Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2 | Board review style question #3 | Board review style answer #3Cite this page: Martinez A. Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticpleomorphicdermalsarcoma.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- An undifferentiated pleomorphic tumor with overlapping features of atypical fibroxanthoma but a higher rate of local recurrence and metastasis
Essential features
- Undifferentiated pleomorphic tumor involving the dermis that histologically looks like an atypical fibroxanthoma and has any of the following:
- Size > 2 cm
- Shows extensive involvement of deeper tissue (subcutis, skeletal muscle, fascia)
- Necrosis
- Perineural
- Lymphovascular invasion
Terminology
- Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma (PDS)
- Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma of the skin
- Superficial malignant fibrous histiocytoma (terminology no longer used)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: C49.9 - malignant neoplasm of connective and soft tissue, unspecified
Epidemiology
- Predominantly affects elderly patients on sun damaged skin
- Median decade: ninth (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1317)
- M > F (Cancer 1973;31:1541)
Sites
- Head and neck, predilection for scalp
Etiology
- Ultraviolet radiation induced damage and immunosuppression
Clinical features
- Rapidly growing nodules or plaques, often > 2 cm (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1317)
- Ulceration can be present
Diagnosis
- Dependent on clinical and tissue pathologic correlation
Prognostic factors
- Local recurrence rate of 20 - 30% (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1317, J Cutan Pathol 2016;43:101)
- Median time to recurrence: 10 months (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1317)
- Metastatic rate of 10 - 20% (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1317, J Cutan Pathol 2016;43:101)
- Presence of metastatic disease associated with increased mortality
Case reports
- 58 year old woman with a multifocal tumor arising in areas of alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency panniculitis and a history of lung transplantation (J Med Case Rep 2019;13:169)
- 69 year old man with an enlarging, asymptomatic nodule on his forehead (An Bras Dermatol 2018;93:307)
- 77 year old man with a large nodular scalp lesion (Cureus 2018;10:e2979)
- 82 year old woman with a 3.5 cm sized, well circumscribed, nodular skin lesion on the cheek (Case #546)
- 91 year old woman with a mass on the lateral aspect of the right upper eyelid (Ann Dermatol 2016;28:632)
Treatment
- Surgery is gold standard
- Adjuvant radiation employed in setting of metastatic or locally recurrent, unresectable disease (Curr Treat Options Oncol 2017;18:50)
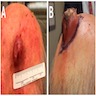
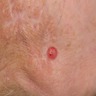
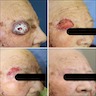
Clinical images
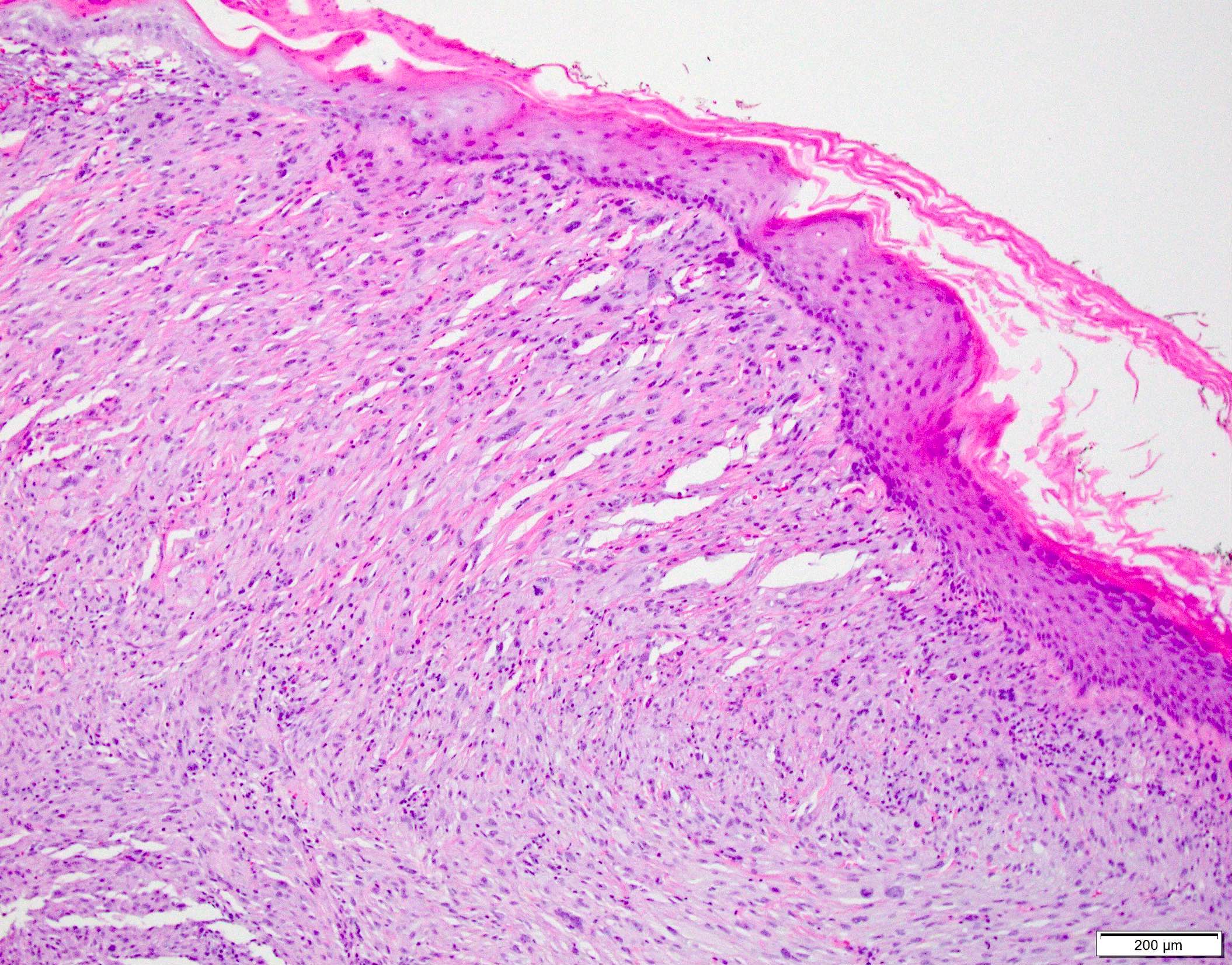
Microscopic (histologic) description
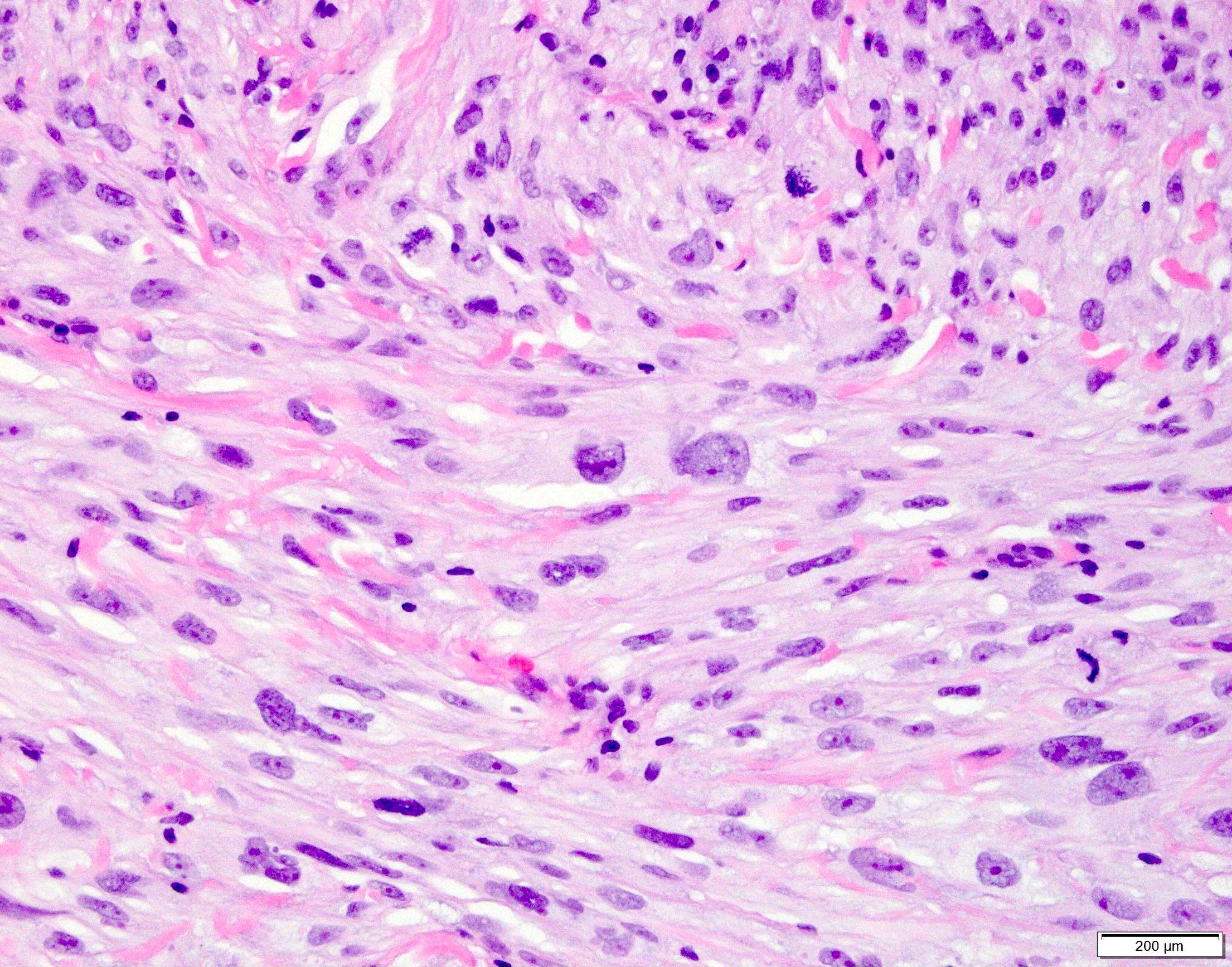
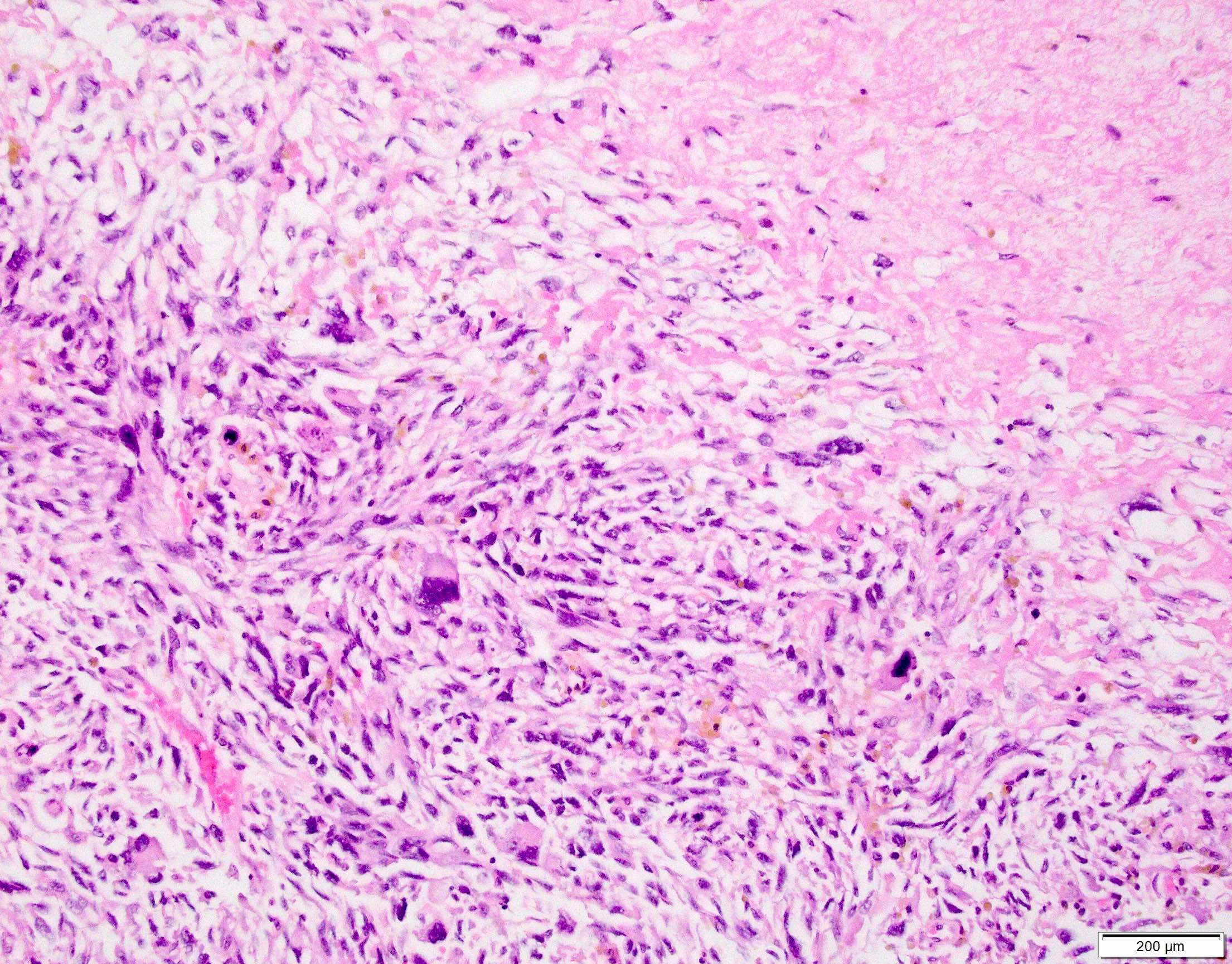
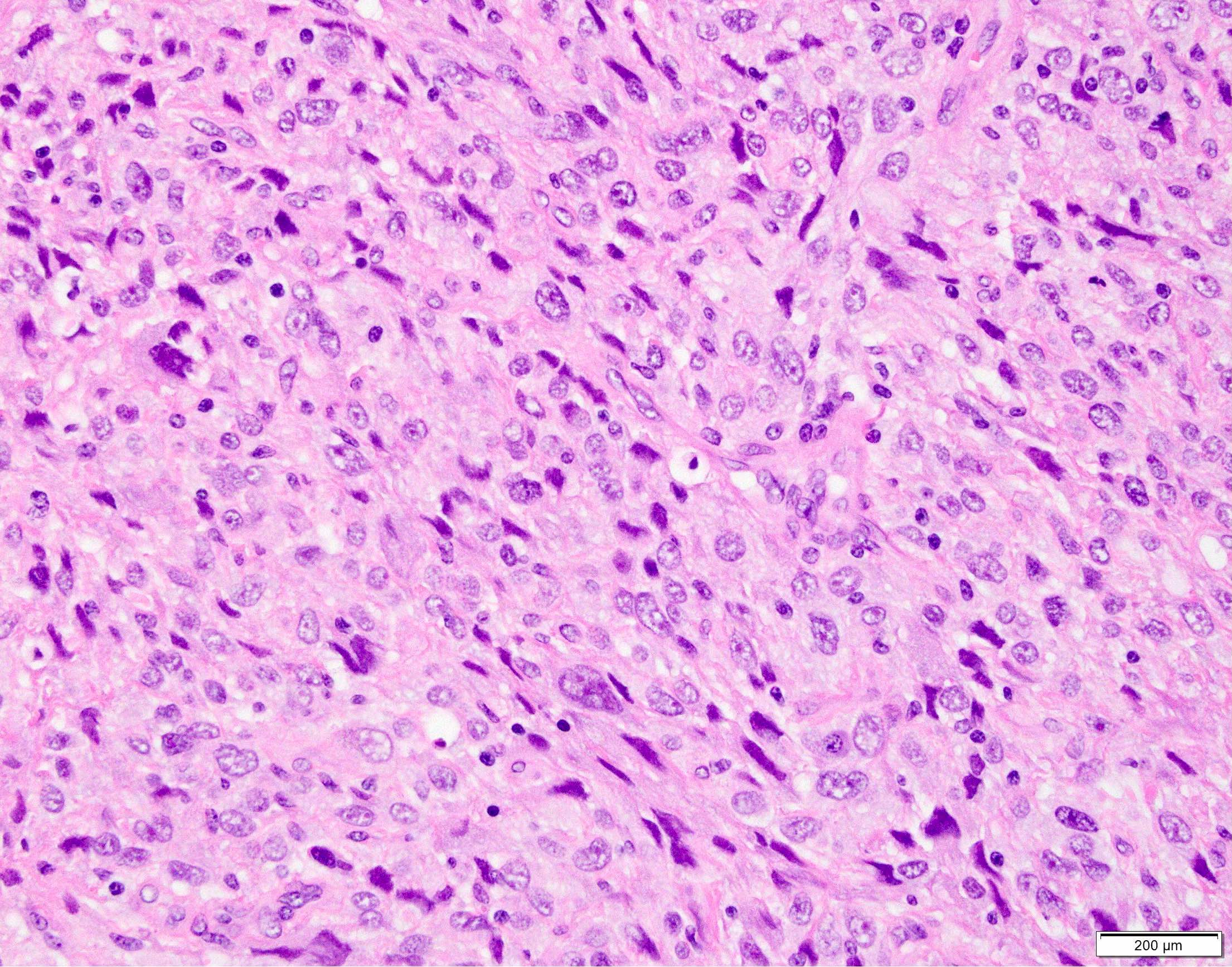
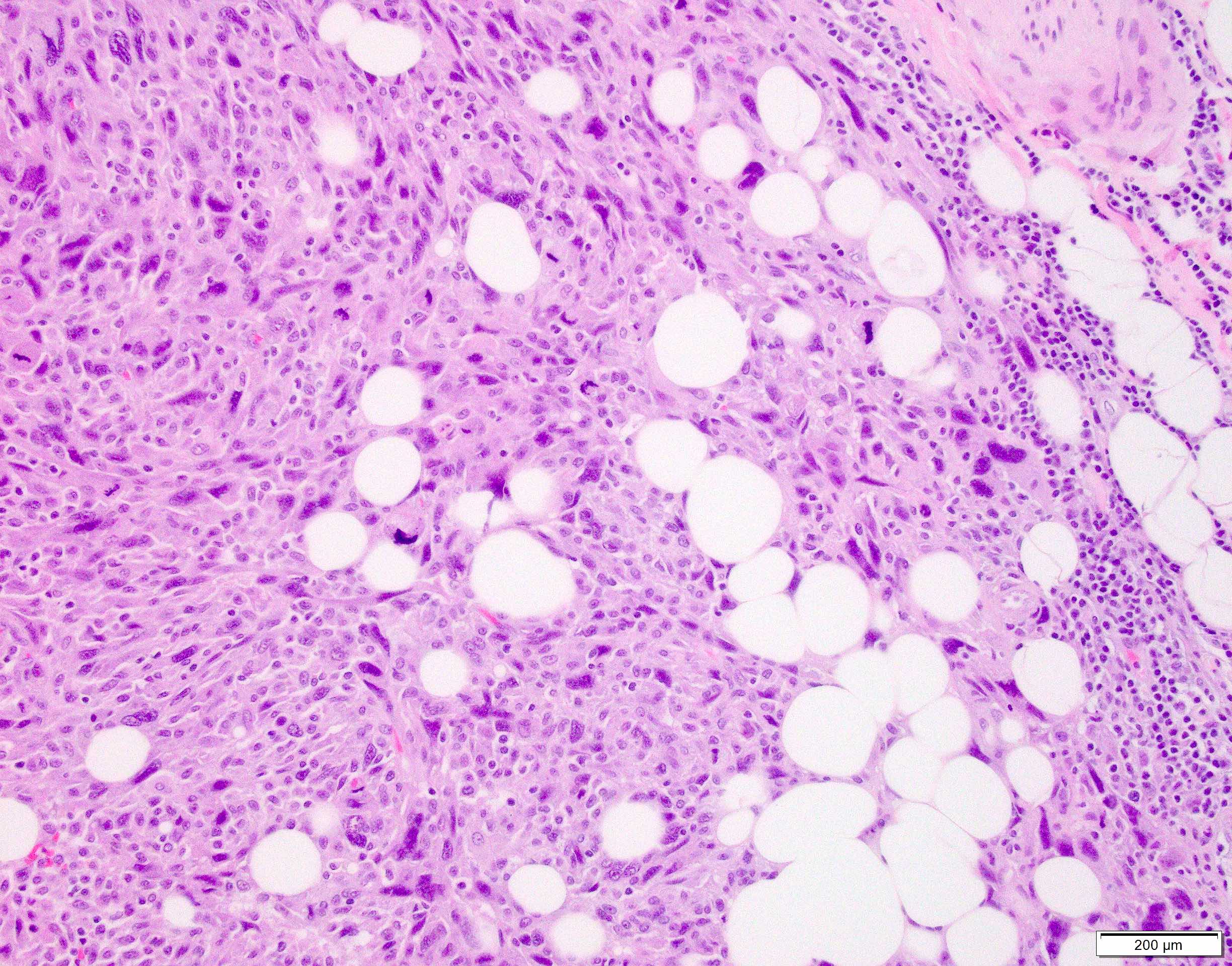
- Dermal based lesion composed of pleomorphic cells with vesicular nuclei and prominent nucleoli (Cancer 1973;31:1541)
- Cells can be spindled or epithelioid, often with admixed multinucleated giant cells
- Cells can be arranged in sheets and fascicles
- Necrosis often present
- Perineural and lymphovascular invasion can be seen
- Infiltration into subcutis, skeletal muscle or fascia
- Additional findings include myxoid change, pseudoangiomatous growth and storiform growth (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1317)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Anthony Martinez, M.D., Hyunkyu Shin, M.D. and Christian M. Schürch, M.D., Ph.D. (Case #546)
Positive stains
- CD10
- Actin - alpha smooth muscle (usually nonspecific staining)
- References: J Cutan Pathol 2018;45:880, Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1317
Negative stains
- Both high and low weight cytokeratins: AE1 / AE3, 34betaE12 / HMWCK / high molecular weight, CK5 / 6
- p40
- Desmin, S100 protein, SOX10, MelanA
- Reference: J Cutan Pathol 2018;45:880
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- 50 - 70% NOTCH1 / 2 and FAT1 mutations (Mod Pathol 2018;31:418)
- TERT promoter mutations in > 70% (Mod Pathol 2014;27:502)
- TP53 mutations in > 80% (Mod Pathol 2018;31:418)
Sample pathology report
- Skin, scalp, excision:
- Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma
- Tumor measures 3.5 cm in greatest dimension and extensively involves the subcutaneous tissue
- Necrosis is present: 30%
- Lymphovascular invasion is not identified
- Perineural invasion is not identified
- Margins are negative
Differential diagnosis
- Atypical fibroxanthoma:
- May be identical histologically, especially if only a superficial shave biopsy is performed
- Tends to have a well circumscribed and pushing border with less infiltration into deep soft tissue
- Should not have perineural invasion
- Should not have lymphovascular invasion
- More than a minute focus of necrosis should raise suspicion
- Cutaneous leiomyosarcoma:
- Will also be dermal based
- Composed of intersecting fascicles of spindled cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm
- Intersecting fascicles will often create halo effect around nuclei cut on cross section
- Should express multiple smooth muscle markers such as desmin, caldesmon, actin - alpha smooth muscle
- Actin - alpha smooth muscle expression by itself is not enough to call leiomyosarcoma
- Sarcomatoid squamous cell carcinoma:
- May have overlying dysplasia of epithelium
- Should express cytokeratins and p63 / p40
- Cellular neurothekeoma:
- Also occurs in the head and neck region
- Occurs in young females instead of elderly males
- Microscopically composed of sheets and nest of spindled and epithelioid cells with gray cytoplasm with cytologic atypia and mitoses
- Usually shows variable expression of CD10, microphthalmia transcription factor (MITF) and actin - alpha smooth muscle
- For board testing purposes, NKI-C3+ and S100A6+
Additional references
Board review style question #1
The following image is from a scalp lesion in an 85 year old man. Immunostains for AE1 / AE3, 34betaE12 / HMWCK / high molecular weight, S100, actin - alpha smooth muscle, desmin and ERG are negative. Which is the best diagnosis?

- Atypical fibroxanthoma
- Leiomyosarcoma
- Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma
- Sarcomatoid squamous cell carcinoma
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
An 80 year old man has a dermal based scalp lesion characterized by pleomorphic cells growing in fascicles. The lesion is < 2 cm, well circumscribed and completely confined to the dermis. Immunostains are negative for high and low molecular weight keratins, S100, actin - alpha smooth muscle and desmin. What is the best diagnosis?
- Atypical fibroxanthoma
- Leiomyosarcoma
- Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma
- Sarcomatoid squamous cell carcinoma
Board review style answer #2
Board review style question #3
Which of the following is a true feature of pleomorphic dermal sarcoma (PDS)?
- Immunochemistry is pivotal for the confirmation of PDS
- Line of differentiation is clearly known for PDS
- PDS is not generally associated with an UV exposure
- PDS should be distinguished from atypical fibroxanthoma (AFX) due to its slightly different prognosis, this can be readily achieved by immunohistochemistry
- Typical features of PDS for distinction from AFX would be necrosis, angiolymphatic / perineural infiltration and infiltrative growth in the subcutaneous tissue
Board review style answer #3
E.Typical features of PDS that distinguish it from AFX are necrosis, angiolymphatic / perineural infiltration and infiltrative growth in the subcutaneous tissue. Answers A and B are incorrect because the precise cell of origin of PDS is unknown and immunohistochemistry is used to exclude tumors of other lineage of differentiation, i.e., epithelial, melanocytic, vascular and muscle neoplasms that should be considered as differential diagnoses. Answer C is incorrect because PDS arises in the dermis of sun damaged skin with the corresponding high mutational load with UV signature and mutation in genes such as TP53. Answer D is incorrect because PDS and AFX cannot be discriminated cytologically or immunohistochemically, so pathologists should be aware of the histologic features which are typical of one over the other. The presence of extended necrosis, angiolymphatic / perineural invasion and infiltrative growth pattern into the subcutaneous tissues / muscle layers favors PDS over AFX.
Comment Here
Reference: Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma
Comment Here
Reference: Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma