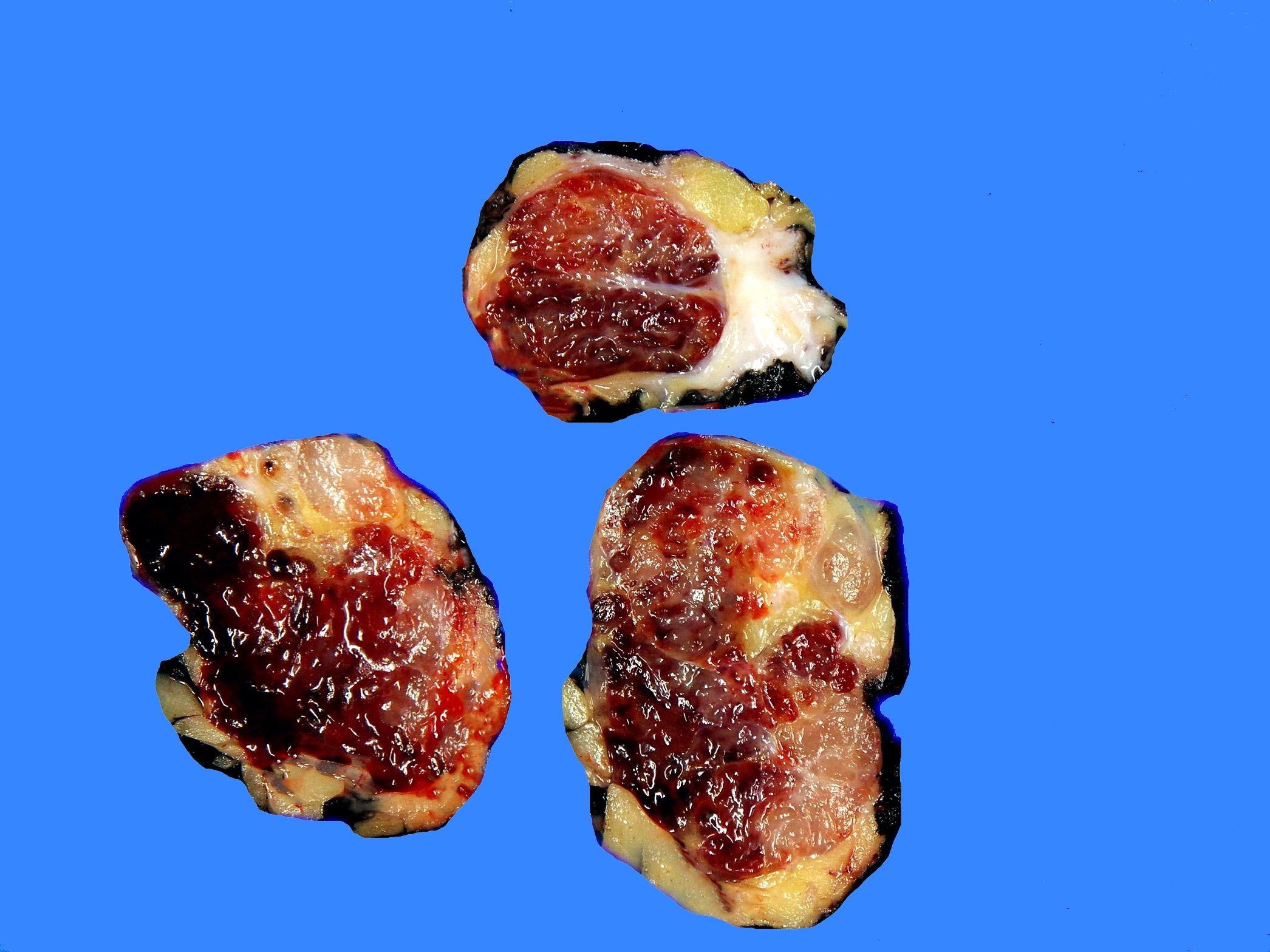
Gross description
- Well demarcated, lobulated (Cancer 1998;83:1504)
- Myxoid nodules separated by fibrous septa
- Cystic areas with hemorrhages
Frozen section description
- Uniform cells with round or spindled shaped nuclei and eosinophilic cytoplasm arranged in cords or clusters within abundant myxoid matrix
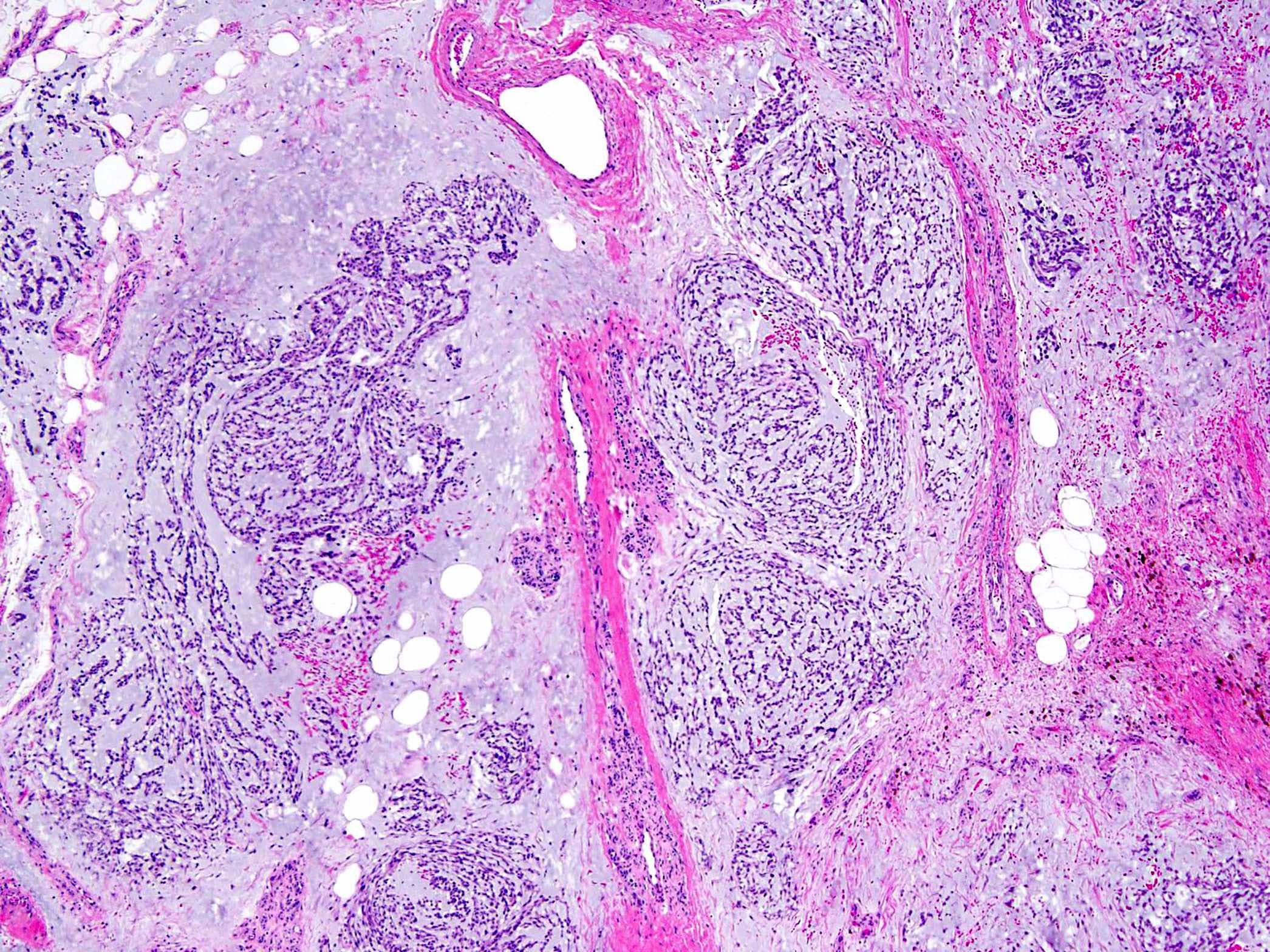
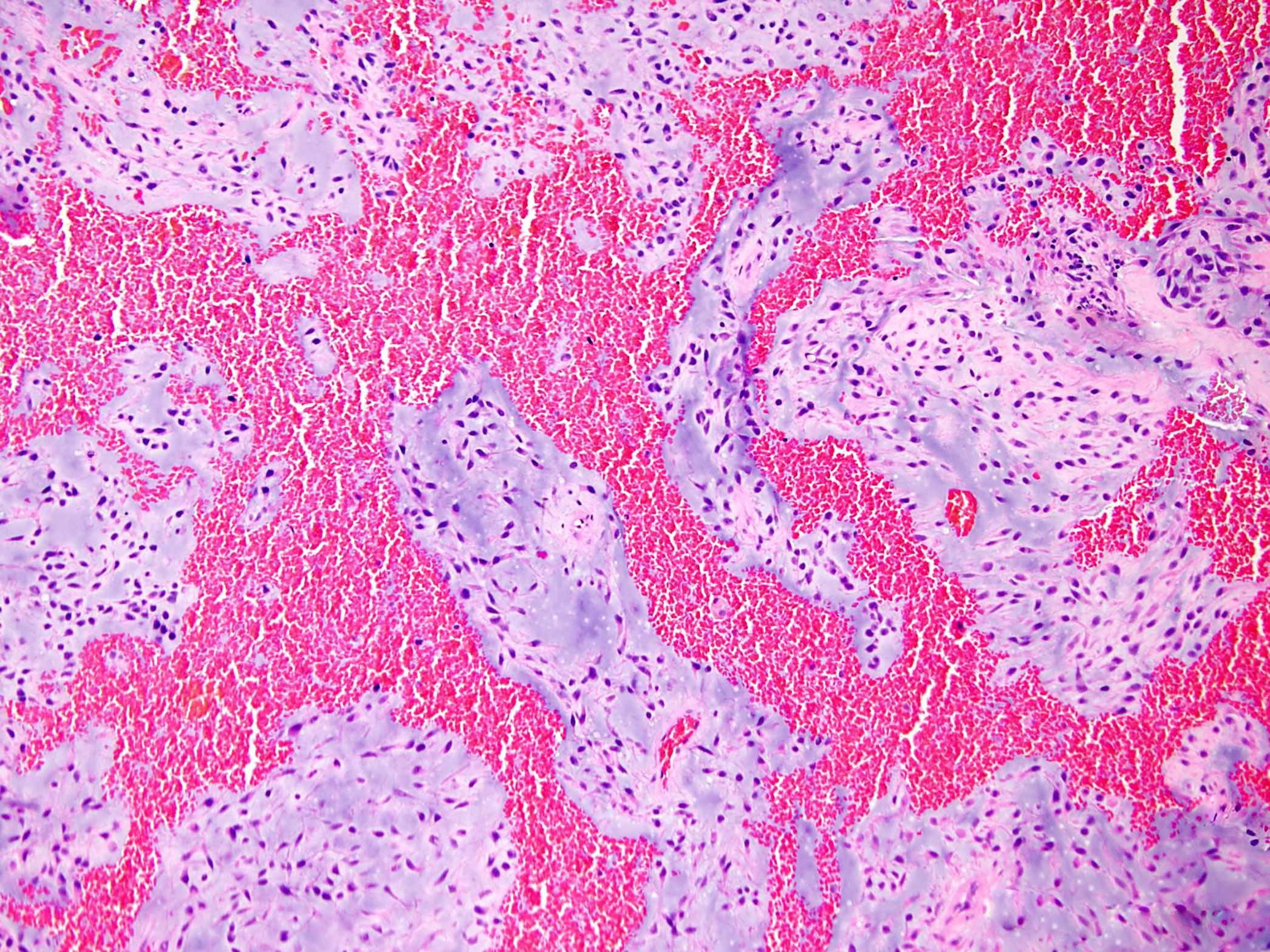
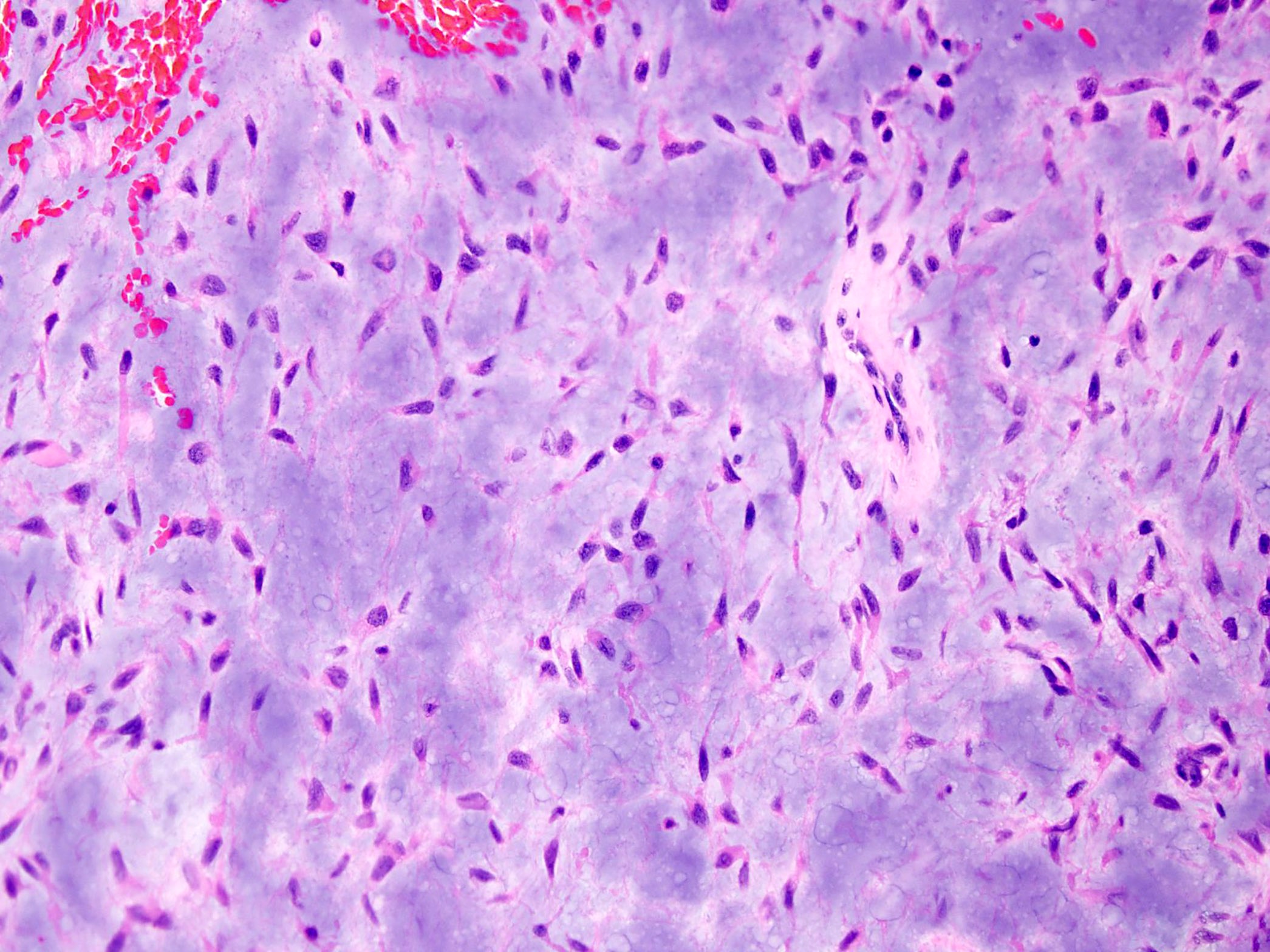
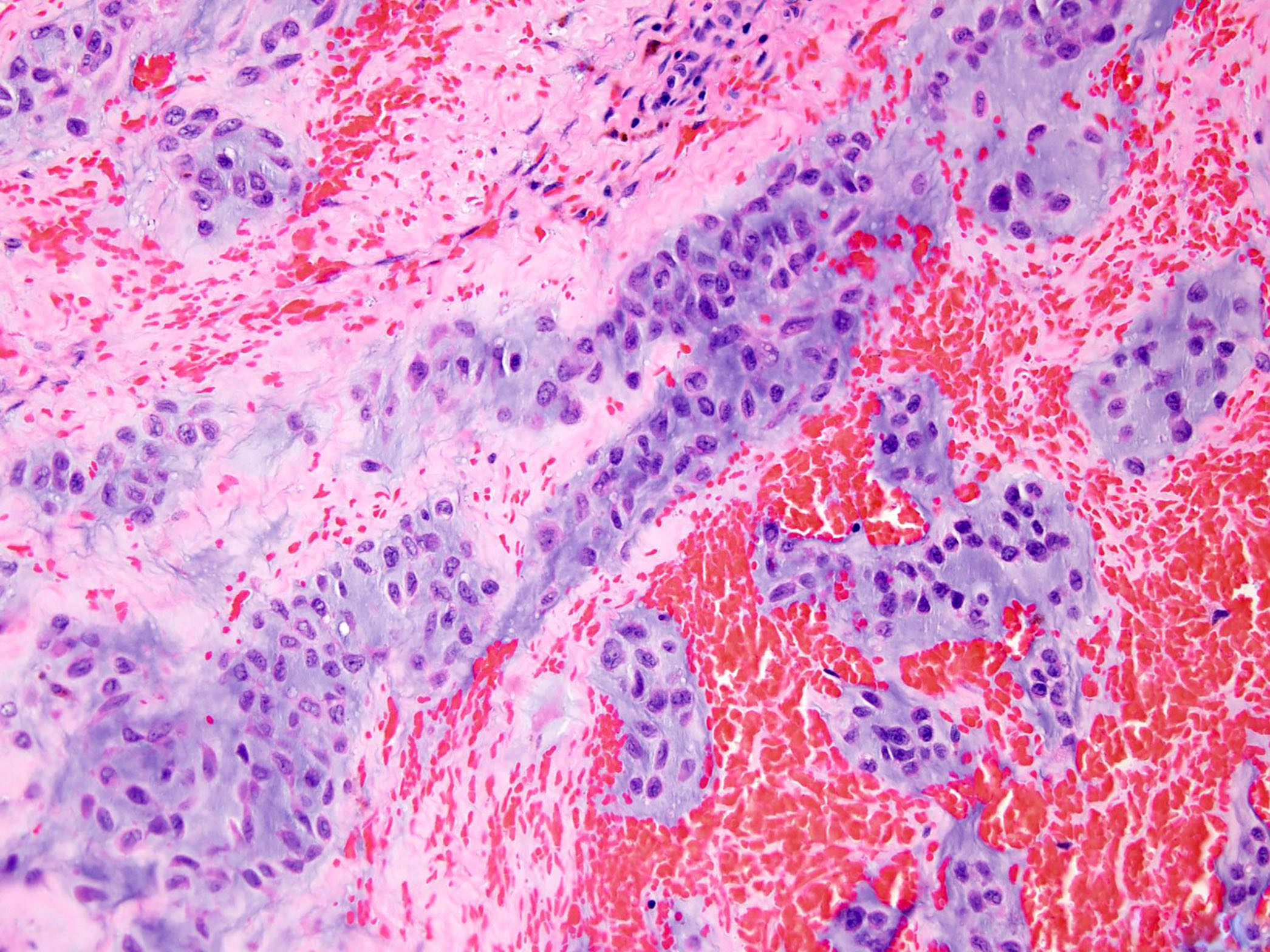
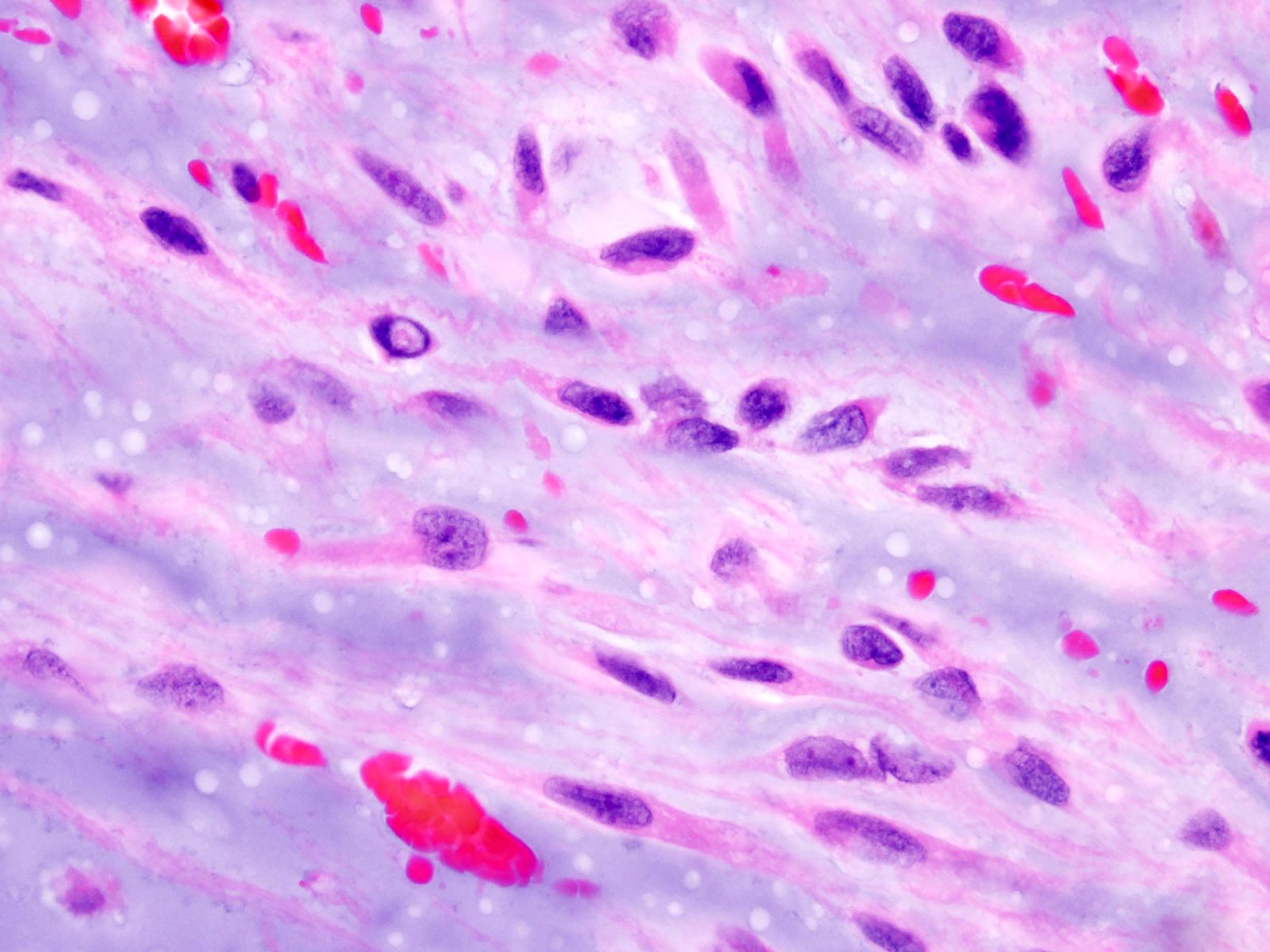
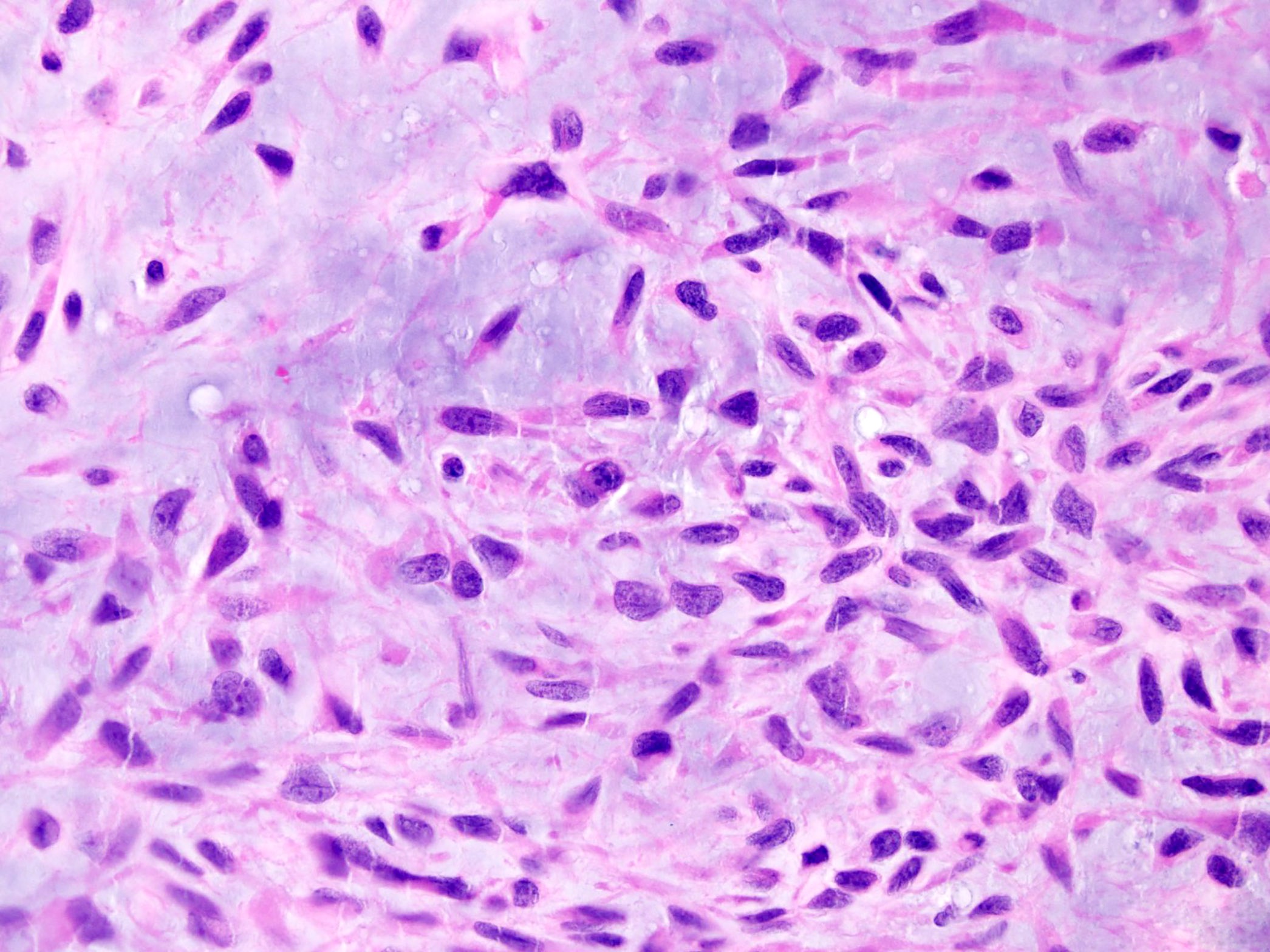
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Multinodular architecture (Cancer 1998;83:1504)
- Fibrous septa divide the tumor in pools of abundant myxoid or chondromyxoid matrix containing tumor cells (Cancer 1998;83:1504, Pathol Int 2005;55:453)
- Uniform cells with eosinophilic to vacuolated cytoplasm, often with long delicate cytoplasmic processes and round to oval nuclei with evenly distributed chromatin and inconspicuous nucleolus (Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:636)
- Tumor cells are characteristically interconnected with one another to form cords, small clusters and complex trabecular or cribriform arrays
- Spindle cell differentiation is common
- Mitotic activity is low
- Stroma is hypovascular
- Foci of intralesional hemorrhages are frequently seen in various proportions (Cancer 1998;83:1504)
- Usually lacks discernible cartilaginous histology (Pathol Int 2005;55:453)
- 80% of EMCs with variant (non-EWSR1) NR4A3 gene fusions (TAF15, TCF12) demonstrate high grade morphology with increased cellularity, proliferation and cytologic atypia, showing epithelioid / rhabdoid features in half of the cases (Hum Pathol 2014;45:1084)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Hypocellular to highly cellular smears composed of polygonal or oval cells arranged in clusters, trabeculae and cords (Diagn Cytopathol 2008;36:868, Cancer 2007;111:298)
- Monotonous uniformity in cell size and nuclear diameter (Cancer 2007;111:298)
- Bland round to indented nuclei with uniform chromatin, displaying nuclear inclusions and grooves (Diagn Cytopathol 2008;36:868)
- Variably sized nucleoli (Cancer 2007;111:298)
- Eosinophilic to finely vacuolated cytoplasm (Diagn Cytopathol 2008;36:868)
- Rhabdoid cells may be observed (Cognition 2005;96:B45)
- Abundant myxoid stroma (Cancer 2007;111:298)
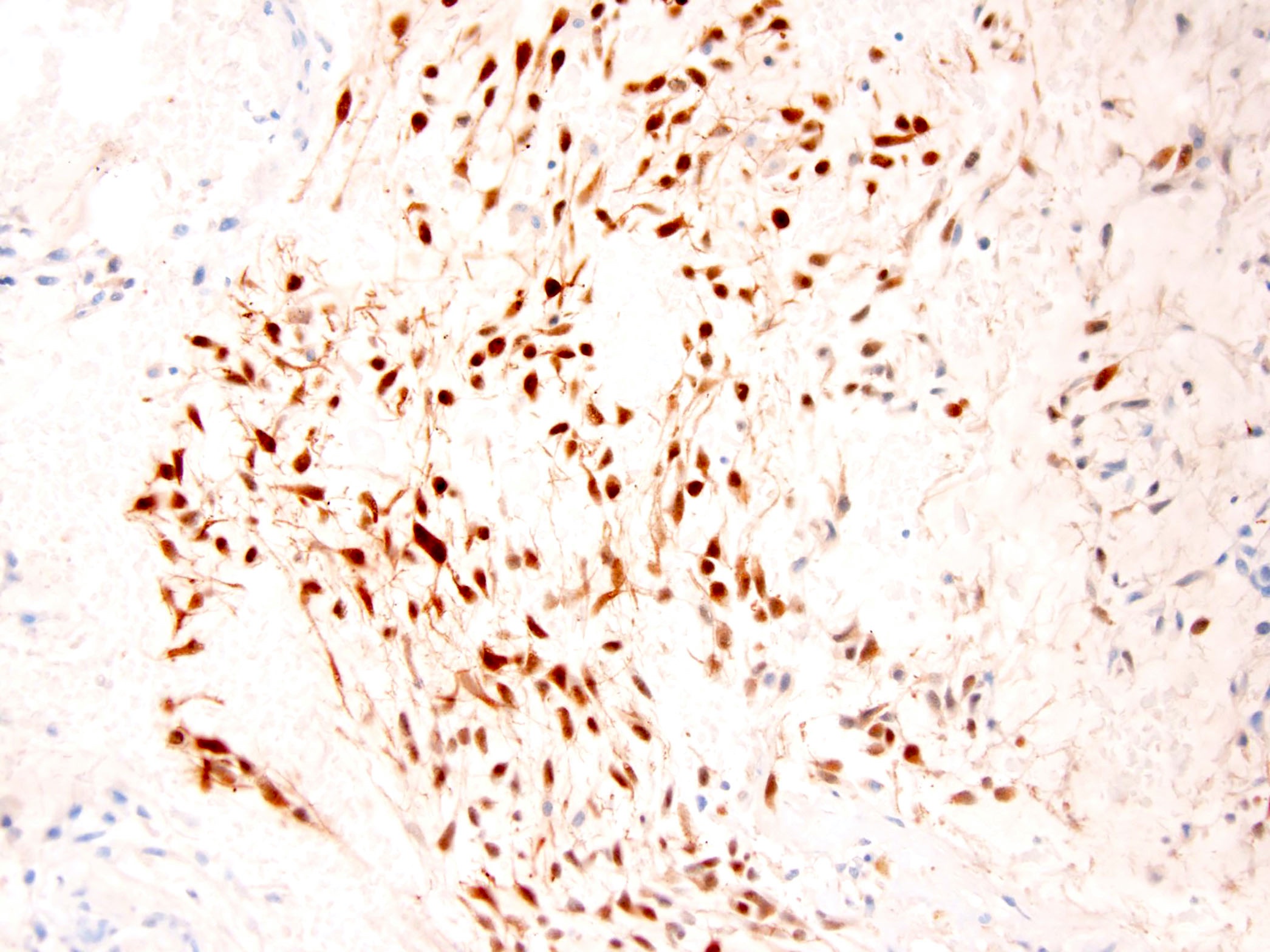
Positive stains
- INSM1 (Mod Pathol 2018;31:744)
- Note: INSM1 positive mimics comprise a small subset of chordoma, soft tissue myoepithelioma, ossifying fibromyxoid tumor and Ewing sarcoma (Mod Pathol 2018;31:744)
- NSE (Histopathology 2001;39:514)
- Synaptophysin (Histopathology 2001;39:514)
- S100 (50%) (Histopathology 2001;39:514)
Negative stains
- Epithelial markers (AE1 / AE3, CAM5.2, EMA) (Hum Pathol 2001;32:1116)
Electron microscopy description
- Distinct cords of cells immersed in glycosaminoglycan rich matrix (Histopathology 2001;39:514)
- Membrane bound dense core granules, compatible with neurosecretory granules (Histopathology 2001;39:514)
- Cells rich in mitochondria and well developed Golgi apparatus
- Intracysternal microtubules (Cancer 1998;83:1504)
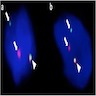
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Characterized by the rearrangement of the NR4A3, which in most cases (about 62 - 75%) is fused with EWSR1 and less frequently with other partners, including TAF15 (27%), TCF12 (4%), TFG, FUS and HSPA8 (World J Surg 1978;2:719, Cancer Genet 2014;207:276, Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2017;56:582)
- t(9;22)(q22;q12) translocation or less frequently a t(9;17)(q22;q11) or t(9;15)(q22;q21) translocation (Oncogene 1999;18:7599, Oncogene 1999;18:7594, Mod Pathol 1995;8:765, Am J Pathol 2003;162:781, Cancer Res 2000;60:6832)
Sample pathology report
- Left thigh, excision:
- Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma (see comment and synoptic report)
- Comment: The tumor has a multinodular architecture. Thick fibrous bands separate pools of myxoid stroma containing uniform tumor cells with eosinophilic or vacuolated cytoplasm and round to oval nuclei with evenly distributed chromatin and inconspicuous nucleolus. The cells are interconnected with one another to form cords and small clusters. Foci of intralesional hemorrhages are frequently seen. Mitotic activity is low (1 mitosis/10 high power fields). Immunohistochemically, the tumor cells are positive for NSE and negative for SMA, desmin, GFAP, CD34, S100, AE1 / AE3 and EMA. FISH studies demonstrate rearrangements of NR4AE at 9q22.33 and EWSR1 at 22q12 gene regions. The findings strongly support the diagnosis of extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma. Although often associated with prolonged survival, extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma has high rates of distant recurrence.
Differential diagnosis
- Soft tissue myoepithelioma:
- A panel including keratin AE1 / AE3, EMA, S100 and GFAP will identify myoepithelial differentiation in the majority of cases (Head Neck Pathol 2015;9:32)
- No rearrangement of NR4A3
- Ossifying fibromyxoid tumor:
- Most cases show a peripheral shell of lamellar bone (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2014;53:183)
- Desmin expression in 70% of cases (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2014;53:183)
- PHF1 gene rearrangement has been observed in 80% of ossifying fibromyxoid tumors, including benign, atypical and malignant subtypes, with fusion to EP400 in 44% of cases (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2016;140:371, Hum Pathol 2013;44:2603)
- ZC3H7B-BCOR and MEAF6-PHF1 fusions occur predominantly in S100 negative and malignant ossifying fibromyxoid tumor (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2014;53:183)
- Soft tissue chordoma:
- Brachyury expression (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:572, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:719)
- No rearrangement of NR4A3
- Myxofibrosarcoma, epithelioid variant:
- MET overexpression (Diagn Pathol 2018;13:56)
- No rearrangement of NR4A3
- Myxoid leiomyosarcoma:
- HMGA2, h-caldesmon and desmin expression (Hum Pathol 2017;59:139, Hum Pathol 1999;30:392, Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:927)
- No rearrangement of NR4A3
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
A 50 year old man presented with a left thigh mass. Hematoxylin eosin stains demonstrated hypocellular lobules with abundant pale blue myxoid matrix containing interconnecting cords and clusters of uniform cells with round to ovoid nuclei and eosinophilic or vacuolated cytoplasm. Foci of intralesional hemorrhages were seen. Occasional mitotic figures were identified (2 mitoses/10 high power fields). Immunohistochemical stain for NSE was positive in tumor cells while all of the following were negative: S100, GFAP, AE1 / AE3, desmin, CD34, ERG and h-caldesmon. FISH studies demonstrated rearrangement of the NR4AE gene at 9q22.33.
Which of the following is most likely the correct diagnosis?
- Epithelioid sarcoma
- Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma
- Metastatic carcinoma
- Myoepithelioma
- Ossifying fibromyxoid tumor
Board review style answer #2