Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Negative stains | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Miller S, Hosler GA. Dermatomyofibroma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticdermatomyofibroma.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign tumor of fibroblastic and myofibroblastic differentiation (J Cutan Pathol 1992;19:85)
- Limited to skin and centered within the dermis
Essential features
- Benign
- Fascicular proliferation of bland spindle cells arranged parallel to the epidermis (J Cutan Pathol 1992;19:85)
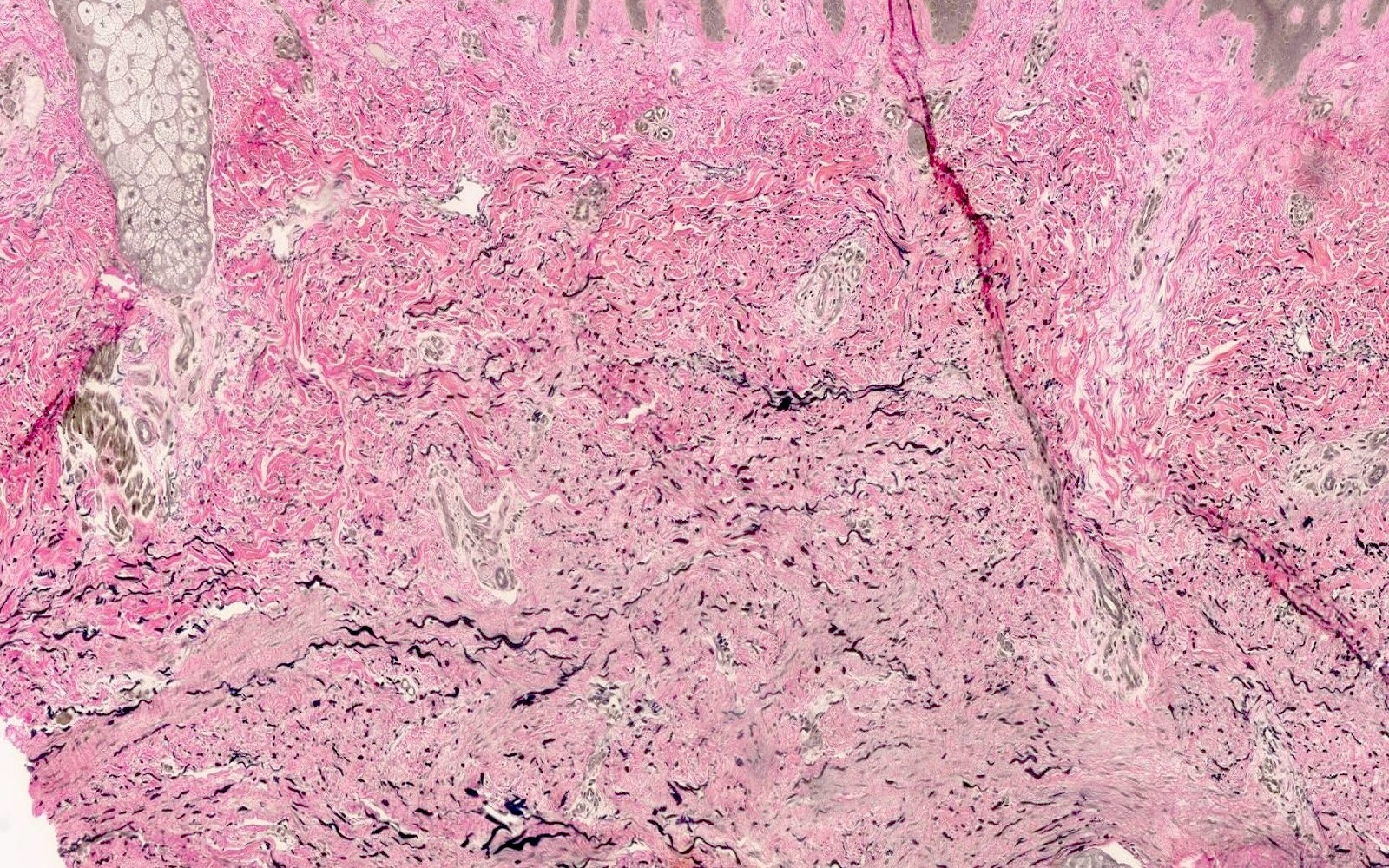
- Increased numbers of elastin fibers (Am J Dermatopathol 2009;31:44)
Terminology
- Plaque-like dermal fibromatosis (no longer used)
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- More common in women (Am J Dermatopathol 2009;31:44)
- Average age of 30
- Cases do occur in pediatric population (J Cutan Pathol 2011;38;967)
Sites
- Shoulder / neck / trunk are most common sites but other sites are seen
Pathophysiology
- Lesion is of myofibroblatic / fibroblastic origin demonstrated by electron microscopy and immunohistochemical studies (Histopathology 1996;29:181)
- Development of this lesion is not well understood
Etiology
- Given the limited numbers of cases, the discrete etiology is not well understood
Clinical features
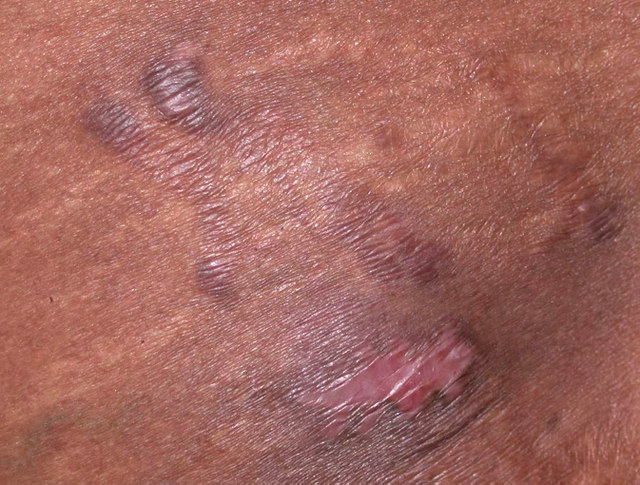
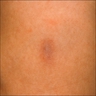
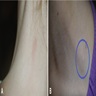
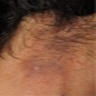
- Solitary plaque, with multiple lesions being exceptional (Calonje: McKee’s Pathology of the Skin, 5th Edition, 2019, An Bras Dermatol 2018;93:268)
- Linear or hemorrhagic appearing cases have been described (Oxf Med Case Reports 2019;2019:513)
- Hypopigmented, skin colored to red-brown (Calonje: McKee’s Pathology of the Skin, 5th Edition, 2019)
- Hypertrophic scar, keloids or dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans may be on clinical differential (Br J Dermatol 1993;129:69)
Diagnosis
- H&E diagnosis
- Support from immunohistochemical or special stains may be necessary to exclude histologic mimics
Prognostic factors
- Favorable prognosis
- Local recurrence in rare cases with no metastases reported (Am J Dermatopathol 2009;31:44)
Case reports
- 7 year old girl who presented with multiple rubbery nodules at the site of a prior embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (JAAD Case Rep 2021;11:96)
- 41 year old woman with an asymptomatic lesion of the neck, growing over 5 years (Oxf Med Case Reports 2019;2019:513)
- 41 year old woman with a history of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome presented with multiple well demarcated, linear lesions (Case Rep Dermatol 2023;15:1)
Treatment
- Full excision is curative with rare local recurrence
- Monitoring is an option for stable lesions
Clinical images
Gross description
- Hypopigmented, skin colored or red-brown plaque
Microscopic (histologic) description
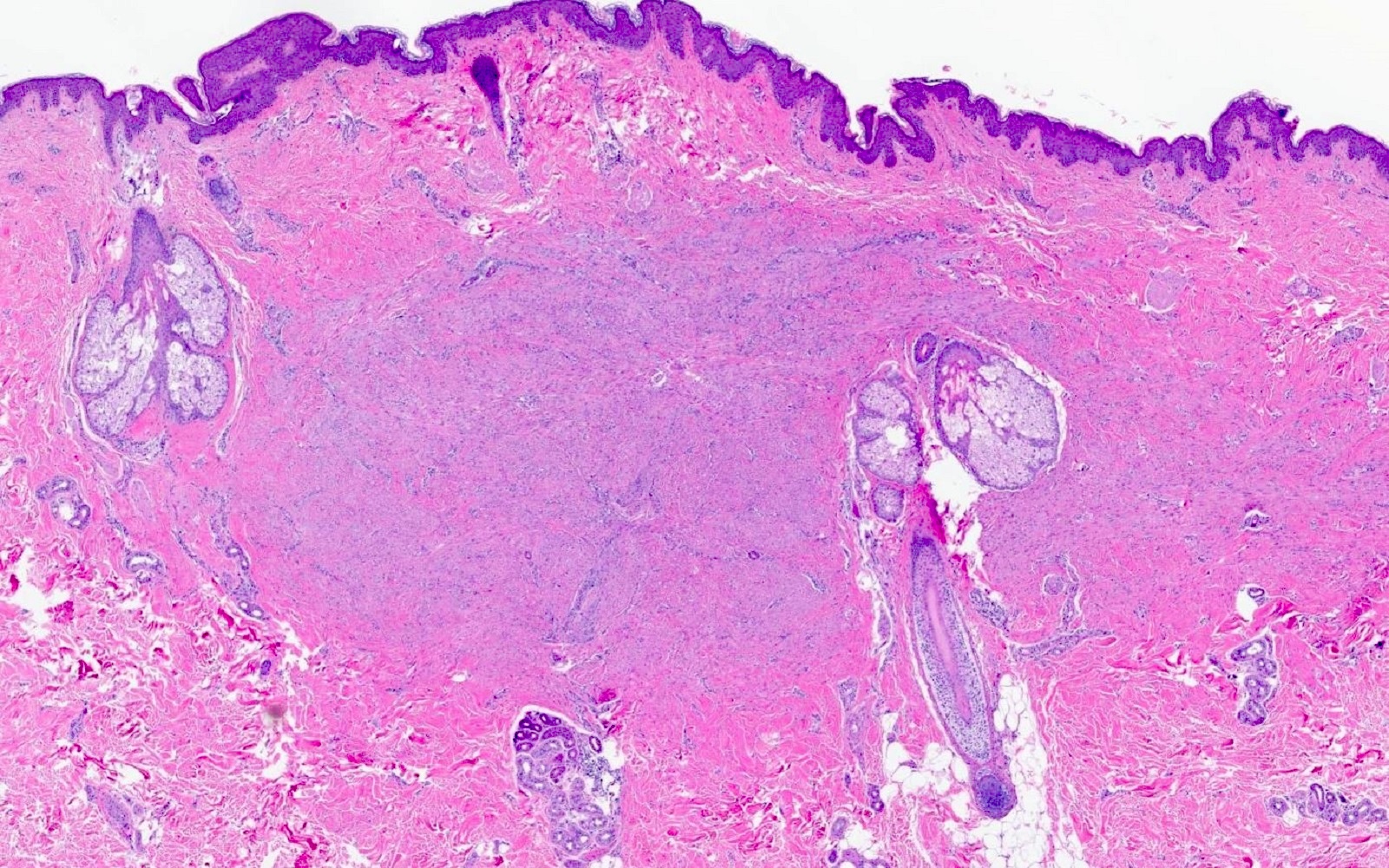
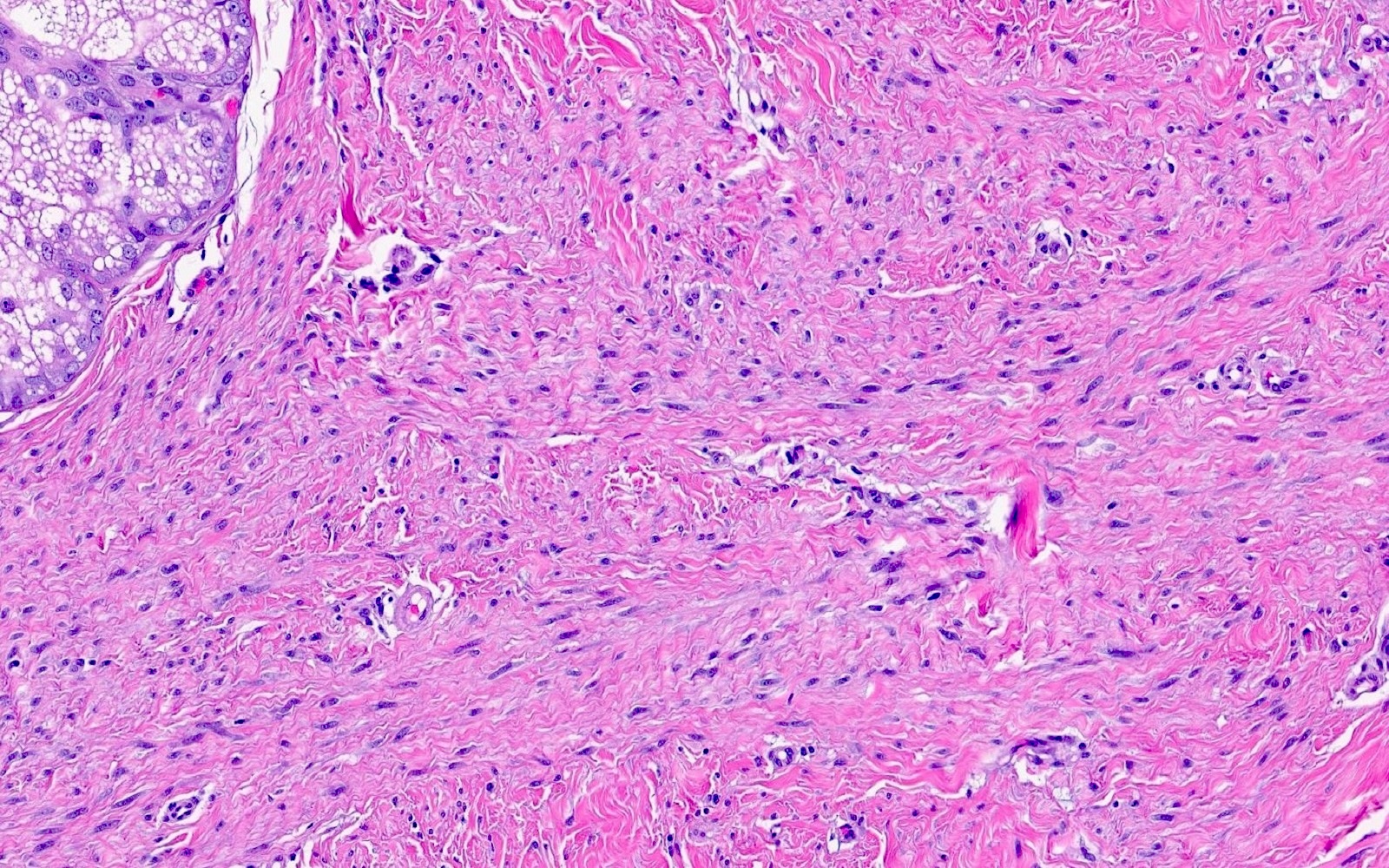
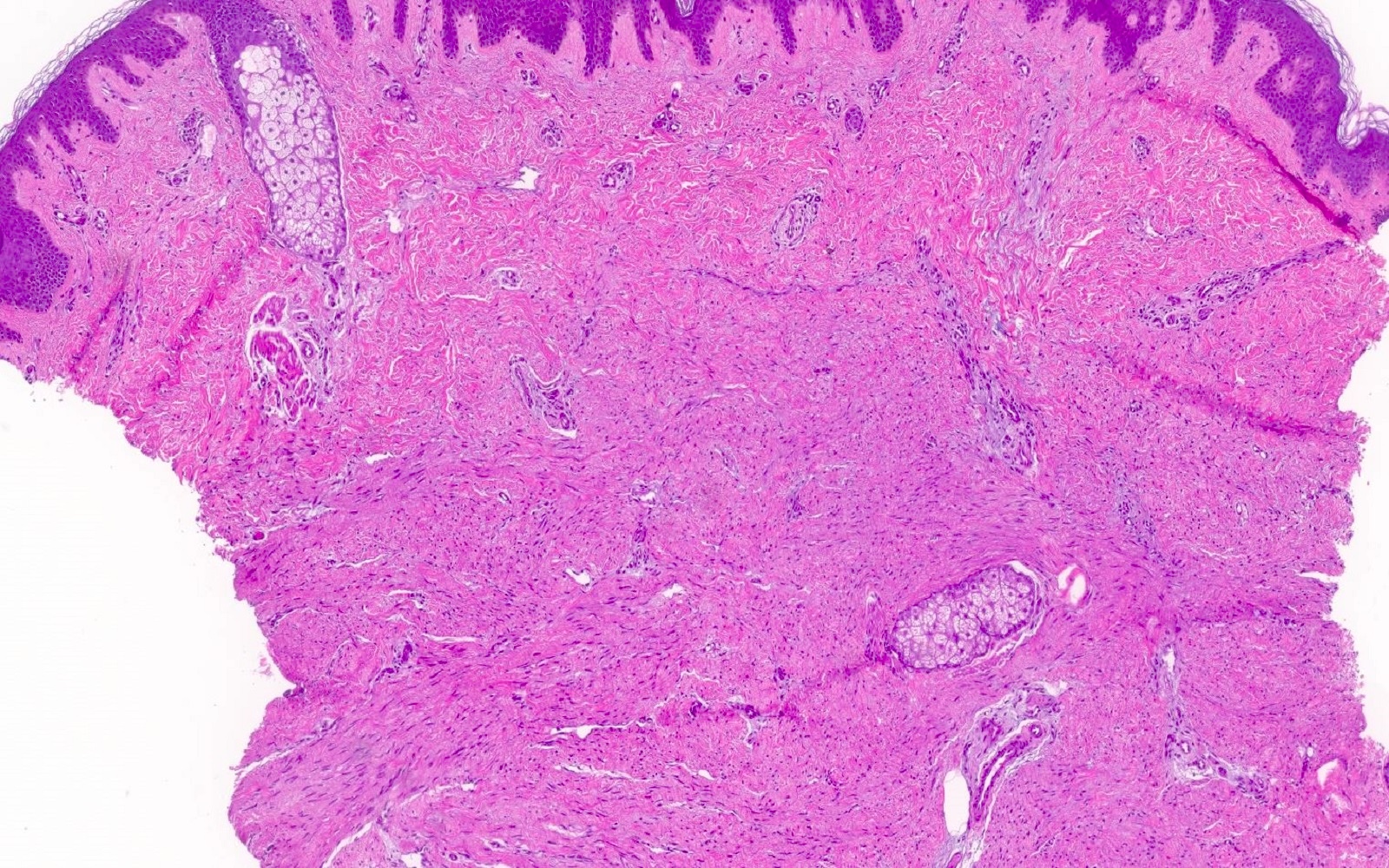
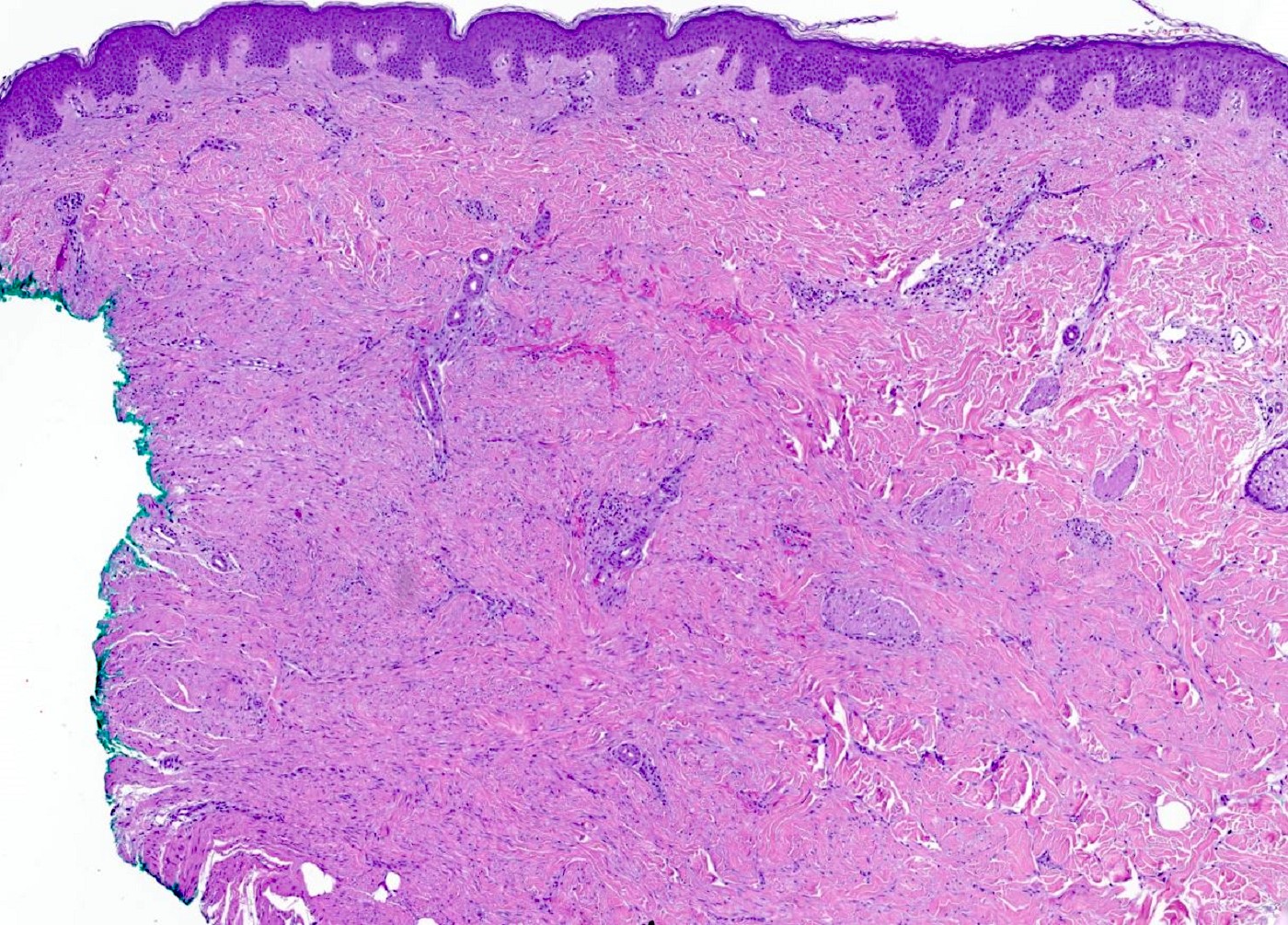
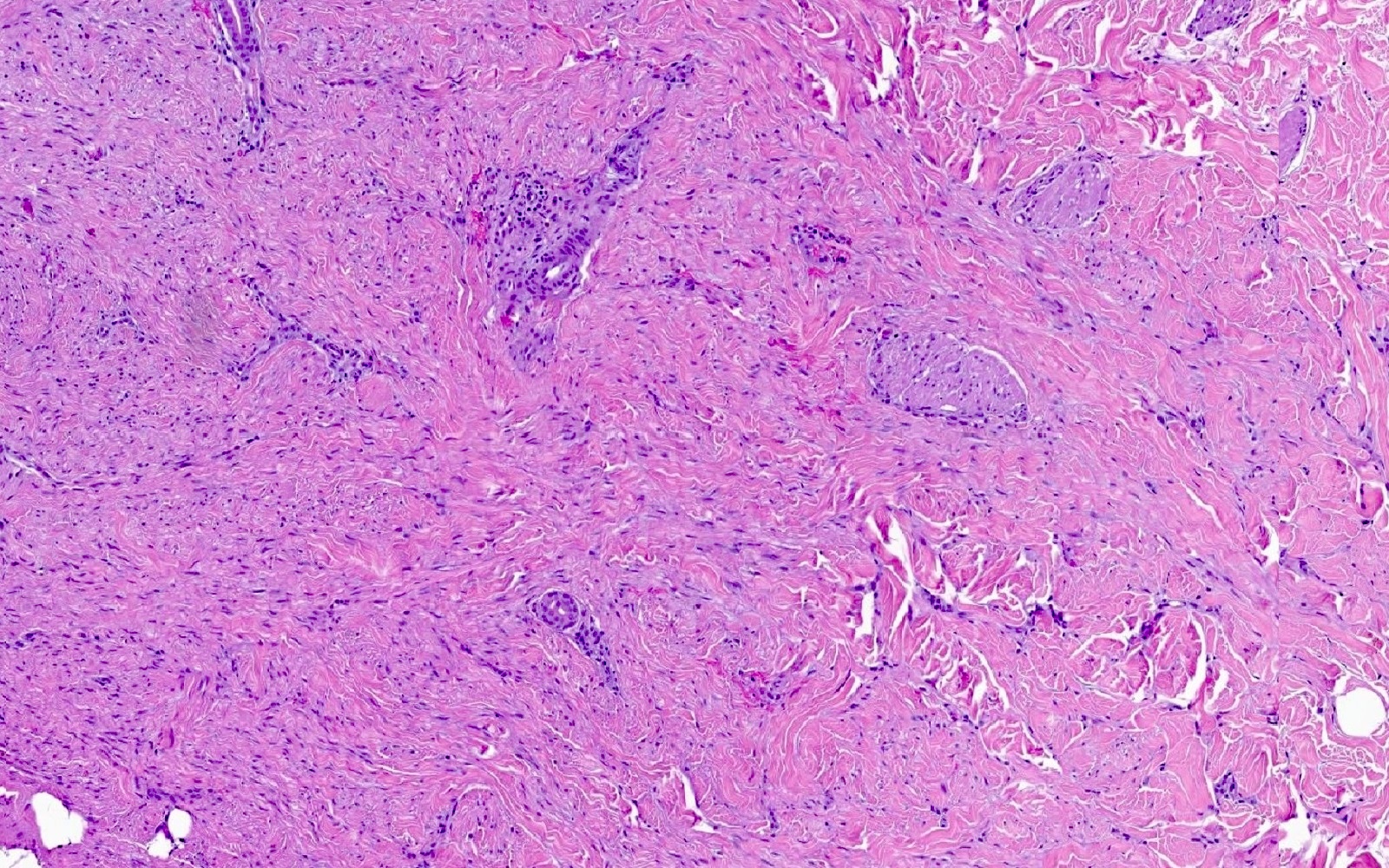
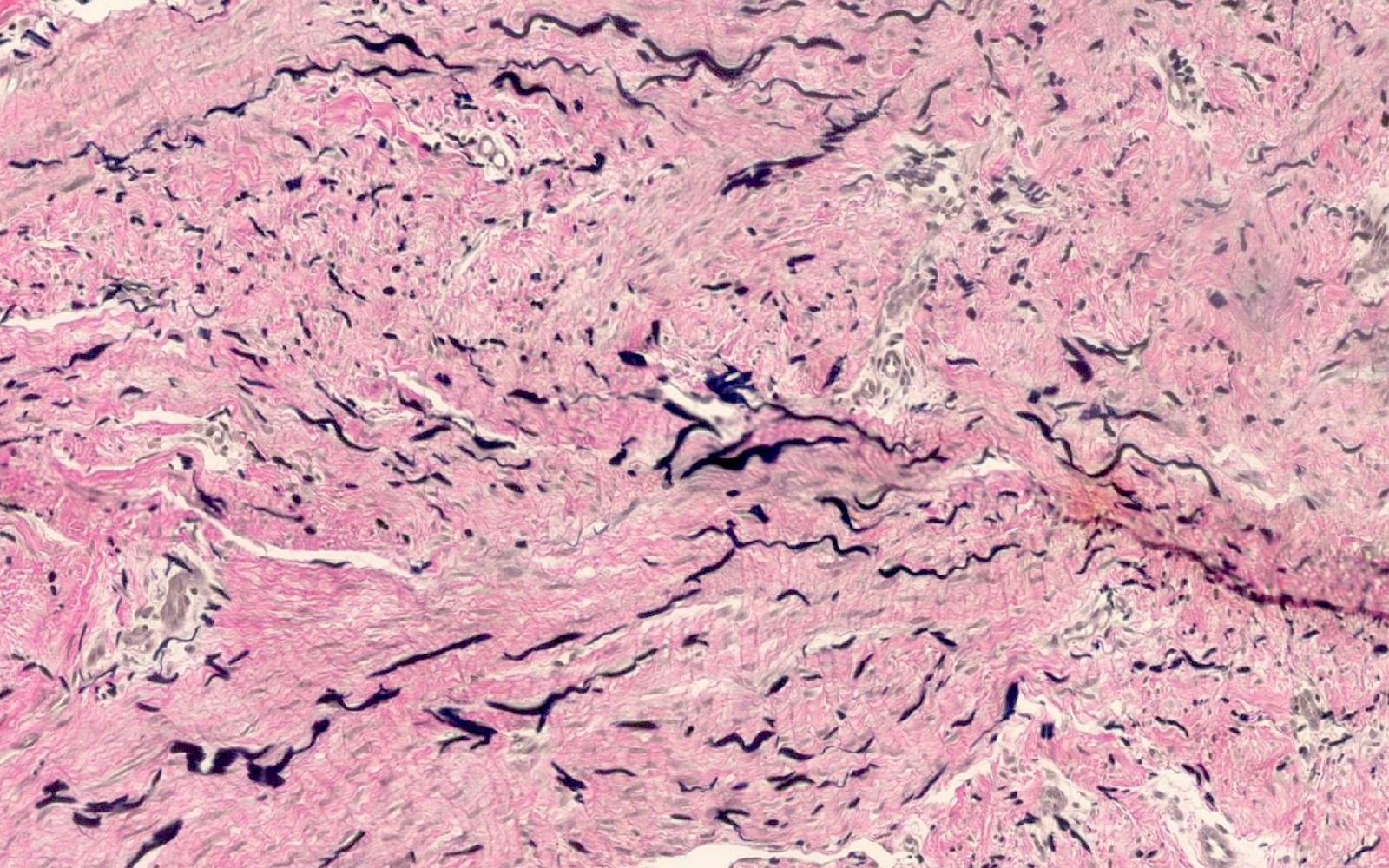
- Somewhat ill defined proliferation of moderately cellular, bland spindled cells arranged in fascicles parallel to the epidermis (J Cutan Pathol 1992;19:85, J Cutan Pathol 2011;38:967)
- No cytologic atypia or mitoses should be present
- Adnexal structures appear trapped but spared (J Cutan Pathol 2011;38:967)
- Bulk of neoplasm is present within the dermis
- Tumor may brush the subcutis but overt involvement is unusual (Am J Dermatopathol 2009;31:44)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
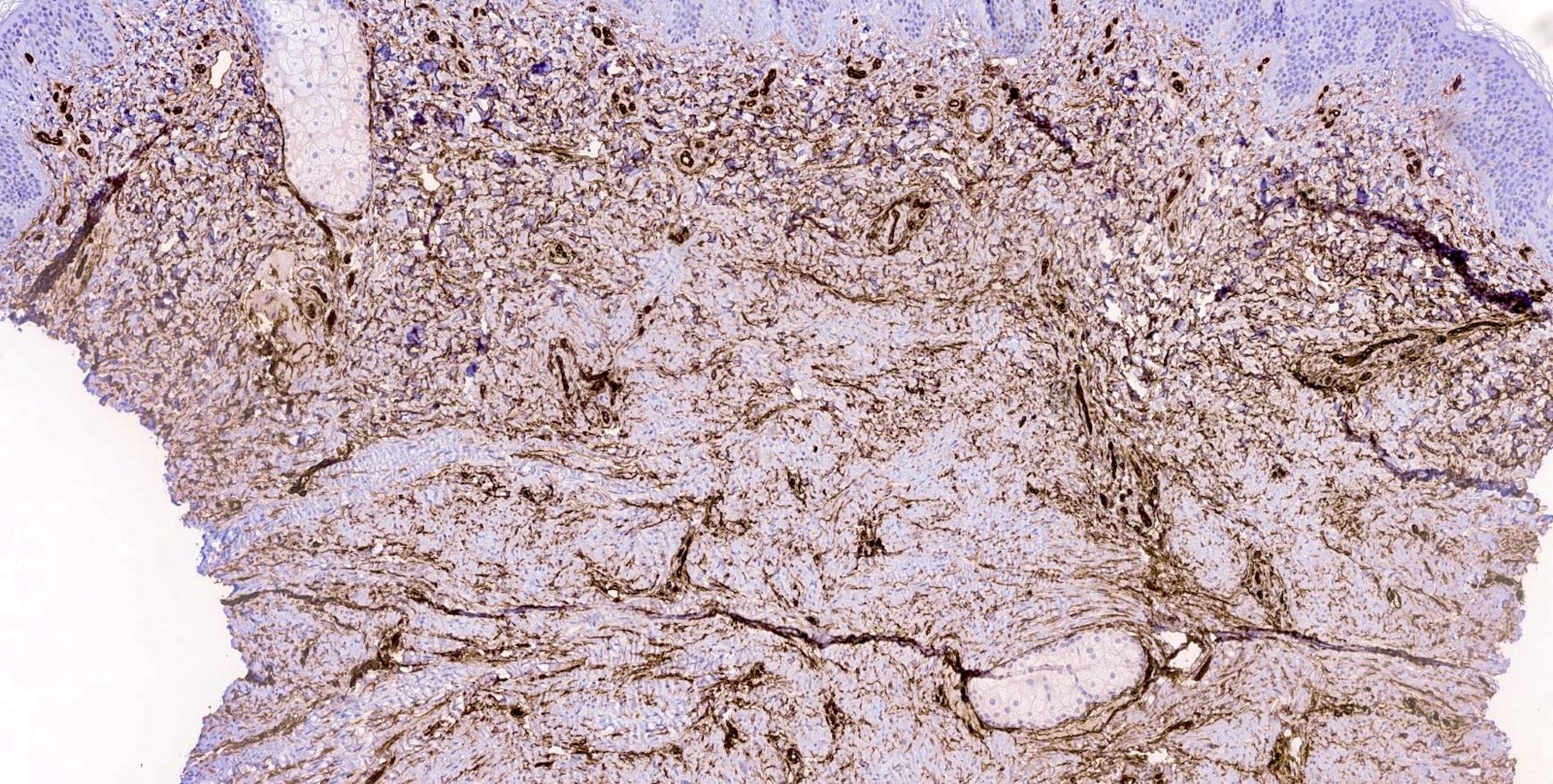
- Immunohistochemistry has poor sensitivity and specificity for dermatomyofibroma
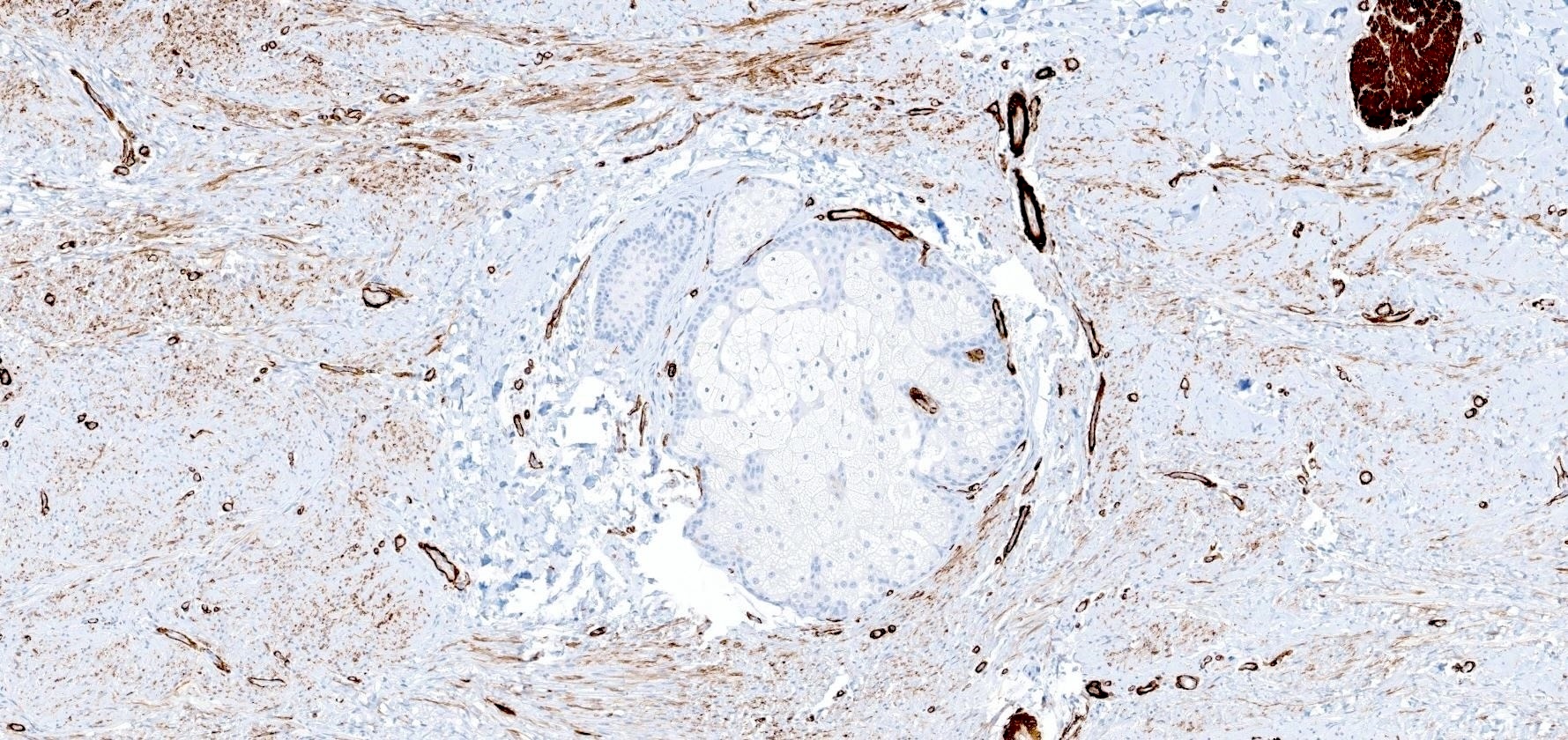
- Smooth muscle actin (SMA): positive in < 50% of cases; may only be patchy or focal (Am J Dermatopathol 2009;31:44)
- Verfoeff-van Gieson (EVG): highlights increased elastin fibers, which are often thick, fragmented and oriented parallel to the epidermis (J Cutan Pathol 2013;40:211)
Negative stains
- CD34: focally positive in < 25% of cases (Am J Dermatopathol 2009;31:44)
- S100, desmin, h-caldesmon, EMA, factor XIIIa
Videos
Fat, muscle, bone & cartilage skin tumors: dermpath board review (25 cases) by Jerad Gardner
Sample pathology report
- Skin, left posterior shoulder:
- Dermatomyofibroma (see comment)
- Comment: Histologic sections are of skin. Within the dermis, there is a proliferation of bland spindle cells arranged in fascicles with a horizontal growth pattern. The lesion does not displace adnexal units. The lesional cells are positive for smooth muscle actin and negative for S100, factor XIIa and CD34. An elastin stain is performed and highlights increased thickened elastin fibers within the lesion.
Differential diagnosis
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans:
- Superficial portion of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans may closely mimic dermatomyofibroma
- Storiform growth
- Stronger and more diffuse CD34 than dermatomyofibroma
- Infiltrative growth often into subcutis with honeycomb pattern
- Dermatofibroma:
- Collagen trapping at the periphery of a dermatofibroma
- Frequently displays epidermal hyperplasia / induction
- Factor XIIIa positive; SMA often negative
- Hypertrophic scar:
- Look for other features of scar, including ablation of rete ridges, perpendicularly oriented vessels, nonspecific arrangement of fibroblasts and collagen
- Decreased elastin fibers by EVG
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 34 year old woman presents with a solitary, red-brown plaque on her left shoulder. The histology is represented in the image above. Which of the following is true regarding this lesion?
- CD34 staining diffusely highlights the neoplasm
- EVG stain highlights decreased, thin elastin fibers
- The lesion is of myofibroblastic / fibroblastic differentiation
- This neoplasm is one of the most common found in the skin
- This tumor is known to metastasize
Board review style answer #1
C. This dermatomyofibroma lesion is of myofibroblastic / fibroblastic differentiation, as demonstrated by its morphologic, immunohistochemical and electron microscopy profile. Answer A is incorrect because CD34 should be negative or only focally positive in dermatomyofibroma. Answer B is incorrect because the opposite is true; there should be increased, thick fibers. Answer D is incorrect because dermatomyofibromas are exceptionally rare, with < 200 cases reported in the literature. Answer E is incorrect because there are no known cases of dermatomyofibroma with metastasis.
Comment Here
Reference: Dermatomyofibroma
Comment Here
Reference: Dermatomyofibroma