Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Renne SL. Lipoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissueadiposelipoma.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign tumor composed of mature adipocytes
Essential features
- Most common soft tissue tumor
- Mostly subcutaneous, < 5 cm
- Radiologically, grossly and microscopically same as normal fat
- In large (> 10 cm) and deep seated / retroperitoneal tumors, exclusion of MDM2 amplification is required for diagnosis
Epidemiology
- Most common mesenchymal tumor in adults (Acta Orthop Scand 1983;54:929)
- M = F (slightly more common in males)
- Rare in children
Sites
- Superficial (subcutaneous) soft tissue
- Upper back, proximal extremities and abdominal region
- Subset deep seated (intramuscular, parosteal, visceral)
Pathophysiology
- Reactivated expression of HMGA2 protein (J Biol Chem 2000;275:14394, Am J Hum Genet 2005;76:340)
Etiology
- Unknown at this time
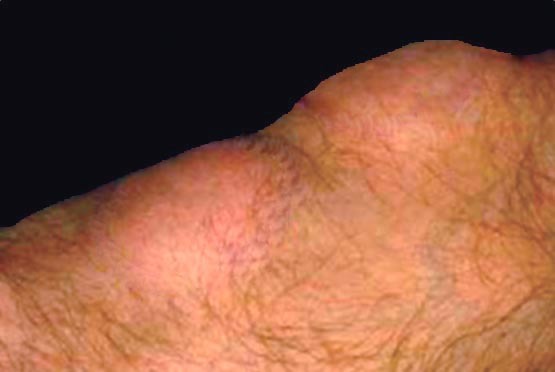
Clinical features
- Painless, subcutaneous mass
- In special site, might have specific symptoms (i.e. gastrointestinal → melena)
- 5% multiple (Acta Orthop Scand 1983;54:929)
- Cowden syndrome (J Med Genet 1999;36:360)
- Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome (GeneReviews: PTEN Hamartoma Tumor Syndrome [Accessed 18 November 2021])
- Associated with obesity
Diagnosis
- Clinical features (Eur J Surg Oncol 2021 Oct 18 [Epub ahead of print])
- < 5 cm
- Soft
- Superficial
- Imaging
- Ultrasonography
- Computed tomography (deep seated)
- Magnetic resonance (deep seated)
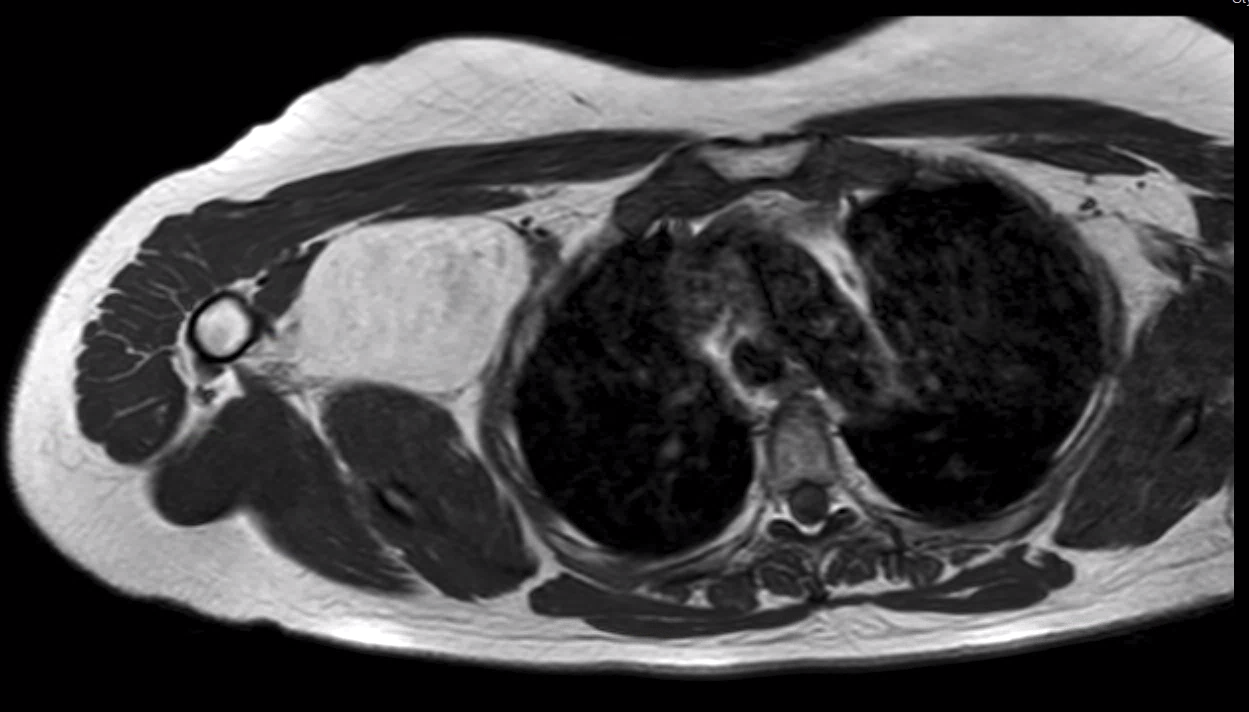
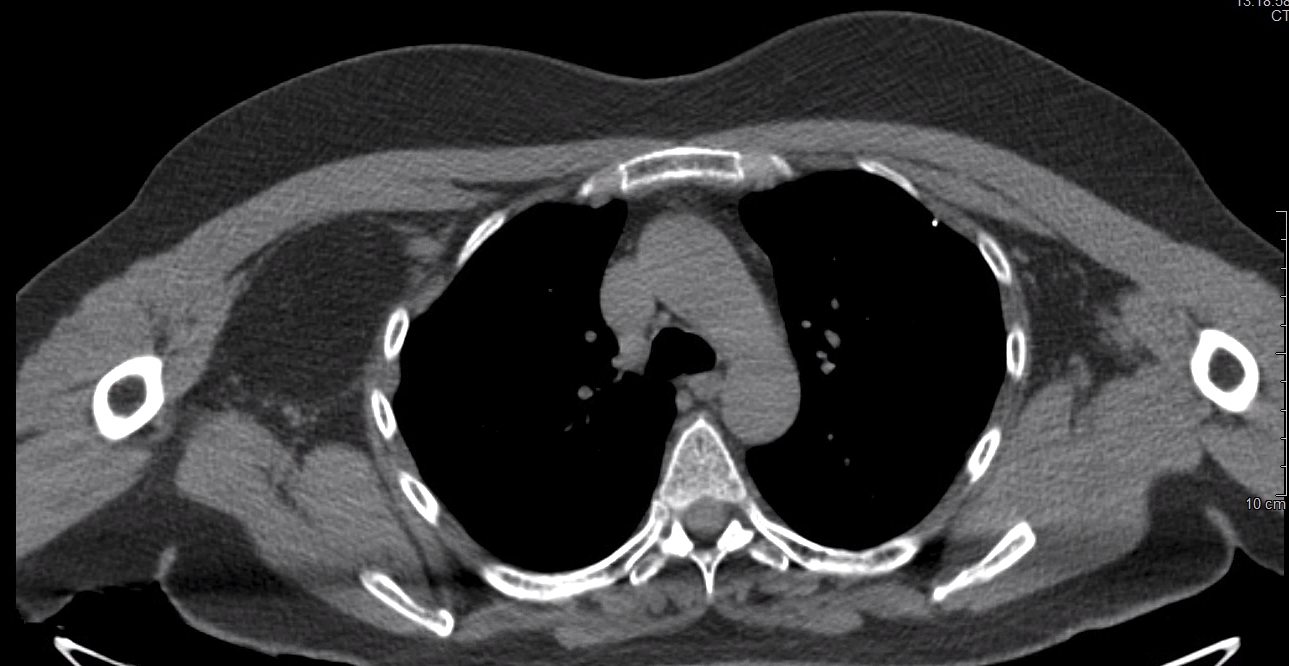
Radiology description
- Ultrasonography
- Variably echogenic mass (Radiographics 2004;24:1433)
- Mostly isoechoic (Radiology 2004;233:763)
- No shadowing
- No flow with color Doppler
- CT (Radiographics 2004;24:1433)
- Superficial
- Circumscribed
- Low attenuation
- Calcification might be present
- MRI
- Same signal as subcutaneous fat in all sequences
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Recurrence < 5%
- Incomplete surgery, higher local recurrence
Case reports
- 37 year old woman with giant infiltrative tumor of face (AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2003;24:283)
- 58 year old and 63 year old women with tumors of pectoralis major muscle simulating a breast mass (Ann Acad Med Singapore 2005;34:275, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2011;135:1061)
- Well circumscribed tumor of sternocleidomastoid muscle (Auris Nasus Larynx 2004;31:283)
Treatment
- Simple excision
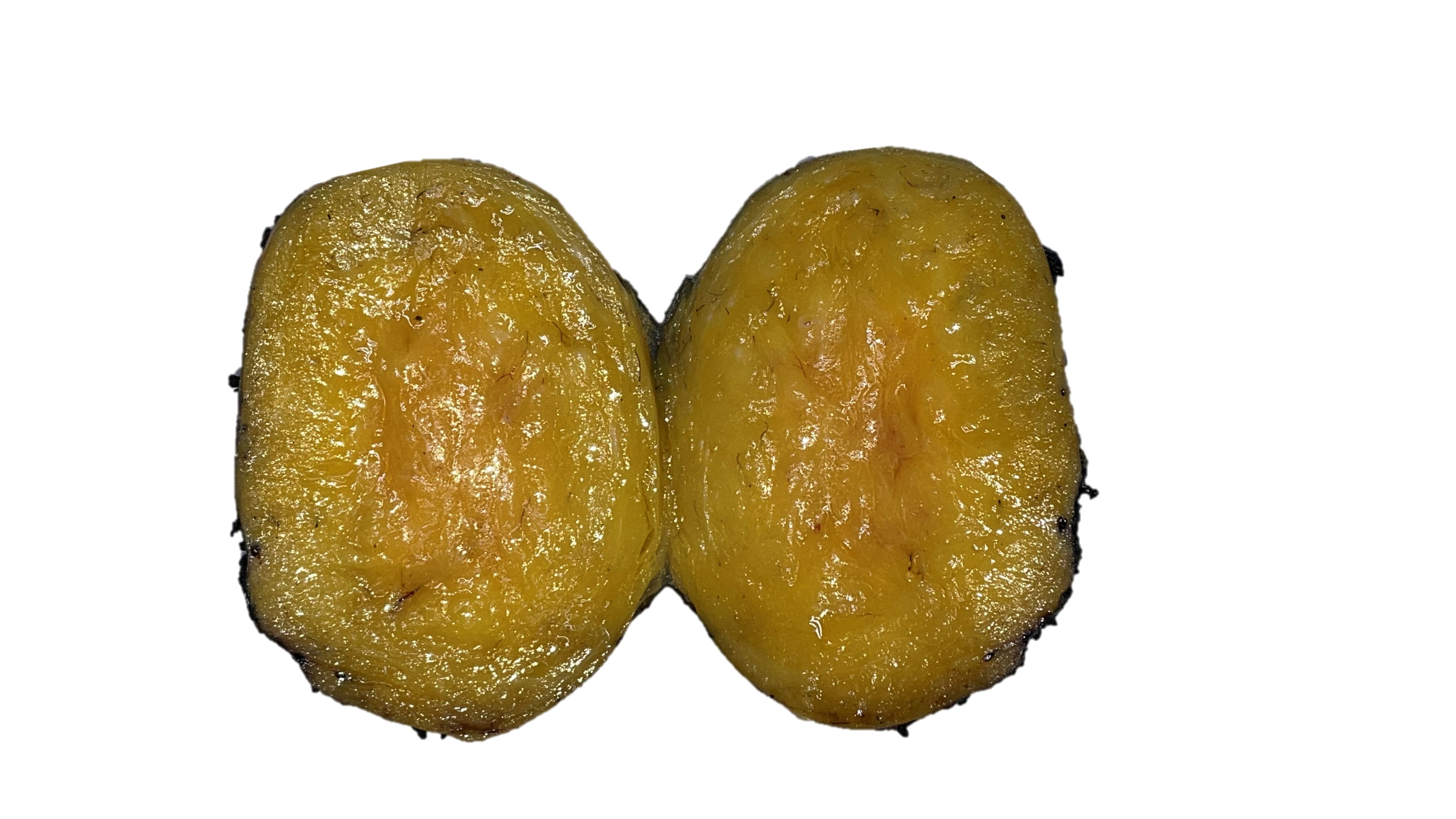
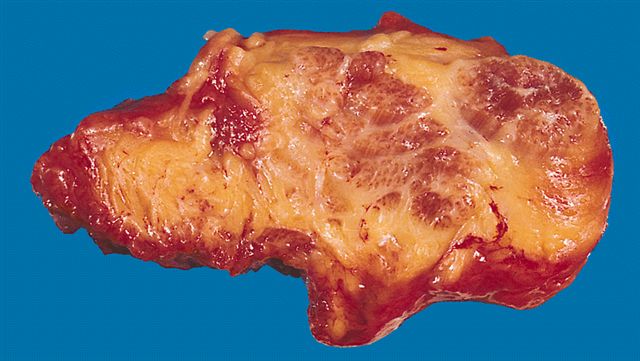
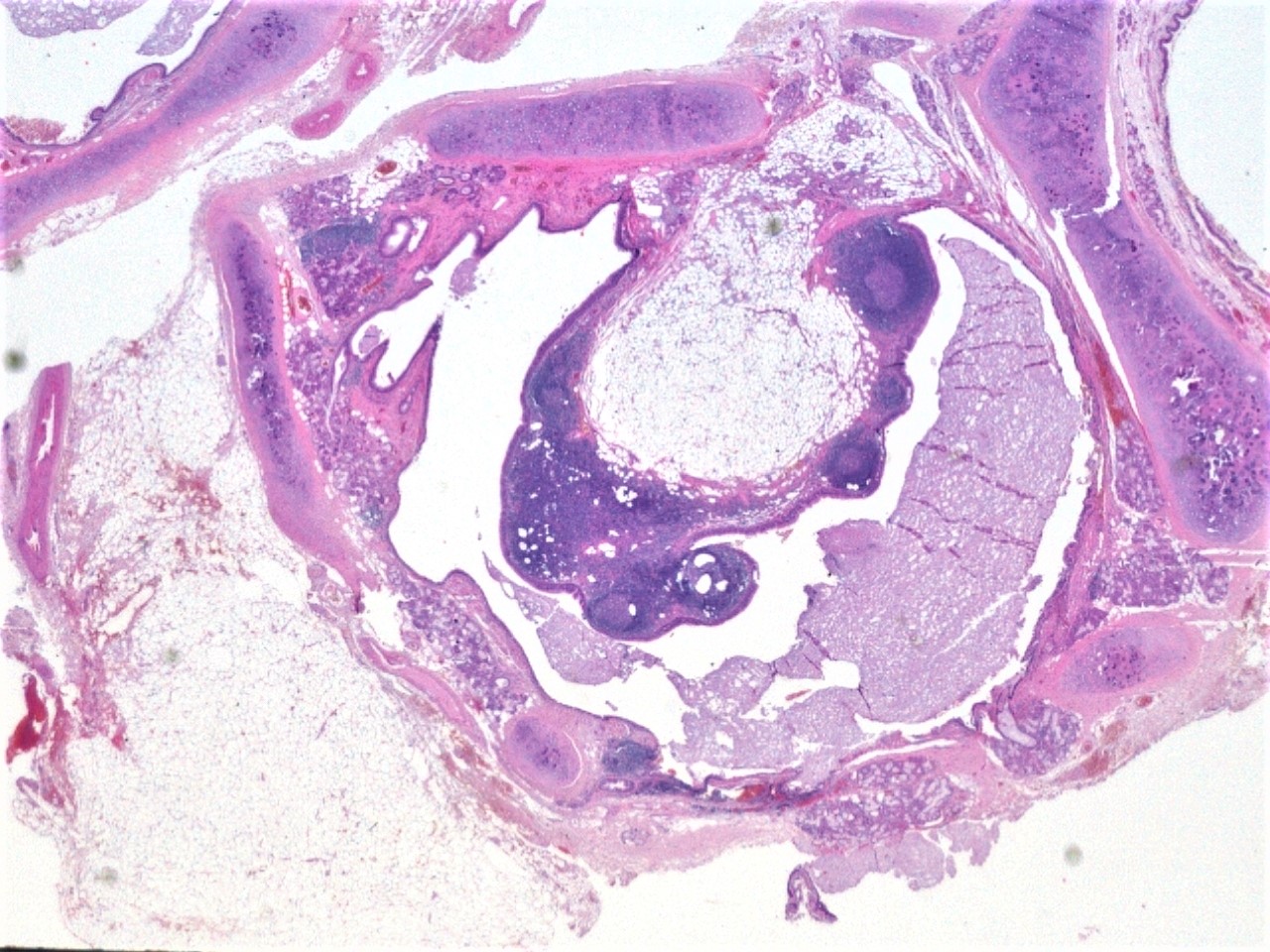
Gross description
- Well circumscribed
- Nodular
- Cut surface homogeneous
- Fatty appearance
- Usually small (< 5 cm)
- Osteolipoma and chondrolipoma can be recognized grossly
Gross images
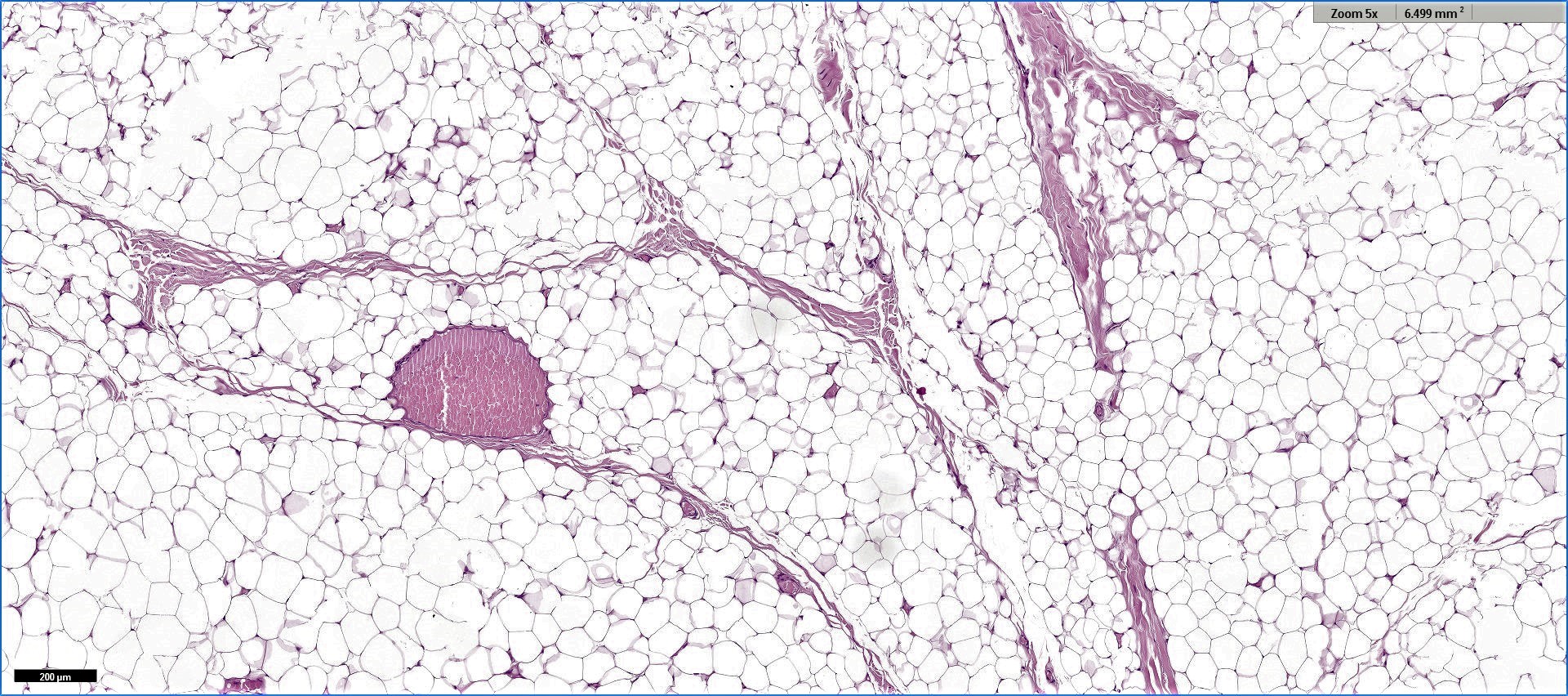
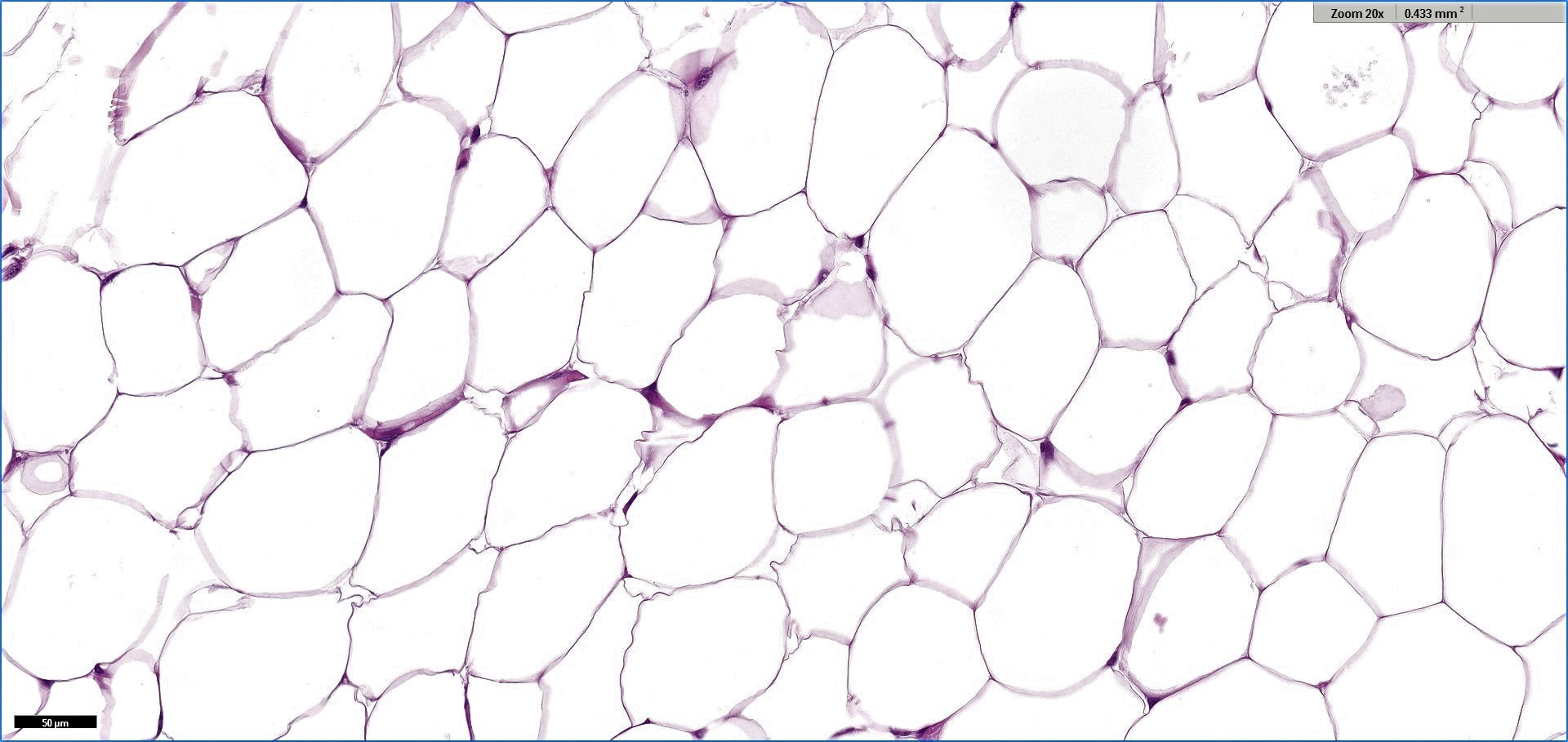
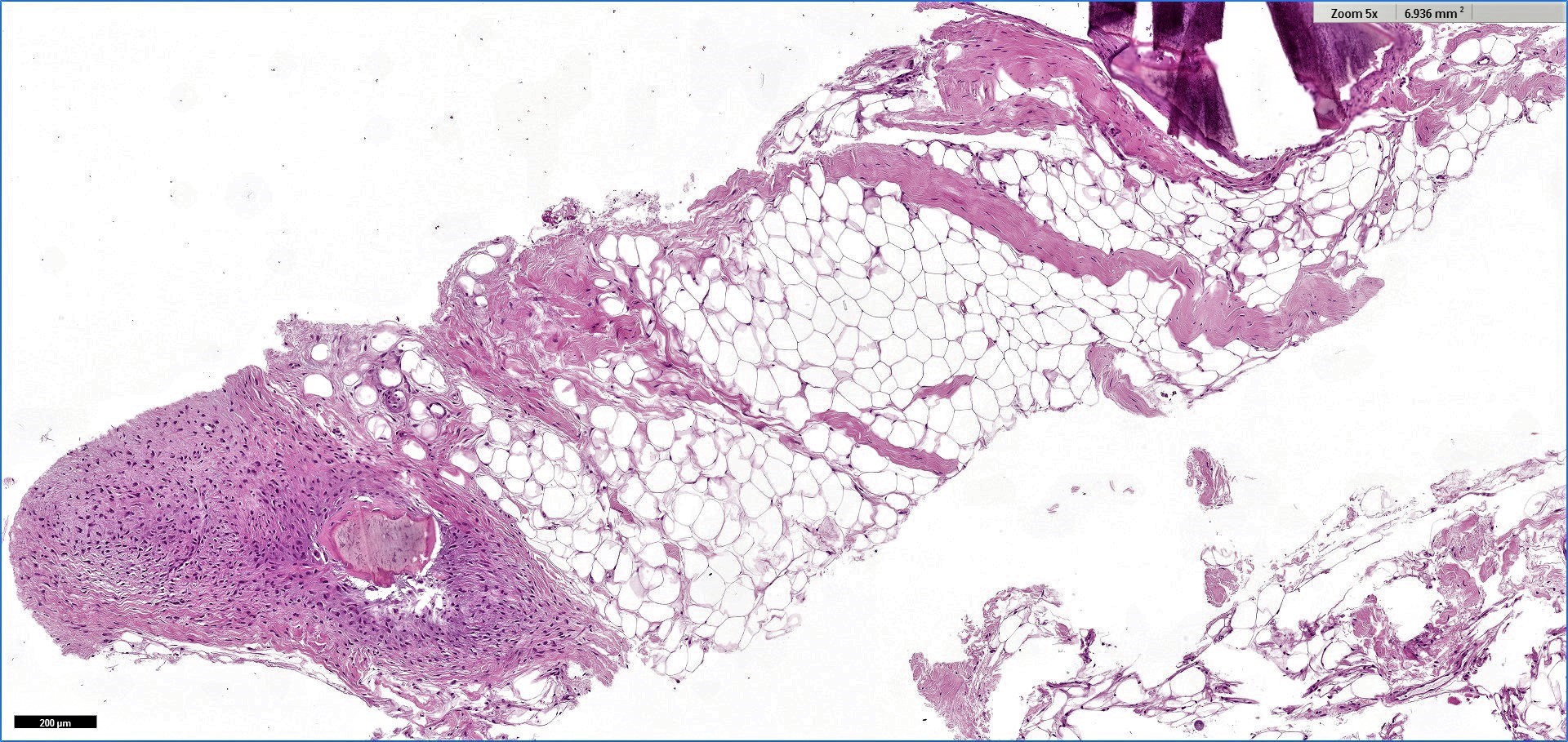
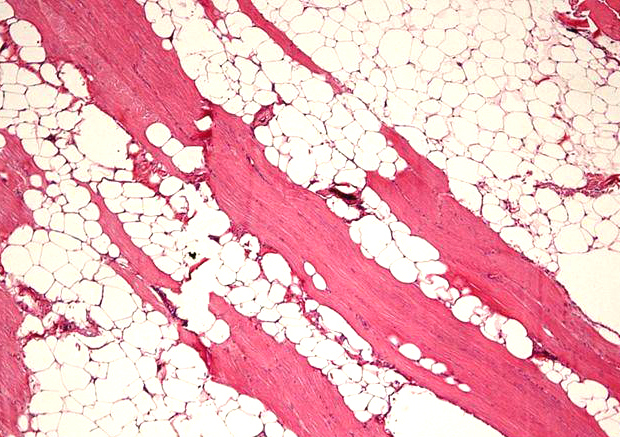
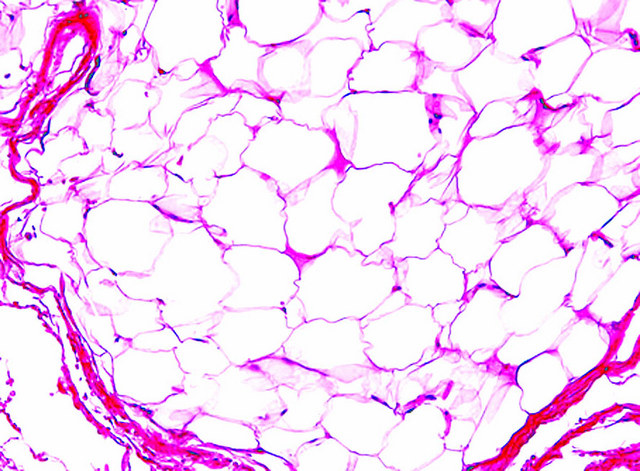
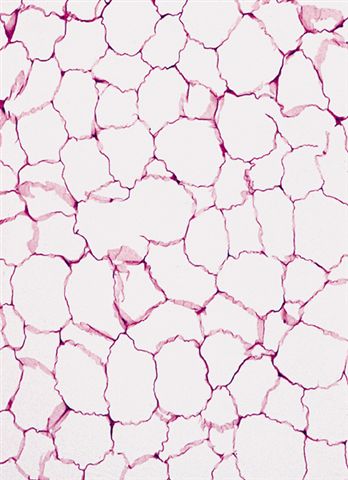
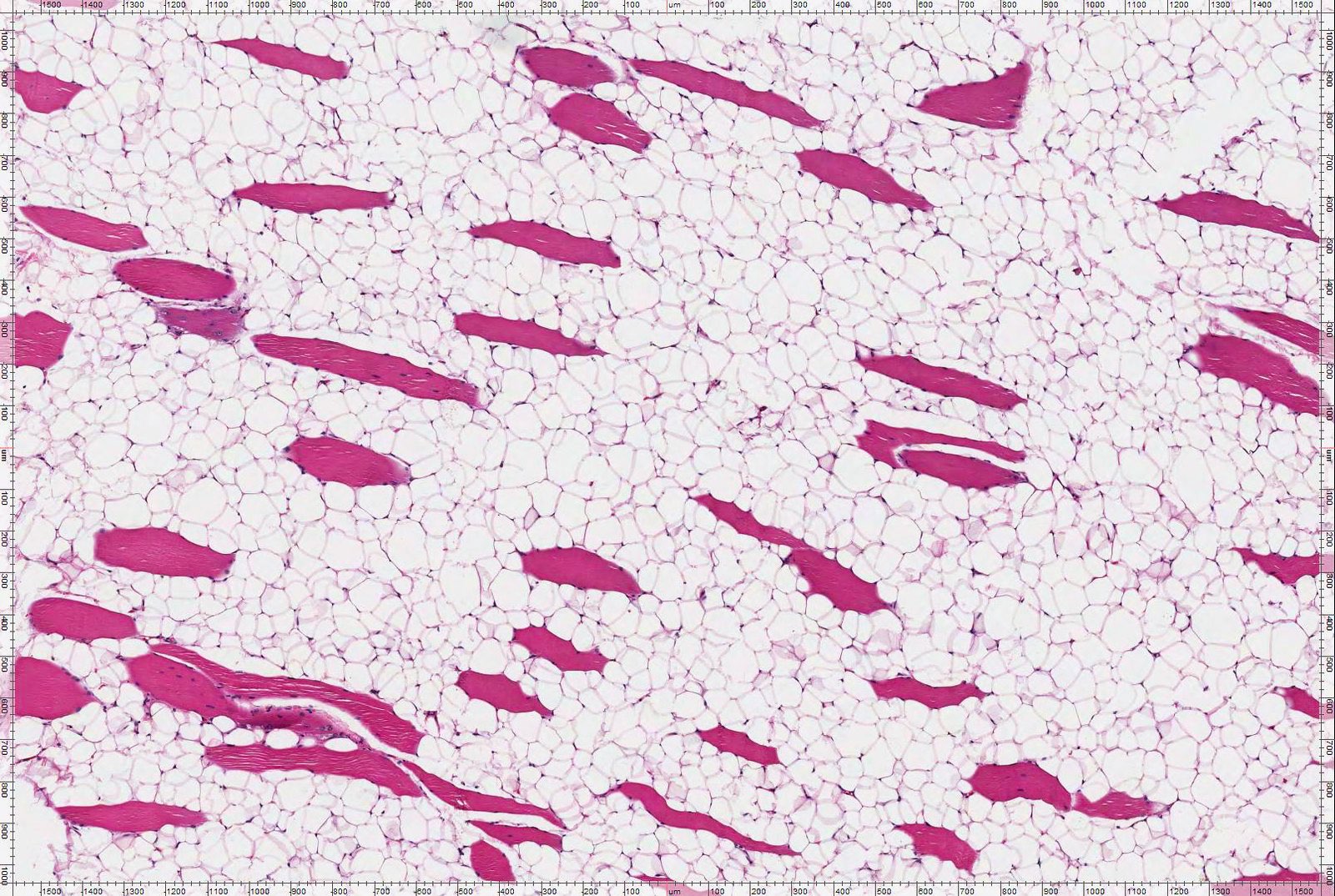
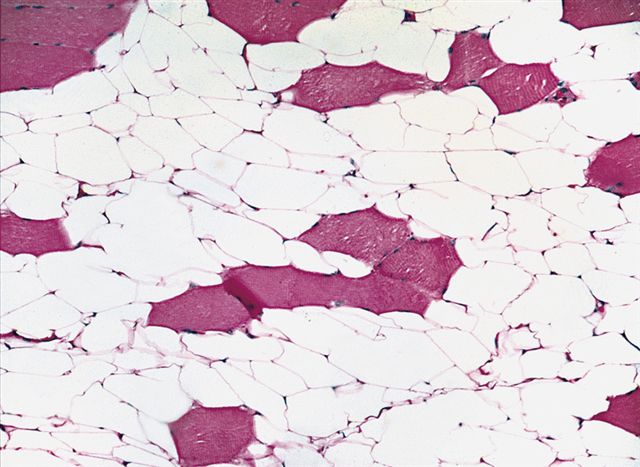
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Proliferation of mature adipocytes
- Paucicellular fibrous septa can be present
- Fat necrosis is often found in larger tumor
- Skeletal muscle fibers are infiltrated in intramuscular lipoma
- Subtypes
- Intramuscular lipoma
- Chondrolipoma
- Visceral sites
- Submucosal lipoma of the colon
- Endobronchial lipoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Salvatore Lorenzo Renne, M.D., Mark R. Wick, M.D., Charanjeet Singh, M.D. and AFIP images
Virtual slides
Cytology description
- Mature adipocytes with single lipid large droplet
- Inconspicuous nucleus
Positive stains
- Rb (G3-245) preserved positivity (lost in spindle cell pleomorphic lipoma) (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1119)
- HMGA2 (negative in normal fat) (Mod Pathol 2010;23:1657)
Negative stains
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Structural rearrangement of chromosome bands12q13-q15 or HMGA2 gene
- Structural rearrangement of chromosome band 6p21 or HMGA1 gene
- Absence of MDM2 amplification (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;3:1476, Histopathology 2021 Sep 14 [Epub ahead of print])
- Absence of CDK4 amplification (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;3:1476)
- Absence of giant marker / ring chromosome (Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2004;150:93)
- Absence of 13p loss (Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2004;150:93)
Videos
Lipoma and its differential diagnosis
Sample pathology report
- Soft tissue, subcutaneous trunk, excision:
- Lipoma
- Soft tissue, deep (deltoid), excision:
- Lipoma, intramuscular (see comment)
- Comment: Sections show a mature adipocytic neoplasm. No cytologic atypia or mitotic activity is identified. Immunohistochemical stain shows negativity for MDM2. Fluorescence in situ hybridization does not show amplification of MDM2 gene.
Differential diagnosis
- Angiolipoma:
- Typically composed of two elements: mature adipocytes and branching capillary sized vessels, which often contain fibrin thrombi
- Relative proportions of adipocytes and vessels varies and some lesions are almost completely composed of vascular channels
- Spindle cell / pleomorphic lipoma:
- Atypical lipomatous tumor / well differentiated liposarcoma:
- Size > 10 cm
- Deep seated
- Atypical cells
- MDM2 IHC positivity
- MDM2 gene FISH cluster amplification
- Mobile encapsulated adipose tissue (MEAT)
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
C. Lipoma. The mass is in the subcutis, small (< 5 cm), well circumscribed and homogenously composed of adipocytes.
Comment Here
Reference: Lipoma
Comment Here
Reference: Lipoma
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is true about a lipoma?
- Diagnosis is often made without immunohistochemistry
- Highly infiltrative lesion, which leads the majority to recur
- It is the most common benign neoplasm
- It is usually large (> 10 cm) and located in deep soft tissue or retroperitoneum
- Patient always reports a history of trauma
Board review style answer #2
A. Diagnosis is often made without immunohistochemistry. Diagnosis can be done on H&E in most cases and in the appropriate clinicopathological setting (i.e. small, superficial, homogeneous lesion, composed of uniform adipocytic cells without atypia).
Comment Here
Reference: Lipoma
Comment Here
Reference: Lipoma