Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Aghighi M, Speiser J. Trichilemmal (pilar) type. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocytickeratinouscysttrichilemmal.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Trichilemmal cyst, also known as a pilar cyst, is a keratin filled cyst that originates from the outer hair root sheath that is commonly located on the scalp
Essential features
- 90% present on scalp
- Circumscribed simple cyst with stratified squamous epithelium lining, which lacks a granular cell layer and contains dense eosinophilic keratin
- Proliferating trichilemmal cyst and other neoplasms, such as Merkel cell carcinoma, can develop from or within a benign trichilemmal cyst
Terminology
- Also called pilar cyst, isthmus catagen cyst or a wen
ICD coding
- ICD-10: L72.11 - pilar cyst
Epidemiology
- Second most common type of cutaneous cyst (Int J Dermatol 2020;59:457)
- More common in adults
- More common in females
Sites
- 90% on scalp
- Scrotum
- Rarely on pulp of finger
Pathophysiology
- Origin unknown but may arise from external root sheath as a genetically determined structural aberration
- Mostly autosomal dominant inheritance (J Invest Dermatol 2019;139:2075)
- Hair follicle's outer root sheath is recapitulated at the level of the follicular isthmus in the cyst wall
Clinical features
- Most commonly found on the scalp (90%) and scrotum
- When present as multiple lesions, autosomal dominance is common
- Asymptomatic, firm, mobile, dermal or subcutaneous nodules measuring 0.5 to 5 cm in diameter
- No central punctum is present
- Typically, encapsulated cyst and uncomplicated lesions are easily shelled out at surgery
- Acute inflammation is usually nonbacterial, may be associated with cyst rupture
- Cholesterol clefts in up to 90%
- Calcification in 25%, independent of patient age or size of cyst (J Ultrasound Med 2019;38:91)
Diagnosis
- Clinical impression or excision
Prognostic factors
- Benign but may be locally aggressive
- Rarely malignant but may result in metastasis
- Rarely other neoplasms, such as Merkel cell carcinoma, colonize or arise in trichilemmal cyst (An Bras Dermatol 2019;94:452)
- Proliferating trichilemmal cysts can develop from a benign trichilemmal cyst; growth may be provoked by an unknown trigger, such as trauma, irritation or inflammation (Arch Craniofac Surg 2017;18:50)
Case reports
- 63 year old man with a proliferating trichilemmal cyst arising from a nevus (J Cutan Pathol 2017;44:639)
- 70 year old woman with proliferating trichilemmal tumor (BMJ Case Rep 2019;12:e226567)
- 76 year old man with pilar cyst on the dorsum of hand (Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99:e21519)
- 85 year old woman with malignant proliferating trichilemmal tumor (Indian J Dermatol 2020;7:40)
Treatment
- No treatment necessary for asymptomatic lesions
- Incision and drainage under local anesthesia
- Enucleation of the cyst
- Incision followed by expression of contents and removal of cyst wall
- Surgical excision if clinically indicated
- Reference: Int J Trichology 2013;5:115
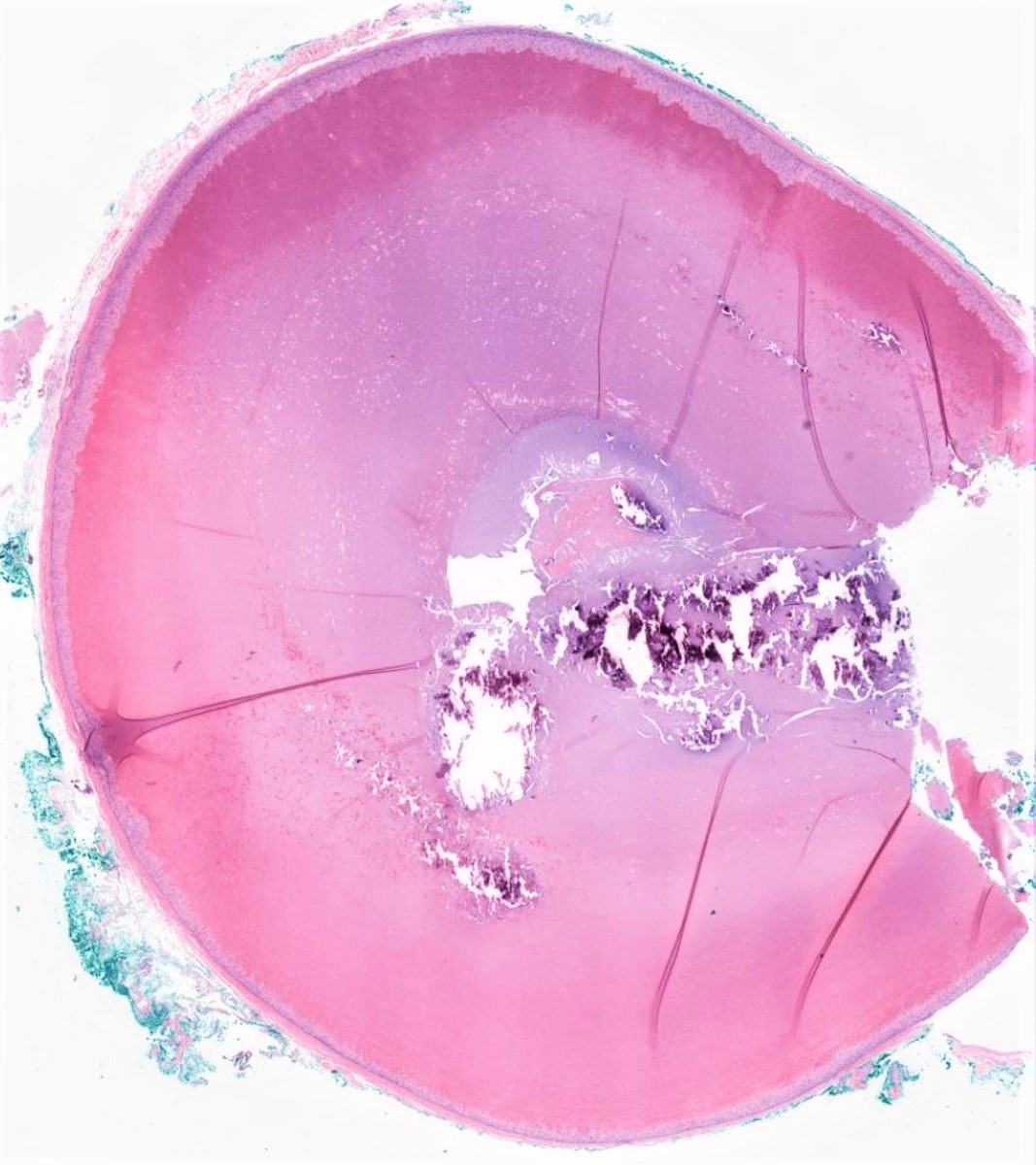
Gross description
- Dermal or subcutaneous cysts filled with solid, homogenous material
- Thick cyst wall
- Reference: Eur J Radiol Open 2019;6:291
Microscopic (histologic) description
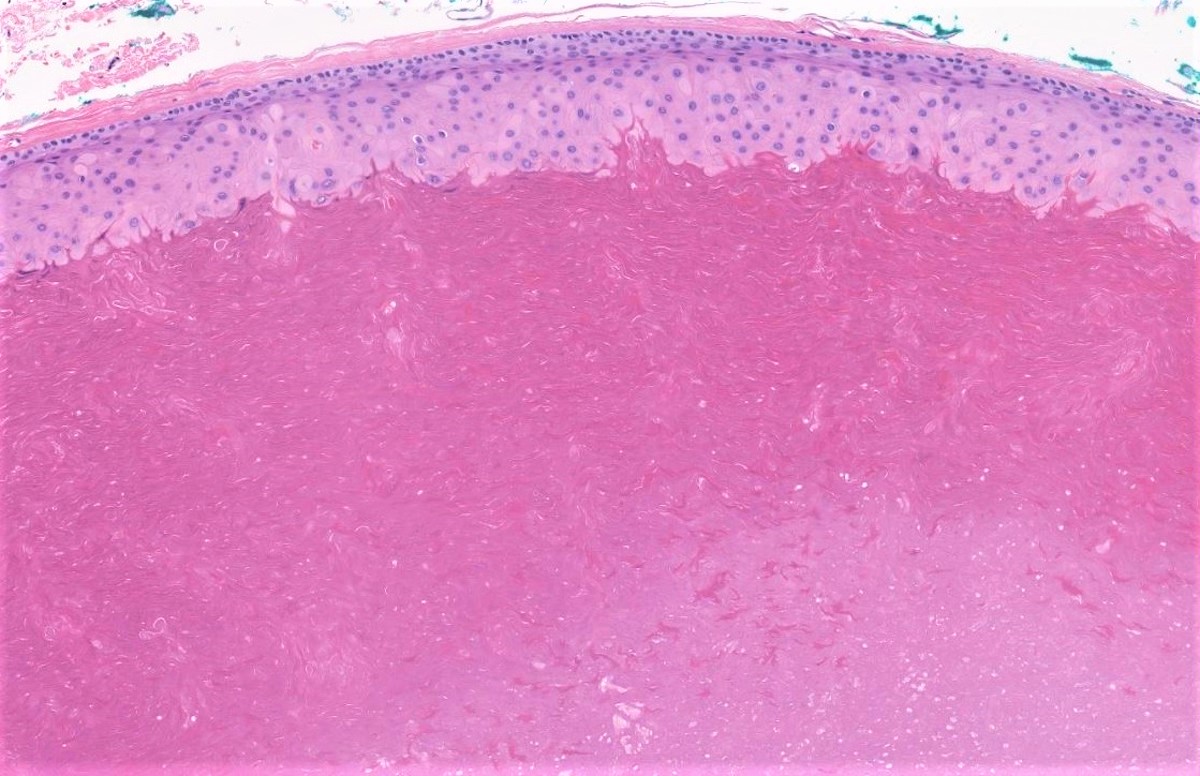
- Well circumscribed subcutaneous or dermal simple cyst, lined by stratified squamous epithelium that has a palisaded outer layer and contains dense laminated eosinophilic keratin
- Granular layer is absent
- Calcification in up to 25%
- Granulomatous response due to rupture
- Sebaceous or apocrine glands may be seen (Requena: Cutaneous Adnexal Neoplasms, 1st Edition, 2017)
- Hidrocystoma-like lining
Microscopic (histologic) images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Phospholipase C delta 1 (PLCD1) mutation identified in hereditary cases (J Invest Dermatol 2019;139:2154, Sci Rep 2020;10:6035)
Sample pathology report
- Scalp, biopsy:
- Trichilemmal (pilar) cyst (see comment)
- Comment: The sections show a dermal cyst lined by stratified squamous epithelium with a palisaded outer layer, lack of granular layer and containing dense laminated eosinophilic keratin.
Differential diagnosis
- Infundibular cyst:
- Most common sites are face, neck and trunk
- Central punctum is present
- Origin is epithelium of hair follicle infundibulum
- Cyst wall is delicate and prone to rupture
- On histology, the granular cell layer is present
- Contains laminated keratin unlike pilar cyst with dense, eosinophilic keratin material in the cyst lumen and no granular layer
- Proliferating pilar cyst:
- Can grow as large as 25 cm, may cause pressure necrosis (destruction) on underlying tissues, ulceration and foul smelling discharge
- Well defined lobular proliferation of squamous cystic islands centered in the dermis
- The lining epithelium is a stratified squamous epithelium exhibiting trichilemmal keratinization
- Well circumscribed with foci of necrosis and dyskeratosis
- Increased typical mitotic figures in basilar epithelium along with mild cytologic atypia
- Squamous eddies are common
- Hidrocystoma:
- Uni or multi locular cyst in dermis
- Consist of two or more layers of columnar-cuboidal epithelium with an outer layer of myoepithelial cells
- Malignant pilar tumor:
- Infiltrative border
- Marked cytologic atypia with numerous atypical mitotic figures
- Perineural or vascular invasion
- Geographic necrosis
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 68 year old man presents with a dermal nodule on his scalp. Which of the following statements is correct?
- Histology shows marked cytologic atypia with numerous atypical mitotic figures
- Histology shows simple cyst with squamous epithelium lining, lack of a granular cell layer and containing dense keratin
- Histology shows thin walled clear cystic spaces in dermis
- Histology shows well defined lobular proliferation of squamous cystic islands centered in the dermis
Board review style answer #1
B. Histology shows simple cyst with squamous epithelium lining, lack of a granular cell layer and containing dense keratin
Comment Here
Reference: Trichilemmal (pilar) cyst
Comment Here
Reference: Trichilemmal (pilar) cyst
Board review style question #2
A 50 year old woman presents with an encapsulated cyst on her scalp. The gross findings include a dermal cyst with a thick cyst wall filled with solid, homogenous material. Which of the following is the most likely neoplasm to arise within this cyst?
- Basal cell carcinoma
- Malignant proliferating pilar cyst
- Merkel cell carcinoma
- Proliferating pilar cyst
- Squamous cell carcinoma
Board review style answer #2