Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Sites | Clinical features | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Gonzalez RS. Malignant GI neuroectodermal tumor. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/smallbowelmaliggastroneuroectodermaltumor.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rare malignant mesenchymal neoplasm of the gastrointestinal tract
Essential features
- Mesenchymal malignancy that grows in sheets or cords and may have osteoclast-like giant cells
- Positive for S100 and synaptophysin; negative for HMB45 and MelanA
- Harbors EWSR1 translocation
Terminology
- Also known as clear cell sarcoma-like tumor of the gastrointestinal tract
Sites
- Small bowel is most common site in gastrointestinal tract, followed by stomach (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:857)
Clinical features
- Median age 35 years; no sex predilection (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:407)
- Most common symptoms are abdominal pain and intestinal obstruction
- Tumor can spread to lymph nodes and liver and may cause death
Case reports
- 17 year old boy with stomach mass (Oncol Lett 2014;8:2687)
- 18 year old man with small bowel mass (Diagn Pathol 2017;12:29)
Treatment
- Surgery; possible adjuvant role for c-Met / ALK inhibitors and VEGF inhibitors (Oncology 2016;91:348)
Gross description
- Large mass (mean 5 cm)
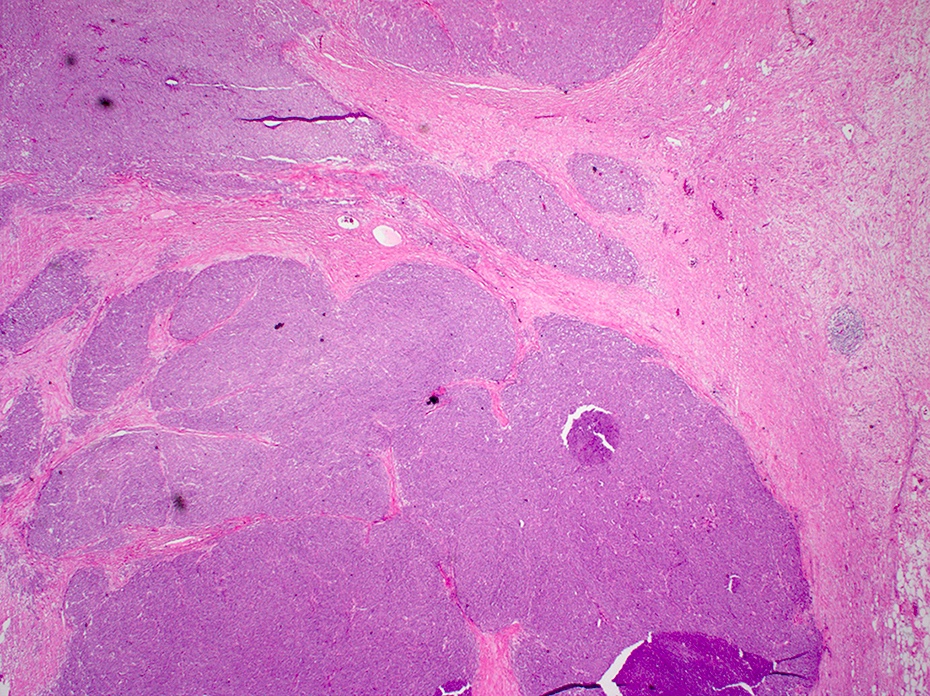
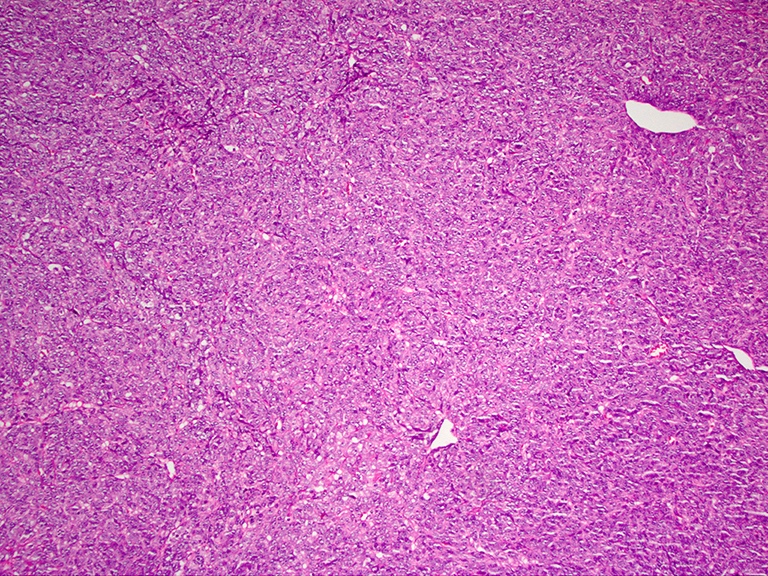
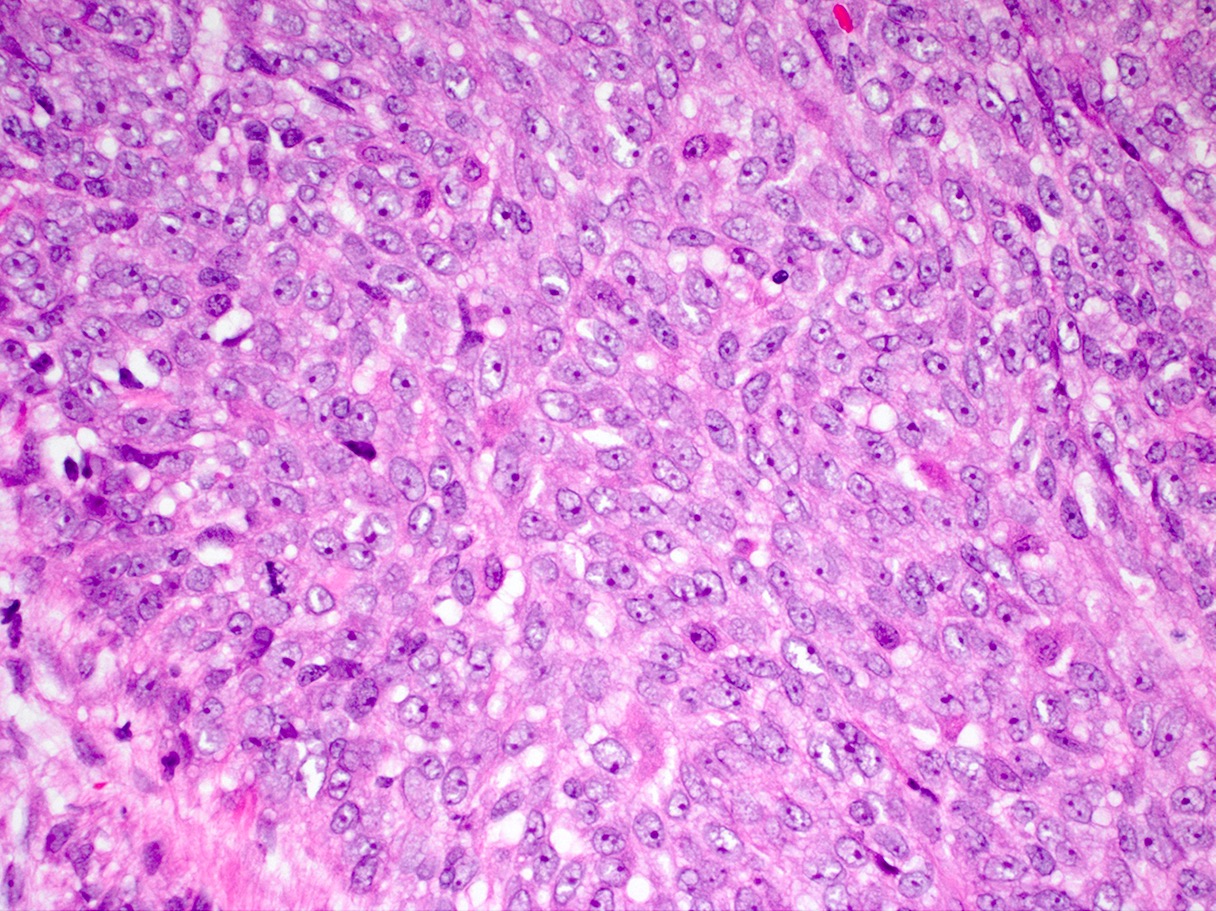
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Sheets or nests of oval / spindled mesenchymal cells with clear or eosinophilic cytoplasm, visible nucleoli and often mitoses
- Osteoclast-like giant cells may be seen
- Tumor often spans the entire wall
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
Negative stains
- HMB45, MelanA, CD117, DOG1, cytokeratin
Electron microscopy description
- Secretory vesicles and dense core granules
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Translocation involving EWSR1 (most commonly EWSR1-ATF1 [t(12;22)] or EWSR1-CREB1)
Sample pathology report
- Jejunum, resection:
- Malignant gastrointestinal neuroectodermal tumor (6.1 cm) (see comment)
- Lymphovascular invasion present.
- Margins of resection unremarkable.
- Three of eight lymph nodes involved by metastatic tumor (3/8).
- Comment: Gastrointestinal neuroectodermal tumor is a rare malignancy that can metastasize distantly and has a poor prognosis. Immunohistochemical stains show the tumor is positive for S100 and synaptophysin.
Differential diagnosis
- Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma:
- Clear cell sarcoma:
- Gastrointestinal stromal tumor:
- Synovial sarcoma:
- Positive for keratins, harbors t(X;18) translocation
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is true about malignant gastrointestinal neuroectodermal tumor?
- It can demonstrate a t(12;22) EWSR1-ATF1 translocation
- It most commonly occurs in the colon
- Its preferred site of metastasis is the lungs
- It stains positive for S100 and cytokeratin by immunohistochemistry
- Most patients are in their sixth decade or older
Board review style answer #1
A. It can demonstrate a t(12;22) EWSR1-ATF1 translocation
Comment Here
Reference: Malignant GI neuroectodermal tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Malignant GI neuroectodermal tumor