Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Ahmed R, Anjum S, Ud Din N. Angiofibroma of soft tissue. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissueangiofibroma.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign fibroblastic neoplasm of uniform spindle cells
- Variable myxoid and collagenous stroma with a network of thin walled, branching blood vessels
Essential features
- Clinically well defined mass located in the soft tissues of the extremities, often in association with joints or fibrotendinous structures
- Histologically uniform spindle cells, myxoid / collagenous stroma, network of thin walled, branching blood vessels
- Cytogenetically NCOA2 gene rearrangements
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Wide age range: 6 - 68 years (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:500)
- Most commonly in middle aged adults (Cureus 2019;11:e6225)
- Slight female predominance (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6:2208)
Sites
- Typically arises in extremities, mainly the legs (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11:3777)
- Frequently involving or adjacent to large joints, such as knee (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:500)
- Unusual locations include back, abdominal wall, pelvic cavity, breast (Hum Pathol 2013;44:438)
- Often subcutaneous but may be intramuscular and deep (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2017;56:750)
Pathophysiology
- Angiofibromas have near diploid karyotypes with recurrent t(5;8)(p15;q13), which results in fusion of AHRR in chromosome band 5p15 and NCOA2 in 8q13 (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2012;51:510)
- AHRR::NCOA2 chimera, including basic helix - loop - helix and PAS domains of AHHR and 2 transcriptional activation domains of NCOA2, is present in 60 - 80% of tumors
- Variant GTF2I::NCOA2 or GAB1::ABL1 fusions have been found in a single case (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2013;52:330, Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2017;56:750)
- AHRR::NCOA2 chimera is expected to upregulate AHRR / ARNT signaling and aryl hydrocarbon receptor target genes (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2012;51:510)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Slow growing, painless mass (Skeletal Radiol 2014;43:403)
- Preoperative duration may be long
- Most lesions are sharply demarcated (Cureus 2019;11:e6225)
- Infiltration into adjacent structures may be encountered on imaging
Diagnosis
- Requires interpretation of clinical, radiological and histopathological findings
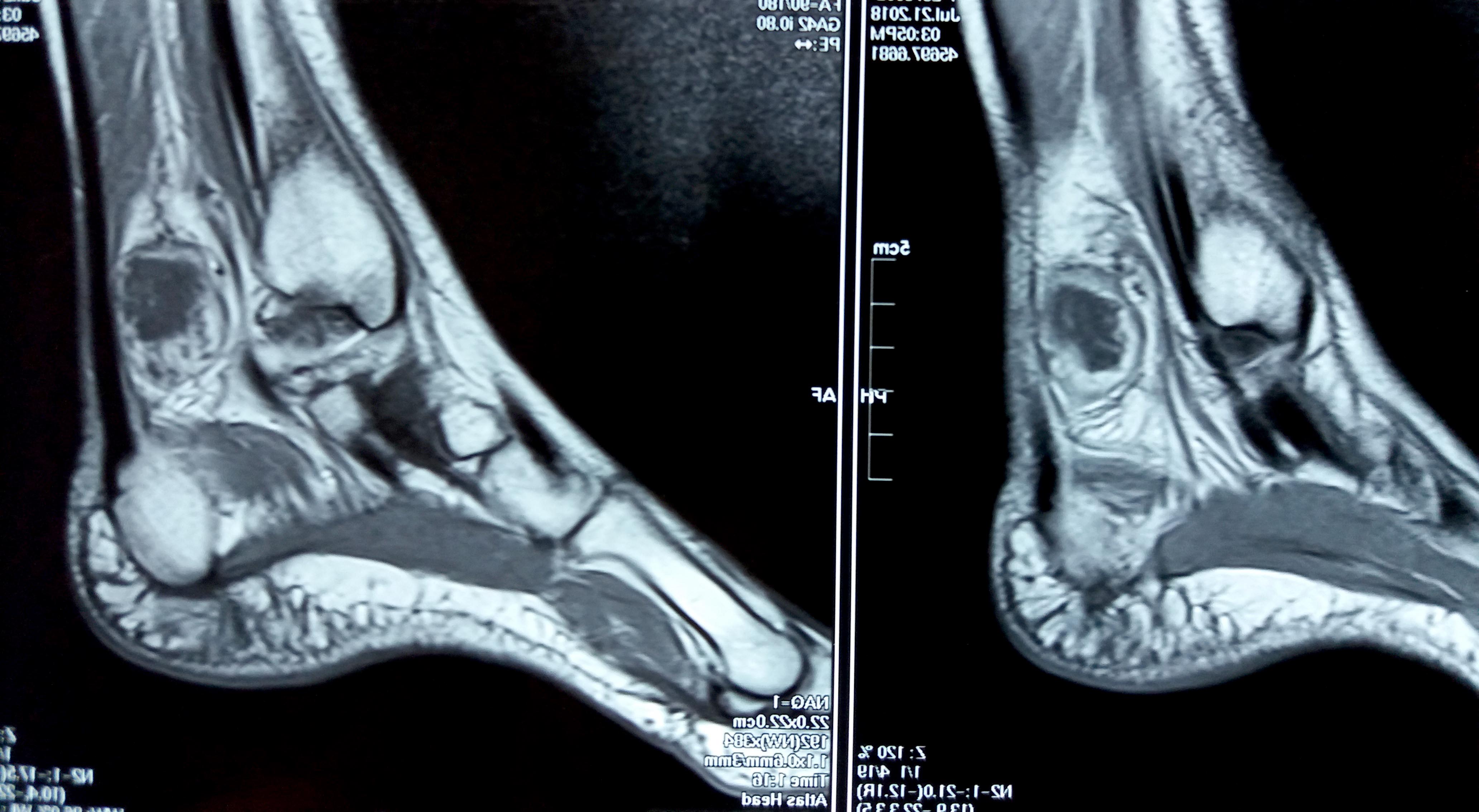
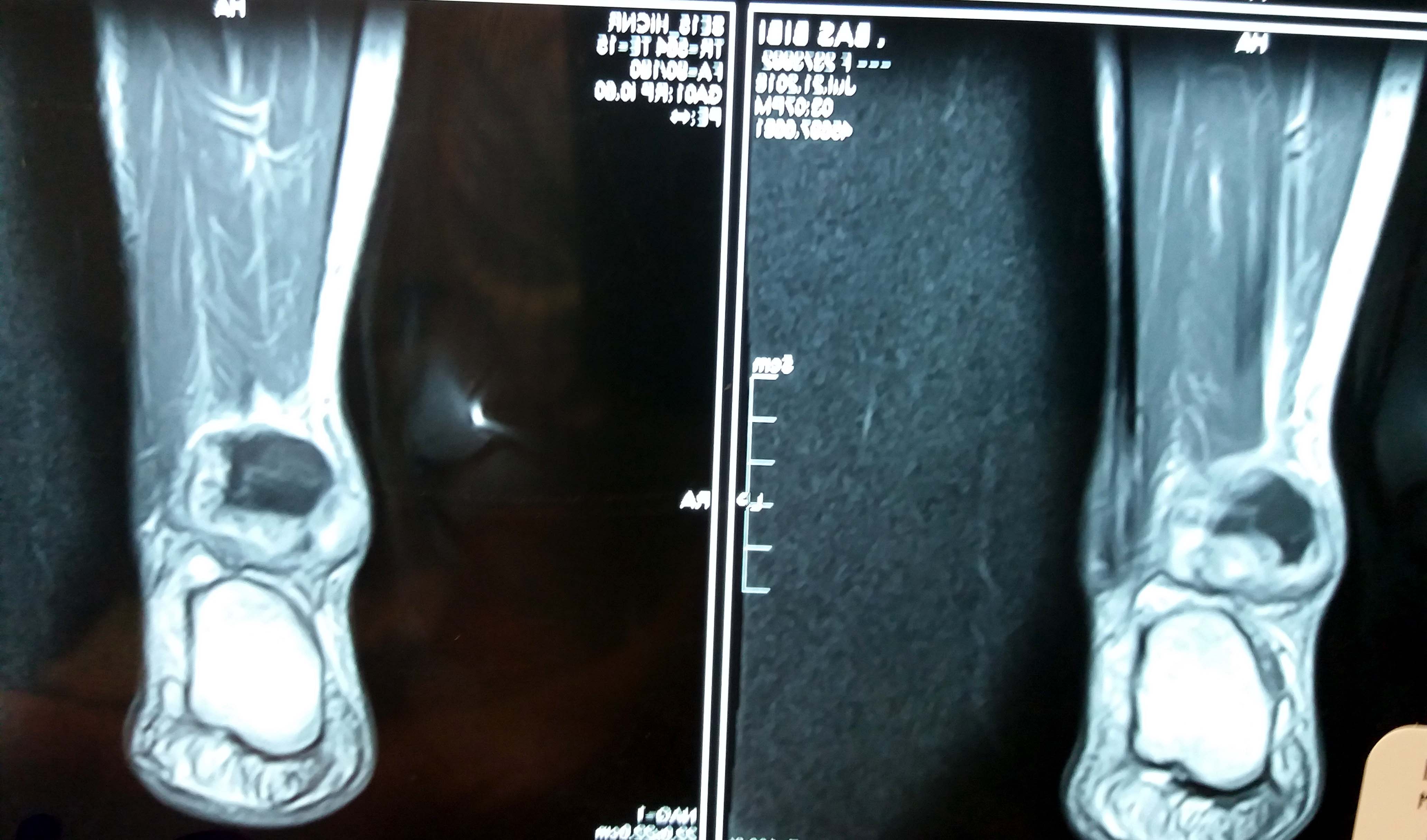
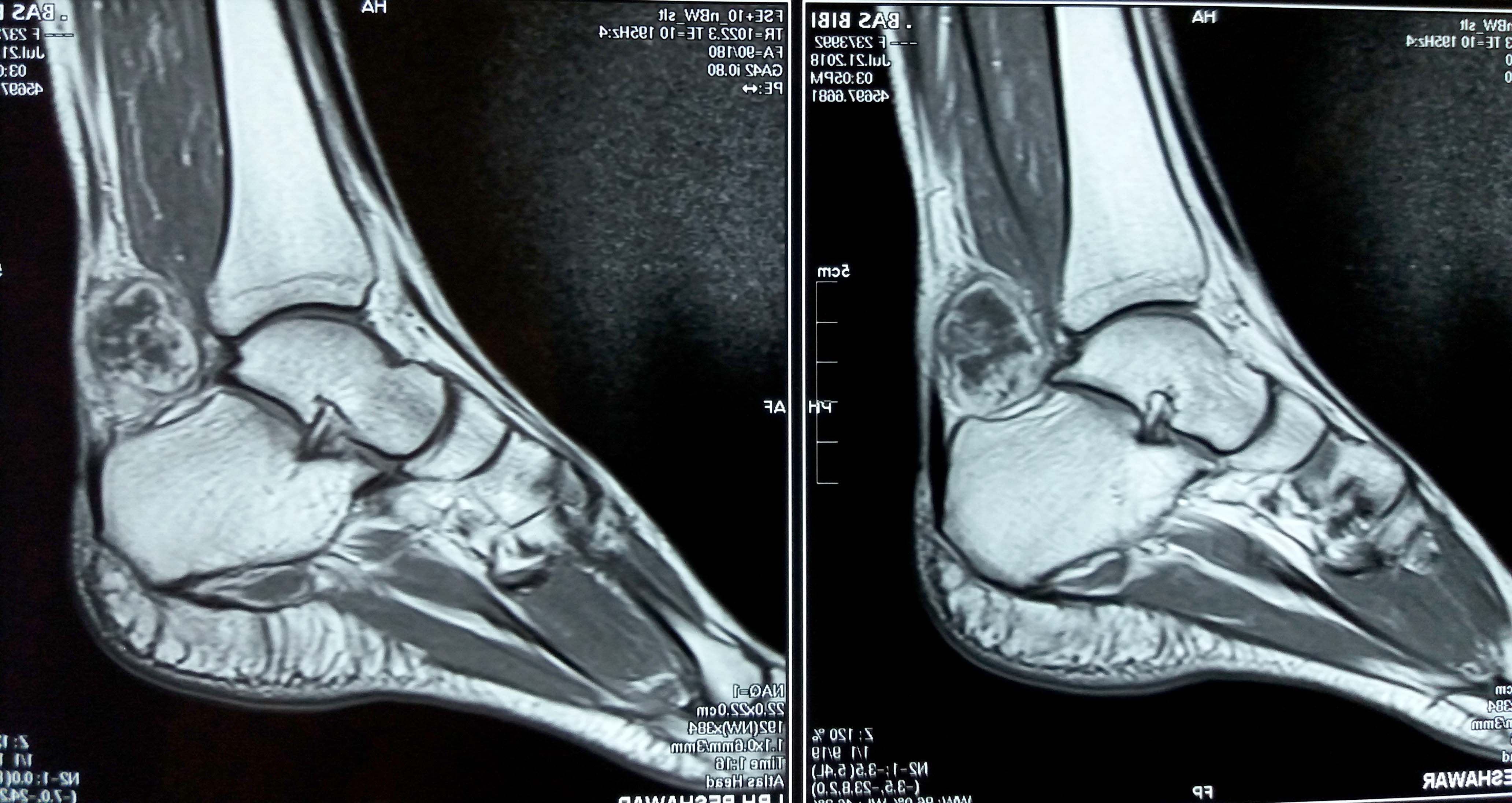
Radiology description
- MRI
- Limited descriptions of the appearance of angiofibroma of soft tissue on imaging
- A few reports have described it as a well circumscribed mass
- Signal characteristics and enhancement are presumed to be variable, subject to the cellular, myxoid, collageneous and vascular content of the lesion
- T1: roughly isointense to skeletal muscle; T2: heterogeneous high signal intensity; T1C+ (Gd): variable from homogeneous to a peripheral enhancement (Mol Clin Oncol 2017;7:229)
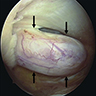
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Angiofibroma of soft tissue pursues a benign clinical course
- Rare local recurrence and no evident metastatic potential
Case reports
- 50 year old woman with a tumor on cheek (Acta Derm Venereol 2017;97:133)
- 54 year old man with mass in left posterior neck (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6:2208)
- 55 year old woman with mass on left foot (Cureus 2019;11:e6225)
- 57 year old man with mass in right thigh (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6:2208)
Treatment
- Treatment is simple excision (Skeletal Radiol 2014;43:403)
Gross description
- Well demarcated, nodular or multinodular solid tumor
- Infiltration of the surrounding tissues does occur
- Range in size from 1.2 to 10.0 cm (mean 5.1 cm)
- White to yellow, often glistening cut surface
- Cystic or hemorrhagic areas may be present (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2017;56:750)
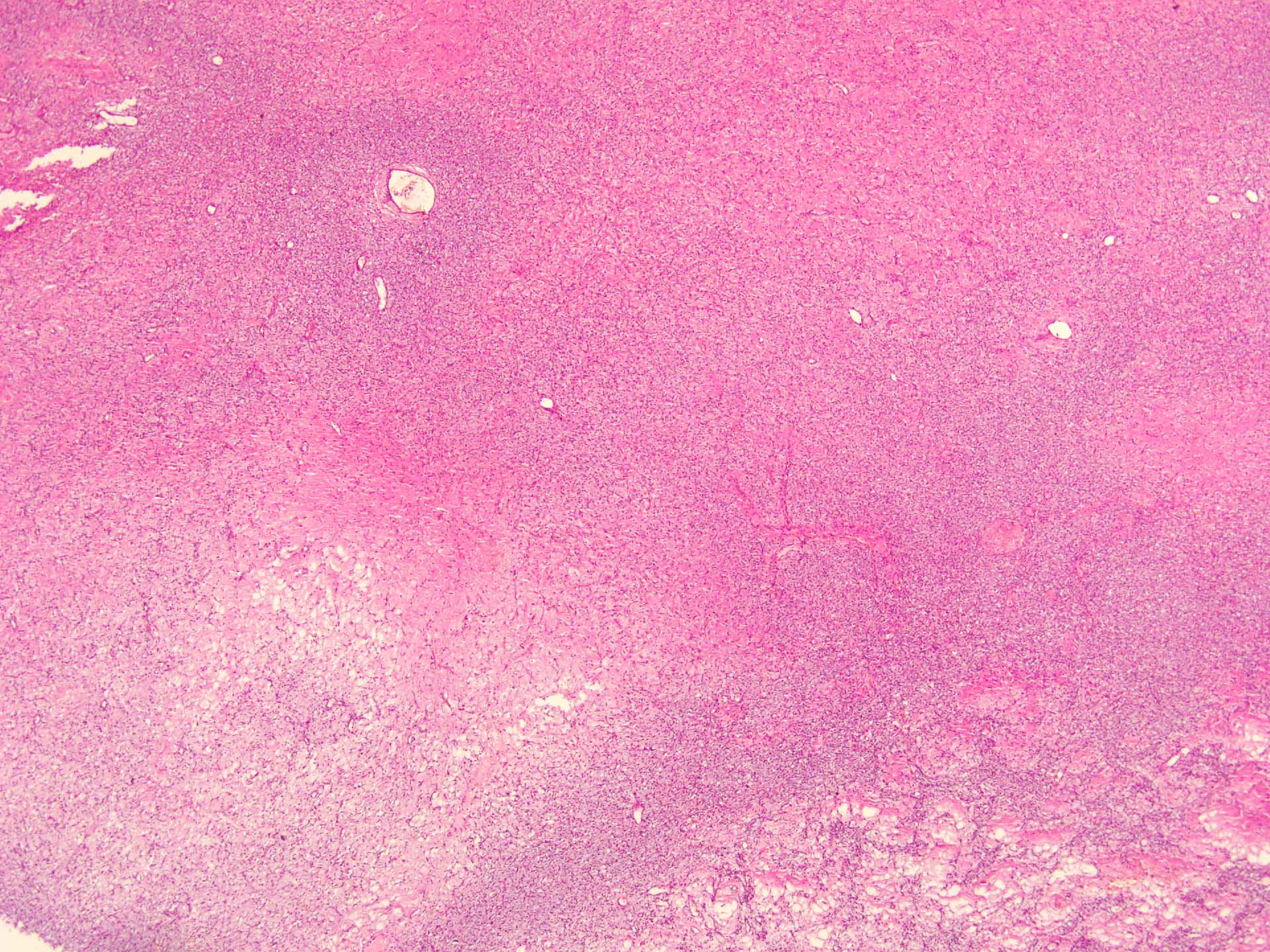
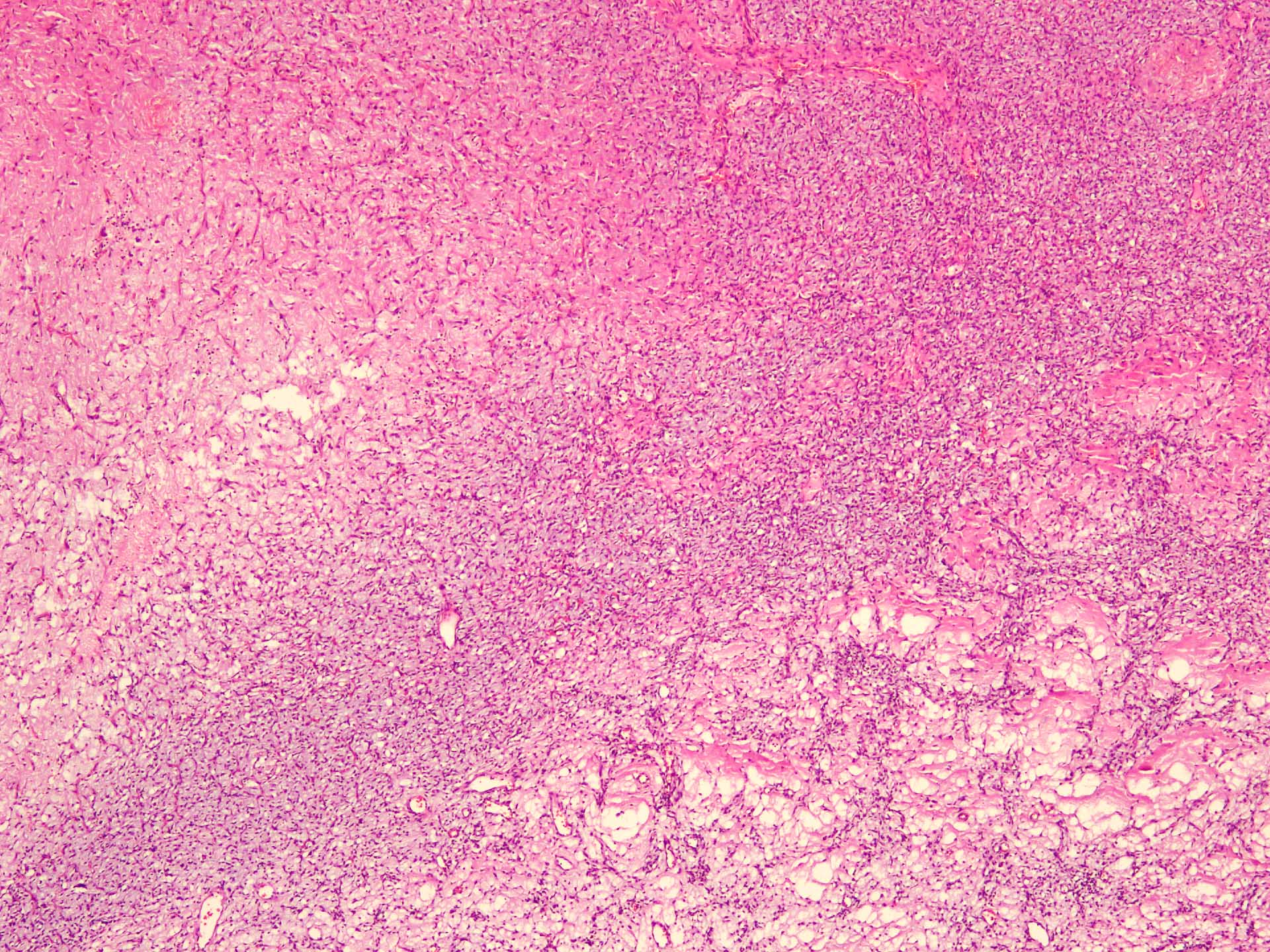
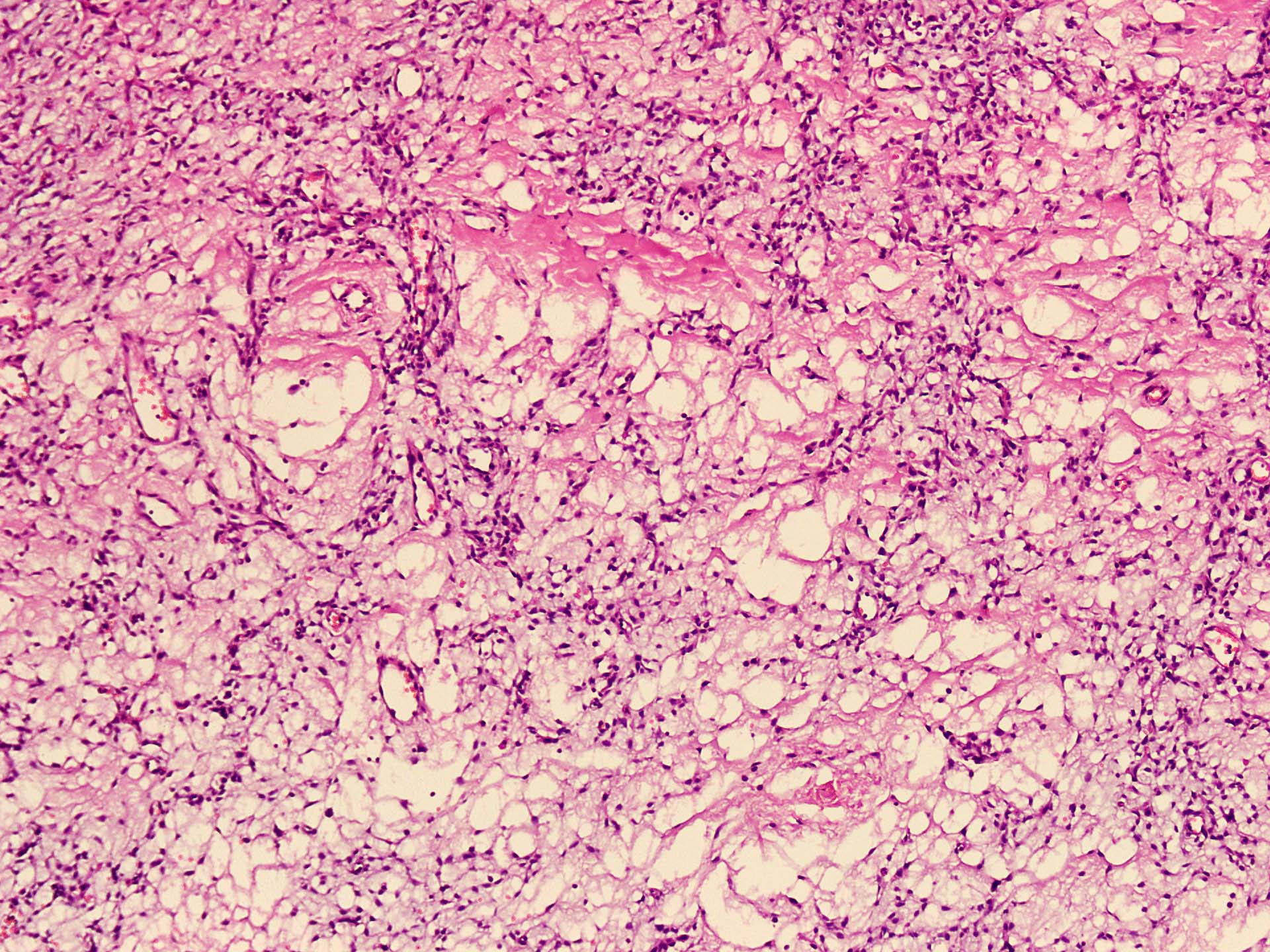
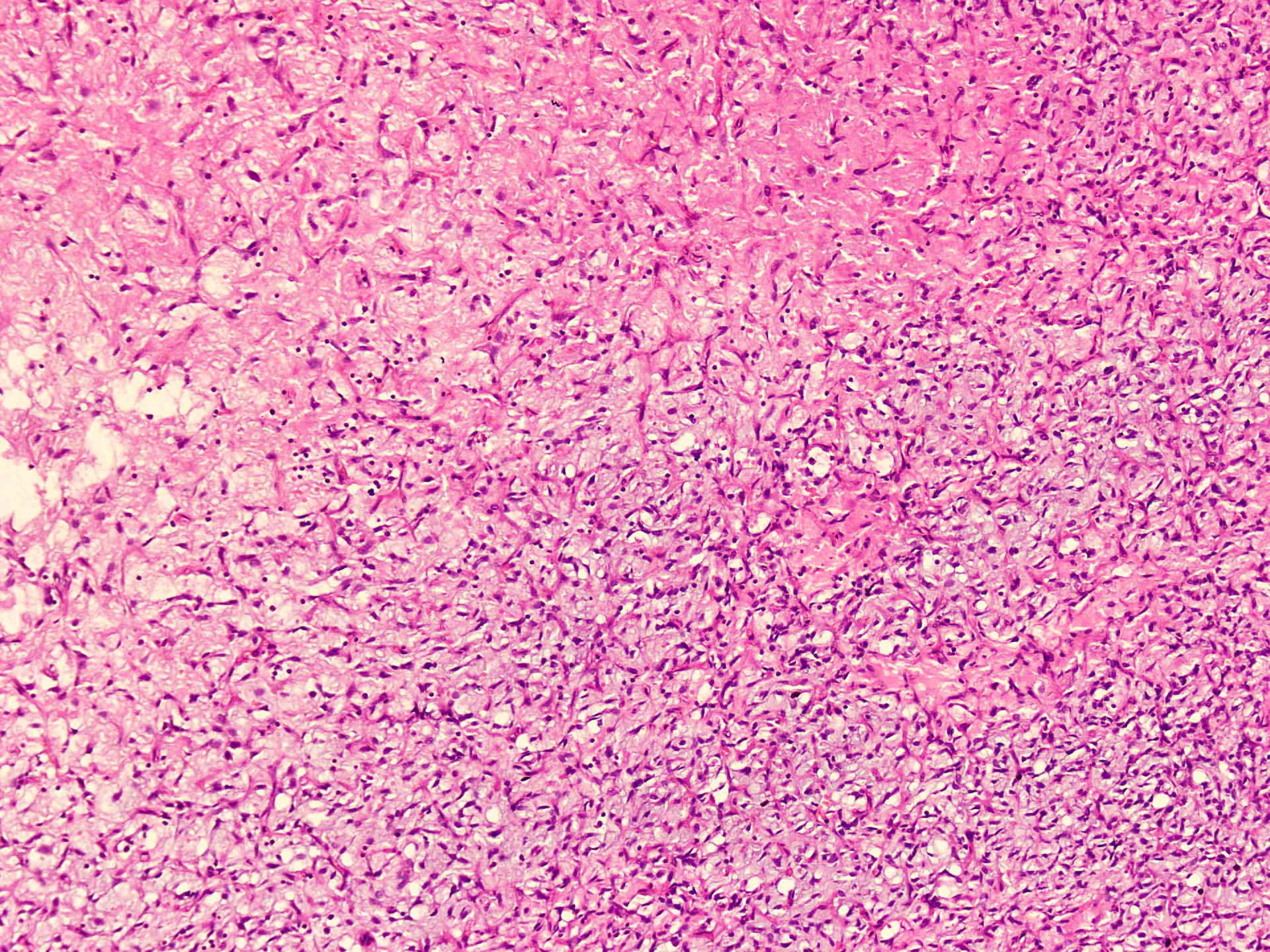
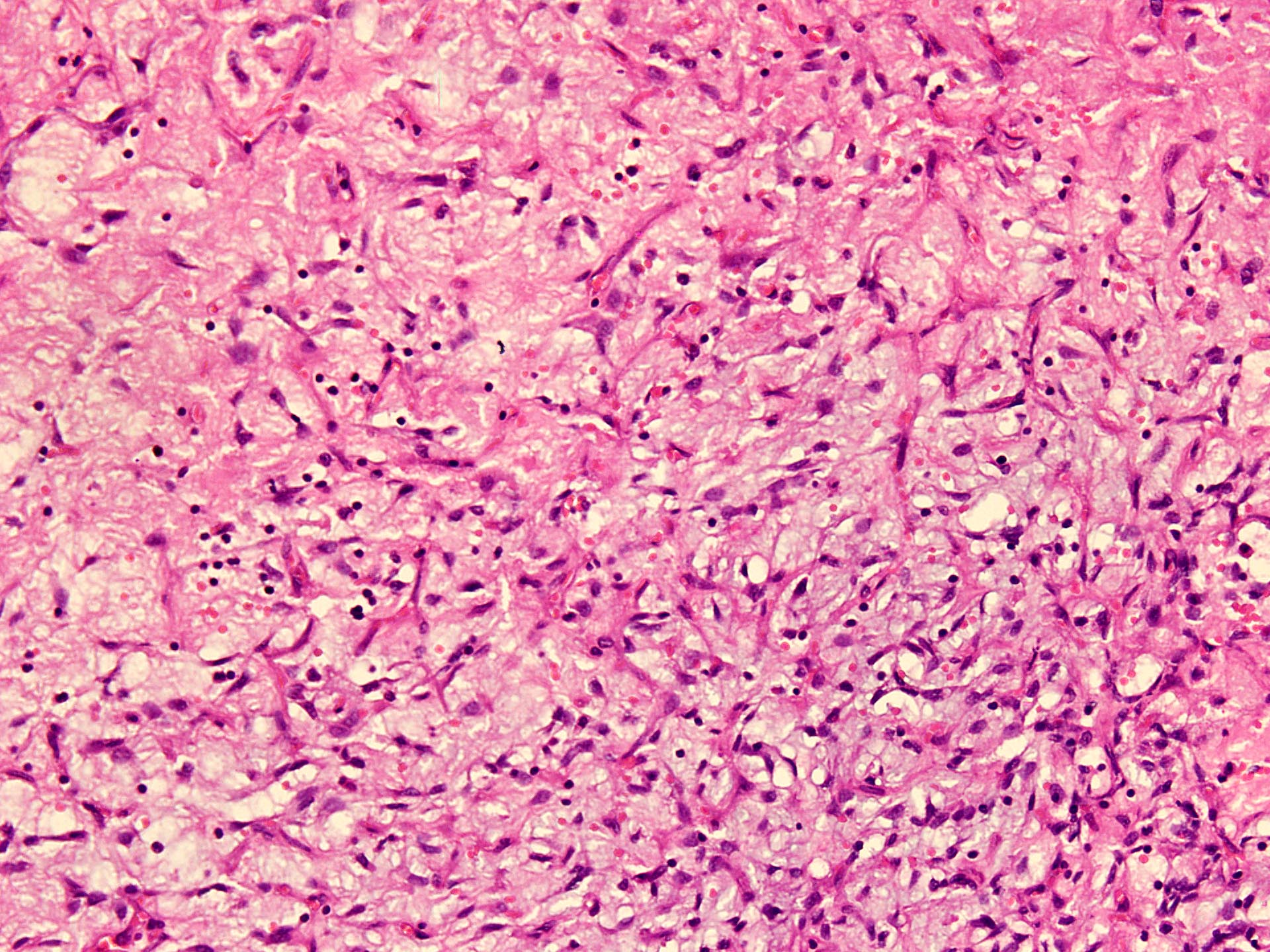
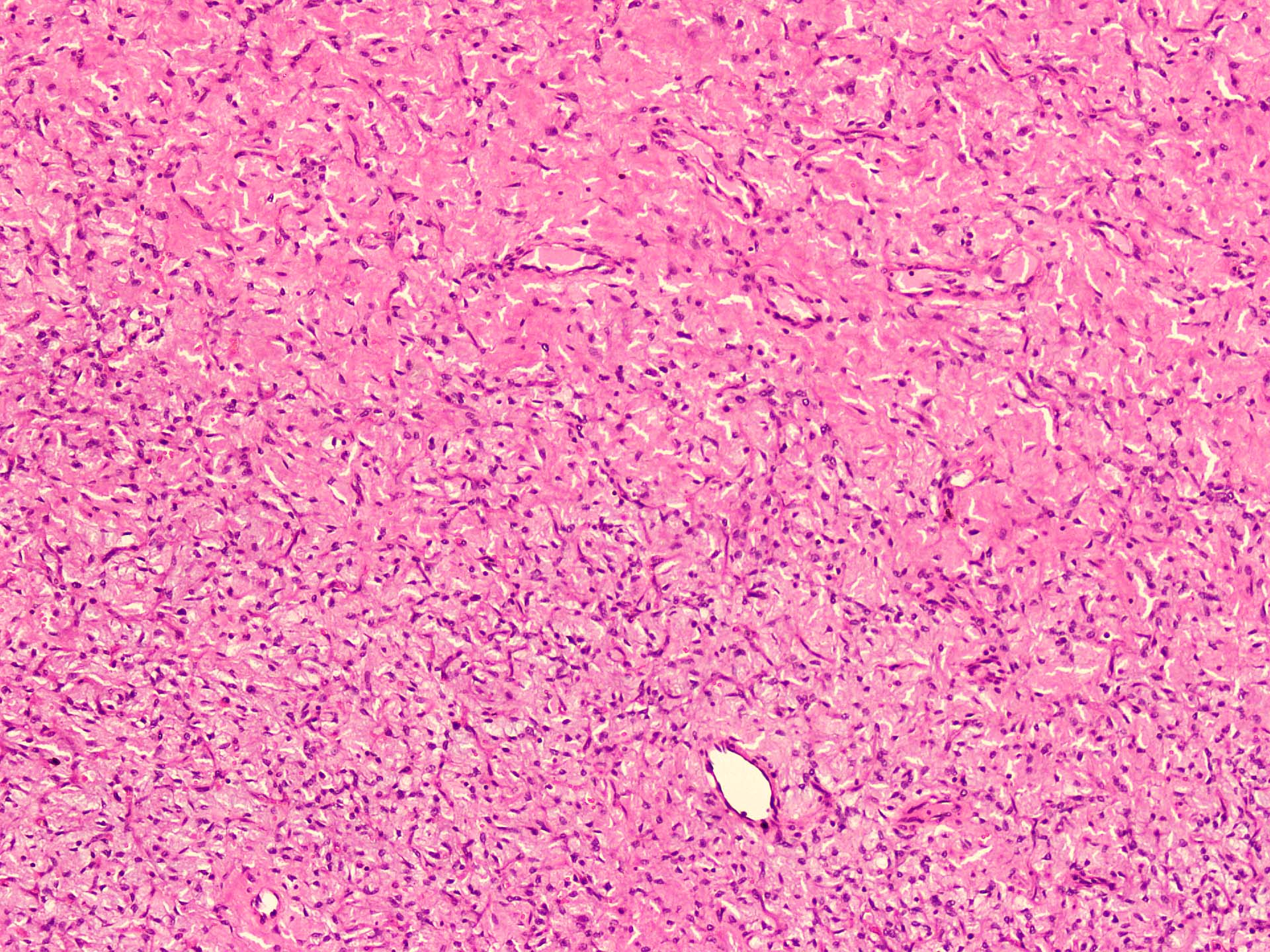
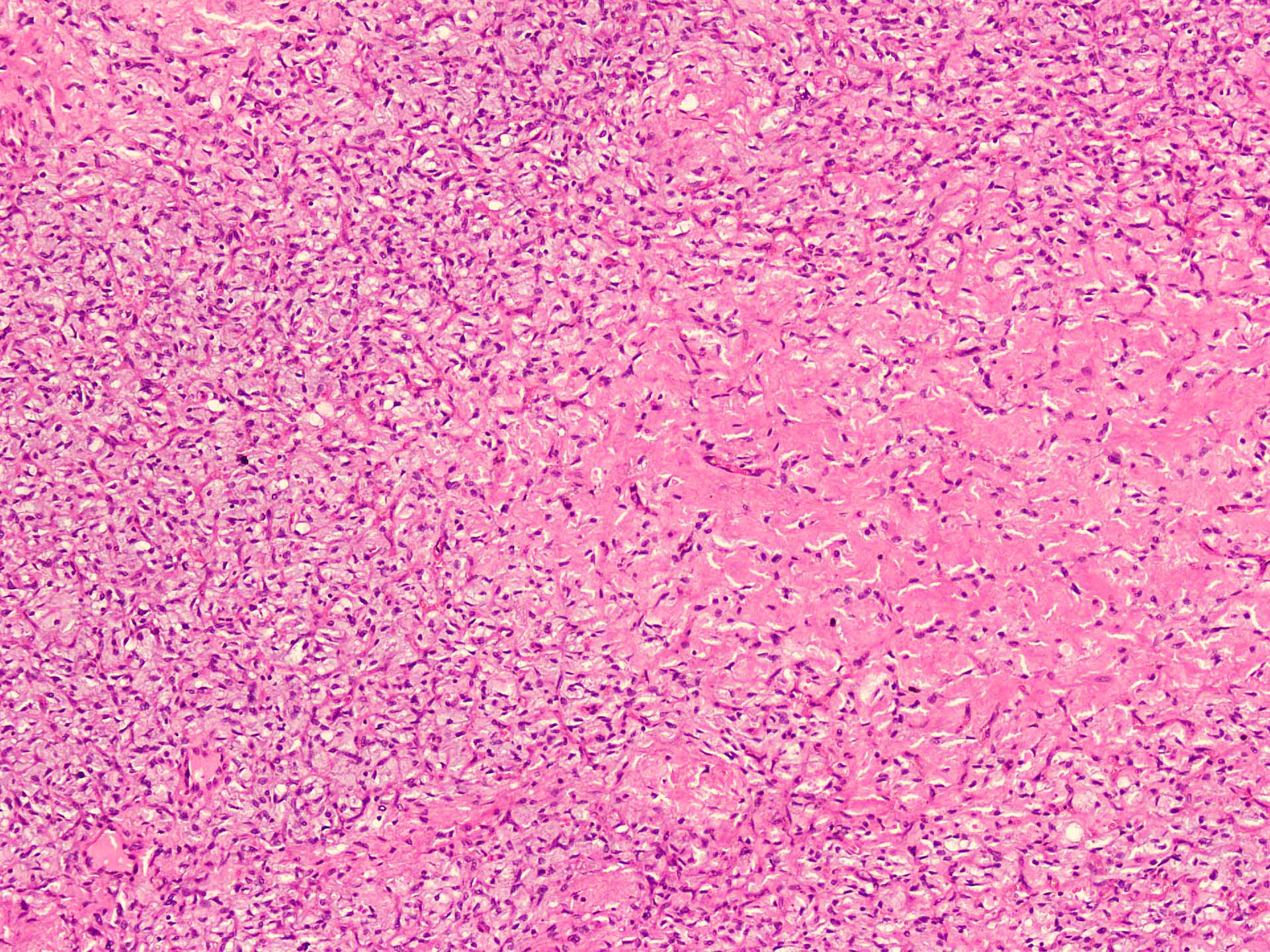
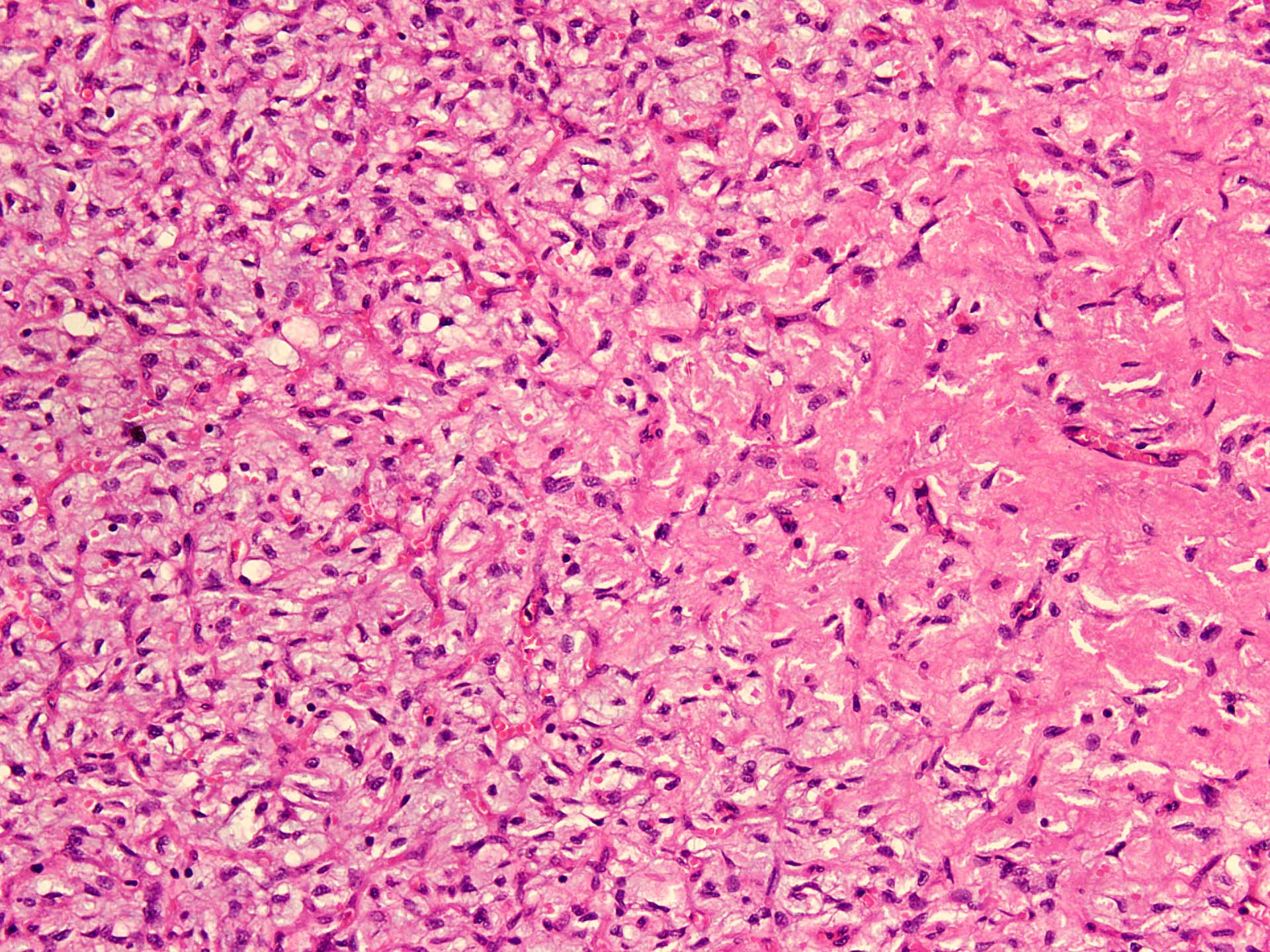
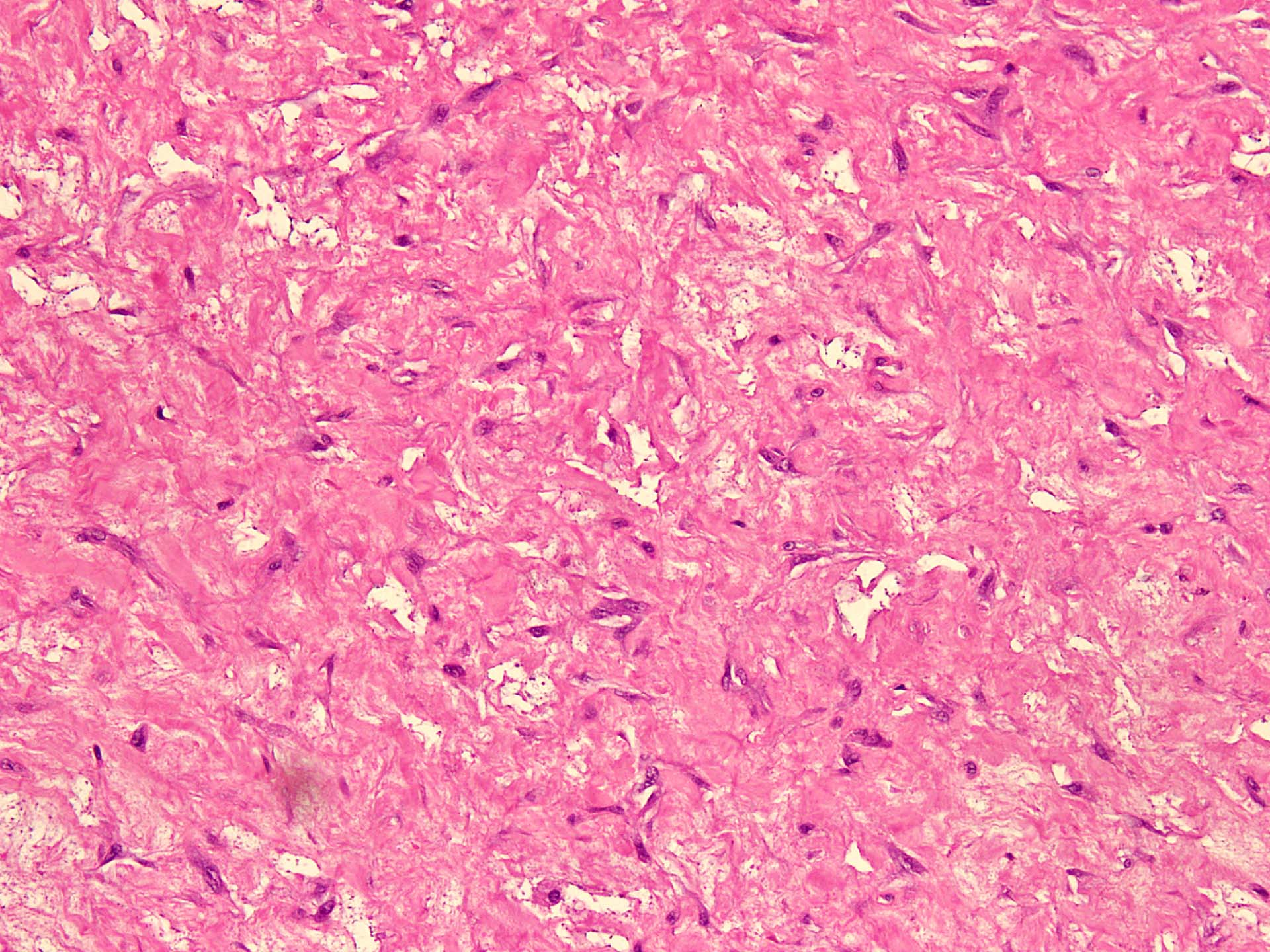
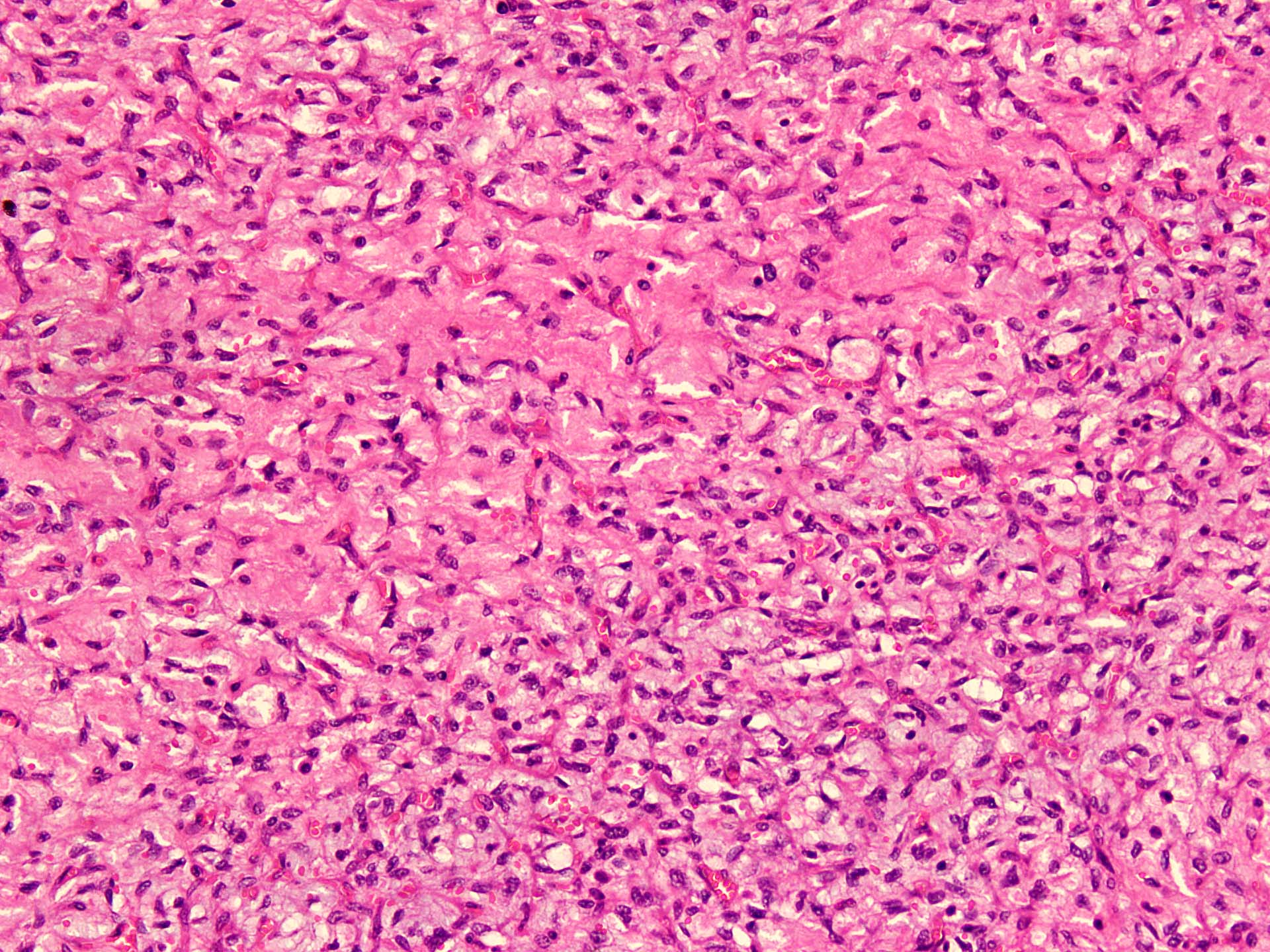
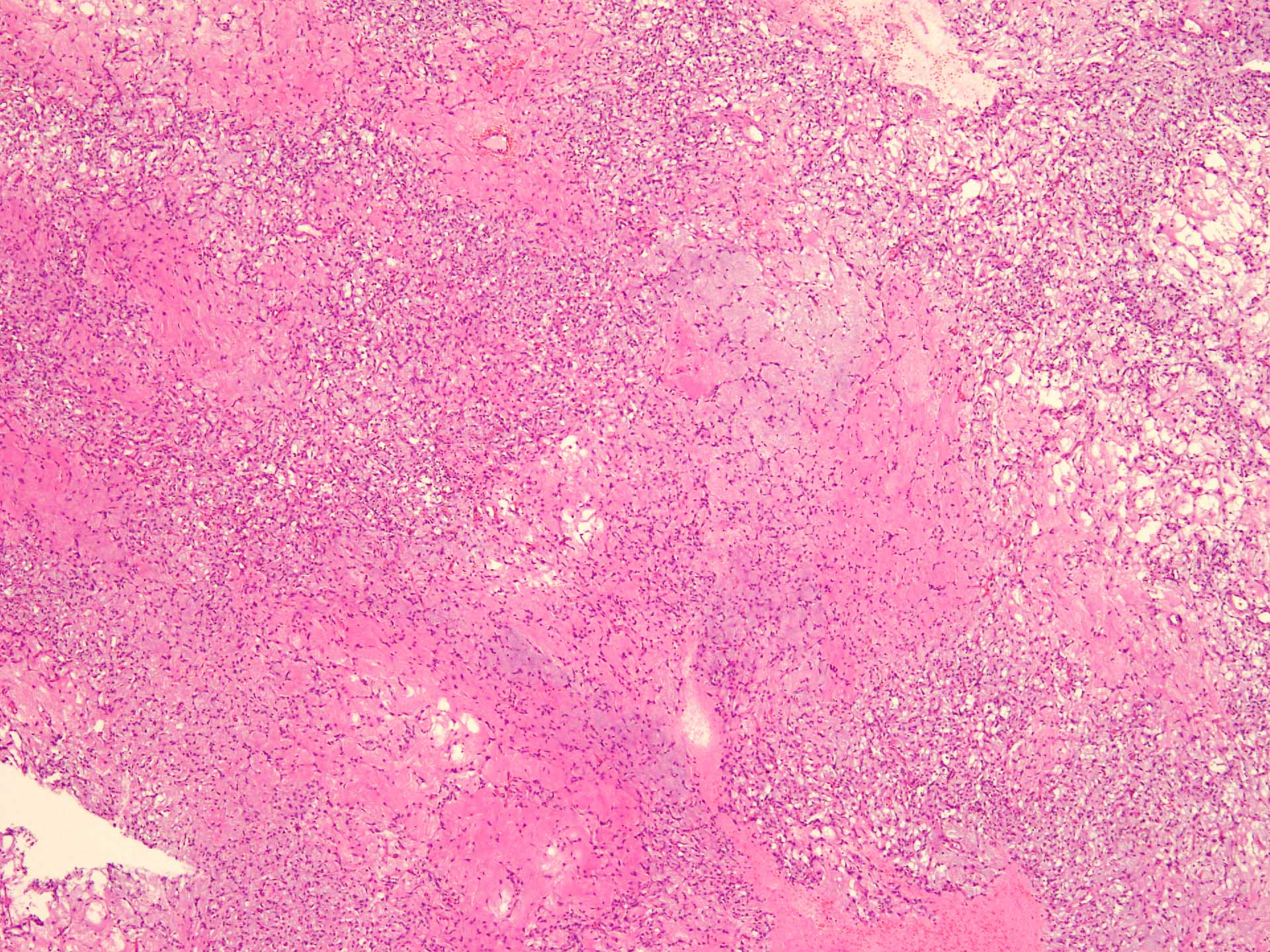
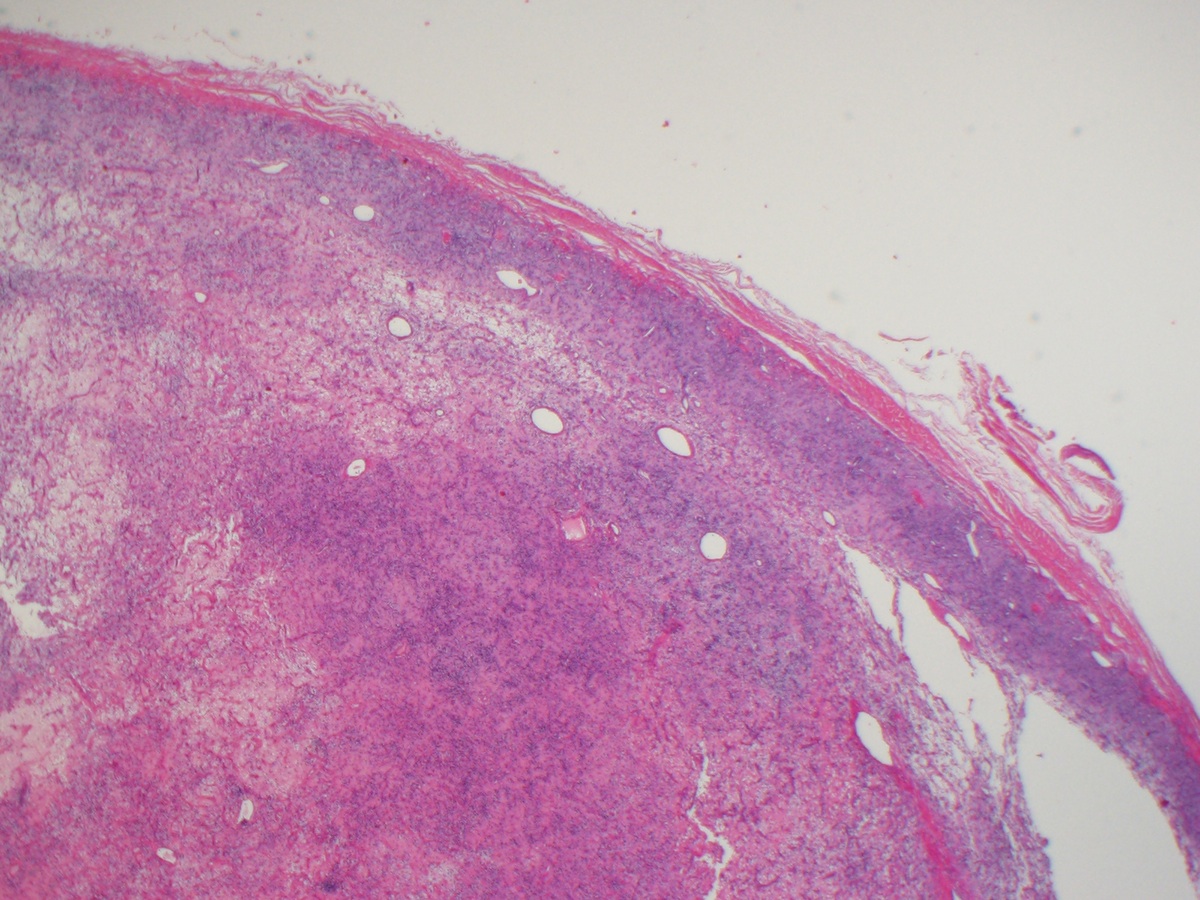
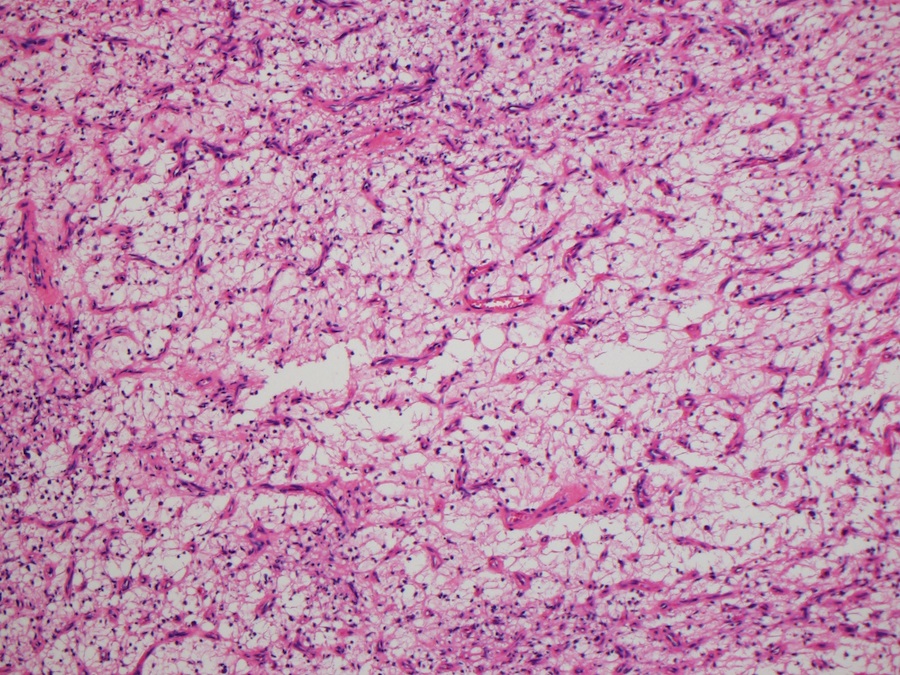
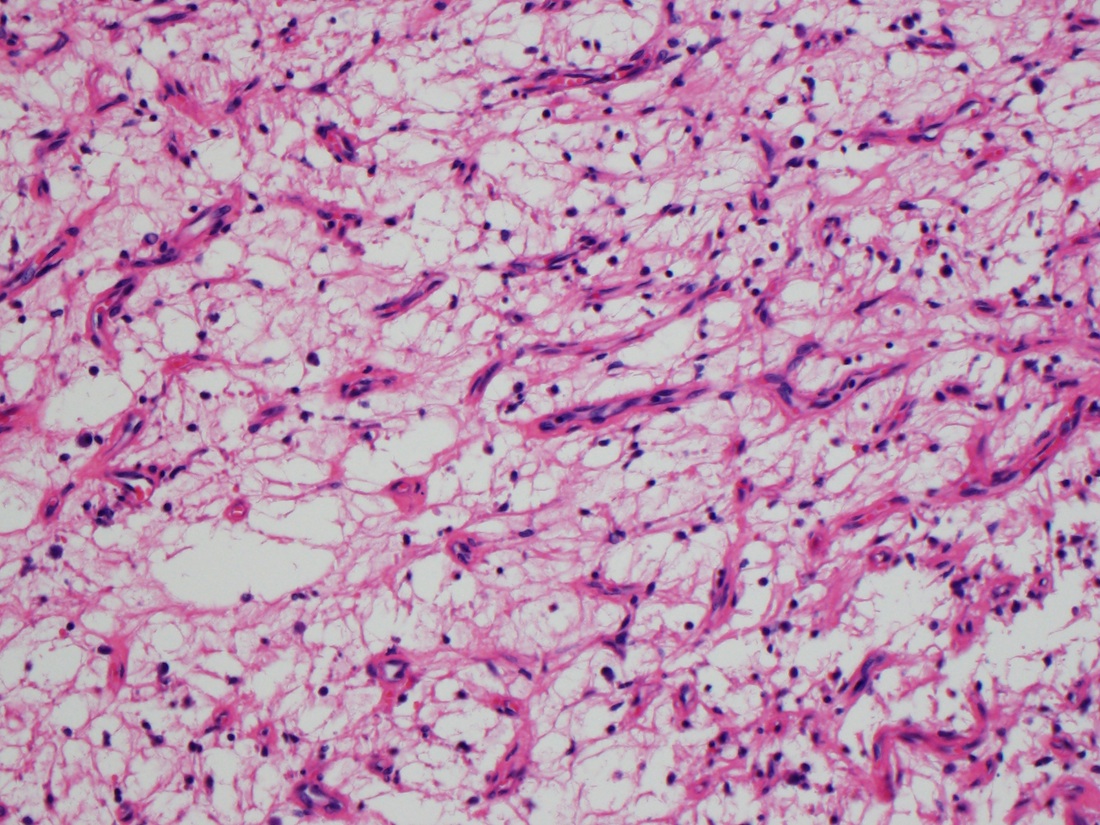
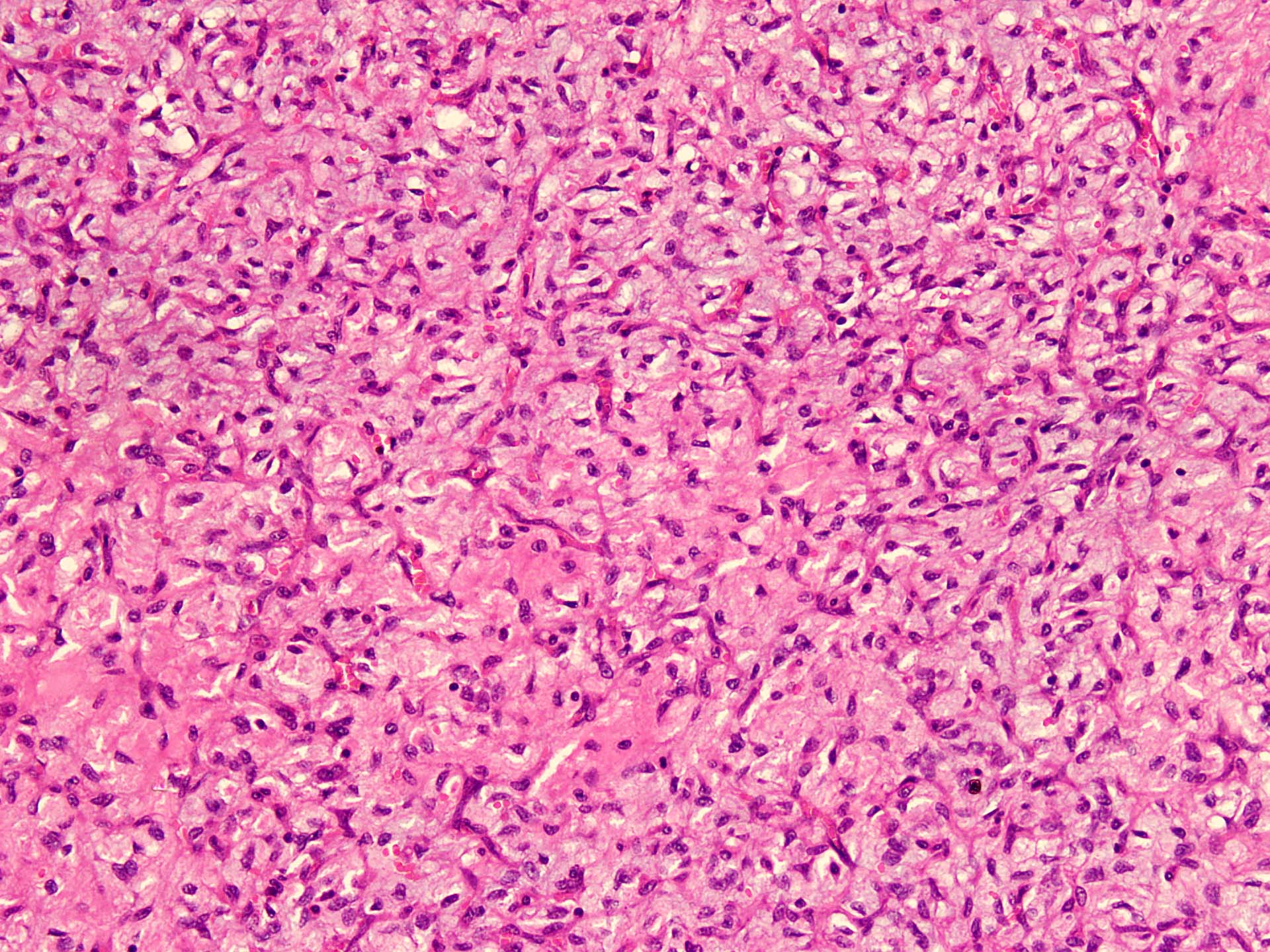
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Well circumscribed
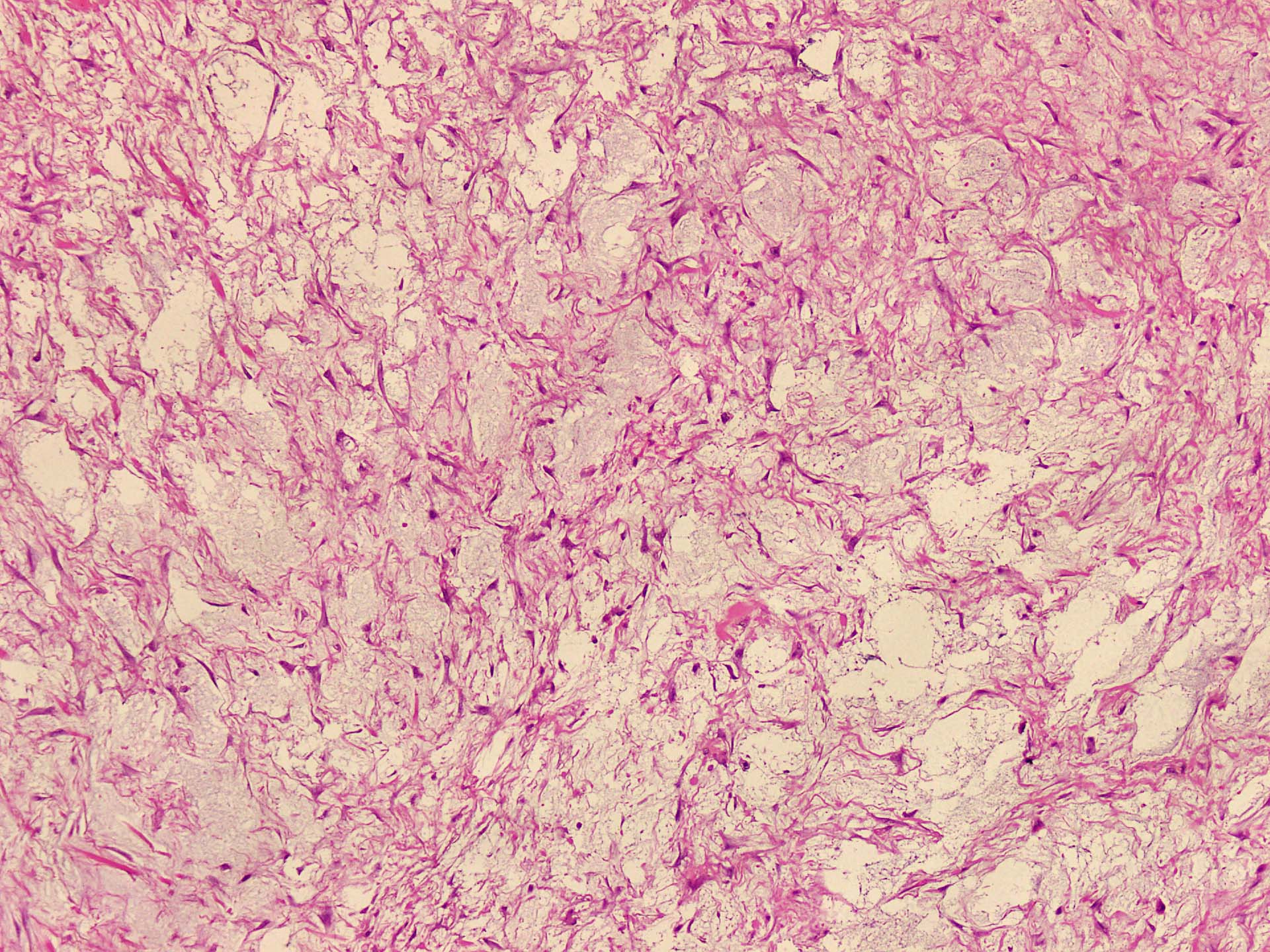
- Vaguely lobulated architecture
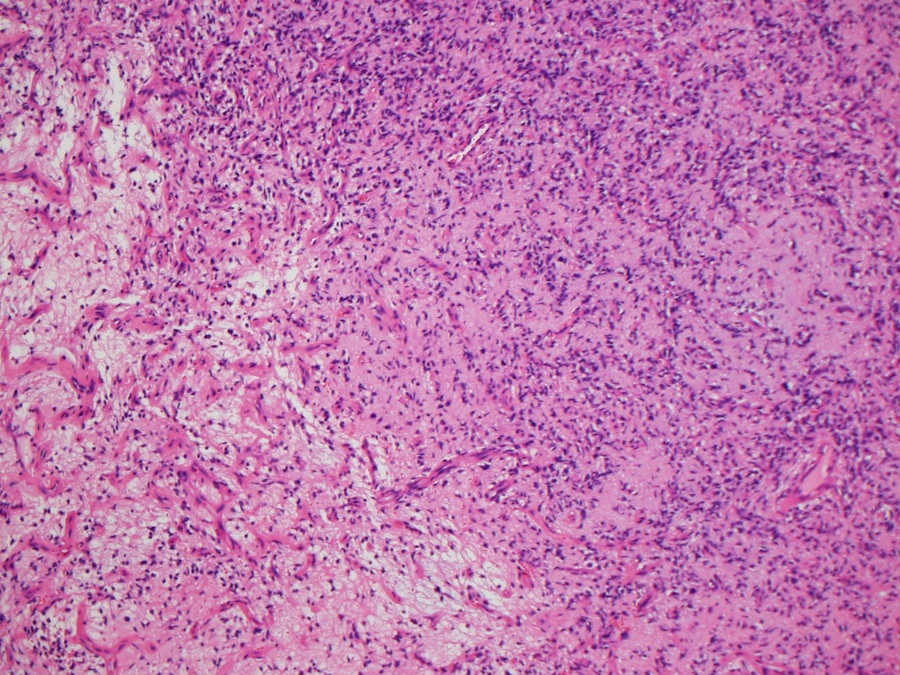
- Alternating myxoid and collagenous areas
- Regional variation in cellularity (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2017;56:750)
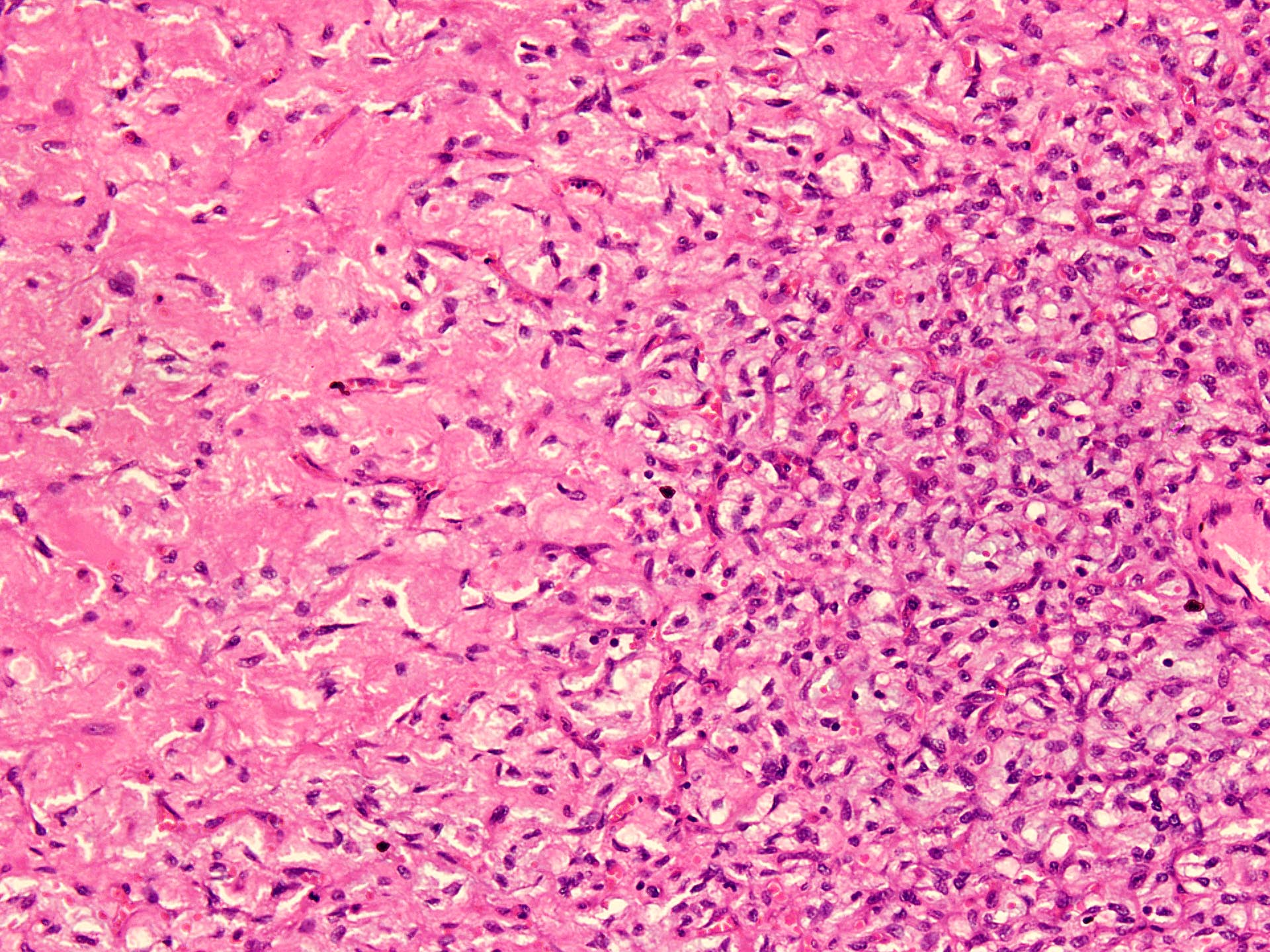
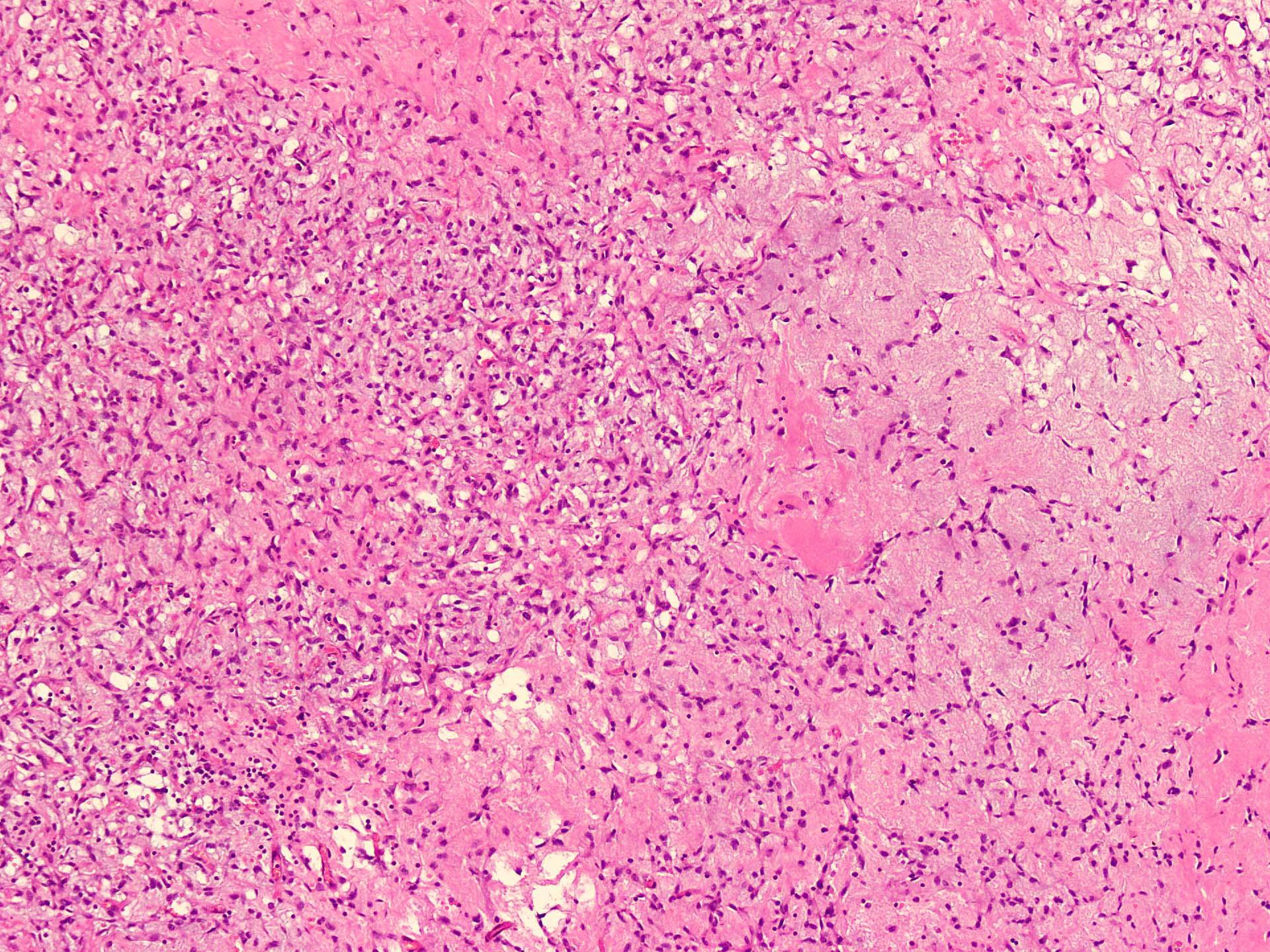
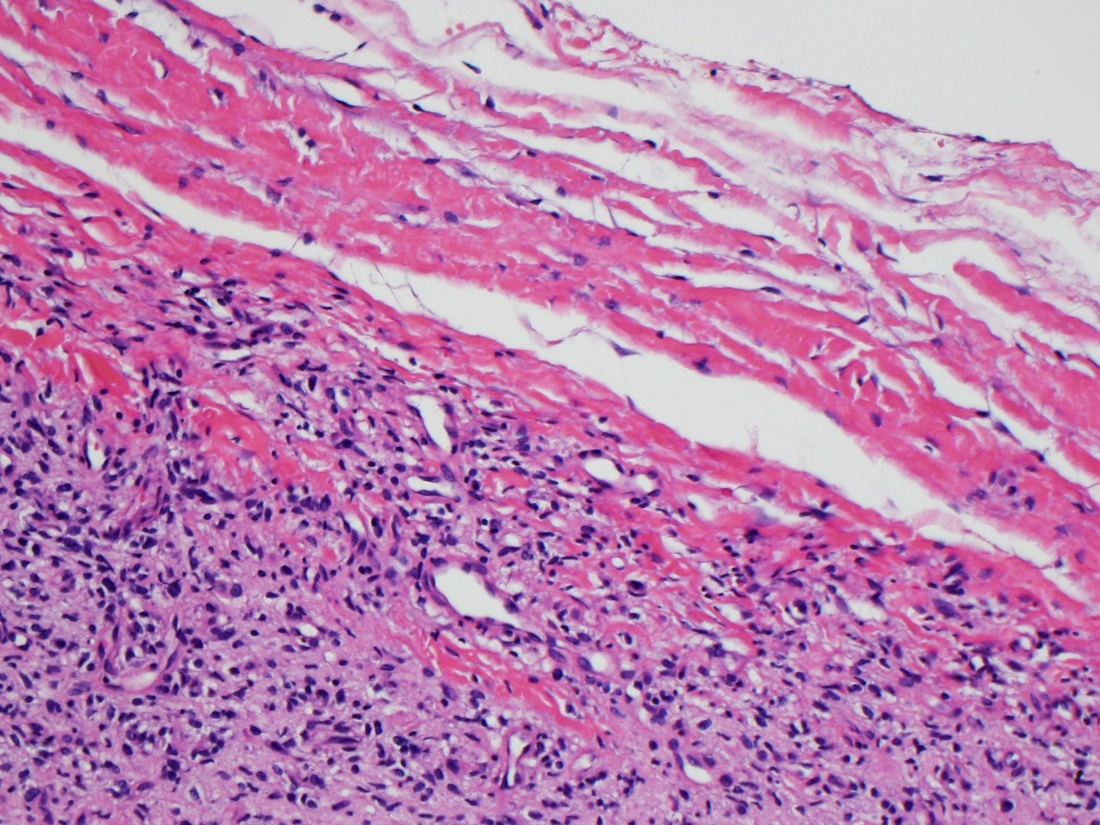
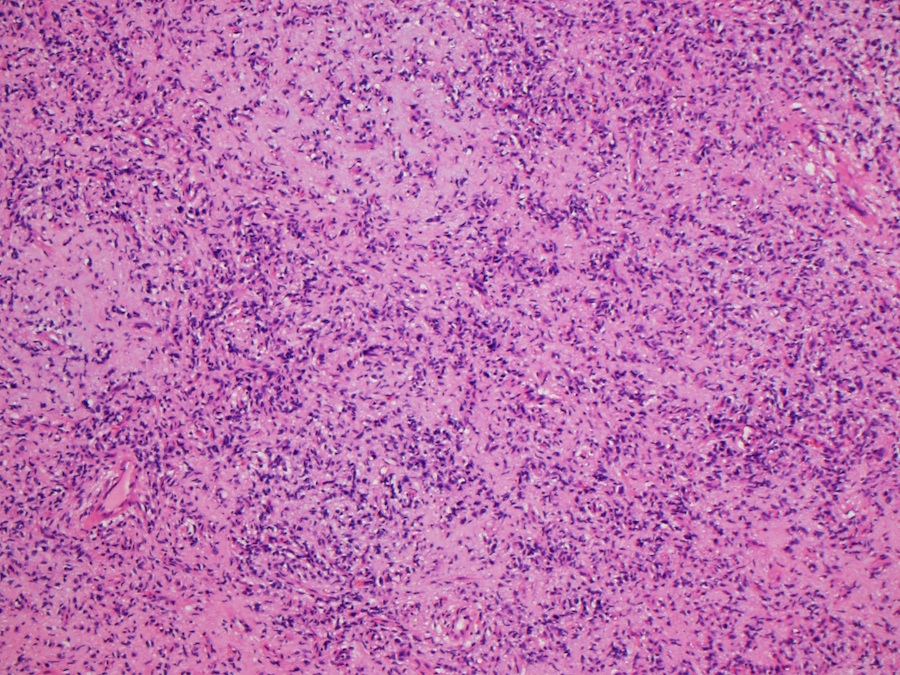
- Uniform bland spindle cells
- Prominent vascular network
- Spindle cells have inconspicuous palely eosinophilic cytoplasm
- Short ovoid or tapering nuclei, irregular nuclear contours, fine chromatin and indistinct nucleoli
- Cytological atypia and nuclear hyperchromasia are generally absent
- Vascular network is composed of innumerable small, thin walled blood vessels evenly distributed throughout the lesion
- Less prominent medium or large sized blood vessels with variably thick walls are usually present (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:500)
- Perivascular collagen deposition and marked hyalinization or fibrinoid necrosis of medium sized vessel walls
- Occasional degenerative atypia (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:500)
- Degenerative changes may be focally present, including chronic inflammation, hemorrhage and aggregates of foamy histiocytes (Histopathology 2016;69:459)
- Variably dense infiltrate of lymphocytes, sometimes perivascular in distribution
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
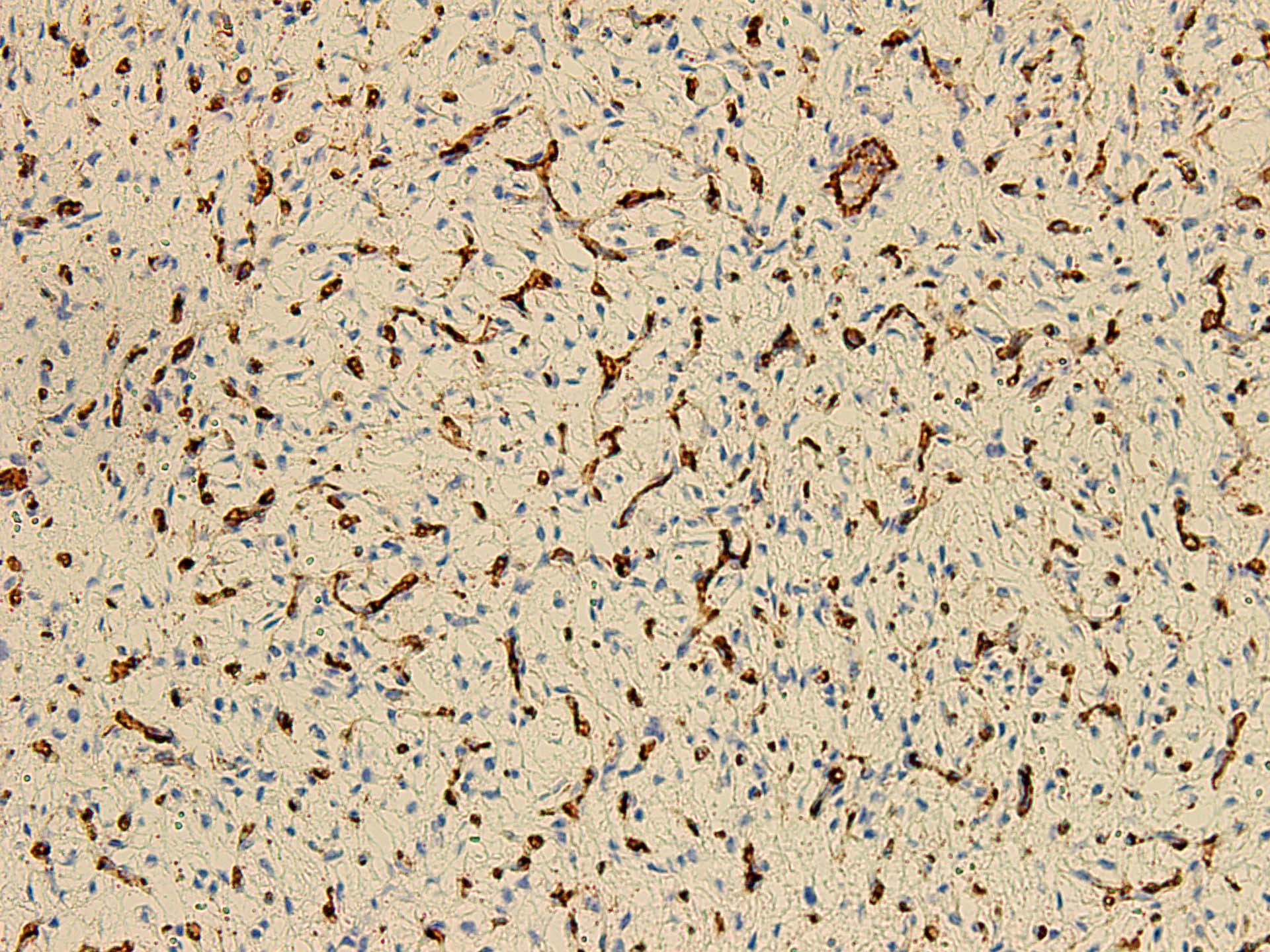
- Nuclear expression of NCOA2 (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2017;56:750)
- Variable expression of EMA, CD34, SMA
- Sometimes expression of desmin in dentritic cells
Negative stains
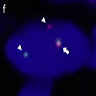
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Detection of NCOA2 rearrangement or AHRR::NCOA2 fusion gene (or a variant fusion) (Oncol Rep 2016;36:2455)
- Variant GTF2I::NCOA2 or GAB1::ABL1 fusions have been found in a single case (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2013;52:330, Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2017;56:750)
- NCOA2::ETV4, ETV4::AHRR, P4HA2::TBCK and TBCK::P4HA2 have also been reported (Oncol Rep 2016;36:2455)
Videos
Angiofibroma of soft tissue
Sample pathology report
- Soft tissue, thigh, excision:
- Angiofibroma of soft tissue (see comment)
- Comment: The sections reveal a fibroblastic neoplasm composed of uniform spindle cells in a variable myxoid and collagenous stroma with a network of innumerable small, thin walled, branching blood vessels. No necrosis, marked cytologic atypia or significant mitotic activity is identified. It is positive for CD34 and EMA on immunohistochemistry. These support the above diagnosis.
Differential diagnosis
- Cellular angiofibroma:
- Solitary fibrous tumor:
- Low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma:
- Low grade myxofibrosarcoma:
- Lobulated growth pattern, myxoid background, infiltrative borders
- Long curvilinear vessels with perivascular hypercellularity
- Cells have pleomorphic hyperchromatic nuclei and mitoses
- Myxoid liposarcoma:
- Prominent chicken wire vasculature
- Numerous signet ring lipoblasts particularly at periphery of lobules
- Mucoid matrix rich in hyaluronidase sensitive acid mucopolysaccharides; may have large mucoid pools
- DDIT3 rearrangement
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 40 year old woman presented with a slowly growing mass on left thigh. Grossly, the tumor was well circumscribed with yellow-white cut surface. Microscopically, the tumor showed numerous small, branching, thin walled blood vessels in a collagenous and myxoid stroma. On immunohistochemistry, the tumor cells showed positivity for CD34 and EMA. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Angiofibroma of soft tissue
- Cellular angiofibroma
- Low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma
- Myxofibrosarcoma
- Myxoma
Board review style answer #1
A. Angiofibroma of soft tissue. It is a fibroblastic neoplasm that commonly arises in lower extremities, often in relation to joints or fibrotendinous structures of middle aged females. It is composed of uniform spindle cells in a variable myxoid and collagenous stroma with a network of innumerable small, thin walled, branching blood vessels. It is positive for CD34 and EMA on immunohistochemistry.
Comment Here
Reference: Angiofibroma of soft tissue
Comment Here
Reference: Angiofibroma of soft tissue
Board review style question #2
A 55 year old woman presented with a mass on lateral aspect of left ankle for last 5 years. MRI revealed a well demarcated, enhancing, round mass that measured 4 cm. Excision biopsy was performed and microscopic examination revealed a lesion in given photomicrograph. Which cytogenetic aberration is associated with this tumor?
- AHHR::NCOA2
- FUS::CREBB3L2
- FUS::DDIT3
- NAB2::STAT6
- RB1 / FOXO1 deletion
Board review style answer #2
A. AHHR::NCOA2. The photomicrograph shows a tumor composed of uniform spindle cells in a variable myxoid and collagenous stroma with a network of innumerable small, thin walled, branching blood vessels, characteristic of angiofibroma of soft tissue. It is associated with NCOA2 rearrangement or AHRR::NCOA2 fusion gene in most cases.
Comment Here
Reference: Angiofibroma of soft tissue
Comment Here
Reference: Angiofibroma of soft tissue