Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Electron microscopy images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Warmke L, Meis J. Spindle cell / pleomorphic lipoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissueadiposepleomorphicgeneral.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Spindle cell lipoma and pleomorphic lipoma are benign adipocytic tumors, currently regarded as morphologic variants of a single neoplasm
- Compose approximately 1.5% of all lipomatous tumors (Histopathology 1987;11:803)
- First described in 1975 by Enzinger and Harvey (Cancer 1975;36:1852)
Essential features
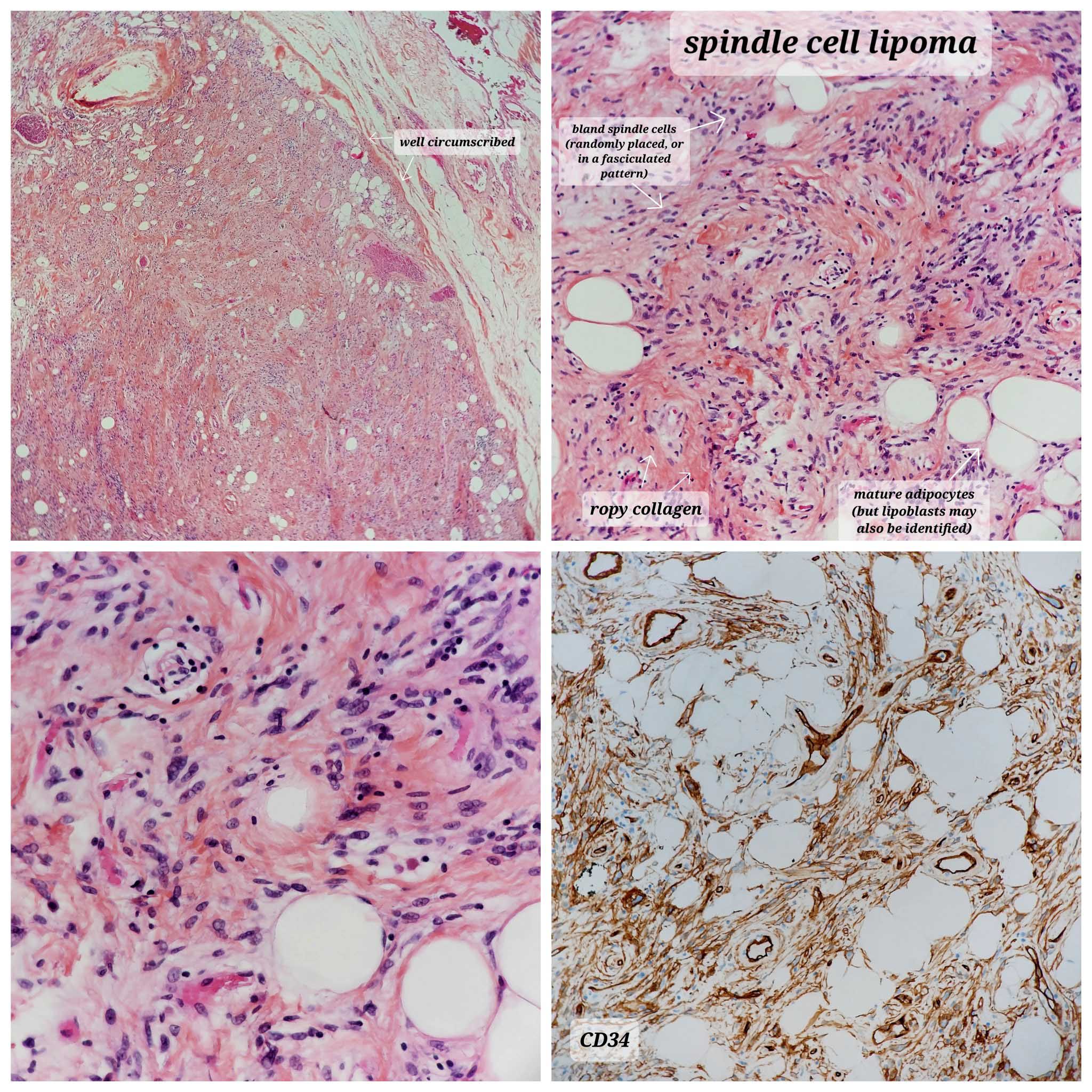
- Spindle cell lipoma contains a varying mixture of mature adipocytes, bland spindle cells and ropy collagen fibers (Cancer 1975;36:1852)
- Pleomorphic lipoma also contains pleomorphic and multinucleated floret-like giant cells
Terminology
- Dendritic fibromyxolipoma (not recommended)
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8857/0 - spindle cell lipoma
- ICD-11:
- 2E80.0Z & XH30M7 - lipoma, unspecified site & pleomorphic lipoma
- 2E80.0Z & XH4E98 - lipoma, unspecified site & spindle cell lipoma
Epidemiology
- Commonly affects middle aged to elderly men (45 - 70 years) (Cancer 1975;36:1852)
- Very rare in patients < 20 years
- < 10% of cases occur in women
- Uncommon compared with conventional lipoma (ratio = 1:60)
Sites
- Mostly superficial, extremely rare in deep soft tissue
- 80% arise in the subcutaneous tissue of the posterior neck, back and shoulders (Cancer 1975;36:1852, Cancer 1981;47:126)
- 20% involve different sites, including face, oral cavity and trunk / extremities (Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A 1976;84:477, Histopathology 1987;11:803, Histopathology 2015;66:430, Am J Clin Pathol 2016;146:487)
- Cases in women more likely to arise in atypical locations (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:1267)
- Intramuscular and dermal based lesions rarely seen (Am J Clin Pathol 2016;146:487, Am J Dermatopathol 2000;22:496)
Pathophysiology
- Characterized by partial or whole chromosome 13 or 16 deletions (Histopathology 1997;31:222)
- Breakpoints cluster around 13q14 where the RB1 gene resides (Int J Cancer 2003;103:616)
- Part of the so called 13q / RB1 family of tumors, which includes myofibroblastoma and cellular angiofibroma (Hum Pathol 2012;43:1887, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:3617, Mod Pathol 2011;24:82)
Etiology
- Familial cases with multiple lesions have been described (Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:40, J Am Acad Dermatol 2003;48:82)
Clinical features
- Asymptomatic
- Longstanding, mobile lesion in subcutaneous tissue
- Usually solitary
- Shawl region of posterior neck / shoulder / upper back (Cancer 1975;36:1852)
- Small size (most < 5 cm)
Diagnosis
- Superficial, well circumscribed adipocytic lesion involving characteristic shawl region in a middle aged to elderly man (Cancer 1975;36:1852)
- Demonstration of CD34 positivity and loss of RB1 helpful
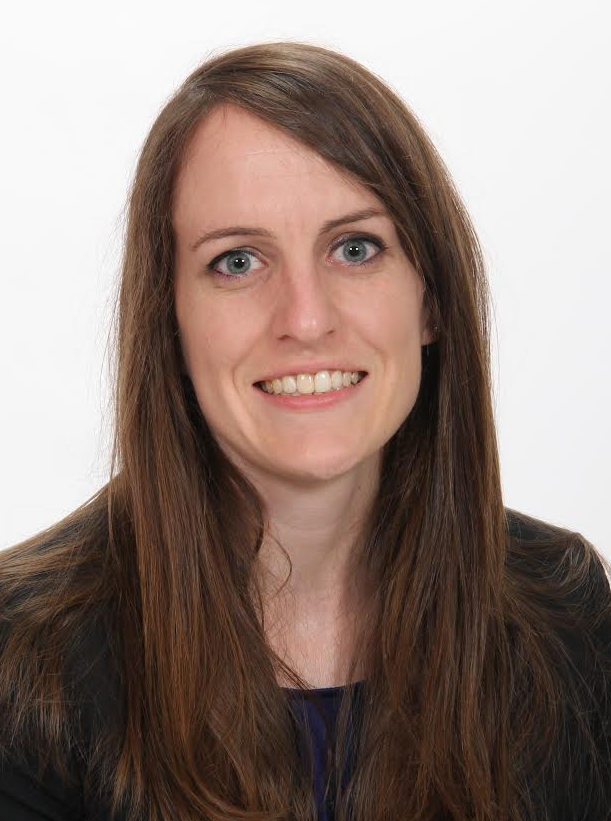
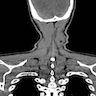
Radiology description
- MRI
- Appearance can vary from completely nonfatty to lipoma-like (Clin Radiol 2020;75:396.e15)
- Findings nonspecific
- Helpful in determining extent of lesion
- Fat free variant may be misdiagnosed as sarcoma
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Benign lesion, no risk of metastasis
- Local recurrence is rare even with incomplete excision (Cancer 1975;36:1852)
Case reports
- 47 year old man with upper back mass (J Clin Diagn Res 2017;11:ED10)
- 57 year old man with subscapular angiomatous spindle cell lipoma (Pathol Int 2007;57:26)
- 58 year old man with intramuscular spindle cell lipoma (J Med Case Rep 2015;9:38)
- 61 year old woman with spindle cell lipoma of oral cavity (Acta Cytol 2001;45:93)
- 62 year old man with spindle cell lipoma of tongue (Head Neck Pathol 2015;9:253)
- 66 year old man with subcutaneous mass on posterior neck with palisading pattern (J Dermatol 2021;48:e351)
Treatment
- Conservative surgical excision only
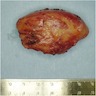
Gross description
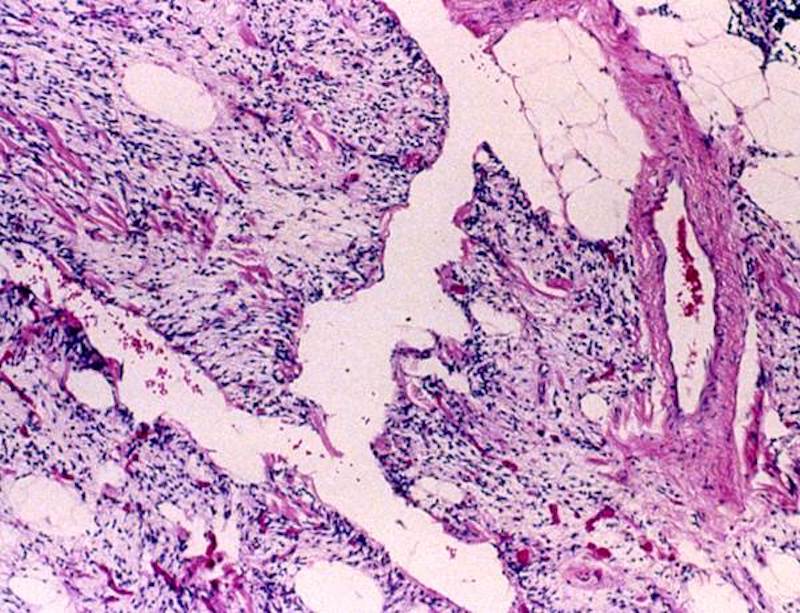
- Well circumscribed, oval mass in subcutaneous tissue (Semin Diagn Pathol 2019;36:105)
- Yellow-tan cut surface with grey-white and myxoid foci
- Texture firmer than ordinary lipoma
- Dermal and intramuscular tumors may have an infiltrative appearance
Gross images
Frozen section description
- Mature adipocytes mixed with bland spindle cells
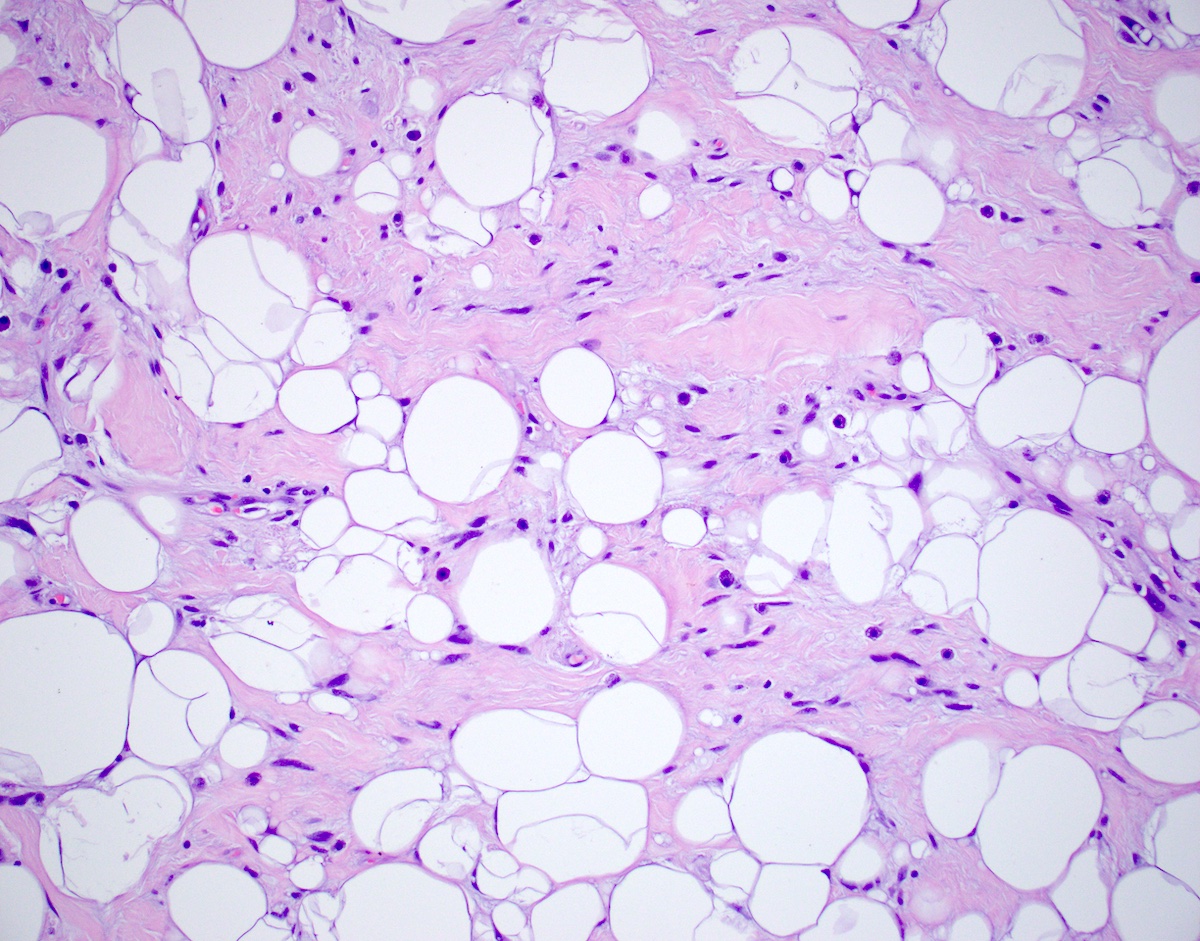
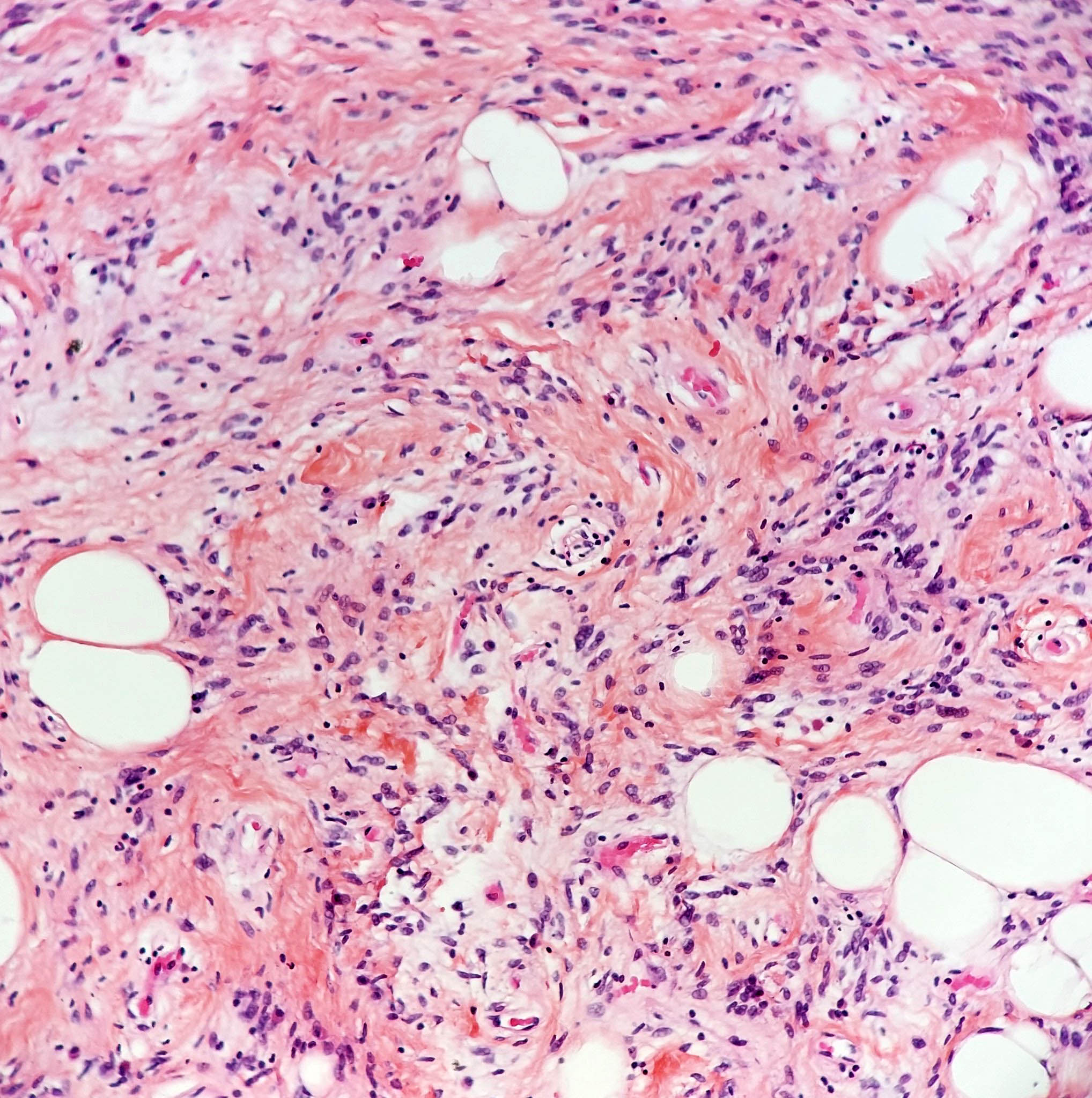
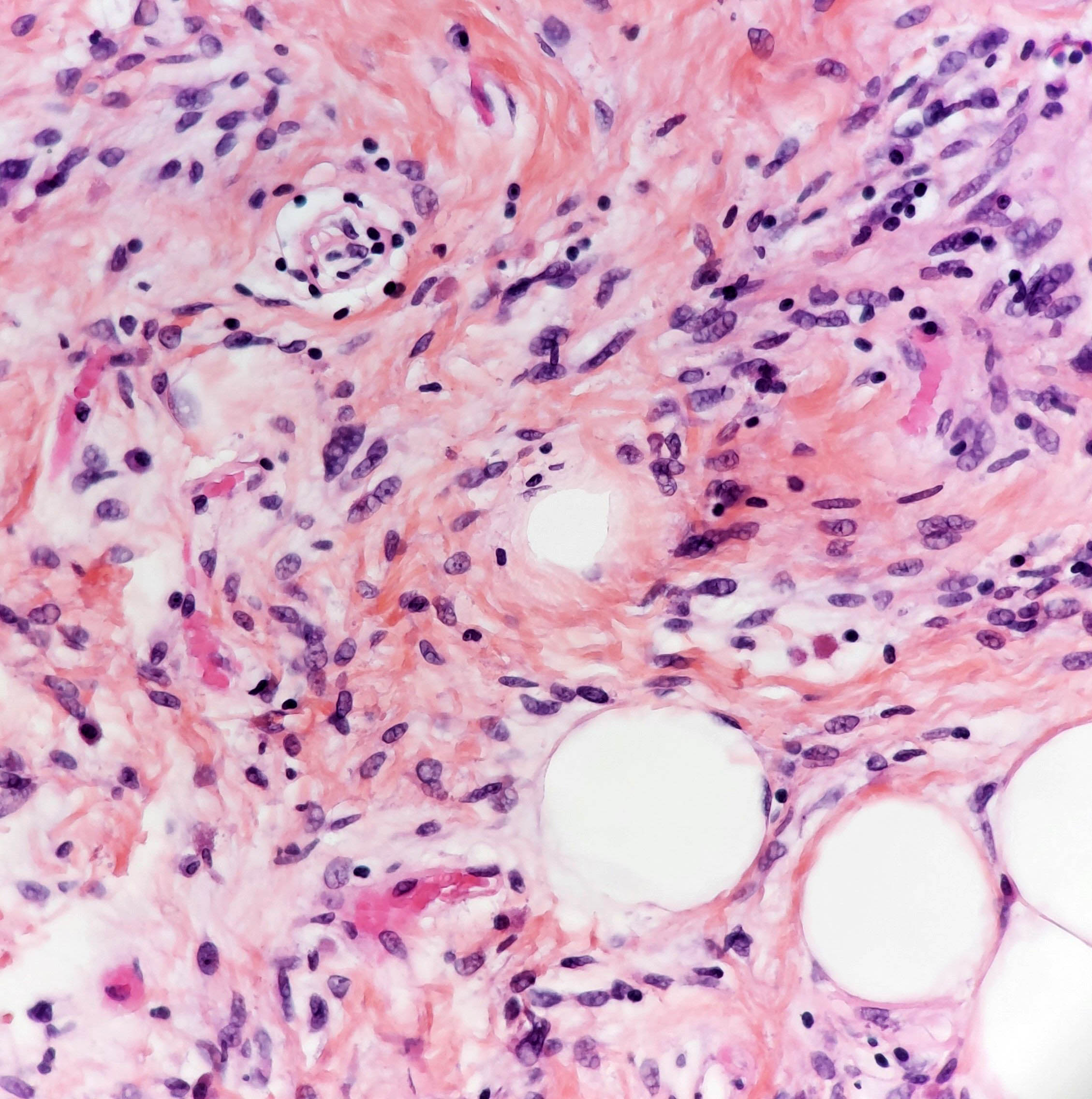
Microscopic (histologic) description
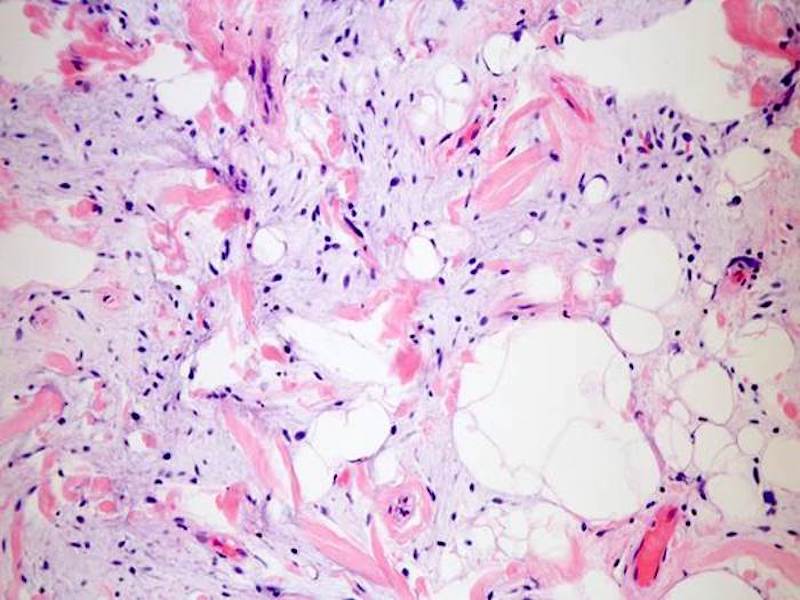
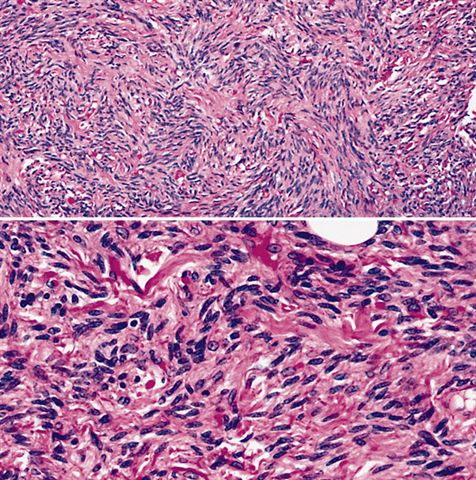
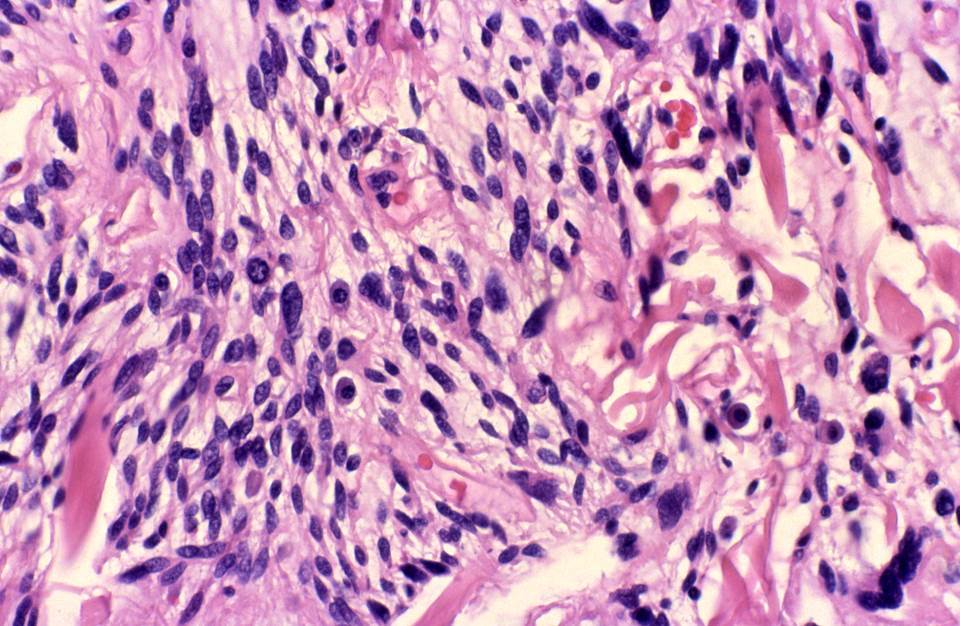
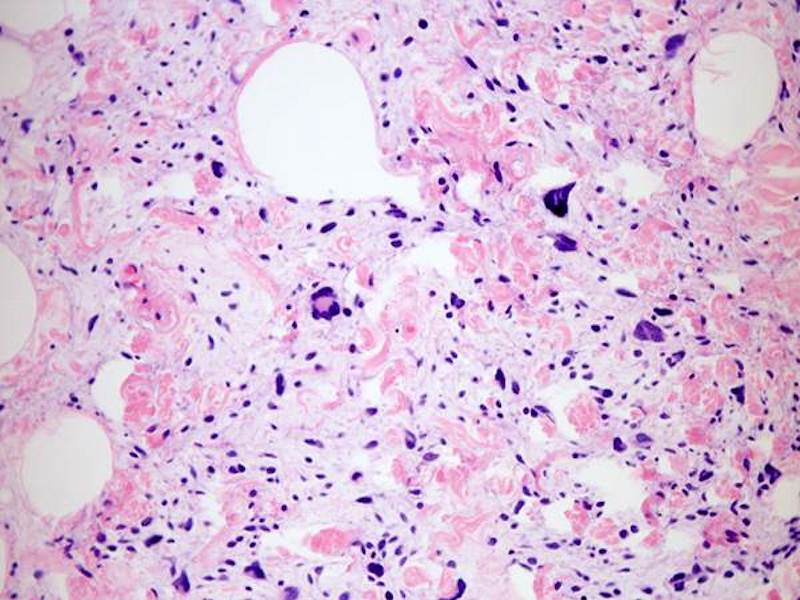
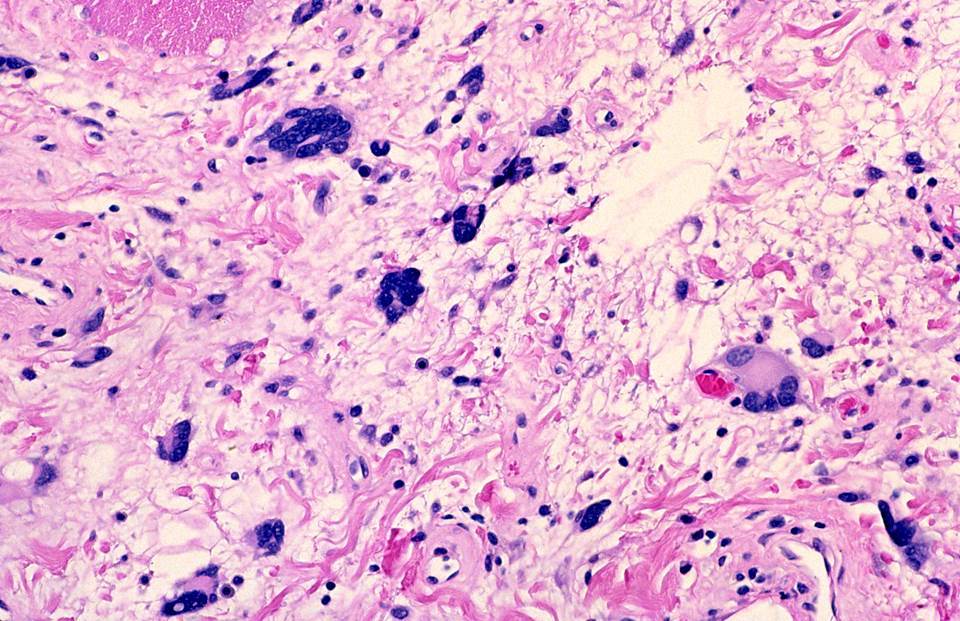
- Triad of mature adipocytes, bland spindle cells and hyalinized rope-like collagen fibers
- Multinucleated stromal giant cells and floret cells in pleomorphic lipoma
- Myxoid background with mast cells frequent
- Short and stubby spindle cells show occasional palisading
- Rare lipoblasts present in half of cases (Hum Pathol 2017;65:140)
- Infiltrative growth, necrosis, atypical spindle cells, pleomorphic lipoblasts and significant mitotic activity usually absent (Semin Diagn Pathol 2019;36:105)
- Fat poor and fat free subtype: contains little (< 5%) to no fat (Am J Dermatopathol 2007;29:437, Am J Dermatopathol 2009;31:423)
- Myxoid subtype: contains abundant myxoid stroma (Pathol Int 2014;64:346)
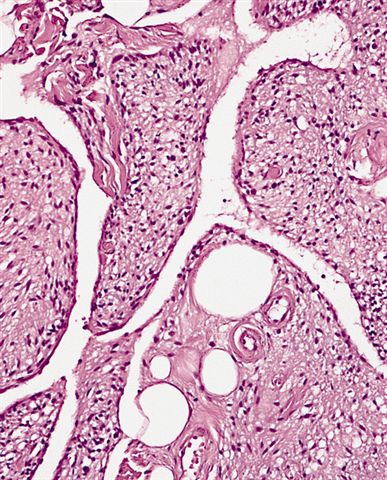
- (Pseudo) angiomatous subtype: contains dilated endothelial lined channels and nodules of floating tumor (Histopathology 1994;24:565, Pathol Int 2007;57:26)
- Plexiform variant has been described (Histopathology 1995;27:533)
- Focal cartilaginous and osseous metaplasia rarely present (Histopathology 1987;11:803)
- Extramedullary hematopoiesis may occur (Histopathology 2001;39:215)
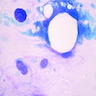
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
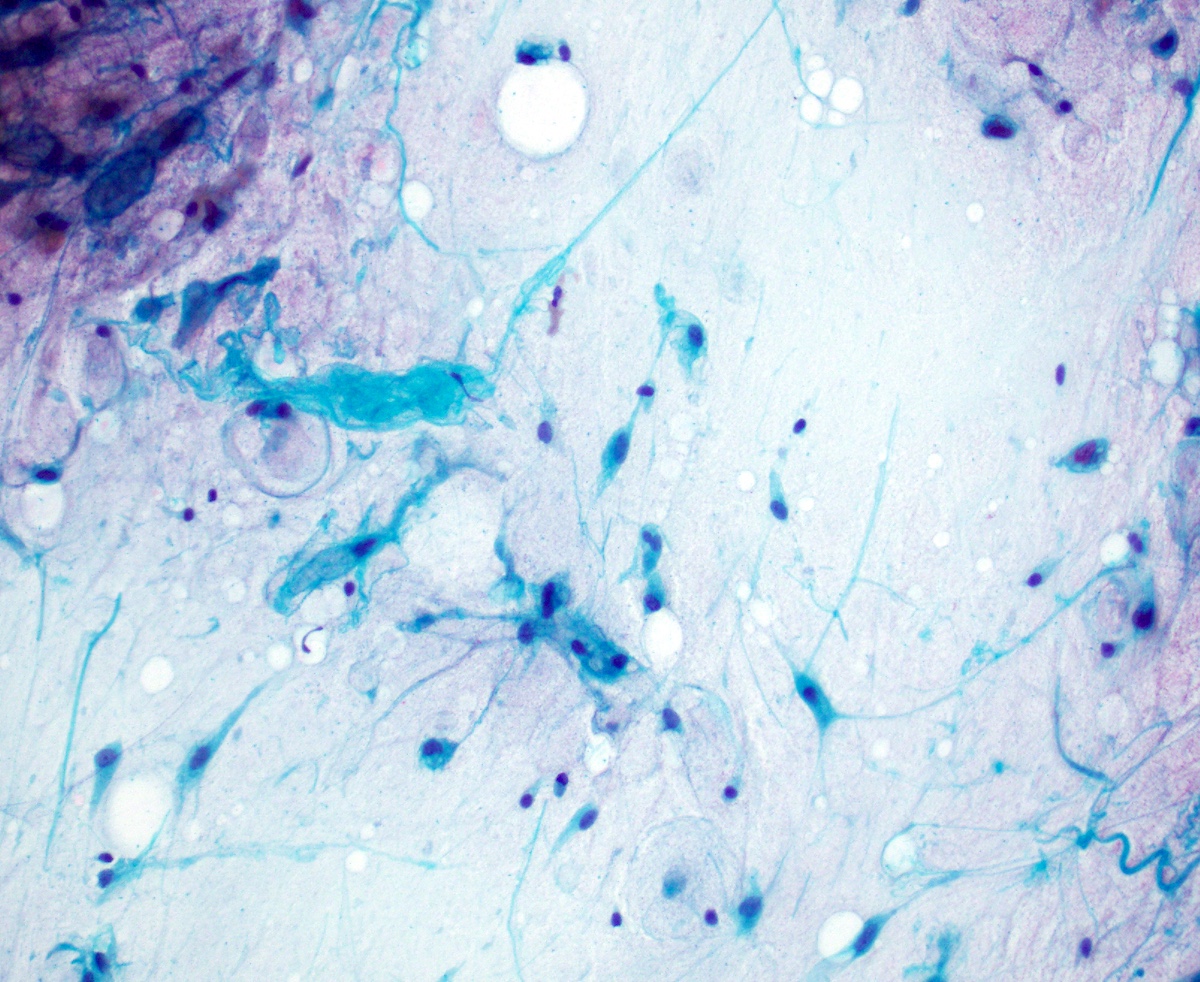
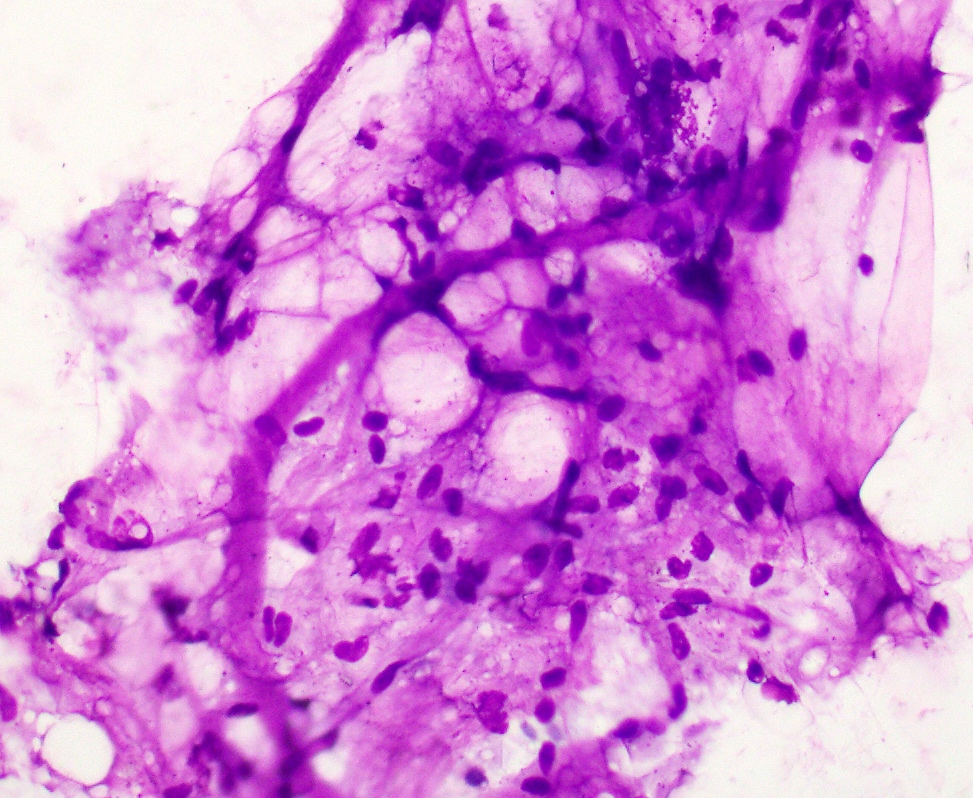
- Mixture of mature adipocytes, uniform spindle cells and collagen fibers (Cancer 2001;93:381)
- Spindle cell nuclei fusiform to ovoid with poorly defined, bipolar cytoplasmic processes
- Nuclear grooves may be present
- Myxoid background with mast cells common
- Mitotic activity and nuclear pleomorphism typically absent
- Multinucleated giant cells in pleomorphic lipoma
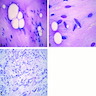
Cytology images
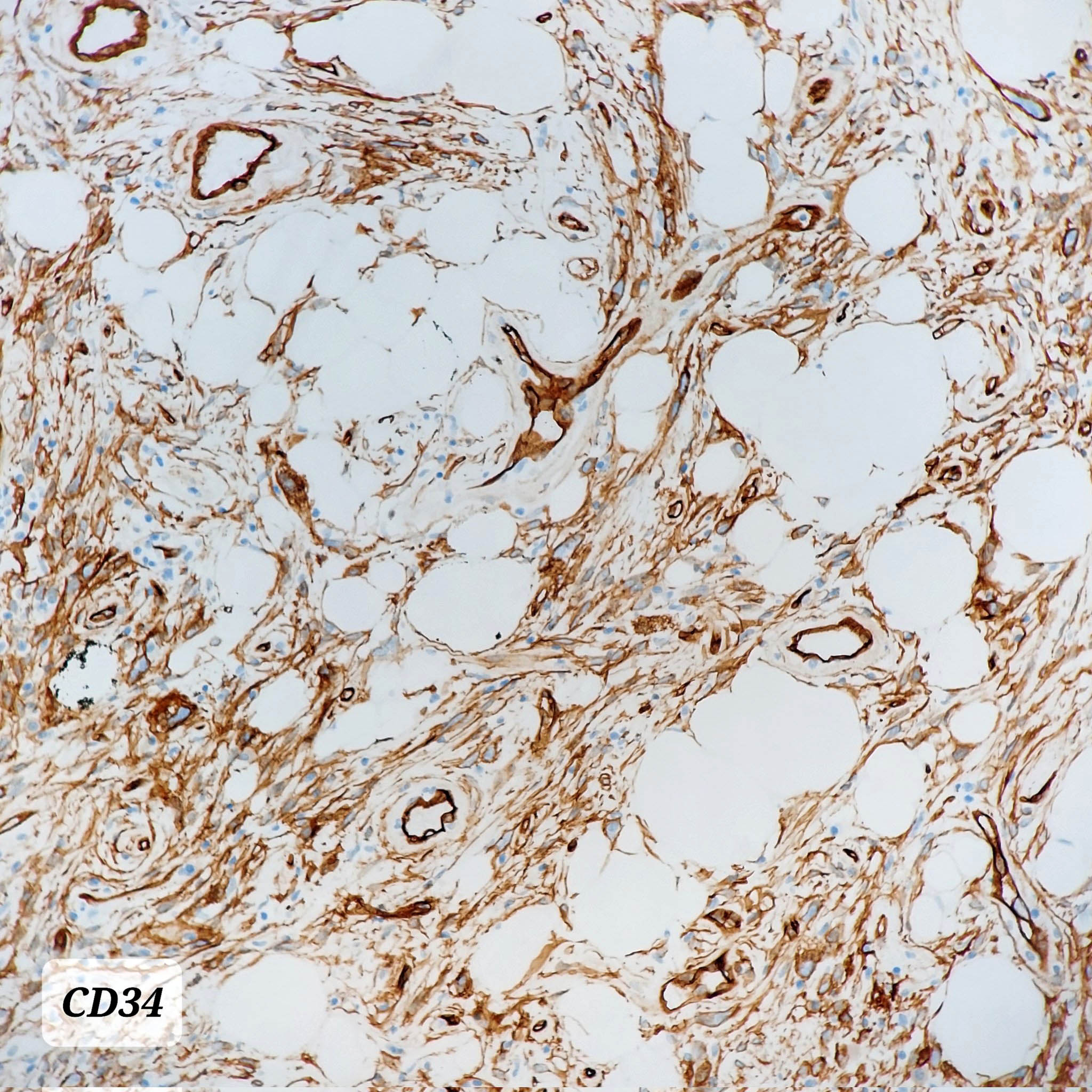
Positive stains
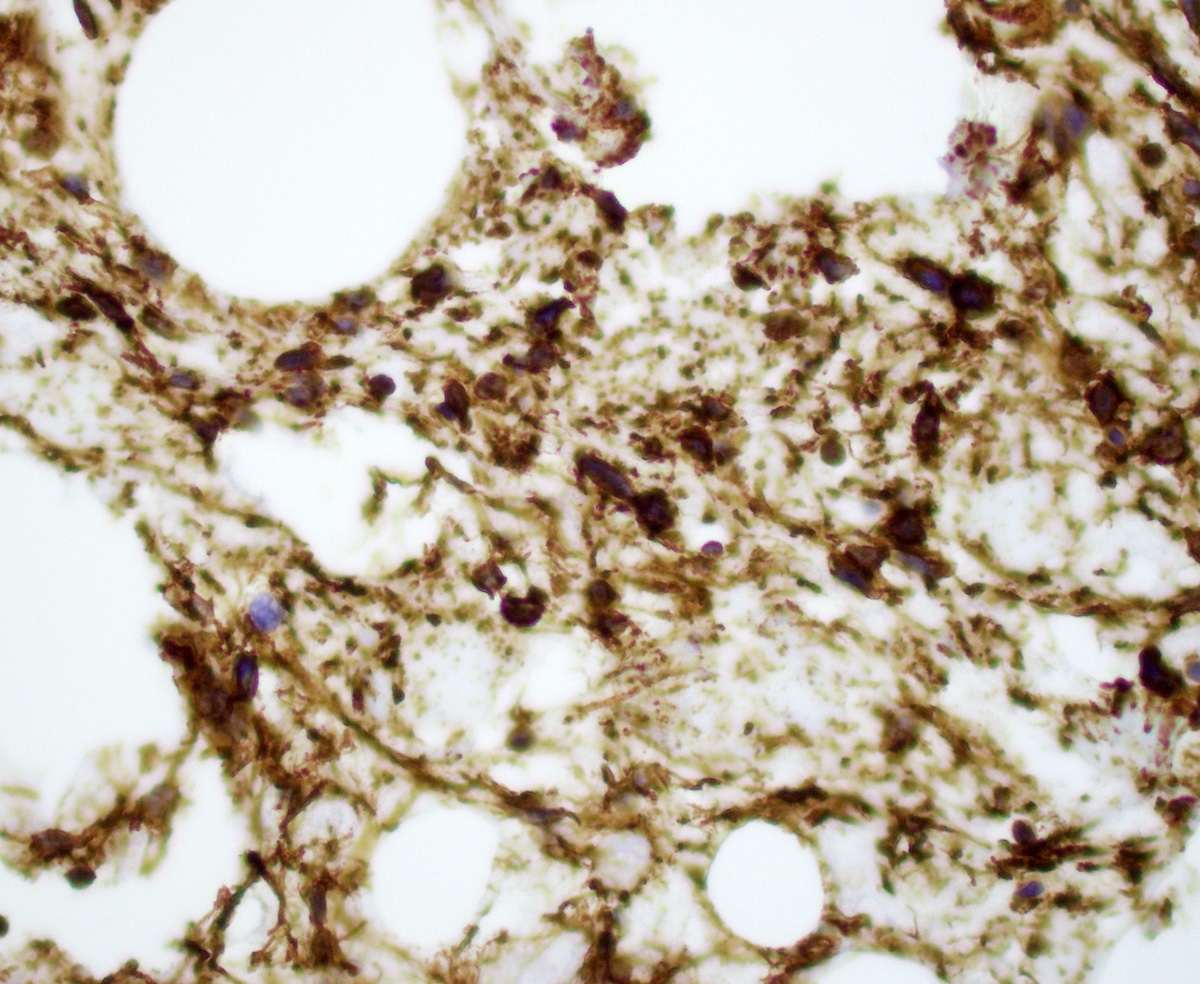
- CD34, strong and diffuse (J Cutan Pathol 1996;23:546)
- Loss of nuclear RB1 protein expression (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1119)
- Vimentin
Negative stains
- Keratin
- S100 protein, occasional expression seen (Virchows Arch 2016;469:435)
- SOX10
- Smooth muscle actin (SMA)
- Desmin, occasional expression seen (Virchows Arch 2004;445:354)
- STAT6
- Estrogen receptor (ER) in 20 - 25% (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:1267)
Electron microscopy description
- Spindle cells with some features of fibroblasts
- Nonmembrane bound lipid droplets, suggesting possible prelipoblastic nature (Cancer 2001;93:381)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Many show monosomy and partial chromosomal loss involving chromosomes 13 and 16 (Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2004;150:93)
- Demonstration of loss of the RB1 locus (Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2011;50:619)
Videos
Spindle cell lipoma
Pleomorphic lipoma
Sample pathology report
- Soft tissue, back, excision:
- Spindle cell lipoma (see comment)
- Comment: Sections show a benign adipocytic neoplasm with bland spindle cells and eosinophilic collagen bundles in a myxoid background with scattered mast cells. No necrosis, marked cytologic atypia or significant mitotic activity is identified. Immunohistochemical stains show that the spindle cells are diffusely positive for CD34, while demonstrating loss of RB1. These results support the above diagnosis.
Differential diagnosis
- Fibrolipoma:
- Ordinary lipoma with fibrous connective tissue
- Lacks uniform short and stubby cells of spindle cell lipoma
- Atypical lipomatous tumor (ALT) / well differentiated liposarcoma (WDLS):
- Pleomorphic liposarcoma:
- Pleomorphic lipoblasts
- Infiltrative border
- Atypical mitotic figures and necrosis common
- Complex chromosome losses and gains
- Myxoid liposarcoma:
- Younger patient population
- Characteristic plexiform capillary network
- Small signet ring lipoblasts common
- FUS-DDIT3 gene rearrangement
- Low grade myxofibrosarcoma:
- Frequently in limbs and limb girdles
- Elongated, curvilinear blood vessels
- Pseudolipoblasts may be present
- Varying cellularity and histologic grade
- Solitary fibrous tumor (especially fat forming / lipomatous variant):
- Mammary type myofibroblastoma:
- Cellular angiofibroma:
- CD34 positive
- RB1 (13q14) deletion / loss of nuclear Rb expression
- Hyalinized vessels common
- Vulvovaginal / inguinoscrotal region
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP):
- CD34 positive
- Prominent storiform growth pattern
- Infiltrative growth pattern (honeycomb infiltration)
- Can show myxoid change
- COL1A1-PDGFB gene fusion
- Schwannoma:
- S100 positive
- Hyalinized blood vessels
- More extensive nuclear palisading
- Neurofibroma:
Additional references
Board review style question #1
What is the most typical clinical presentation of a patient with a spindle cell lipoma?
- 30 year old woman soft tissue mass (9 cm) involving her right lateral thigh
- 45 year old woman with subcutaneous mass (3 cm) involving her left arm
- 55 year old man with subcutaneous mass (4 cm) involving his upper back
- 60 year old man with soft tissue mass (15 cm) involving his retroperitoneum
Board review style answer #1
C. 55 year old man with subcutaneous mass (4 cm) involving his upper back. Spindle cell lipoma usually occurs in middle aged to elderly men. The lesion is often small (< 5 cm) and frequently involves the subcutaneous tissue of the upper back, shoulder or posterior neck.
Comment Here
Reference: Spindle cell / pleomorphic lipoma
Comment Here
Reference: Spindle cell / pleomorphic lipoma
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2
A. Spindle cell lipoma is diffusely positive for CD34 and demonstrates loss of expression of RB1. Atypical lipomatous tumor / well differentiated liposarcoma is positive for both MDM2 and CDK4. Solitary fibrous tumor is positive for both CD34 and STAT6. Desmin positivity and loss of expression of RB1 can be seen in mammary type myofibroblastoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Spindle cell / pleomorphic lipoma
Comment Here
Reference: Spindle cell / pleomorphic lipoma