Table of Contents
Definition / general | Sites | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Tranesh GA, Qu H. Metastatic. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticmetastaticcarcinoma.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Cutaneous metastases from many internal organ sites or soft tissue sarcomas are uncommon (J Surg Case Rep 2014 Sep 9;2014)
- Men: usually from lung (25%), colon, melanoma, kidney, upper aerodigestive tract
- Women: usually from breast (69%), lung, melanoma, kidney, ovary
- Metastasis is often close to site of primary
Sites
- Local recurrence / regional metastasis most commonly occurs upon anterior chest wall
- Scalp is tmost commonly observed distant metastatic site
Case reports
- 73 year old woman with cutaneous metastases as only sign of extranodal tumor spread (ISRN Surg 2011;2011:902971)
- 83 year old woman with herpetiform cutaneous metastases from transitional cell carcinoma of bladder (J Clin Pathol 2006;59:1331)
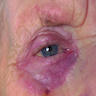
- 91 year old woman with seven month history of redness and swelling around her right eye (BMJ 2007;334:1228)
Treatment
- Treat underlying malignancy, possible excision of metastasis
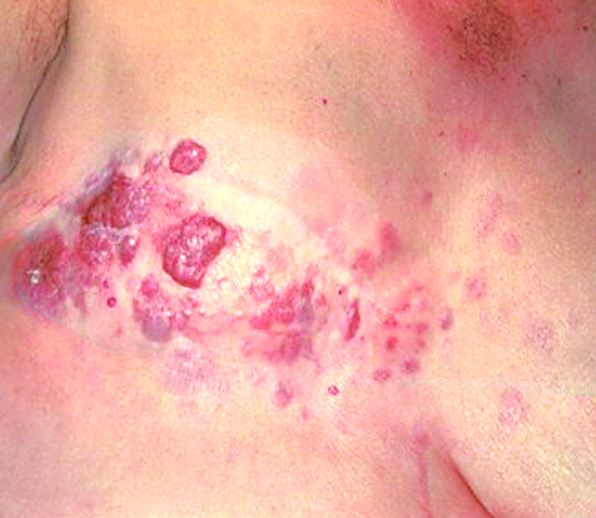
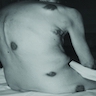
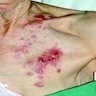
Clinical images
Gross description
- Often multiple, firm, nonulcerated nodules, but may be solitary
Microscopic (histologic) description
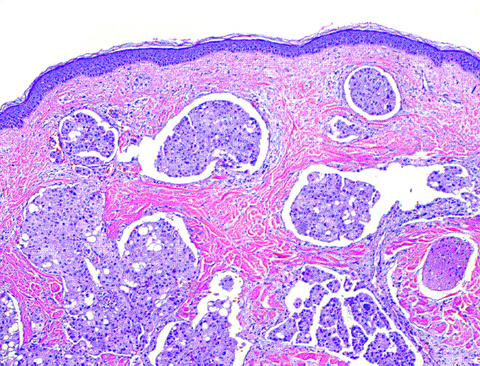
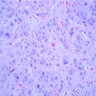
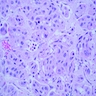
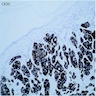
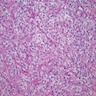
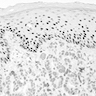
- Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma within dermis and often underlying subcutaneous tissue
- Tumor cells in sheets or clusters or as single detached cells
- Either abortive gland formation or "signet ring" cells (with central, cleared mucin-filled space which compresses and marginalizes the cell nucleus)
- Tumor cells may show a "single file" appearance (metastatic lobular breast carcinoma)
- Cytologic atypia in small to large epithelioid cells, often with striking nuclear pleomorphism
- Tumor cells may produce mucin, or mucinous debris may separate collagen bundles
- Variable desmoplasia or sclerosis of dermal collagen
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Immunohistochemical studies are often essential for diagnosis of cutaneous metastasis by breast carcinoma
- Tumor cells are usually positive for CK7, mammoglobin, or GCDFP-15
- May be positive for estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and HER2/neu
- Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) may highlight gland or signet ring cell lumina
- CK5/6 or p63 may distinguish primary apocrine or eccrine adnexal neoplasms (positive) from metastatic breast adenocarcinoma (generally negative)
Negative stains
Differential diagnosis
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: may resemble metastatic signet ring cell carcinoma
- Merkel cell carcinoma: resembles neuroendocrine metastases
- Sweat gland tumor: may resemble metastatic renal cell carcinoma
Additional references