Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Russell-Goldman E. Trichoepithelioma / trichoblastoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocytictrichoepithelioma.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Trichoepitheliomas and trichoblastomas are benign adnexal tumors, which may show morphologic overlap and recapitulate features of germinative hair bulb epithelium and associated mesenchymal stroma
Essential features
- Trichoepitheliomas and trichoblastomas are benign adnexal tumors which may display some features that mimic basal cell carcinoma
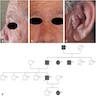
- Multiple trichoepitheliomas can be associated with Brooke-Spiegler syndrome and multiple familial trichoepithelioma (CYLD mutations)
- Trichoblastomas are not known to be familial but are the most common tumor type found in association with nevus sebaceus
Terminology
- Previous names not widely used: trichogenic tumors, giant solitary trichoepithelioma, trichogerminoma
ICD coding
- ICD-10: D23.9 - Other benign neoplasm of skin, unspecified
Epidemiology
- Adults
- Sporadic trichoepithelioma:
- Rare
- Incidence unknown
- Trichoblastoma:
- Rare
- F = M
- Brooke-Spiegler syndrome / multiple familial trichoepitheliomas:
- Multiple trichoepitheliomas may present in adolescence / early adulthood
- F > M
- CYLD mutations
- Reference: Cureus 2020;12:e8272
Sites
- Trichoepithelioma (solitary):
- Face
- Rarely scalp, trunk, extremities, genital area
- Trichoepithelioma (multiple / familial):
- Symmetrical distribution over central face
- Rarely other sites as above
- Rarely dermatomal
- Trichoblastoma:
- Scalp, head and neck
- Occasionally trunk, extremities, genital area
Pathophysiology
- CYLD mutations give rise to inherited forms of trichoepithelioma
- Loss of function of CYLD, a deubiquitinating enzyme, results in constitutive NFκB signaling (Nature 2003;424:801)
- Molecular pathogenesis of sporadic forms of trichoepithelioma unknown
- Although there may be morphologic overlap, trichoblastomas lack PTCH mutations, distinguishing them molecularly from basal cell carcinomas (Hum Pathol 2007;38:1496)
Clinical features
- Brooke-Spiegler syndrome:
- Multiple cylindromas, trichoepitheliomas, spiradenomas, milia (Am J Dermatopathol 2013;35:34, Head Neck Pathol 2016;10:125)
- Multiple familial trichoepitheliomas:
- Multiple trichoepitheliomas only (Am J Dermatopathol 2013;35:34, Head Neck Pathol 2016;10:125)
- Nevus sebaceus:
- Trichoblastomas are the most common associated tumor (Am J Dermatopathol 2000;22:108)
Diagnosis
- CYLD germline testing can be considered if:
- Multiple trichoepitheliomas are present
- Patient has a solitary trichoepithelioma with another affected first degree relative
- Patient is asymptomatic but has known family history of CYLD mutations
- Reference: PLoS Curr 2015;7:ecurrents.eogt.45c4e63dd43d62e12228cc5264d6a0db
Prognostic factors
- Benign tumors; good prognosis
Case reports
- 34 year old woman with multiple unilateral face nodules (Case Rep Dermatol Med 2019;2019:6821854)
- 40 year old woman with a pigmented nodule on the scalp (Pathol Res Pract 2017;213:860)
- 62 year old woman with a buttock nodule (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11:2884)
- 2 family members, 53 year old man and 19 year old woman, with multiple facial nodules (Am J Dermatopathol 2019;41:778)
Treatment
- Surgical excision
Clinical images
Microscopic (histologic) description
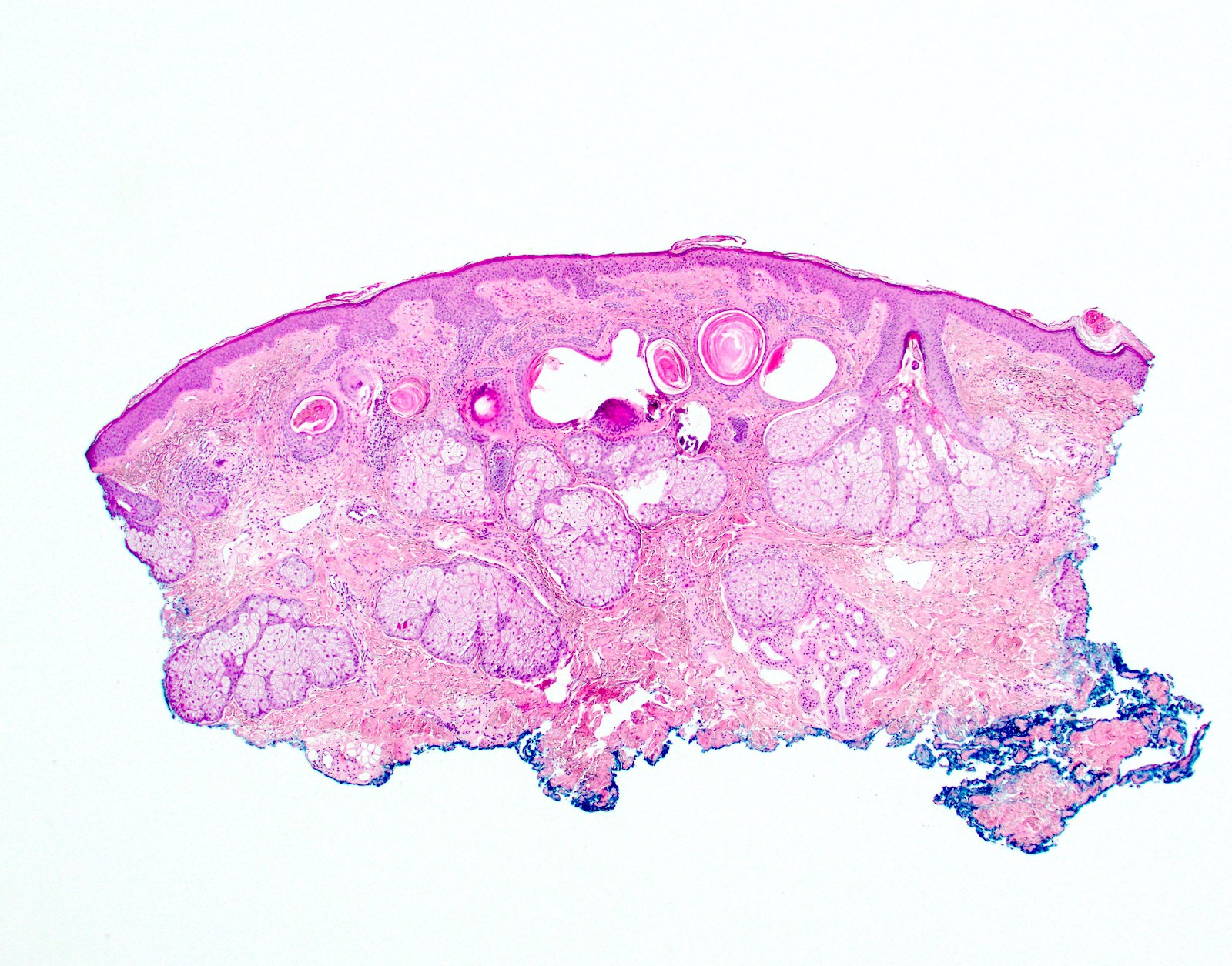
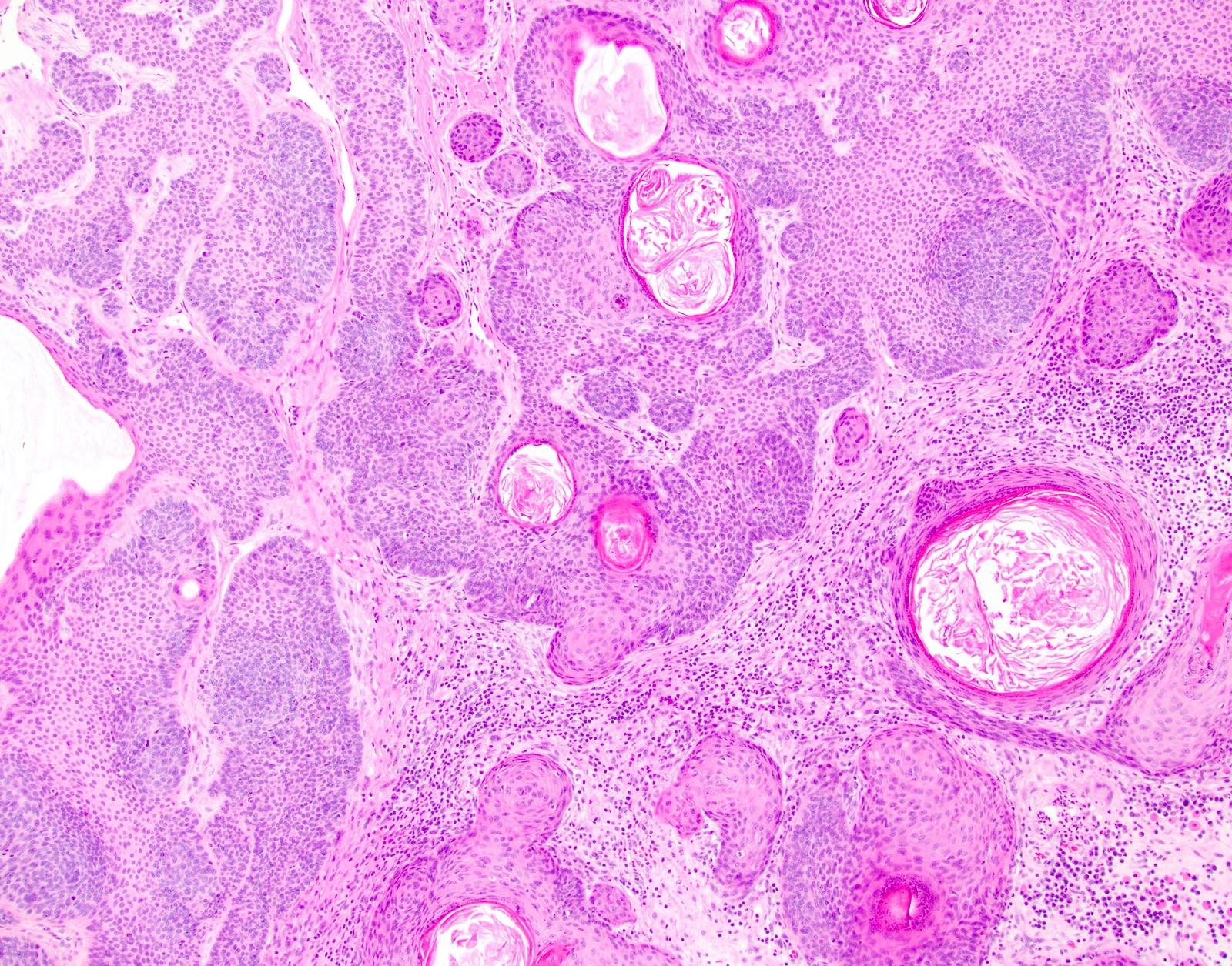
- Trichoepithelioma (Am J Dermatopathol 2011;33:251):
- Usually superficial dermal tumors
- Superficial nests of basaloid cells with keratin horn cysts
- Can show leaf-like or frond-like architectural pattern
- Fibrous cellular stroma closely associated with the epithelial components
- May have papillary mesenchymal bodies and calcifications
- May have epidermal connection
- Ulceration rare
- Can be basaloid cell predominant with few horn cysts making distinction from trichoblastoma or basal cell carcinoma more difficult
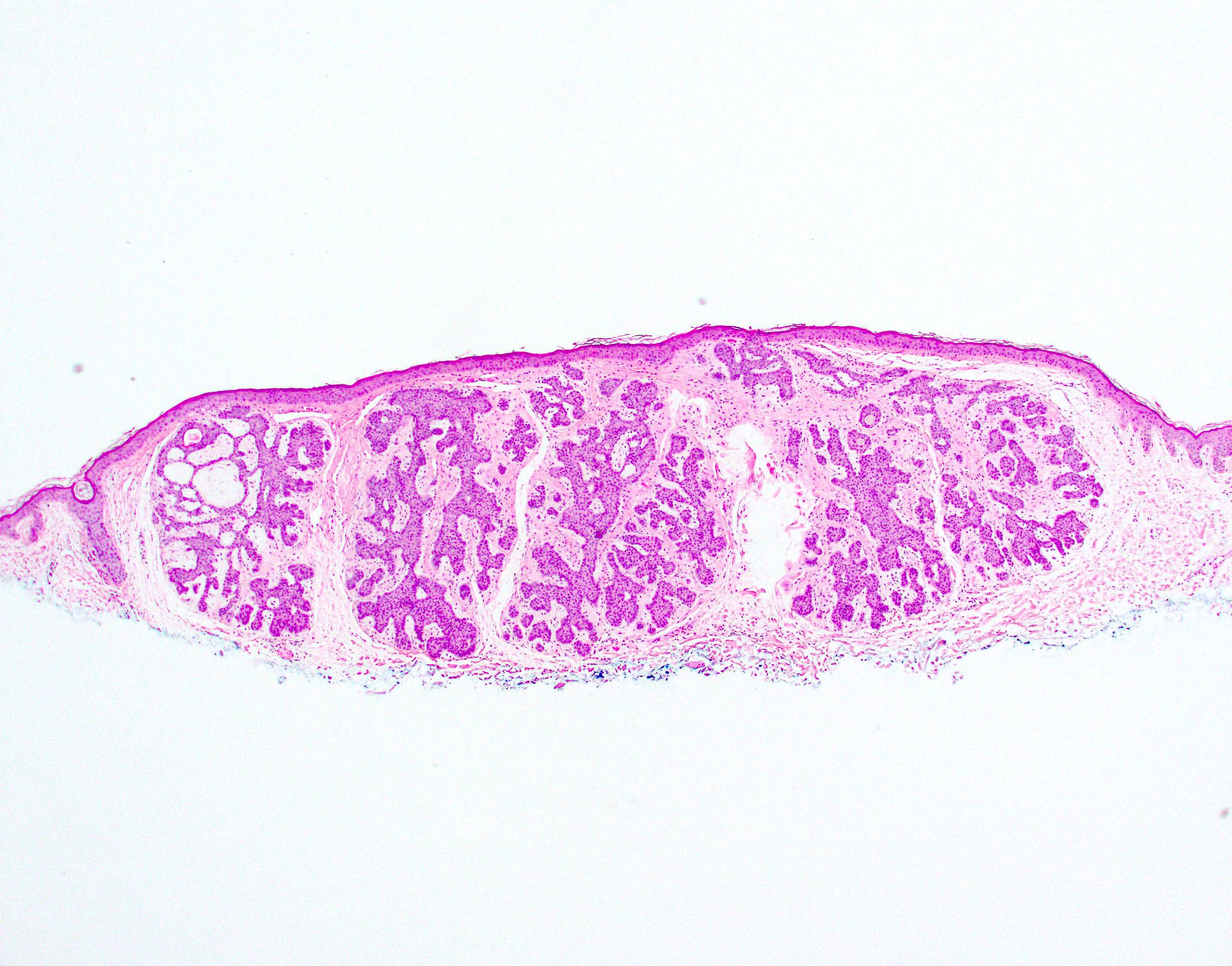
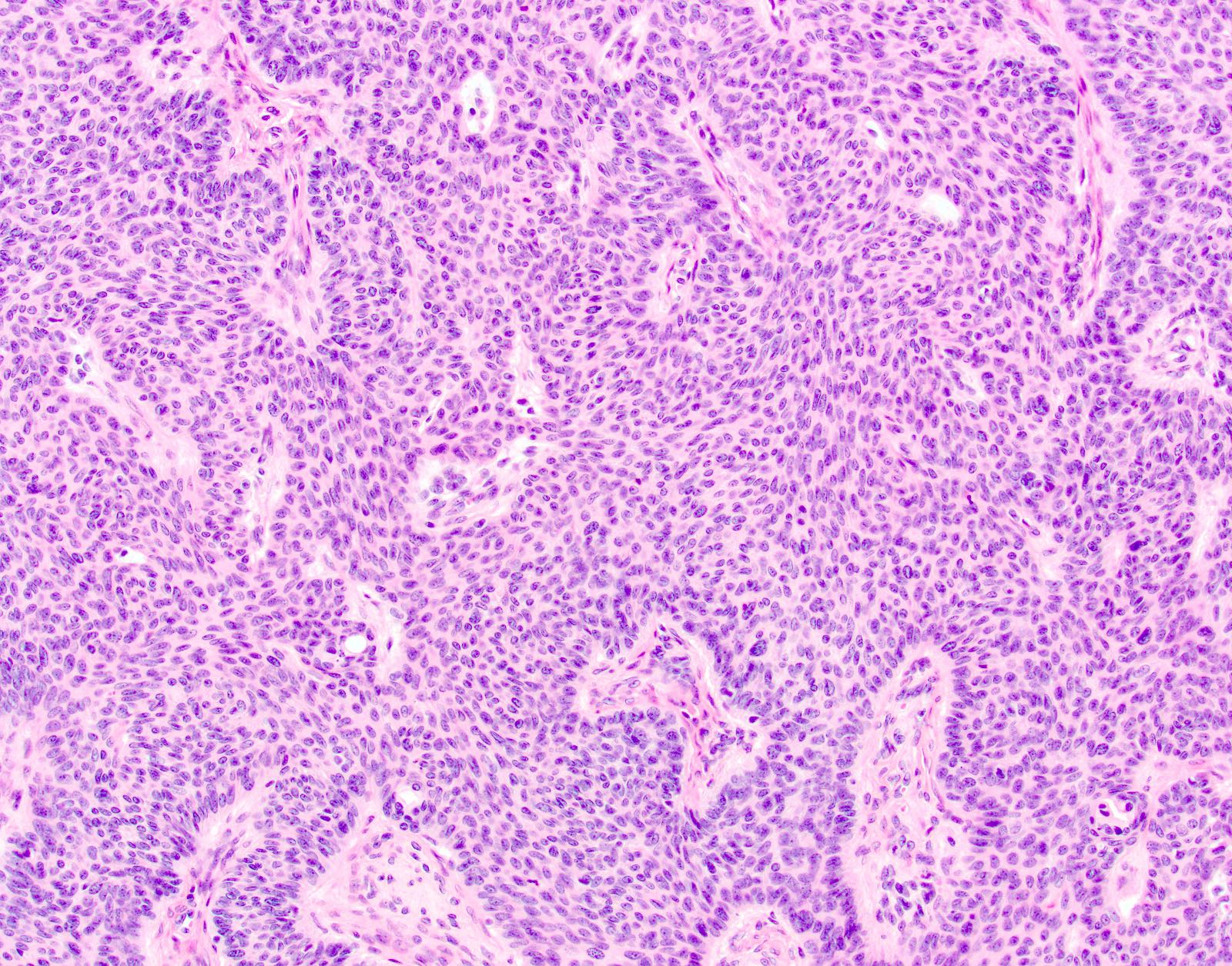
- Trichoblastoma:
- Well circumscribed, predominantly dermal tumor nodule which may extend to subcutis
- Predominantly basaloid epithelial cells in nests with peripheral palisading
- May have keratin cysts
- Mitoses and apoptosis can be evident but cellular pleomorphism is minimal
- Prominent cellular stromal component with papillary mesenchymal body formation
- Clefting occurs between the epithelial stromal tumor mass and surrounding dermis rather than between epithelial and stromal components
- May show cribriform, rippled or solid patterns
- May contain dendritic melanocytes and appear pigmented
- Typically retains CK20 positive Merkel cells (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1490)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- CK20 positive Merkel cell retention is more common in benign follicular tumors versus basal cell carcinoma, although is not specific (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017;141:1490)
- This staining pattern should be interpreted with caution as CK20 positive Merkel cells may be only focally represented and may not be apparent without multiple sections
Sample pathology report
- Skin, right cheek, shave biopsy:
- Trichoepithelioma / trichoblastoma (see comment)
- Comment: If partially sampled and a basal cell carcinoma cannot be excluded, recommend complete excision.
Differential diagnosis
- Basal cell carcinoma
- Nodular basal cell carcinoma:
- Clefting between epithelial stromal components
- Cellular pleomorphism
- Mucin
- Frequent epidermal connection
- Infundibulocystic basal cell carcinoma:
- Basaloid nests with prominent follicular differentiation
- May have clefting between epithelial stromal components
- Less well developed stroma
- Nodular basal cell carcinoma:
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
D. Trichoepithelioma / trichoblastoma. Trichoepithelioma is shown.
Comment Here
Reference: Trichoepithelioma / trichoblastoma
Comment Here
Reference: Trichoepithelioma / trichoblastoma