Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Immunohistochemistry & special stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Doyle K, Qiao J. Lipomatosis of the ileocecal valve. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/smallbowellipomatosisileocecalvalve.html. Accessed December 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Mature adipocyte proliferation within the submucosal layer of the ileocecal valve not contained within a capsule (Iran J Radiol 2014;11:e4336)
- Rarely extends into serosa and mesenteric fat (Iran J Radiol 2014;11:e4336)
Essential features
- Diffuse infiltration of the fatty tissue mainly in the submucosal layer is characteristic
- Usually asymptomatic and found incidentally
- Lack of encapsulation differentiates it from lipoma
- Cause of the fat deposition is not known
Terminology
- Lipomatosis of the ileocecal valve
- Lipohyperplasia
ICD coding
- ICD-10: E88.2 - lipomatosis, not elsewhere classified
Epidemiology
- M > F
- Uncommon under age 40
- More common with obesity
Sites
- Ileocecal valve and ileum
- Also can occur in cecum and ascending colon
Pathophysiology
- Benign mature adipocyte proliferation within the submucosal layer of the ileocecal valve
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Commonly asymptomatic
- May present with
- Right lower quadrant pain
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Obstruction
- Bleeding
- Hemorrhage
- Intussusception
- Can mimic appendicitis
- Risk factors: female, obese, age > 40
Diagnosis
- Incidental diagnosis of right colon resection, which usually includes terminal ileum and ileocecal valve
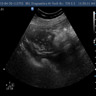
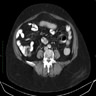
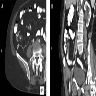
Radiology description
- Commonly visualized on abdominal CT as well defined circumferential thickening of the lips of ileocecal valve with fat attenuation (Radiopedia: Lipomatosis of the ileocecal valve [Accessed 19 March 2019], Iran J Radiol 2014;11:e4336)
- Barium enema may show smooth mass-like enlargement of ileocecal valve
- Lips can be thickened with nodularity but margins are smooth (Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 1973;119:323, Cancer 1972;119:323, J Korean Radiological Soc 2001;45:43)
- Ultrasound can show bulky and hyperechoic ileocecal valve with intussusception if present
Radiology images
Case reports
- 45 year old man with melena and anemia (BMJ Case Rep 2013 Jul 8;2013)
- 50 year old woman with intestinal symptoms, anemia and positive fecal occult blood test (Tech Coloproctol 2007;11:278)
- 70 year old woman with abdominal pain (Iran J Radiol 2014;11:e4336)
Treatment
- Usually asymptomatic
- Surgical resection if causing obstruction, significant symptoms or concern for malignancy
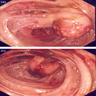
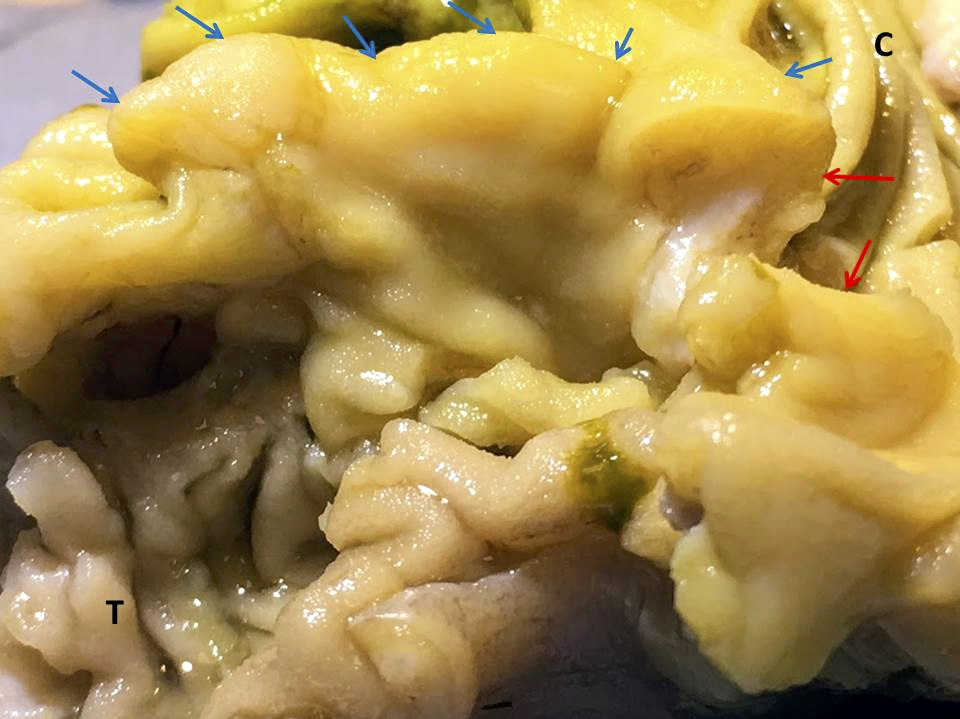
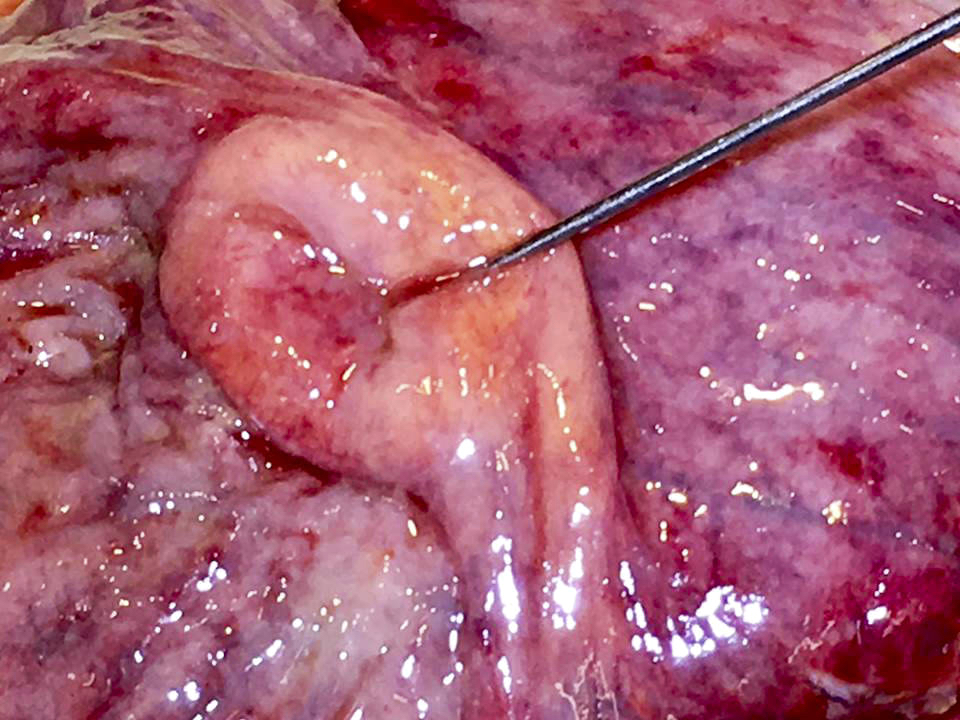
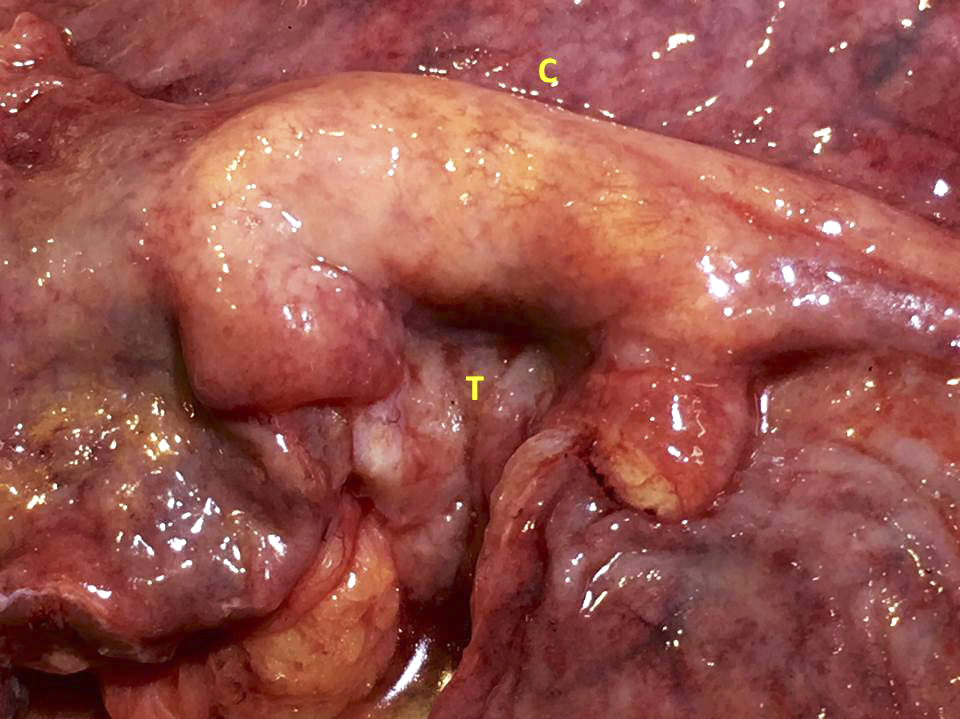
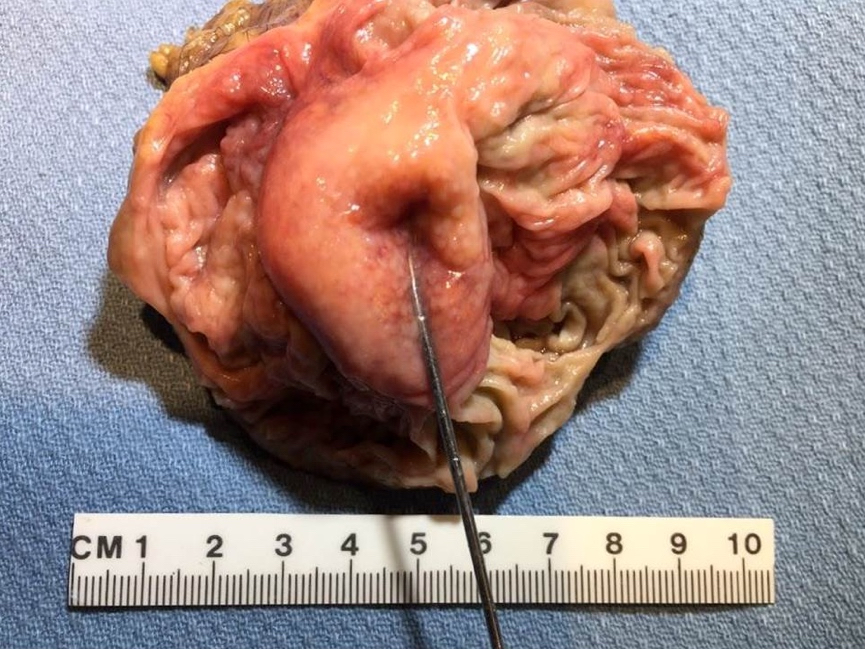
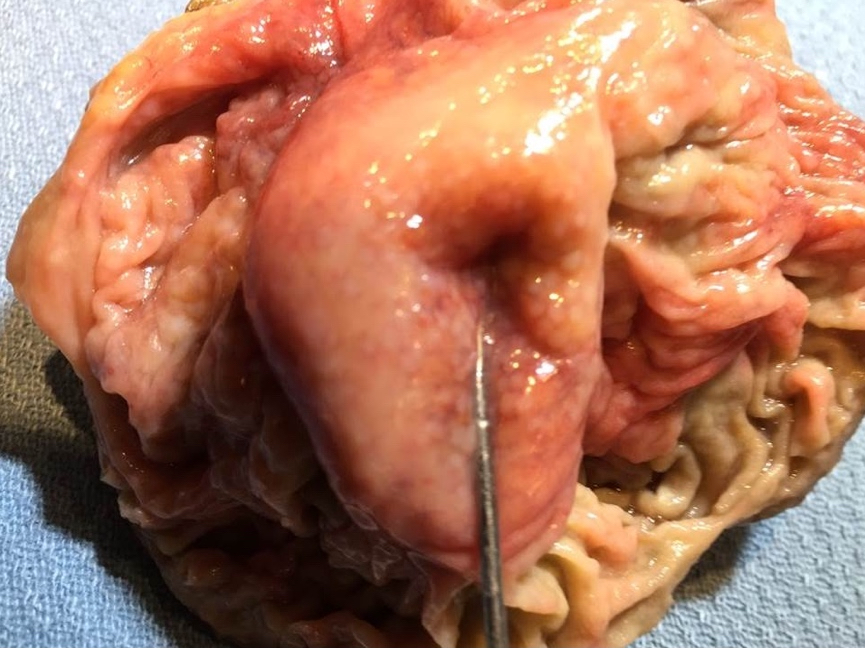
Gross description
- Prominent and thickened ileocecal valve, usually an incidental finding during gross exam of right colectomy specimen
Gross images
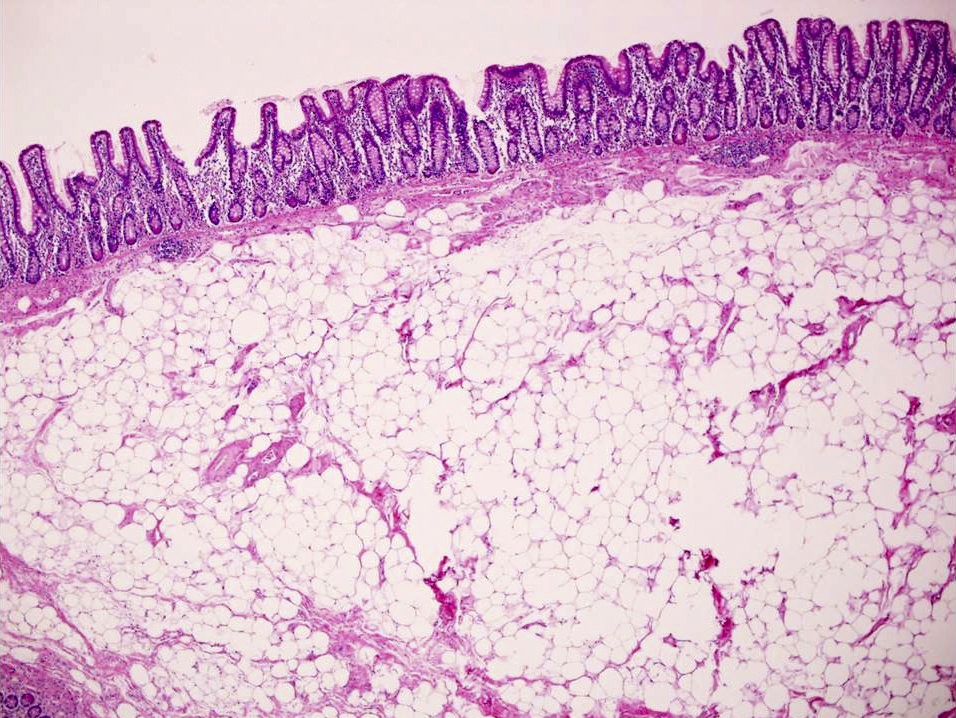
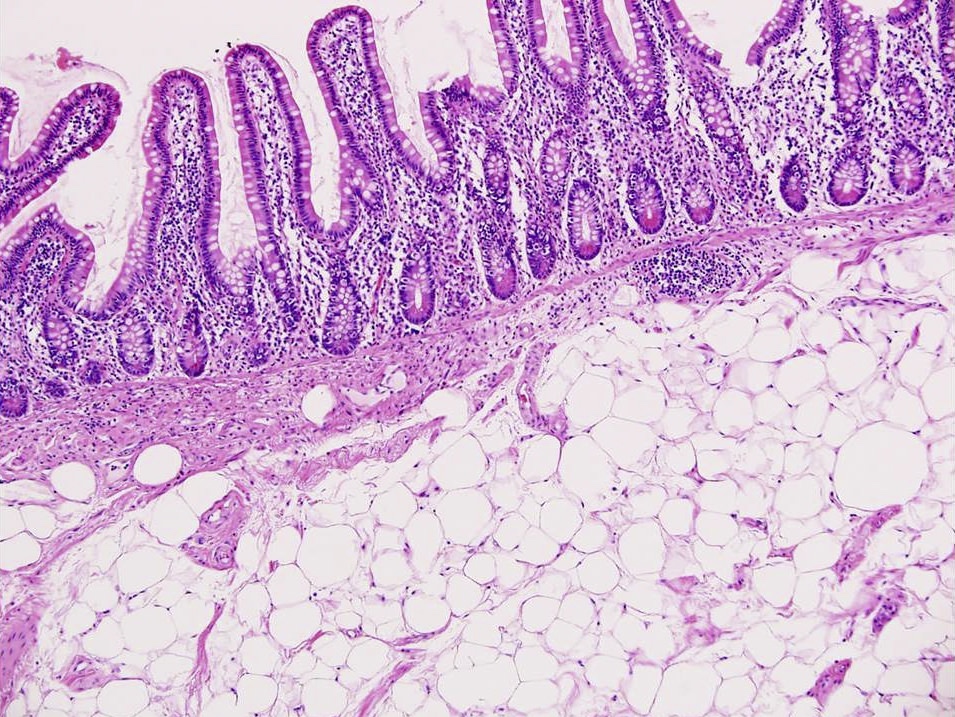
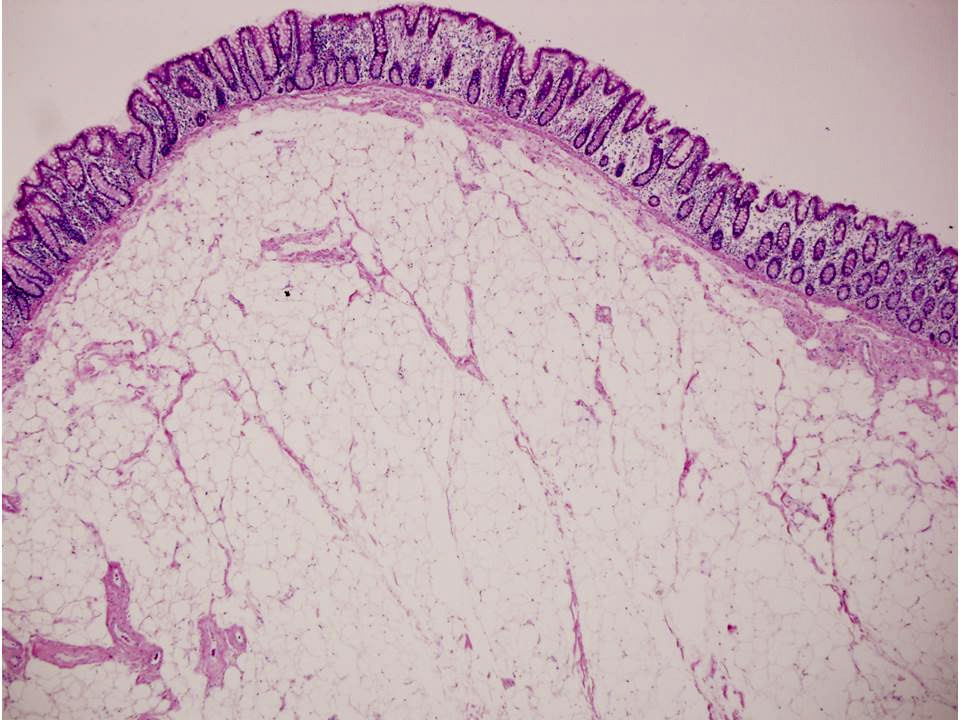
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Ileocecal valve mucosa with extensive submucosal proliferation of lipomatous mature adipocytes
- Fibrous septa and vascular congestion are usually present
- No surrounding fibrous capsule
Microscopic (histologic) images
Immunohistochemistry & special stains
- Not indicated
Sample pathology report
- Right hemicolectomy
- Adenocarcinoma of ascending colon (see synoptic report)
- Lipomatosis of ileocecal valve (incidental finding)
- 20 mesenteric lymph nodes negative for metastatic tumor (0/20)
Differential diagnosis
- Lipoma:
- True lipoma of ileocecal valve is rare
- Has demarcating capsule around the fatty tissue and is confined to only one of the ileocecal lips
- Crohn's disease:
- Crohn's ileocolitis can be associated with lipomatosis of the ileocaecal valve
- Can cause difficulty in diagnostic imaging studies
- Gross and microscopic examination will show characteristic fissuring, skipping ulceration and transmural lymphoid aggregates
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL):
- Can involve ileocecal valve and forming obstructive mass lesion or circumferential infiltration
- Microscopic examination will show malignant lymphoma cells with specific IHC staining patterns
- Adenomatous polyp:
- Can involve ileocecal valve
- Grossly, it is usually focal polypoid lesion rather than diffuse thickening
- Microscopic exam will show adenomatous tubules
- Adenocarcinoma of the ileocecal valve:
- Usually an irregular mass lesion with ulceration and obstruction
- Microscopic exam will show malignant tumor glands
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A middle aged man underwent a right hemicoloectomy for cecal adenocarcinoma. Grossly, the ileocecal valve was prominent and diffusely thickened but no tumor was noted. What is your diagnosis?
- Crohn's disease
- Lipoma of the ileocecal valve
- Lipomatosis of the ileocecal valve
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- Normal ileocecal valve
Board review style answer #1
C. Lipomatosis of the ileocecal valve. Submucosal nonencapsulated adipose tissue proliferation is
diagnostic for lipomatosis of the ileocecal valve.
Comment here
Reference: Lipomatosis of the ileocecal valve
Comment here
Reference: Lipomatosis of the ileocecal valve
Board review style question #2
A 45 year old woman presents with sudden right lower quadrant abdominal pain. She has been experiencing on and off abdominal pain for the past 4 weeks. CT abdomen reveals small bowel obstruction near the ileocecal valve. She undergoes exploratory laparotomy and is later diagnosed with lipomatosis of the ileocecal valve by pathological examination. Which of the following is diagnostic for lipomatosis of the ileocecal valve?
- Adipocyte proliferation in the muscularis propria not contained within a capsule
- Adipocyte proliferation in the submucosa contained within a capsule
- Adipocyte proliferation in the submucosa not contained within a capsule
- Diffuse gland proliferation
- Inflammatory cells predominately lymphocytes
Board review style answer #2
C. Adipocyte proliferation in the submucosa not contained within a capsule is diagnostic for
lipomatosis of the ileocecal valve.
Comment here
Reference: Lipomatosis of the ileocecal valve
Comment here
Reference: Lipomatosis of the ileocecal valve