Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Youssef R, Dehner C. Myolipoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissueadiposemyolipoma.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Myolipoma is a rare, benign tumor composed of mature fat cells and well differentiated smooth muscle; usually found in the retroperitoneum but can also occur in other locations (Am J Surg Pathol 1991;15:121)
Essential features
- Rare, benign tumor composed of mature fat cells and smooth muscle cells (Am J Surg Pathol 1991;15:121)
- Usually in adults, with a female predominance
- Usually located in the retroperitoneum and pelvis
- Immunohistochemistry: positive for actin and desmin and negative for MDM2, HMB45 and CD34
- HMGA2 nuclear staining in 60% of cases (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:153)
Terminology
- Soft tissue lipoleiomyoma (Pathology 1991;23:360)
- Extrauterine lipoleiomyoma
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8890/0 - myolipoma
Epidemiology
- Rare tumor
- Predominantly affects women (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:153)
- Adults; peak incidence is 35 - 94 years (with a median of 55 years) (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:153)
Sites
- Myolipomas are usually deep seated, with the retroperitoneum being the most common location, followed by the pelvic cavity and abdomen (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:153)
- Rare locations include subcutaneous tissue of trunk and head / neck, orbit, nose, tongue, breast, pericardium, spinal - intramedullary and anus (Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 1998;236:630)
Etiology
- Unknown etiology; importantly, it is not associated with tuberous sclerosis (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:153, Am J Surg Pathol 1991;15:121)
Clinical features
- Often asymptomatic
- Occasionally discovered incidentally by computed tomography (CT) or during abdominal surgery
- It may cause pain or discomfort if large or compressing adjacent structures (Diagn Interv Radiol 2010;16:227)
Diagnosis
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) shows heterogeneous mass, predominantly with fat intensity
- Biopsy reveals mature fat cells interdigitating with smooth muscle cells that lack cytologic atypia
- Immunohistochemistry
- Positive for smooth muscle actin and desmin (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:153)
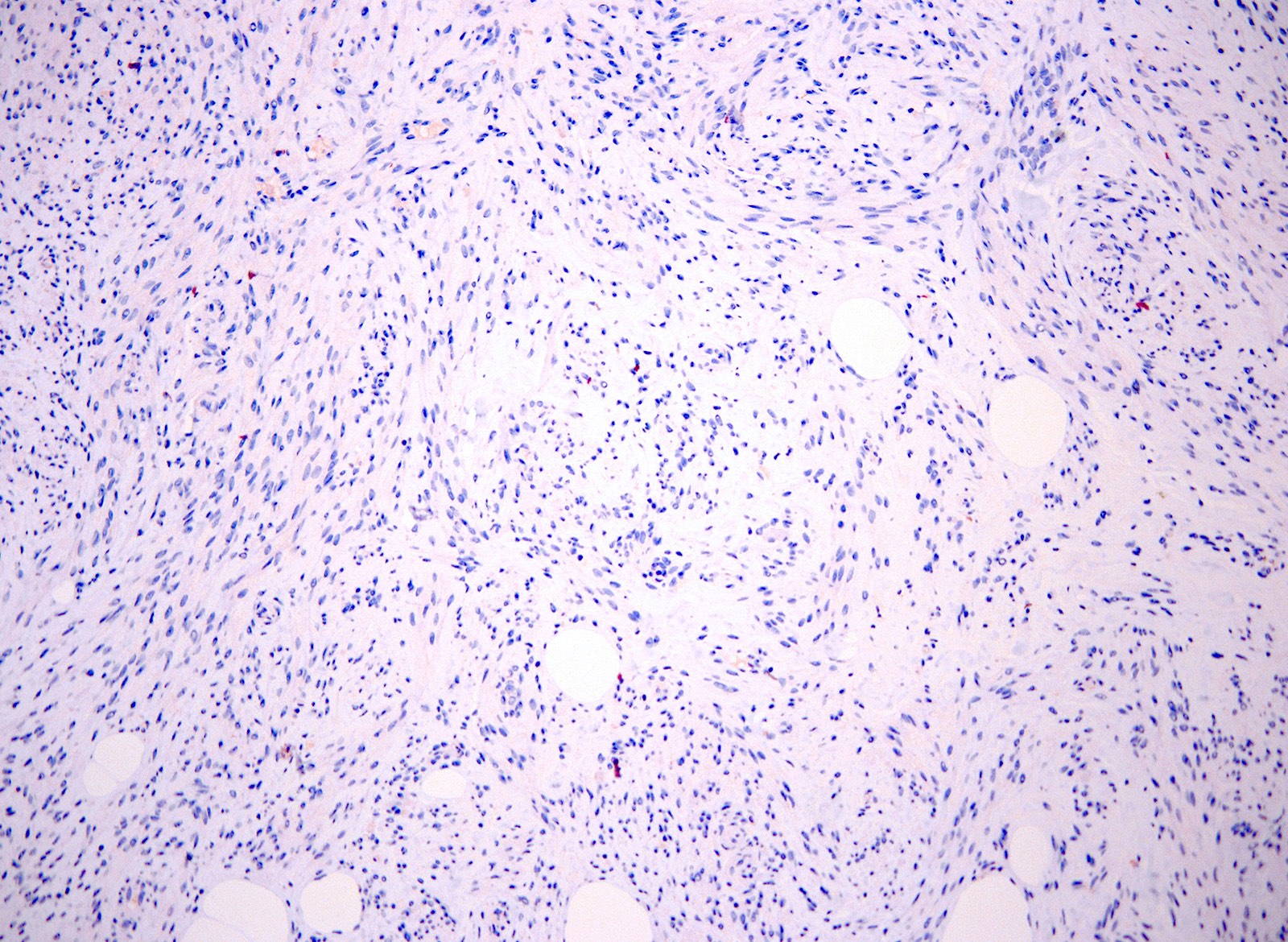
- Negative for MDM2, HMB45 and CD34
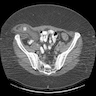
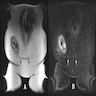
Radiology description
- CT shows a heterogenous mass containing low density areas (Diagn Interv Radiol 2010;16:227)
- MRI shows a heterogeneous mass, predominantly with fat intensity
- Intermediate signal intensity on T1 and intermediate to high signal intensity on T2 weighted images (Diagn Interv Radiol 2010;16:227)
- Coarse calcifications have been reported (Clin Radiol 1996;51:295)
- Ultrasound shows a heterogeneous echoic mass with multiple hyperechoic foci
- Ultrasound is not diagnostic due to hyperechogenicity of the fatty component but can be suggestive (Diagn Interv Radiol 2010;16:227)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Excellent prognosis
- Local recurrence or metastasis has not been reported (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:153)
Case reports
- 39 year old woman with an epipleural lesion (Respirol Case Rep 2021;9:e0853)
- 45 year old woman presented with abdominal cramping and marked distention (World J Surg Oncol 2021;19:144)
- 48 year old man presented with progressive dyspnea and chest pain (World J Radiol 2013;5:446)
Treatment
- Treatment is based on surgical resection
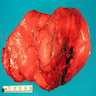
Gross description
- Tumor size: 2 - 35 cm; superficial sites tend to be smaller (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:153)
- Well circumscribed, with nodular, yellowish / tan, whorled cut surface
- May show myxoid areas
- No hemorrhage or necrosis
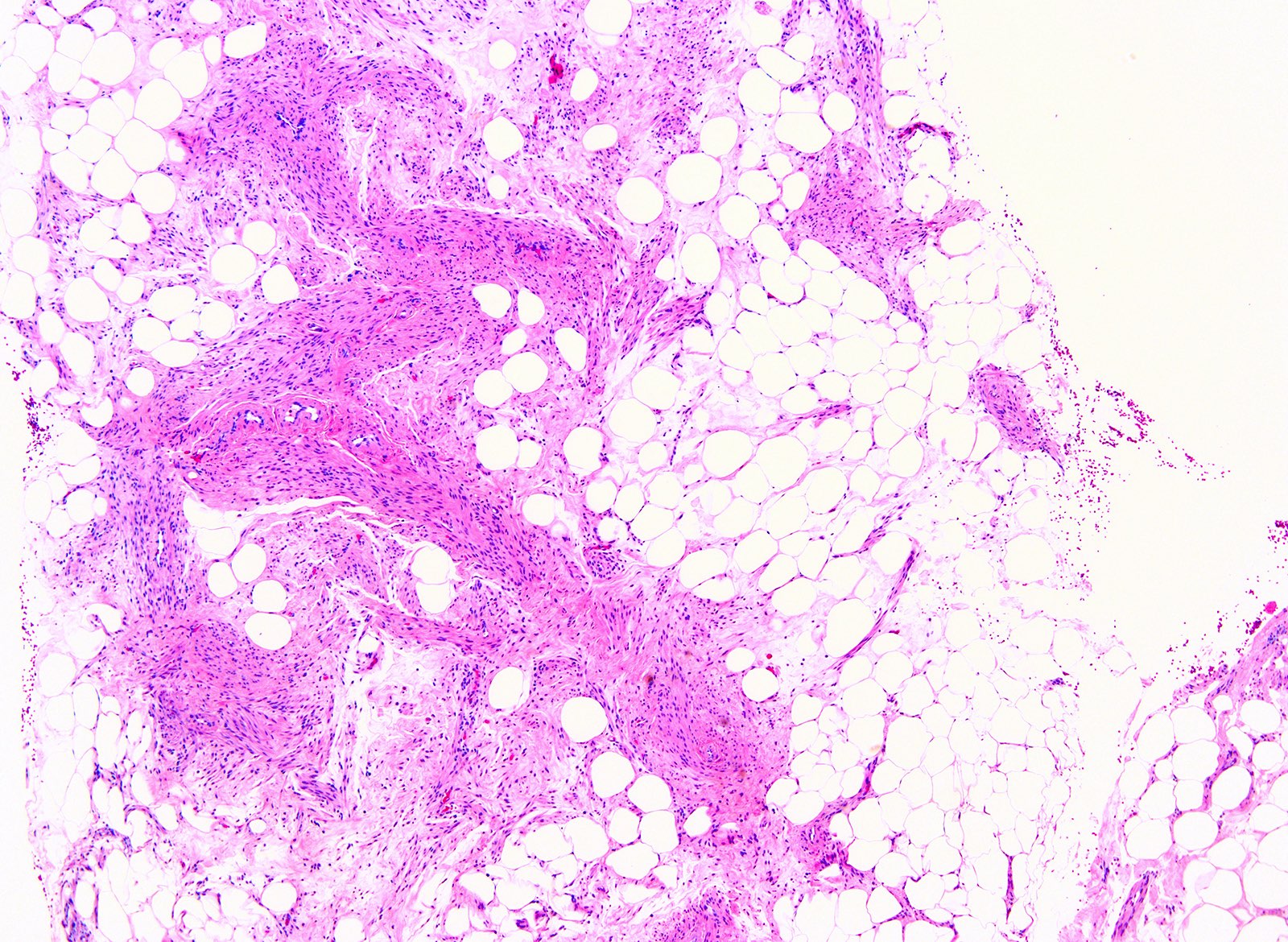
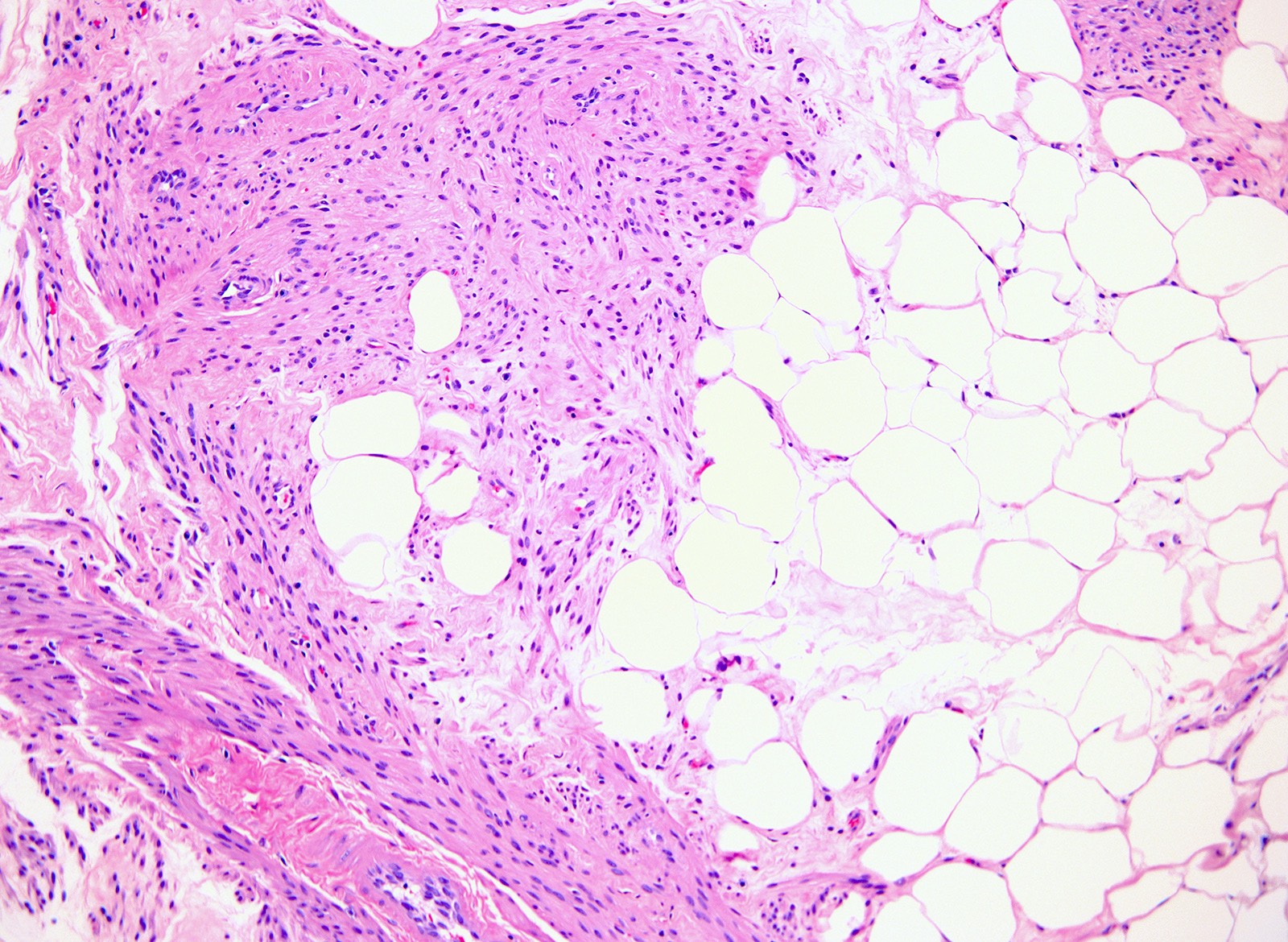
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Composed of mature fat cells interdigitating with smooth muscle cells
- Smooth muscle component is formed of fascicles of spindle cells with brightly eosinophilic cytoplasm and blunt ended nuclei
- Adipocytic component usually does not show lipoblast or floret cells
- Smooth muscle may rarely show bizarre, multilobulated nuclei (Pathologica 1997;89:163)
- May show edematous or hyalinized stroma
- Variable small and thick walled vessels
- Scattered mast cells or lymphocytic infiltrates may be seen in the smooth muscle component (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:153)
- Usually absent or rare mitosis < 1/10 high power fields (HPF)
- No necrosis; however, infarction with hyaline change has been reported
- Tumor cells are usually bland; however, degenerative nuclear atypia can be rarely seen
- Unusual features include (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:153)
- Round cell morphology
- Metaplastic cartilage and metaplastic bone formation
- Eosinophilic infiltrates
- Hemosiderin deposition
Microscopic (histologic) images
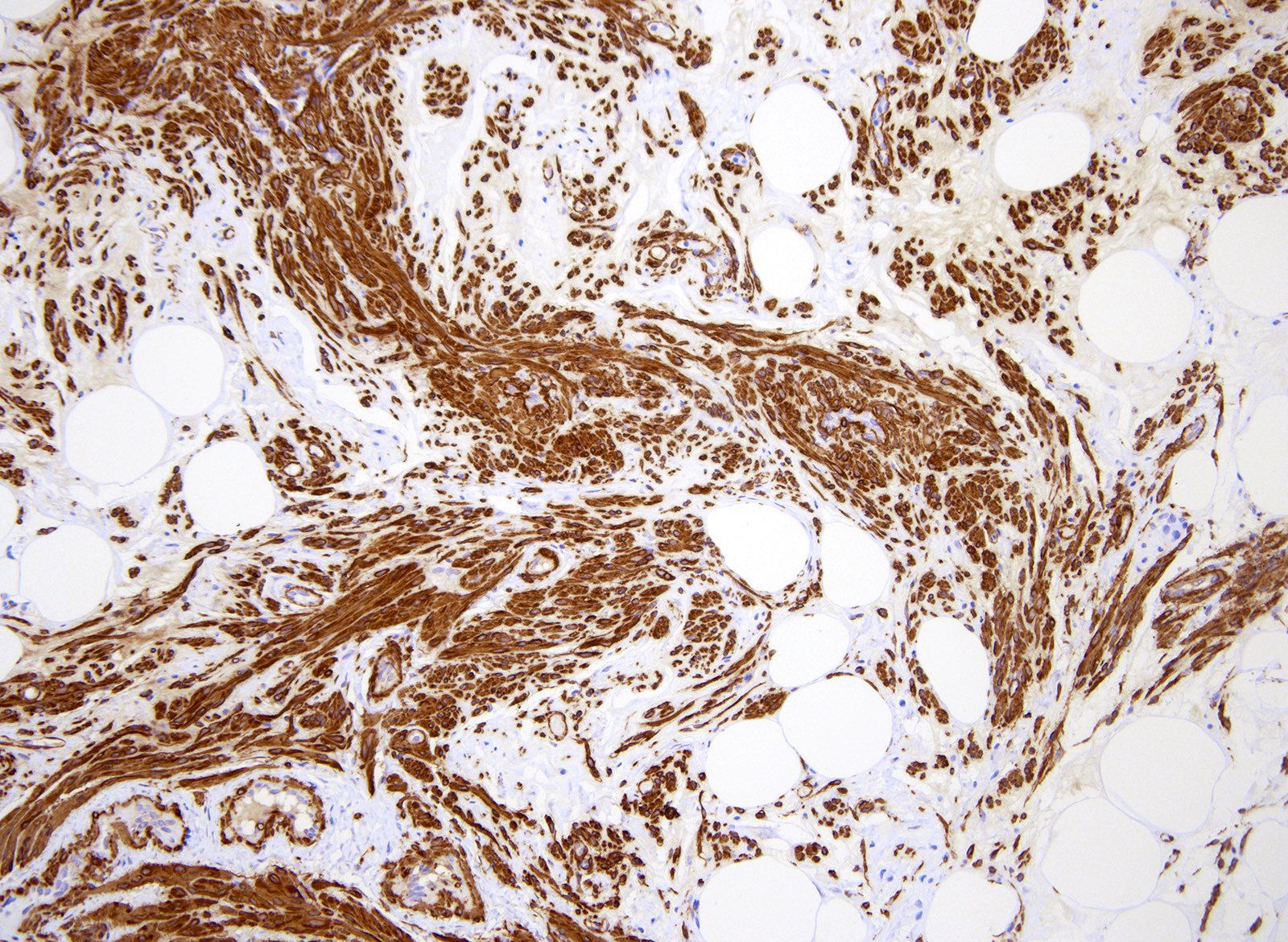
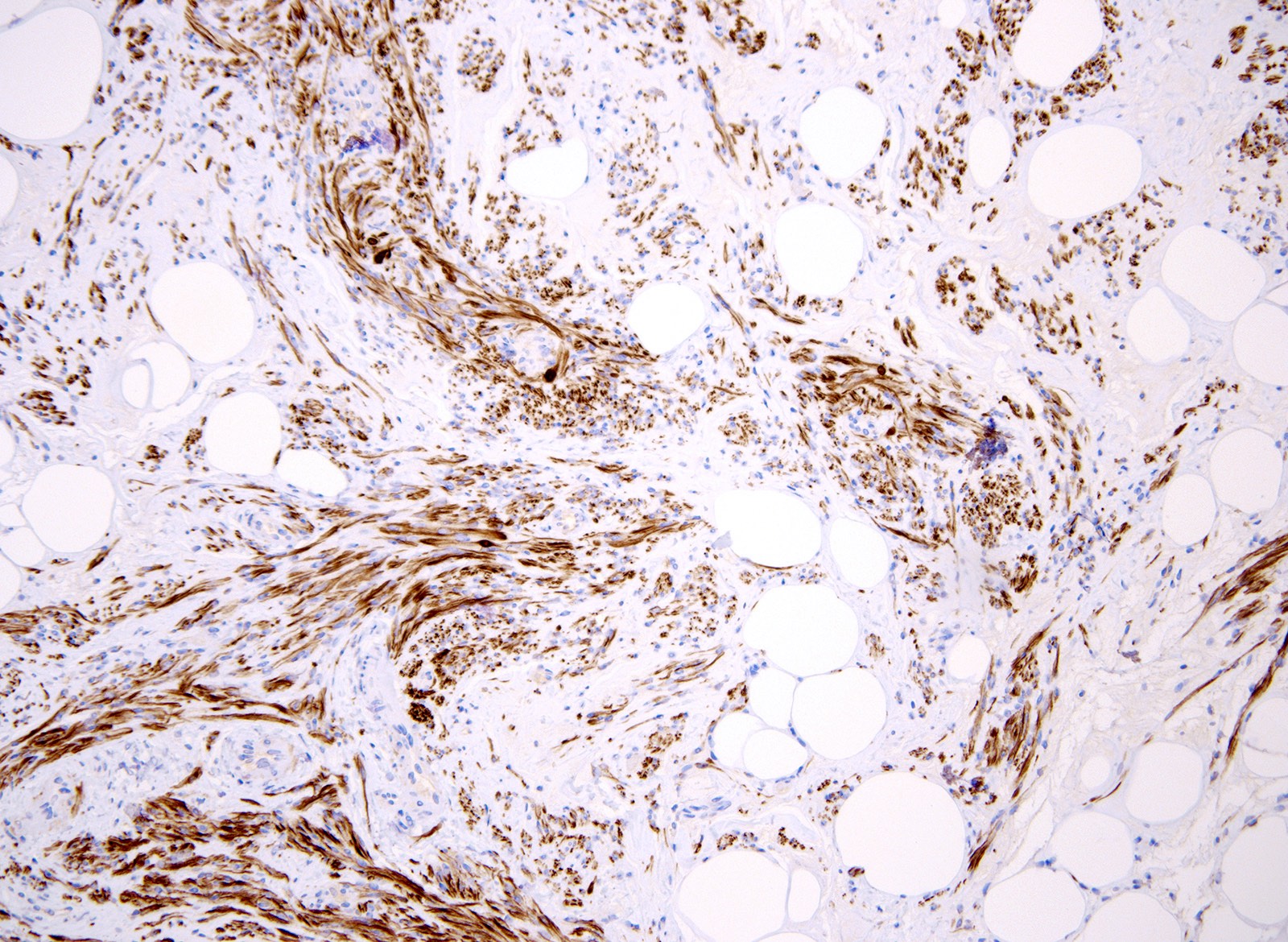
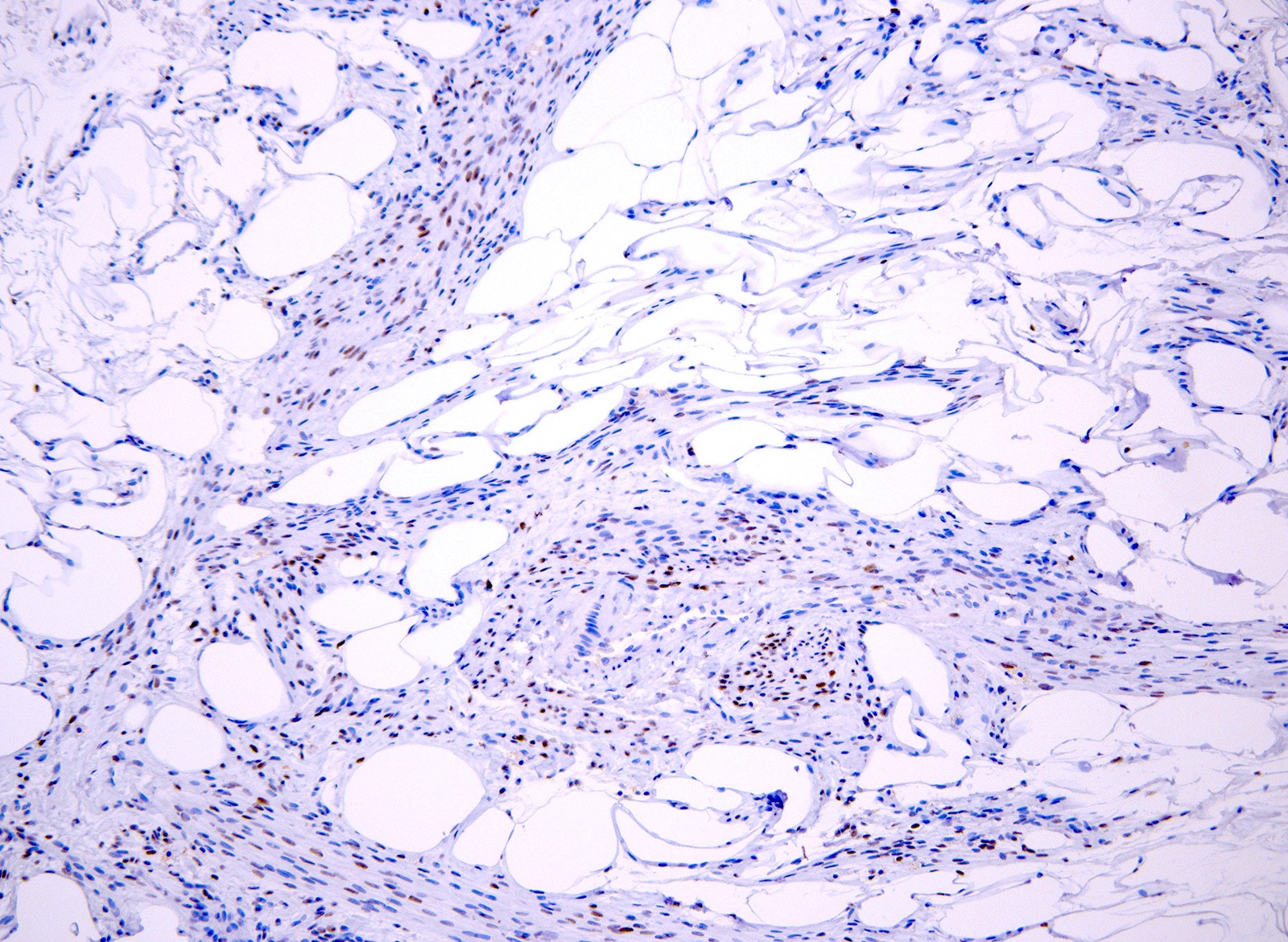
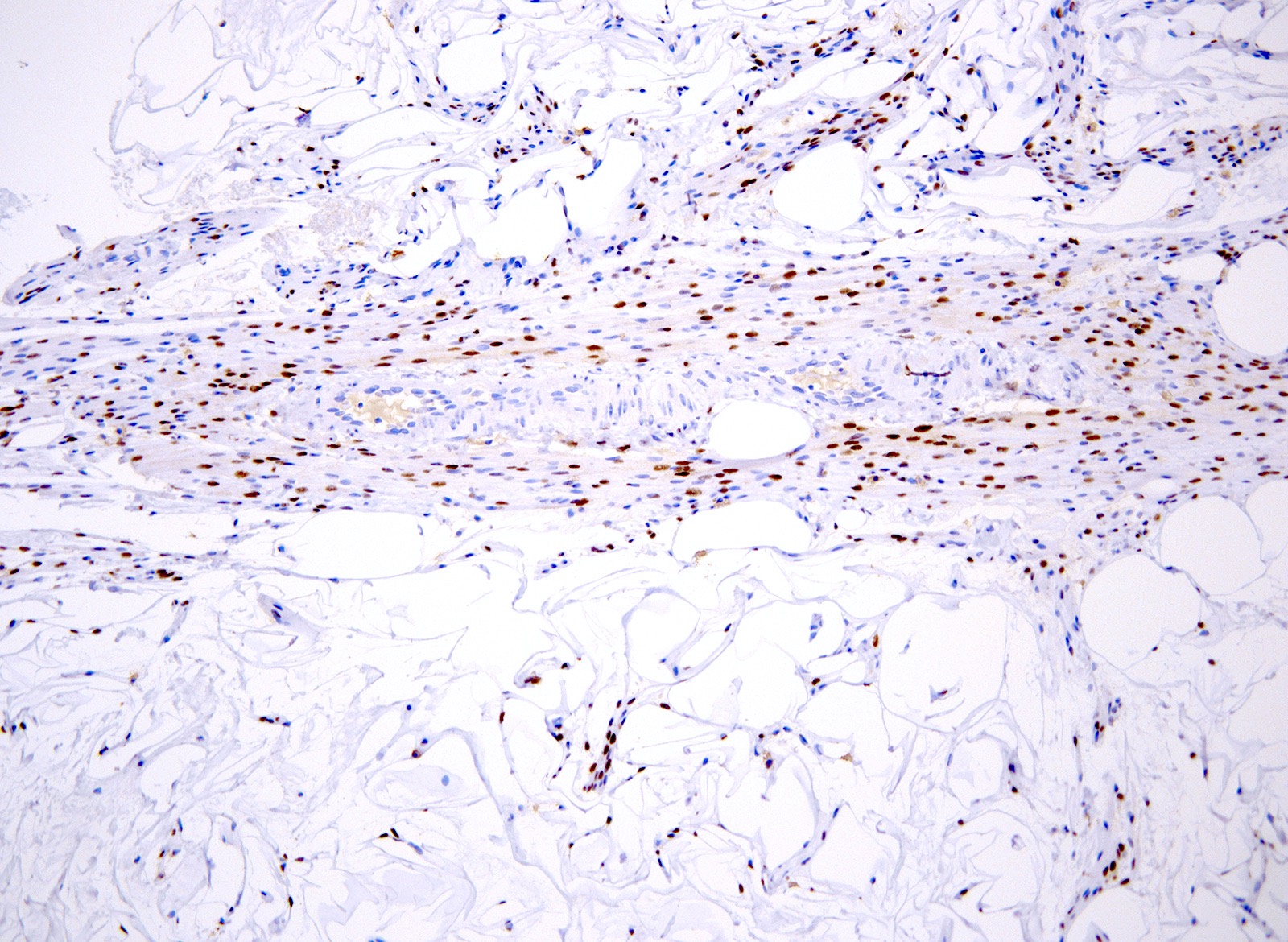
Positive stains
- HMGA2; 1 case has been reported to be negative (Mod Pathol 2010;23:1657)
- Strong diffuse desmin (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:153)
- Strong diffuse smooth muscle actin (SMA) (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:153)
- h-caldesmon
- ER (diffuse in smooth muscle and focal in fat cells) (67%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:153)
- PR (60% of cases) (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:153)
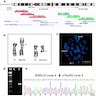
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- HMGA2 rearrangements (nonspecific)
- Molecular genetic analysis showed t(9;12)(p22;q14) resulting in HMGA2::C9orf92 fusion (Diagn Pathol 2016;11:22)
- HMGA2 rearrangement has been reported in other adipocytic and smooth muscle tumors (Int J Cancer 2008;122:2233, Lab Invest 2000;80:359)
- Fluorescence in situ hybridization testing is negative for MDM2 amplification
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Sample pathology report
- Soft tissue, retroperitoneal mass, resection:
- Myolipoma (see comment)
- Comment: The tumor is composed of mature adipose tissue interdigitating with bland smooth muscle. Atypical features such as increased mitotic count, cytologic atypia or necrosis are not identified. Immunohistochemical stains show strong expression of SMA and desmin in the smooth muscle component, while melanocytic markers such as HMB45 and MelanA are negative.
Differential diagnosis
- Spindle cell lipoma:
- Usually found in the subcutaneous tissue of the neck, shoulder and back
- Composed of mature fat cells, short spindle cells and ropey collagen bundles
- Positive for CD34 (strong diffuse) (J Cutan Pathol 1996;23:546)
- Loss of nuclear RB1 protein expression (J Cutan Pathol 1996;23:546)
- Mammary type myofibroblastoma:
- Well circumscribed spindle cell tumor comprising short fascicles of bland spindled cells and dense hyalinized collagen bundles
- Diffuse positivity for CD34 and desmin (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:361)
- Loss of nuclear RB1 protein expression (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:361)
- Lipoleiomyosarcoma:
- Rare variant of well differentiated liposarcoma
- Liposarcoma with smooth muscle component (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:552)
- Lipoblasts or atypical cells with hyperchromatic nuclei in the fibrous septa can be seen
- Positive for MDM2 and CDK4 stains
- Dedifferentiated liposarcoma:
- Fat forming solitary fibrous tumor:
- Spindled cells and fat cells arranged within variably collagenous stroma with branching dilated stag horn vessels
- Positive for CD34 and STAT6 (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:552)
- Negative for desmin
- Angiomyolipoma:
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
A. Actin. The smooth muscle component in myolipoma stains for actin. Answer B is incorrect because CD34 is positive in the spindle cell component of spindle cell / pleomorphic lipoma. Answer C is incorrect because MDM2 is positive in well differentiated and dedifferentiated liposarcoma. Answer D is incorrect because MelanA is expressed in angiomyolipoma. Answer E is incorrect because STAT6 is expressed in solitary fibrous tumors.
Comment Here
Reference: Myolipoma
Comment Here
Reference: Myolipoma
Board review style question #2
Regarding soft tissue myolipoma, which statement is true?
- Could be associated with HMGA2 rearrangements
- ER is usually negative
- FISH usually demonstrates MDM2 amplification
- Predominantly affects men
- Shows loss of nuclear RB1 protein expression
Board review style answer #2
A. Could be associated with HMGA2 rearrangements. Answer E is incorrect because loss of nuclear RB1 protein expression occurs in mammary type myofibroblastoma. Answer D is incorrect because it predominantly affects women. Answer C is incorrect because FISH usually demonstrates MDM2 amplification in well differentiated and dedifferentiated liposarcoma. Answer B is incorrect because ER is usually diffusely positive.
Comment Here
Reference: Myolipoma
Comment Here
Reference: Myolipoma