Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Frozen section images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Beshah FN, Velez Torres JM. Soft tissue chondroma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissueeskchondroma.html. Accessed March 28th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign, cartilage forming tumor that usually arises in the vicinity of joints or tendons in the hands and feet of adults
Essential features
- Arises from soft tissue of fingers, hands and feet
- Not connected to the underlying bone
- Well circumscribed, cartilaginous proliferation
Terminology
- Soft tissue chondroma, extraskeletal chondroma, chondroma of soft parts
ICD coding
- ICD-10: D21.9 - benign neoplasm of connective and other soft tissue, unspecified
Epidemiology
- Age: 30 - 60 years (Surg Pathol Clin 2015;8:419)
- Gender: slight male predominance
Sites
- Mostly occurs in the fingers
- Hands, toes, feet and trunk are less frequently affected
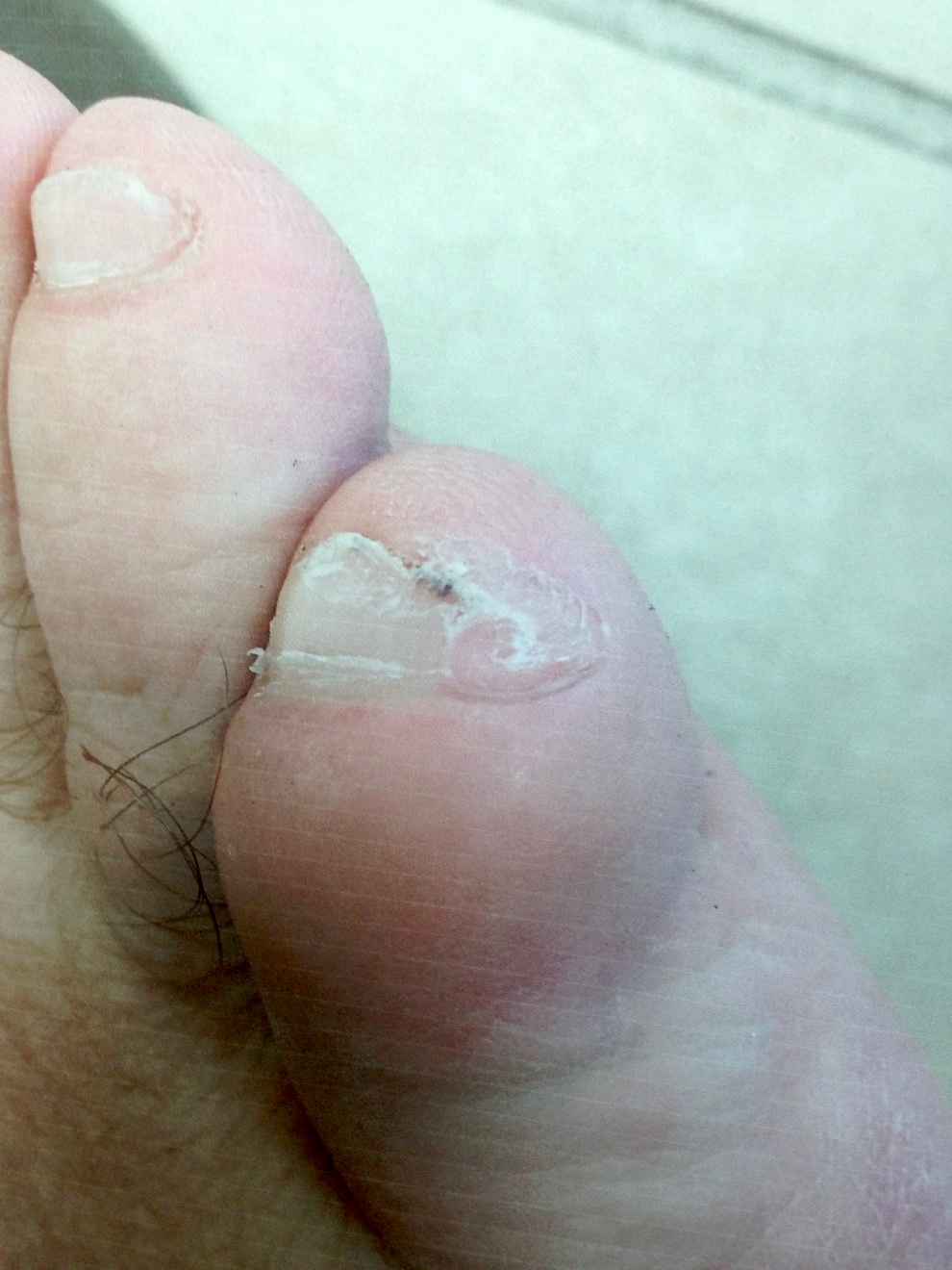
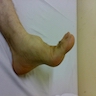
Clinical features
- Occurs in soft tissue of hands and feet
- Solitary, slowly enlarging nodule; occasionally causes pain or tenderness
- Reference: Histopathology 1986;10:147
Diagnosis
- Clinical presentation
- Solitary nodule
- Involves fingers, toes and hands
- < 3 cm
- Imaging
- Computed tomography
- Magnetic resonance imaging
- Reference: Histopathology 1986;10:147
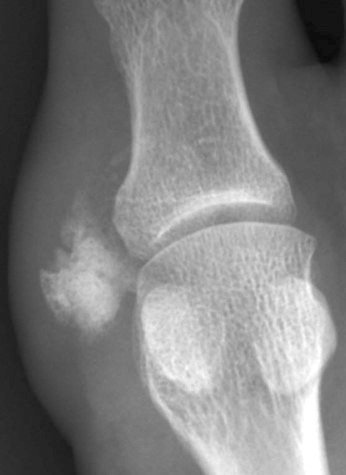
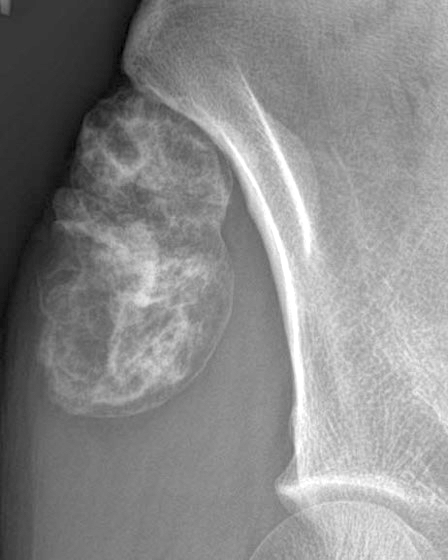
Radiology description
- Well demarcated
- Does not involve bone, although some tumors cause compression deformities or bone erosion
- Discrete, irregular, ring-like or curvilinear calcifications
- Reference: AJR Am J Roentgenol 1985;144:1263
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Favorable prognosis
- 15 - 20% recurrence rate (Surg Pathol Clin 2015;8:419)
Case reports
- 14 year old boy with plantar swelling (Int J Surg Case Rep 2022;90:106688)
- 51 year old man with posterior mediastinal mass (J Int Med Res 2021;49:3000605211053557)
- 84 year old man with palmar mass (Cureus 2021;13:e19467)
Treatment
- Simple excision
Clinical images
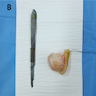
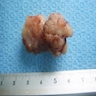
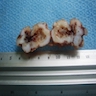
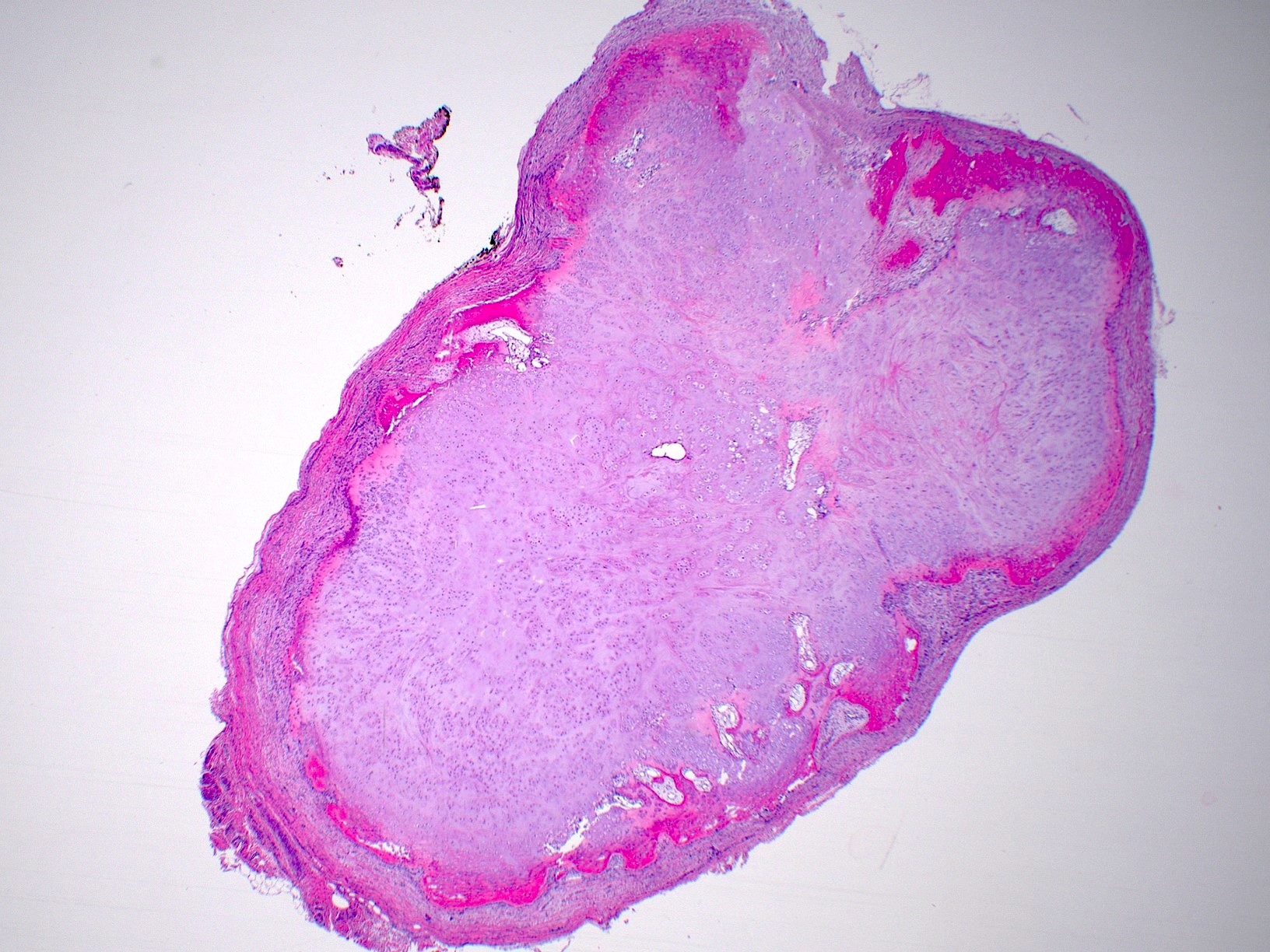
Gross description
- Well demarcated, oval - round
- < 3 cm in size
Frozen section description
Frozen section images
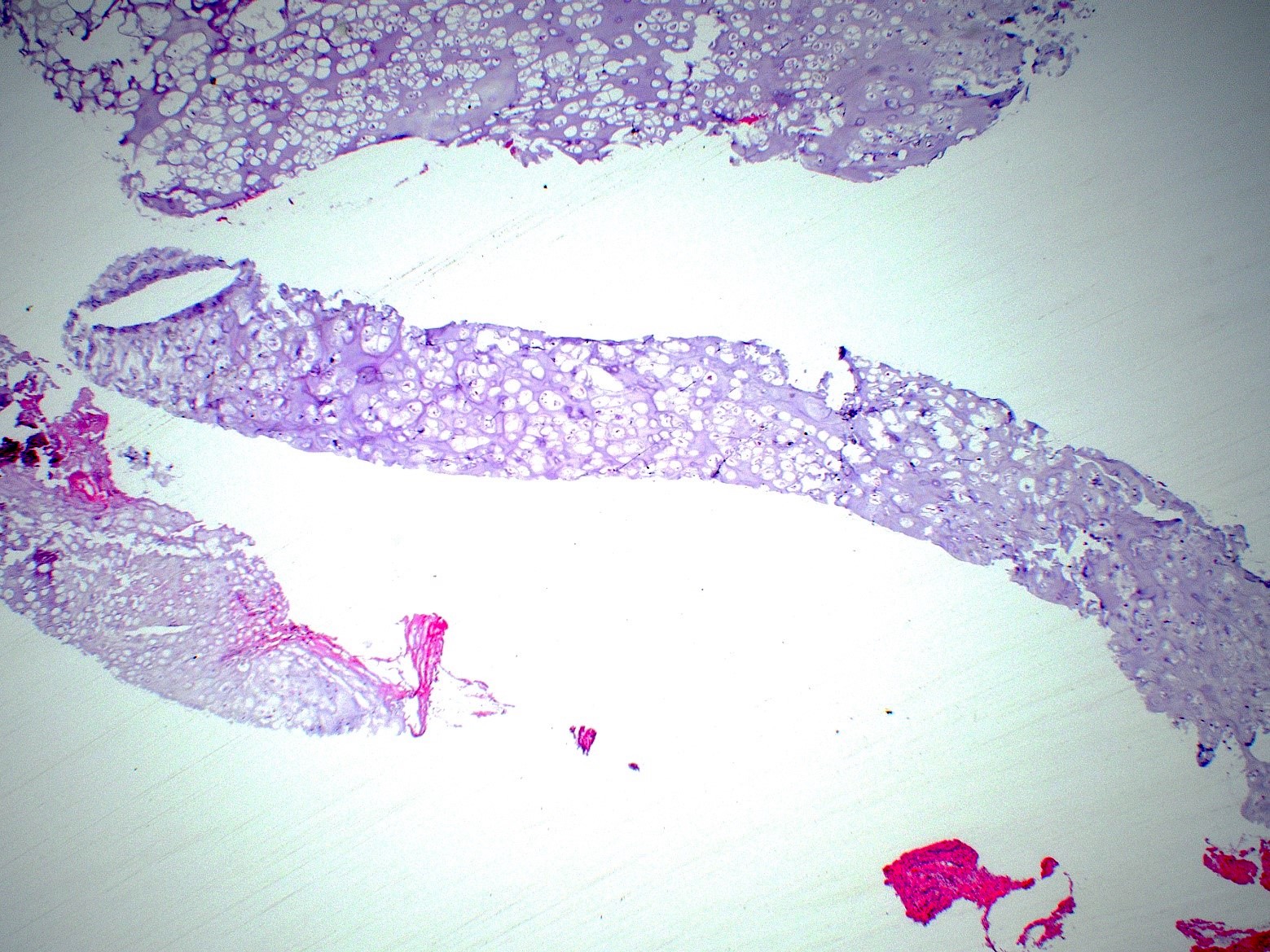
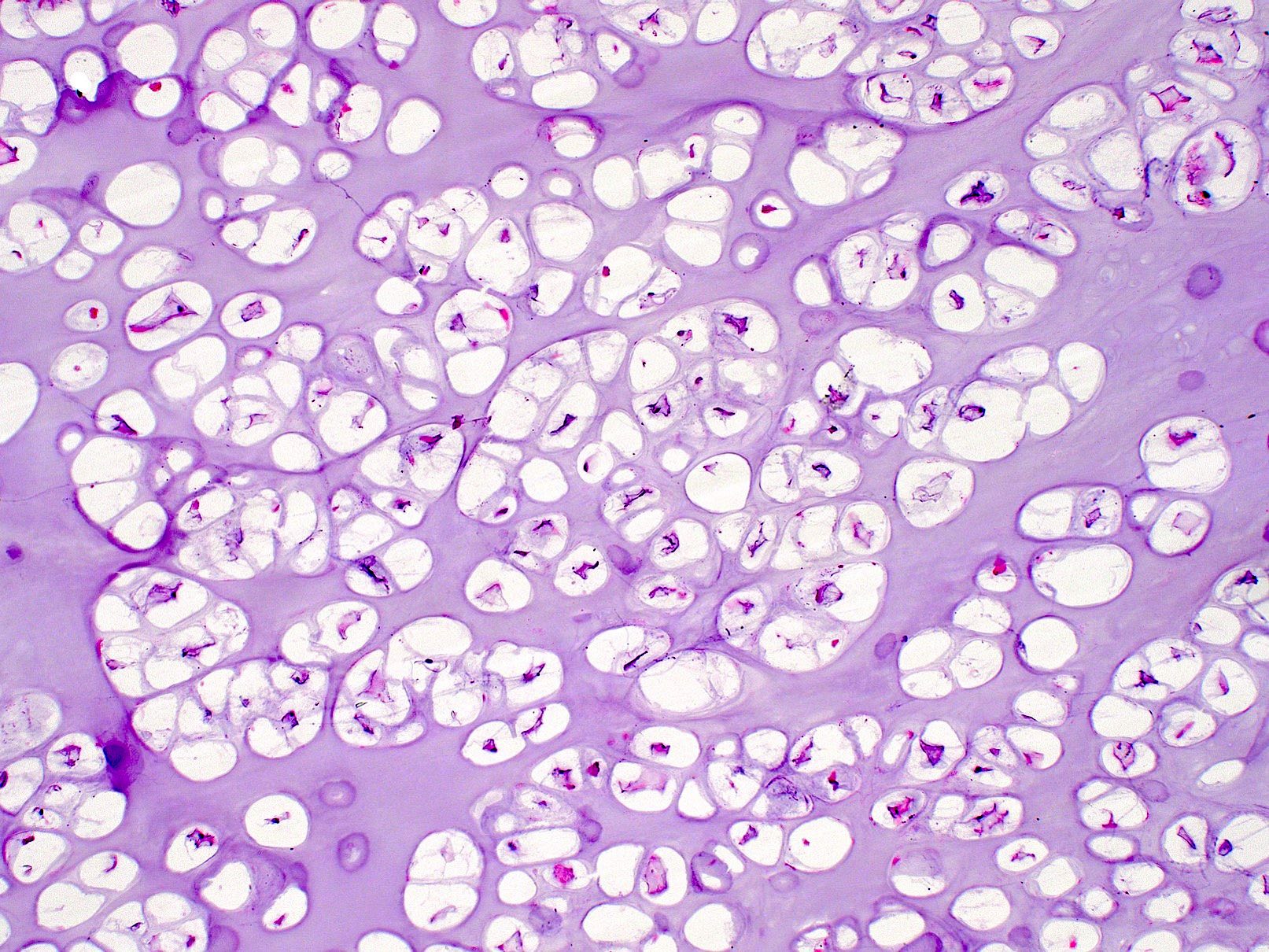
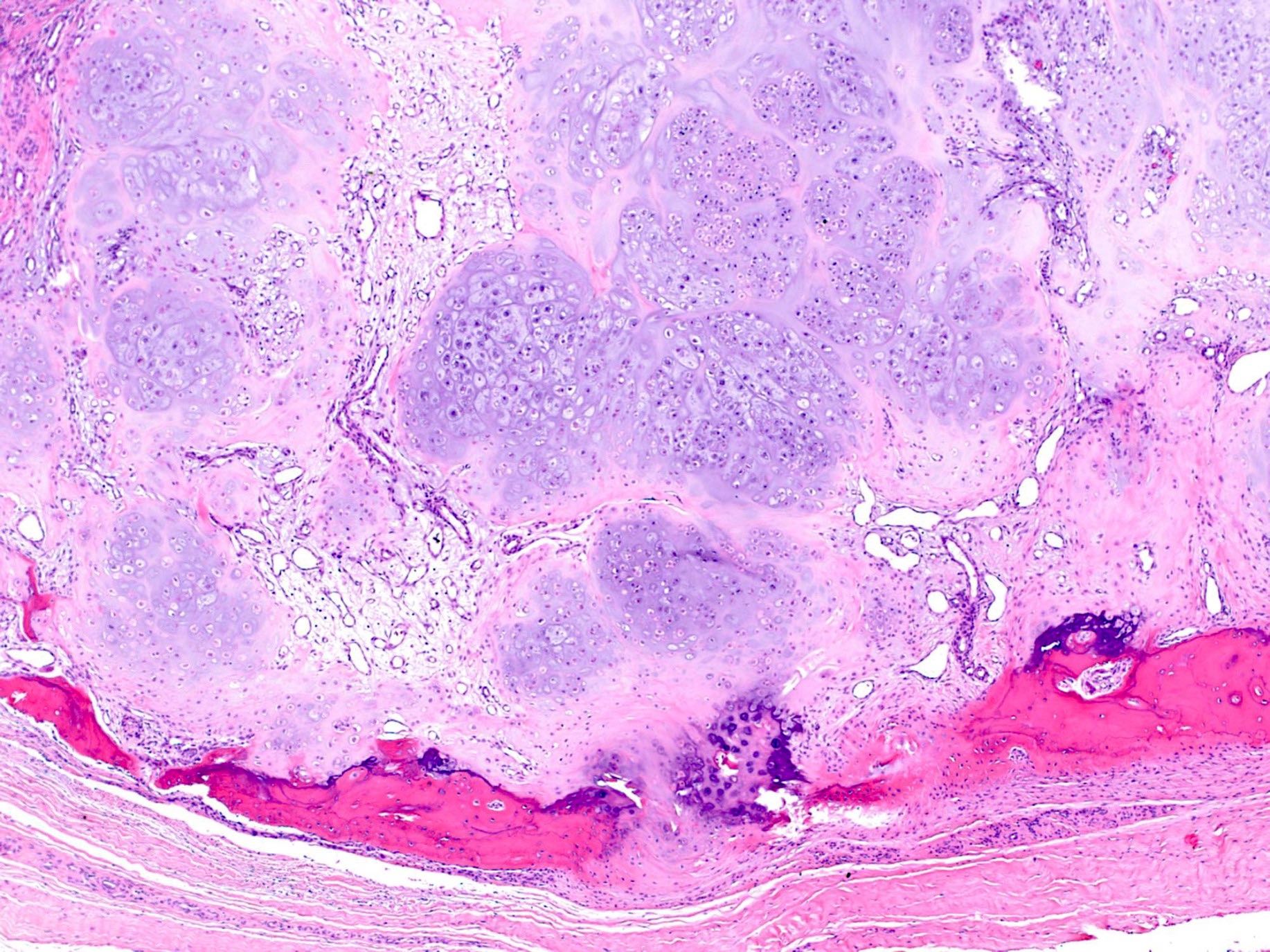
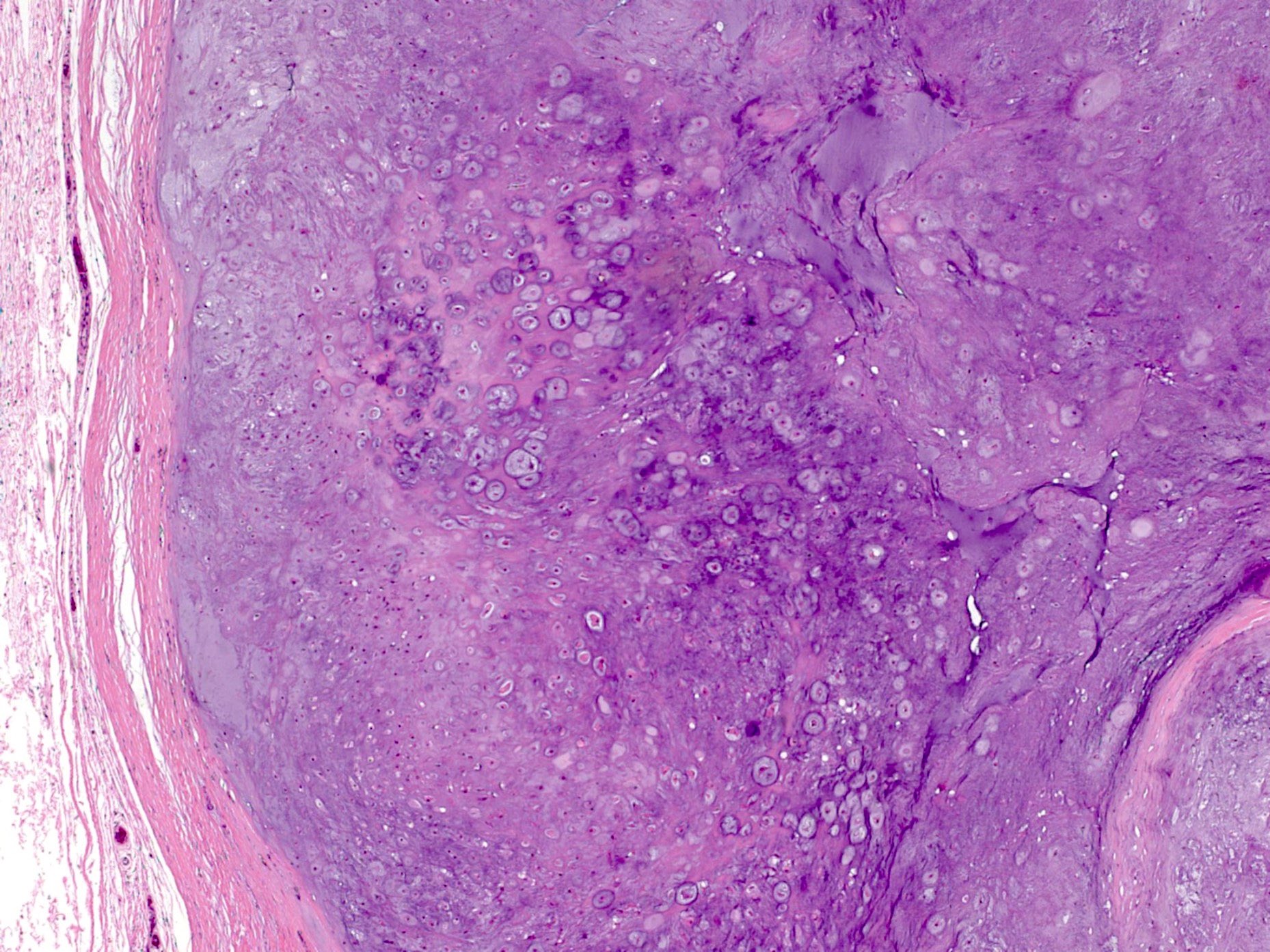
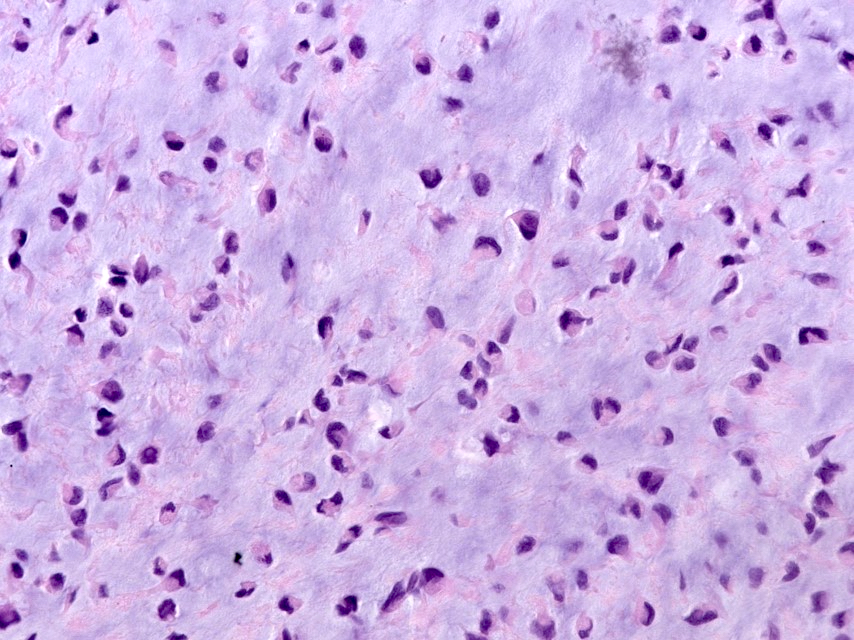
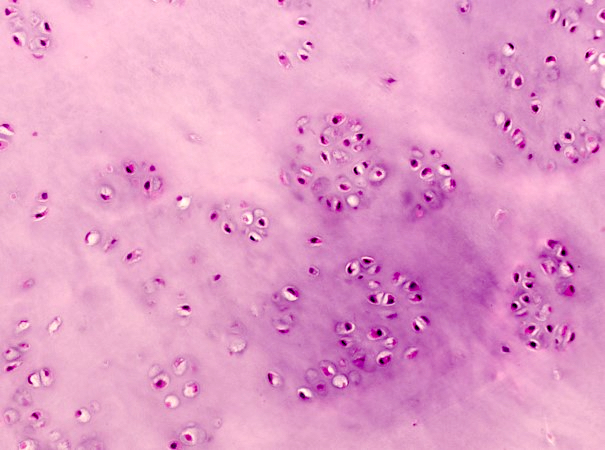
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Mature hyaline cartilage arranged in lobules with sharp borders
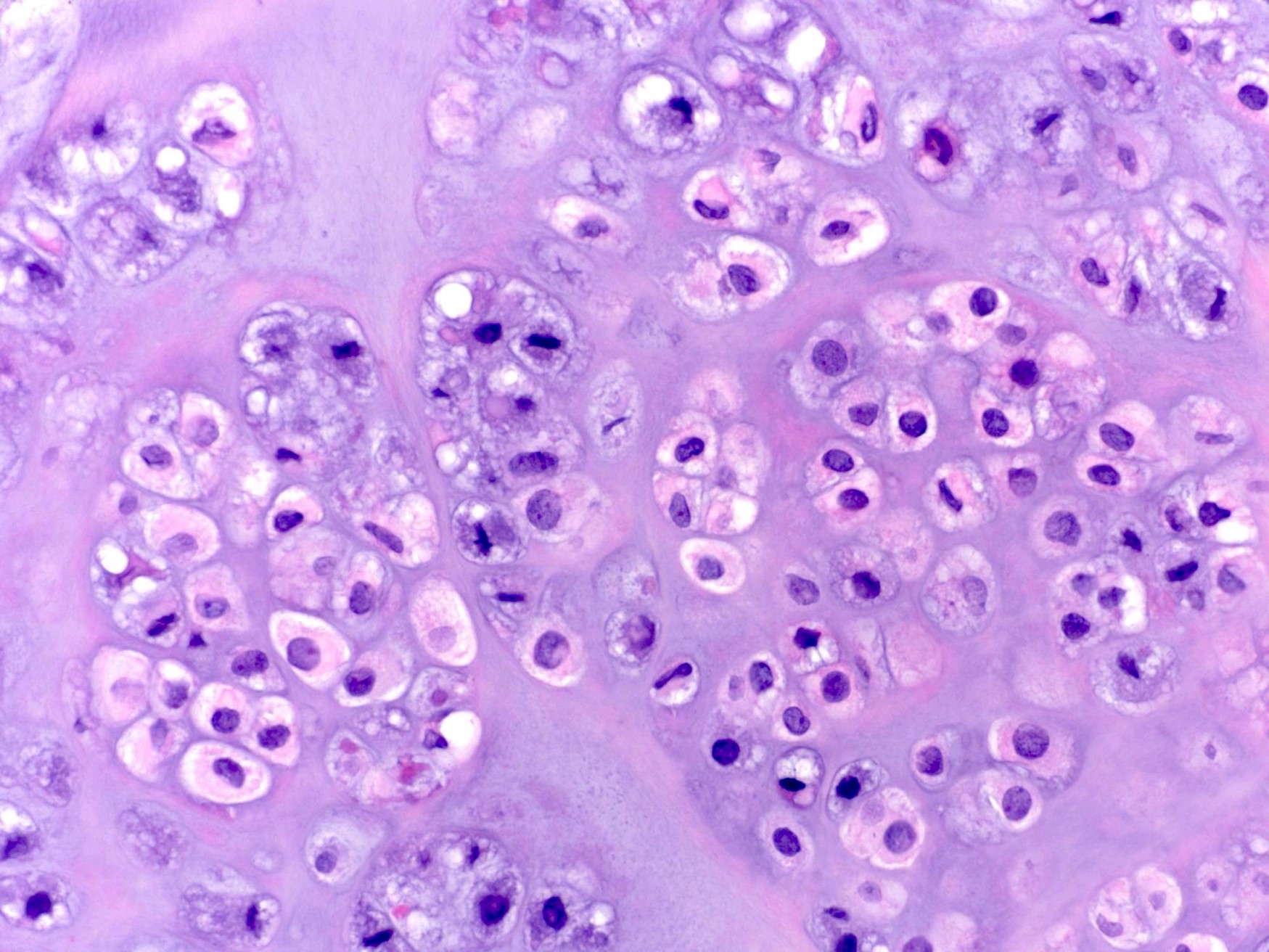
- Chondrocytes in lacunae, arranged diffusely or in small clusters
- Rarely can have moderate pleomorphism
- 33% show focal or diffuse calcifications
- Chondroblastoma-like soft tissue chondroma shows hypercellular areas with cells resembling chondroblasts, recently reclassified as calcified chondroid mesenchymal tumor (Mod Pathol 2021;34:1373)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Negative stains
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- 12q13-q15 rearrangements involving HMGA2 have been reported (Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1993;69:79, Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2000;118:144, J Pathol 2002;196:194, Mod Pathol 2003;16:1132, Clin Neuropathol 2015;34:13)
- Also FN1 rearrangements (Mod Pathol 2019;32:1762)
- Soft tissue chondromas harbor the FN1::FGFR1 fusion (Mod Pathol 2019;32:1762)
Sample pathology report
- Right hip mass, excision:
- Soft tissue chondroma
Differential diagnosis
- Synovial chondromatosis:
- Large joints, multiple small nodules attached to synovial membrane
- Cloning / clustering of chondrocytes
- FN1 gene rearrangement (Mod Pathol 2019;32:1762)
- The mutual exclusivity of ACVR2A rearrangements observed in synovial chondromatosis and FGFR1 / 2 in soft tissue chondromas suggests these represent separate entities (Mod Pathol 2019;32:1762)
- Calcifying aponeurotic fibroma:
- Islands of calcification surrounded by palisaded epithelioid fibroblasts (resembling chondrocytes), poorly circumscribed and infiltrative
- Juxtacortical chondroma:
- Attached to surface of bone
- Acral fibrochondromyxoid tumor:
- Lobular growth pattern with fibrovascular septa (Mod Pathol 2020;33:1360)
- More myxoid stroma
- Calcified chondroid mesenchymal tumor:
- Multinodular architecture with increased cellularity towards the periphery of the nodules (Mod Pathol 2021;34:1373)
- Matrix frequently shows coarse, grungy to lacy calcifications, which are refractive rhomboid crystals under polarized light
- Osteoclast-like giant cells are frequently identified
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 42 year old man presented with a painless soft tissue nodule on the right index finger. Magnetic resonance imaging showed a 2 cm well circumscribed nodule (T1 hypointense) with no connection to the underlying bone. What is the diagnosis?
- Chondrosarcoma
- Osteochondroma
- Soft tissue chondroma
- Synovial chondromatosis
Board review style answer #1
C. Soft tissue chondroma. The histology shows a nodule of cartilage surrounded by fibrous tissue, which is characteristic of soft tissue chondroma. Answer D is incorrect because synovial chondromatosis is characterized by multinodular mass with superficial synovial lining. Answer A is incorrect because chondrosarcomas tend to be hypercellular and have cytologic atypia. Answer B is incorrect because the tumor is not connected to the underlying bone and does not have the characteristic trabecular bone with cartilage cap.
Comment Here
Reference: Soft tissue chondroma
Comment Here
Reference: Soft tissue chondroma
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is a feature of soft tissue chondroma?
- Arises from big joints like hip and knee joint
- Size is usually > 3 cm
- Tends to be a solitary nodule
- Usually arises from the underlying bones
Board review style answer #2
C. Tends to be a solitary nodule. Soft tissue chondroma usually presents as a single nodule. Answer B is incorrect because soft tissue chondromas are < 3 cm in size in the majority of cases. Answer D is incorrect because soft tissue chondromas have no connection to the underlying bone. Answer A is incorrect because soft tissue chondromas usually involve fingers, toes and hands.
Comment Here
Reference: Soft tissue chondroma
Comment Here
Reference: Soft tissue chondroma