Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Asadbeigi SN, Nguyen C. Trichofolliculoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocytictrichofolliculoma.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign adnexal hamartomatous follicular tumor
- Histologically shows multiple follicles in various stages spreading from a central cystic follicle
Essential features
- Solitary papule in adults in the head and neck region
- Central dilated primary follicle with secondary follicles budding from the primary follicle
- Can show a spectrum of morphology depending on the hair follicle cycle
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Mostly solitary papule or nodule
- Occurs in adulthood with no definitive racial or gender predilection (An Bras Dermatol 2015;90:519)
- Rarely occurs as a congenital lesion (Int J Mol Sci 2021;22:4759)
- No proven association with any dermatological or systemic diseases (Am J Pathol 1976;85:479)
Sites
- Face, with nose as the most common site (Am J Dermatopathol 2010;32:35)
Pathophysiology
- Repeated development of hair follicles with disordered hair cycle; defective sonic hedgehog polarization (J Dermatol 2017;44:1050, Am J Dermatopathol 2009;31:248)
- Distorted ability to control the size of hair follicles
- Trichofolliculoma with sebaceous differentiation: follicular and sebaceous components have independent cycles
- Primary follicle: (J Dermatol 2017;44:1050)
- Primary infundibular cystic structure which shows a thin wall with radiating secondary follicles
- Secondary follicles:
- Follicles radiating from the primary follicle
- Most follicles are in anagen phase
- Tertiary follicles:
- Regression of secondary follicles to tertiary follicles
- Shift of anagen hair to catagen phase
- Variation in size of hair from vellus hair to thick terminal hair
- Quaternary follicles:
- Regression of tertiary follicles to quaternary follicles
Clinical features
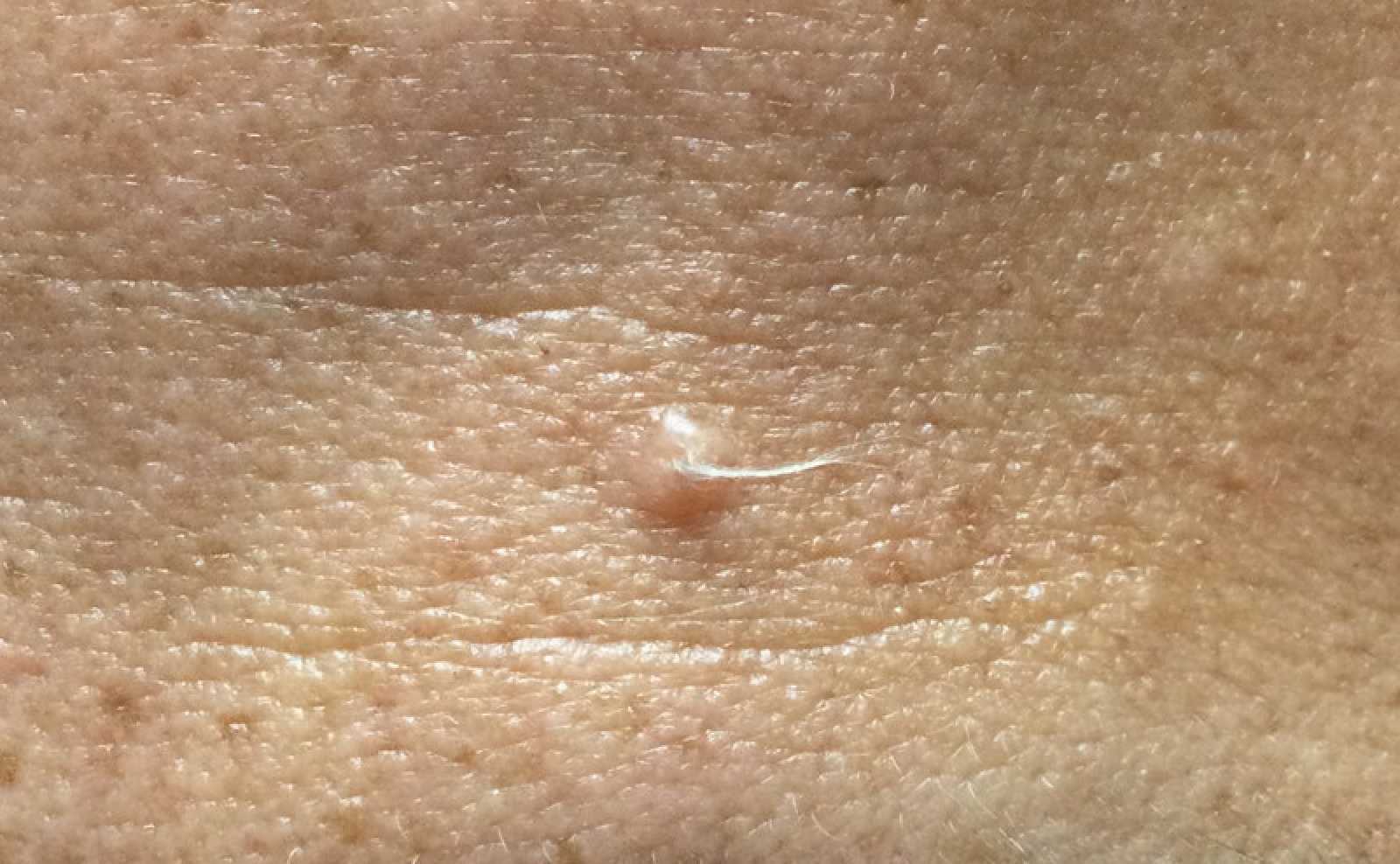
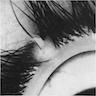
- Solitary, skin colored papule or nodule (approximately 0.2 - 1.5 cm in diameter) with central depression (An Bras Dermatol 2015;90:780, Arch Dermatol 1960;81:922)
- Multiple tufts of vellus and thin hairs emerging from the central section
Diagnosis
- Clinical: central primary follicle with multiple tufts of vellus hair (Am J Pathol 1976;85:479)
- If the hair is plucked, trichofolliculoma can be clinically misdiagnosed as basal cell carcinoma, molluscum contagiosum, keratoacanthoma, milium, trichoepithelioma, syringoma or sebaceous hyperplasia (J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2017;31:e123)
- Dermoscopy: shows troll hair sign - tight plumes of white and thin hairs, similar to children's troll dolls (Australas J Dermatol 2021;62:90)
- Biopsy and histological examination
Prognostic factors
- Excellent prognosis (Dermatol Online J 2013;19:19264)
- Rarely recurs at the primary site (Arch Dermatol 1979;115:1003)
- Rarely coexists with basal cell carcinoma (Australas J Dermatol 2007;48:127)
- Malignant transformation with perineural invasion has been reported in a single case report (Arch Dermatol 1979;115:1003)
Case reports
- 15 year old girl with a hairy papule on nose since birth (Dermatol Online J 2020;26:13030)
- 21 year old woman with multiple skin colored lesions on face (Indian J Dermatol 2015;60:214)
- 52 year old woman with a collision tumor of trichofolliculoma and basal cell carcinoma (Australas J Dermatol 2007;48:127)
- 54 year old woman with multiple soft lesions in zosteriform distribution (Indian J Dermatol 2013;58:330)
- 57 year old man with a tender nodule on canthus (Arch Dermatol 1979;115:1003)
Treatment
- Typically no need for treatment but rarely excision is recommended (Int J Mol Sci 2021;22:4759)
Clinical images
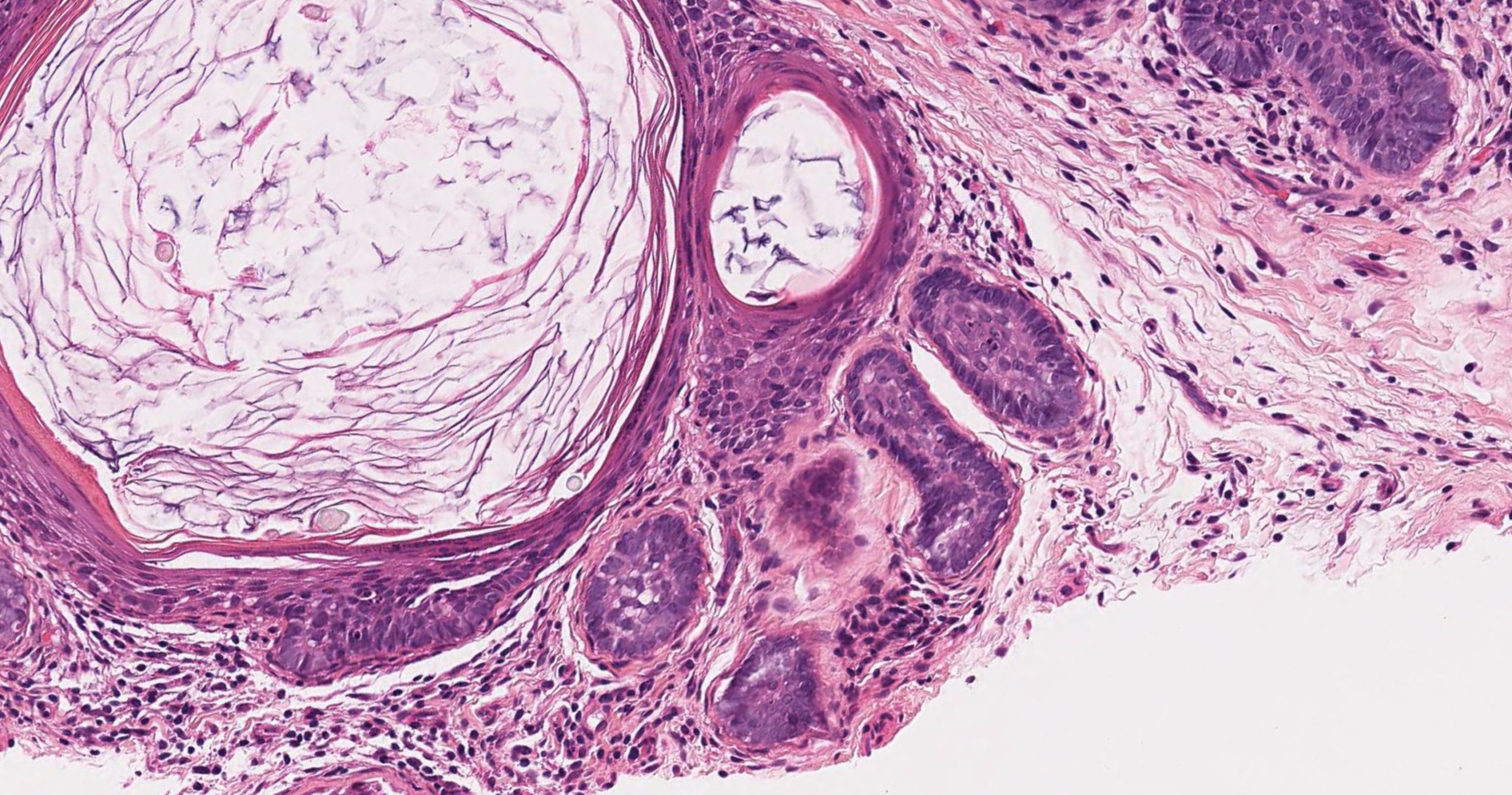
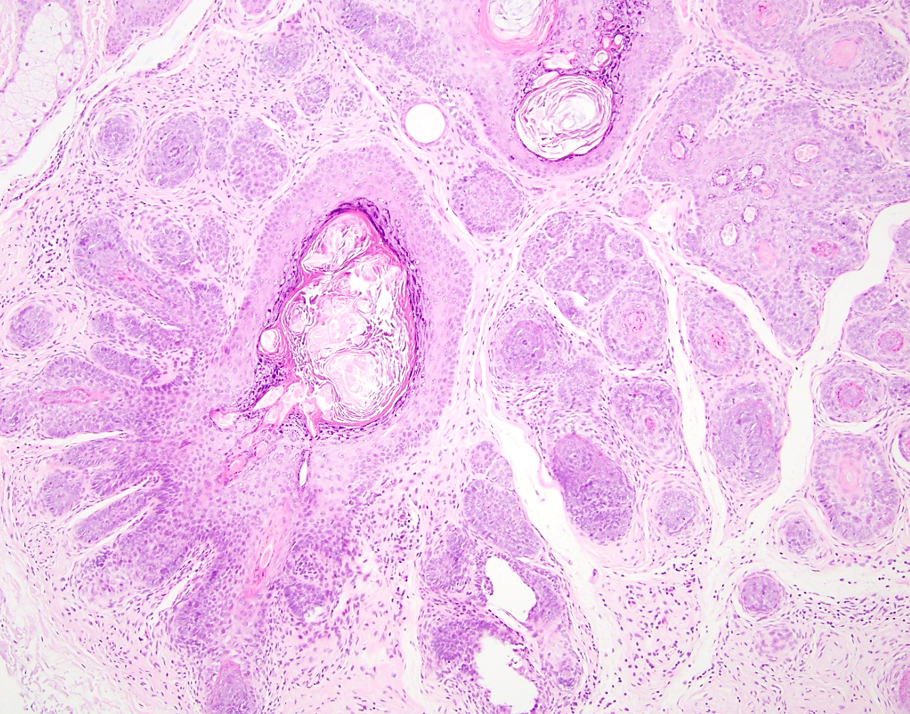
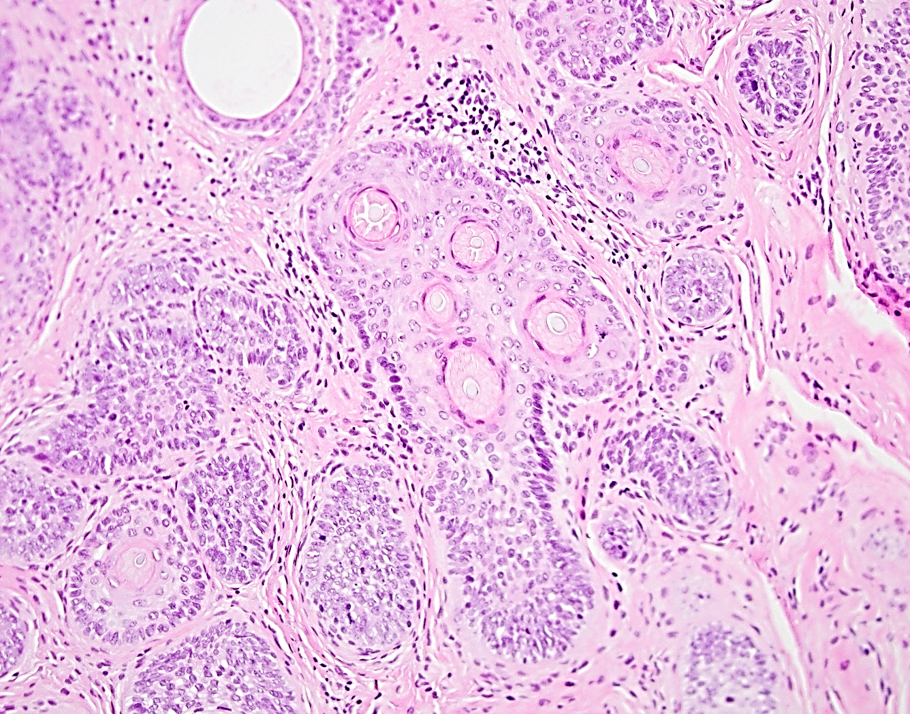
Microscopic (histologic) description
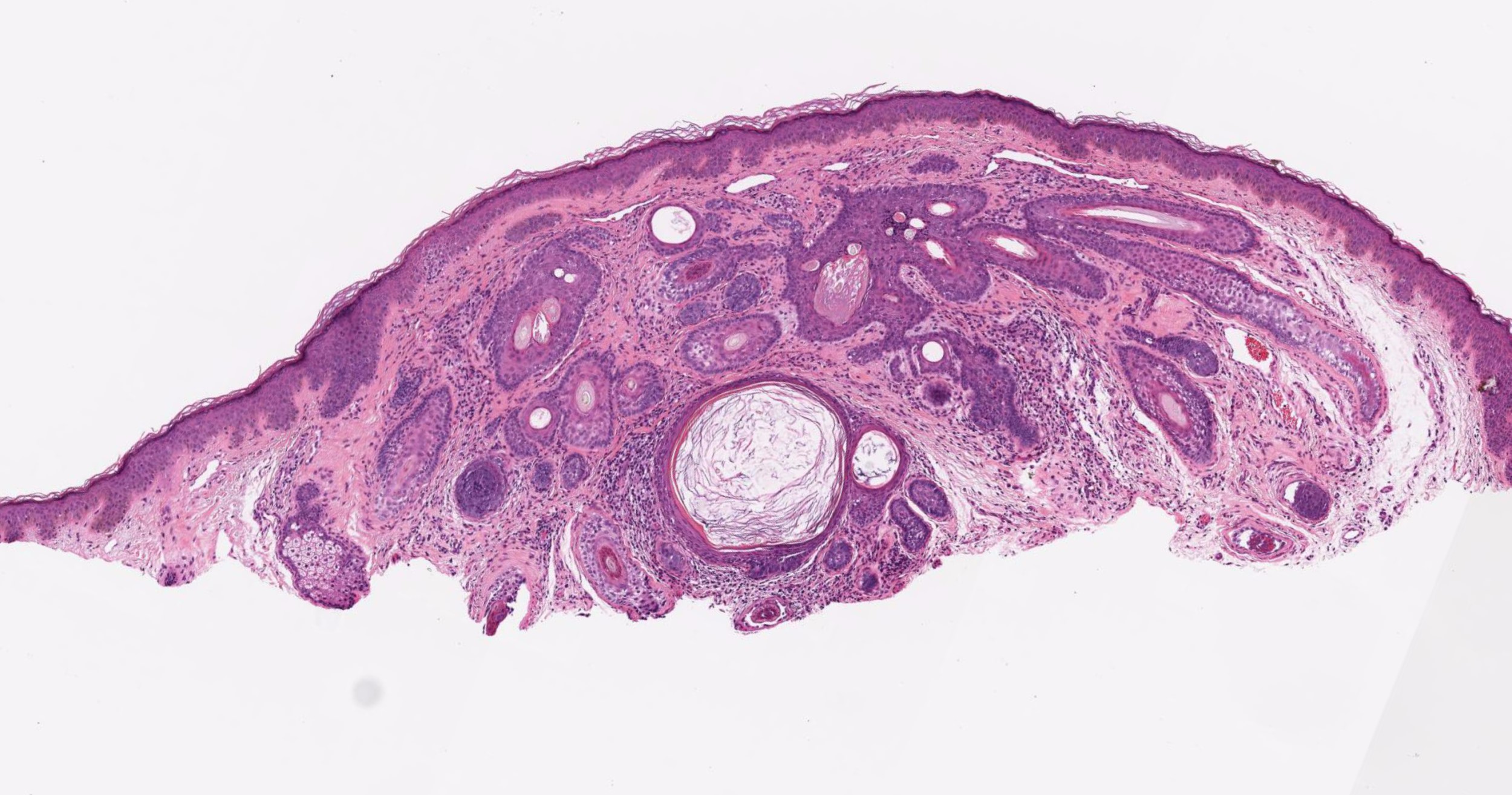
- Dilated central cystic follicle with surrounding multiple fully formed vellus or terminal follicles
- The central cystic follicle shows connection / opening to epidermis
- Early lesion: a mildly dilated infundibulum and radiating secondary curved vellus follicles; cystic dilatation may be absent
- Late lesion: thin walled primary infundibular cystic structure and radiating vellus or terminal follicles that are mostly in the anagen phase
- Trichofolliculoma demonstrates outer root sheath differentiation
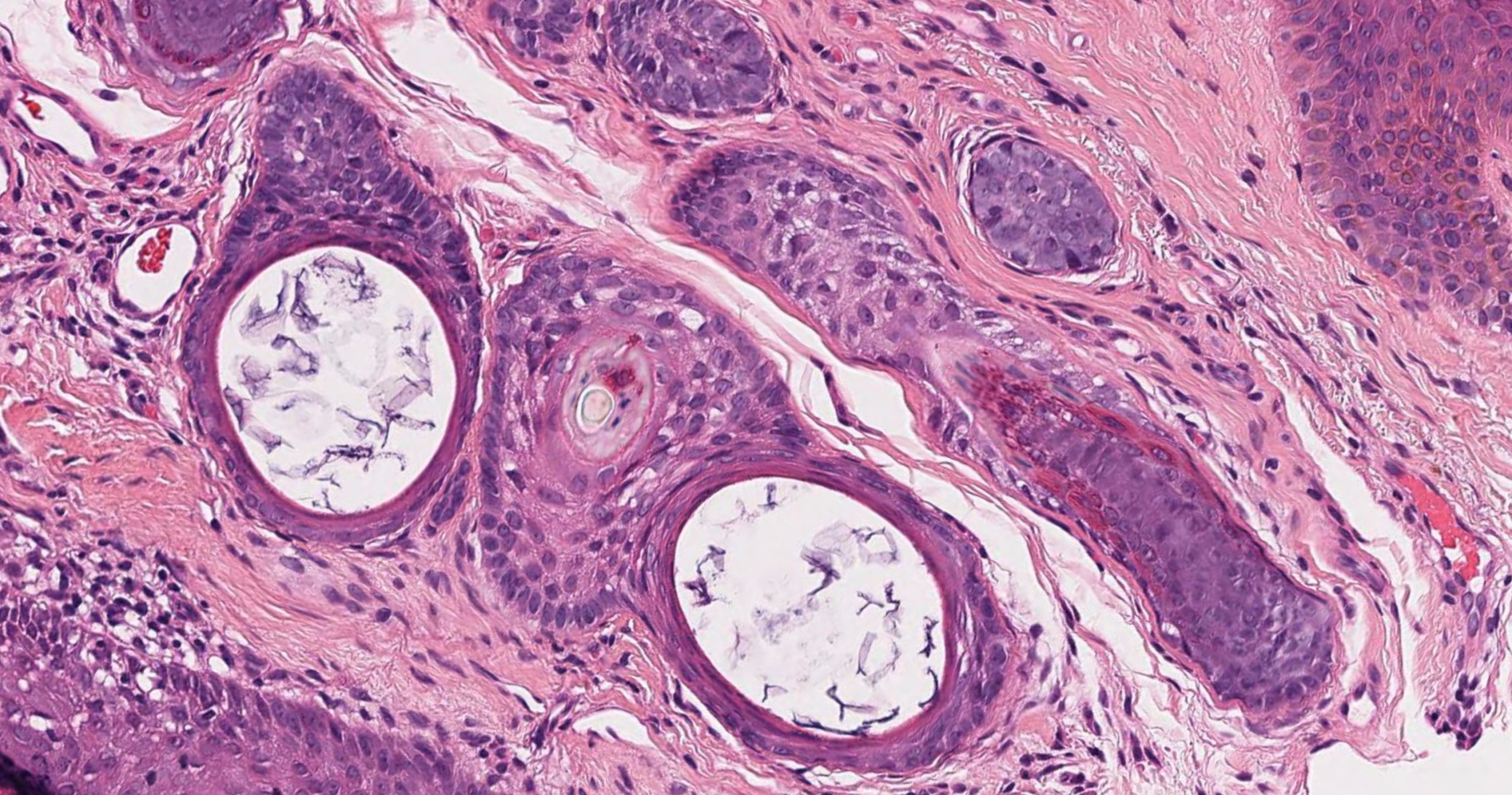
- Central follicle shows stratified squamous cell epithelium with a granular layer with dilation or cystic changes and contains keratinous material and may have vellus hairs
- Primary follicle has keratinized stratified epithelium with keratohyaline granules
- Branched follicles may show varying degree of maturation, including rudimentary structures or epithelial cords and anagen, catagen or telogen hair in older lesions
- Secondary follicles are small with many epithelial strands and abortive pilar formation
- Sebaceous differentiation may be present
- Trichofolliculoma is usually surrounded by well developed connective tissue, which is frequently cellular
- Each follicle is surrounded by an individual perifollicular sheath
- Late stage can show a solid pattern as the regressing secondary follicles and developing tertiary follicles coalesce
- Sebaceous trichofolliculoma variant: sebaceous gland attached to radiating follicles (J Cutan Pathol 1980;7:394)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Immunohistochemistry is not usually needed for diagnosis
- CK15 in the basal cells of the secondary follicles (Br J Dermatol 2003;148:597)
- CK16 and CK17 in the suprabasal cells of the immature secondary hair follicles (Br J Dermatol 2003;148:597)
- BerEP4 expression in basaloid germ-like structures but weak staining in the secondary or tertiary follicles compared to the normal hair (Am J Dermatopathol 2010;32:35)
- CD34 in basal cells of the outer root sheath in the thick terminal follicles (Am J Dermatopathol 2010;32:35)
Negative stains
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- BMP and PYGO2 signaling pathway in experimental studies; not used in clinical setting (Int J Mol Sci 2021;22:4759)
Videos
Trichofolliculoma clinical and pathology by Dr. Michael Lee
Trichofolliculoma histopathology by Dr. Jerad Gardner
Sample pathology report
- Forehead skin, shave biopsy:
- Trichofolliculoma (see comment)
- Comment: Atypia is not identified.
- Microscopic description: Sections demonstrate a centrally dilated follicular unit with multiple radiating follicular units. At the center of the cystic structure there is keratotic debris and immature hair shafts (trichoids). Surrounding the structure is a mantle of well organized connective tissue. Atypical features were not noted.
Differential diagnosis
- Trichoadenoma:
- Multiple multilayered squamous epithelial islands with a central cystic cavity containing keratinous material
- Does not contain hair shafts
- Solitary trichoepithelioma:
- Islands of basaloid cells are present, which is not a feature of trichofolliculoma
- Fibrofolliculoma:
- Both show a large central follicle with multiple arising epithelial attachments
- Fibrofolliculoma only has strands of follicular epithelium and does not contain any hair shafts
- Dilated pore of Winer:
- Widened follicular infundibulum
- Unlike trichofolliculoma, it does not show the radiating secondary follicles
- Hair follicle nevus:
- Both lesions show multiple hair follicles with vellus hairs but trichofolliculoma has a central cystic component
- Follicular infundibulum cyst:
- Does not contain the secondary or tertiary follicular structures
- Pilar sheath acanthoma:
- Less florid pattern than trichofolliculoma
- Dilated central follicle with cystic features and radiating acanthotic epithelium
- Unlike trichofolliculoma, pilar sheath acanthoma does not have hair shafts in the peripheral buds
- Folliculosebaceous cystic hamartoma:
- Folliculosebaceous structures with surrounding stroma with various mesenchymal elements
- Sebaceous component is the more prominent component
- Although it has been suggested that this is a late stage of sebaceous trichofolliculoma, reports of congenital folliculosebaceous cystic hamartoma suggest that this idea is incorrect (Am J Dermatopathol 2008;30:500, J Cutan Pathol 2008;35:843)
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
The biopsy of a skin colored papule on the face of a 34 year old man shows a central dilated follicle with smaller radiating follicular units containing hair shafts. What is the most accurate diagnosis?
- Hair follicle nevus
- Pilar sheath acanthoma
- Trichoadenoma
- Trichofolliculoma
Board review style answer #2