Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Arshia A, Qasem S. Deep fibrous histiocytoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticdeepbfh.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Fibrous histiocytoma is a benign fibrohistocytic tumor that arises within the subcutaneous or deep soft tissues and rarely metastasizes
Essential features
- Well circumscribed lesion located in subcutaneous or deep tissue
- Mixed fascicular or storiform growth pattern
- Monomorphic spindled or histiocytoid cells
- Limited atypia and mitoses
- Rule out other entities in the differential
Terminology
- Dermatofibroma, deep benign fibrous histiocytoma (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019, Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354)
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8831/0 - deep benign fibrous histiocytoma
- ICD-11: 2F7C & XH5DP4 - neoplasms of uncertain behavior of connective or other soft tissue & deep benign fibrous histiocytoma
Epidemiology
- Wide age range, commonly early to mid adult life, 20 - 40 years (median age: 37 years) (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019, Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354)
- Slightly predominant in males
- Rare lesion that represents < 1% of fibrohistocytic tumors (Am J Surg Pathol 1990;14:801)
Sites
- Extremities followed by head and neck and trunk (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019, Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354)
- 10% arise in visceral soft tissue such as the retroperitoneum, mediastinum and pelvis
Pathophysiology
- Rearrangements involving protein kinase C (PKC) isoforms PRKCB and PRKCD have been identified in various subtypes of fibrous histiocytoma
- Recurrent fusions of genes encoding membrane associated proteins (podoplanin, CD63 and LAMTOR1) with genes encoding PKCs are implicated in various cellular processes and tumor development; this mechanism results in constitutive kinase activity, suggesting that distorted PKC activity is essential for tumorigenesis (Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2014;53:475)
Etiology
- Largely unknown
- Some cases have been associated with minor trauma, insect bites or immunosuppressed conditions like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019)
Clinical features
- Solitary, slow growing painless nodule on extremities; < 3 cm in diameter for subcutaneous, while those in deep tissues may be larger (up to 9 cm) (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019, Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354)
- Red nodular or pigmented appearance (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019)
- Metastasis is very rare (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354)
Diagnosis
- Well circumscribed lesion located in subcutaneous or deep tissue
- Mixed fascicular or storiform growth pattern (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354)
- Monomorphic spindled or histiocytoid cells (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354)
- Branching hemangiopericytoma-like vessel pattern in a subset of cases; no specific stains but workup is necessary to rule out other entities with overlapping features (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354)
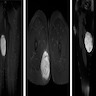
Radiology description
- On imaging, deep fibrous histiocytomas are often described as oval, well delineated tumors with definable borders and an intervening fat plane to the muscular fascia, if found in a subcutaneous location
- Computed tomography (CT) appearance has been described as a nonspecific soft tissue mass with avid enhancement
- Deep fibrous histiocytomas are reported to be mostly homogeneous masses that might show central vascularity, internal hemorrhage or necrosis and the following appearance
- T1: low intensity
- T2: high intensity
- T1 C+ (Gd): avid peripheral enhancement
- Reference: Radiopaedia: Deep Fibrous Histiocytoma [Accessed 19 July 2024]
Prognostic factors
- Deep soft tissue fibrous histiocytomas have higher (20%) rates of recurrence due to their larger size and higher potential for incomplete excision (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019)
- Metastases have been reported in up to 5% of cases in some series
- 50% recurrence is seen in fibrous histiocytomas growing into subcutis and in a multinodular fashion
- Orbital fibrous histiocytomas with infiltrative margins recur in 57% of cases (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019)
- Facial fibrous histiocytomas that invade into subcutis and muscle have high rates of recurrence (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019)
- 22% local recurrence rate in deep fibrous histiocytomas per Gleason et al. (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019)
- Atypical, cellular and aneurysmal fibrous histiocytomas recur locally in 25% of cases (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019, Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354)
Case reports
- 34 year old man with left index finger mass (Case Reports Plast Surg Hand Surg 2023;10:2207637)
- 43 year old man presented with hemoptysis (Lung 2017;195:503)
- 47 year old man with recurrent and metastatic fibrous histiocytoma (J Cutan Pathol 2024;51:214)
- 88 year old woman with a kidney mass (Medicine (Baltimore) 2019;98:e15150)
Treatment
- Wide, local excision and close clinical follow up (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354)
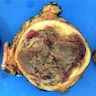
Gross description
- Well circumscribed, white-tan, firm nodule with focal areas of hemorrhage (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019, Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354)
- Central cystic degeneration in some cases (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354)
- Subcutaneous tumors may be attached to fascia or tendon intraoperatively
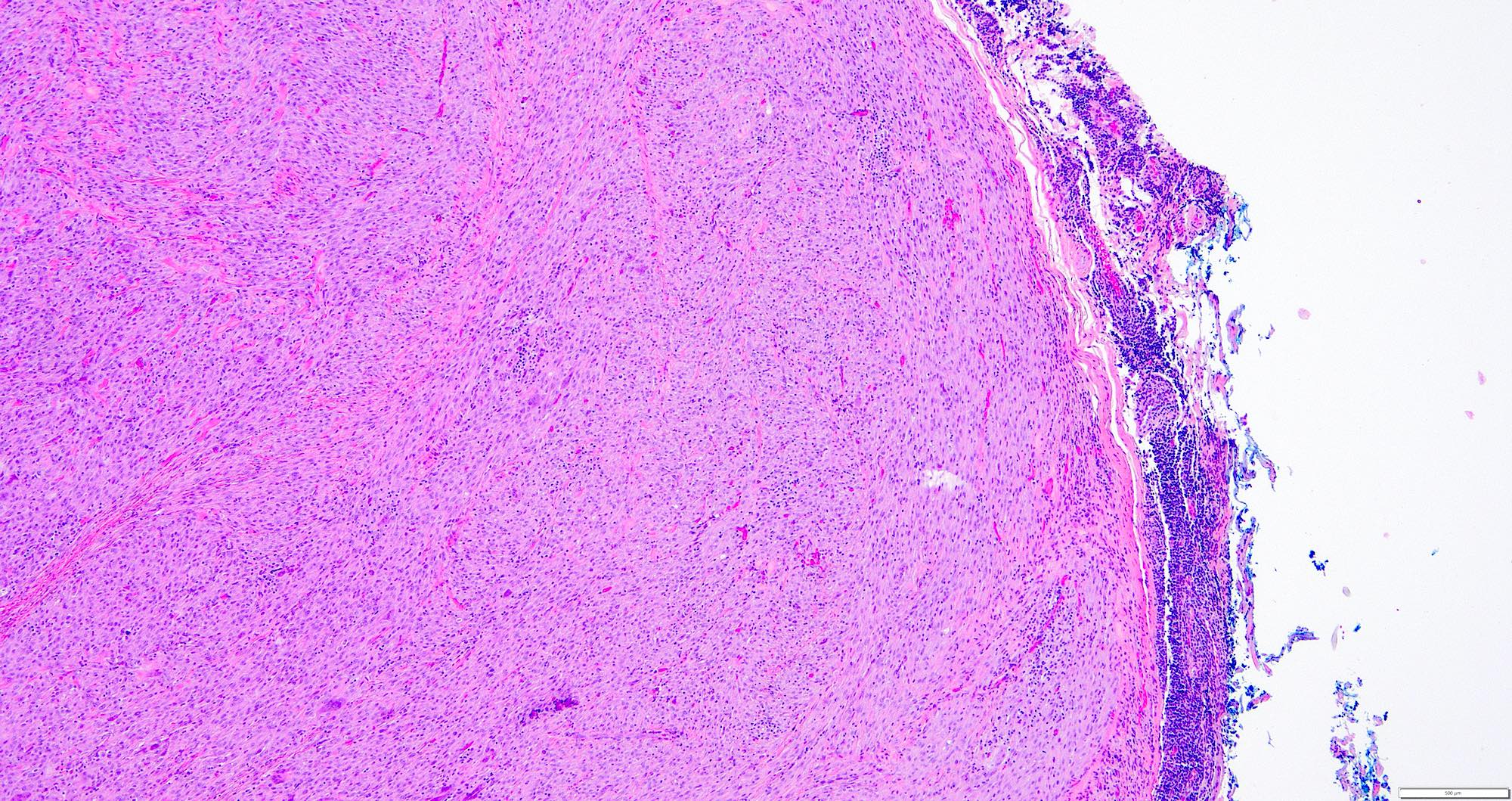
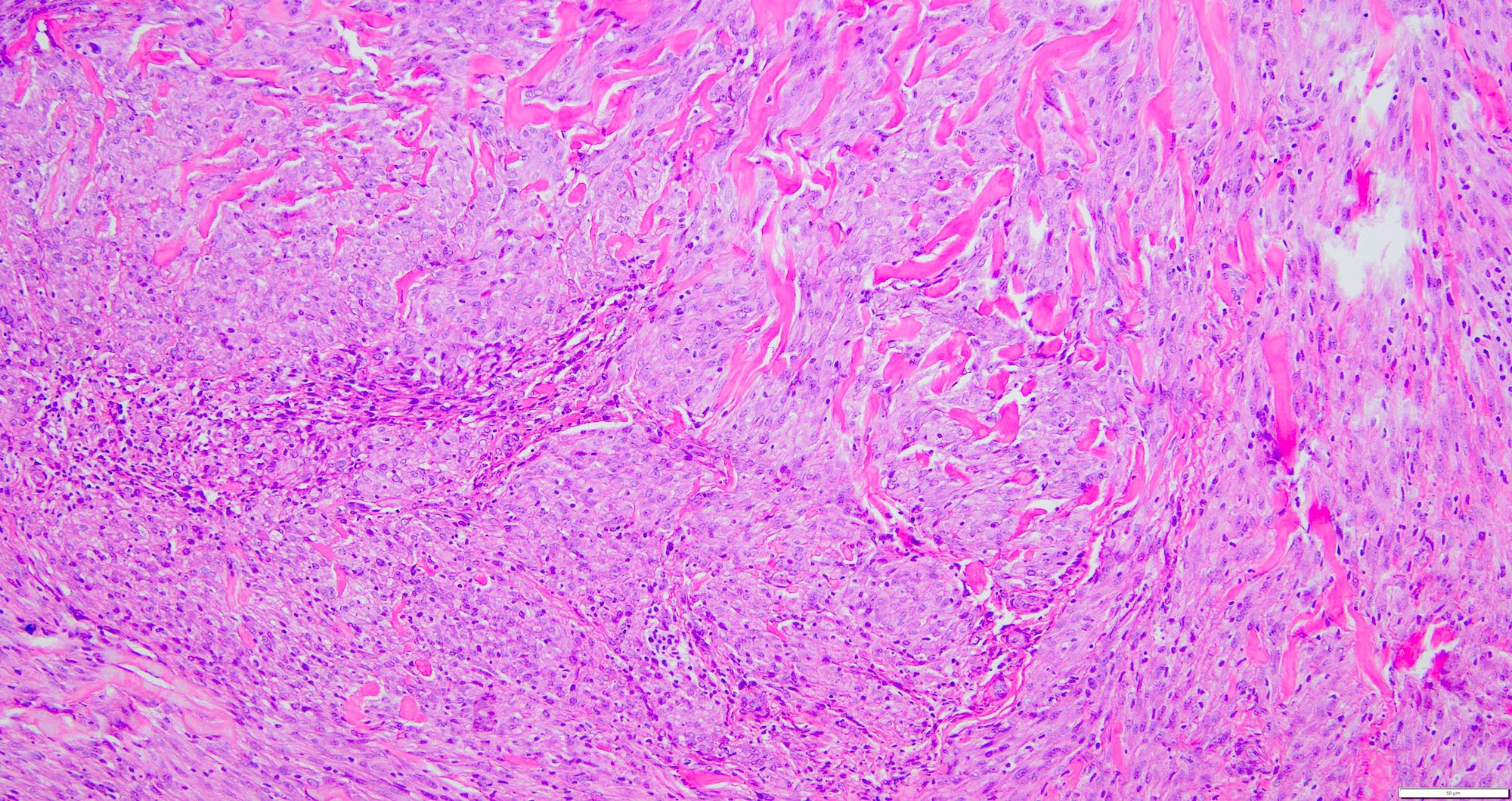
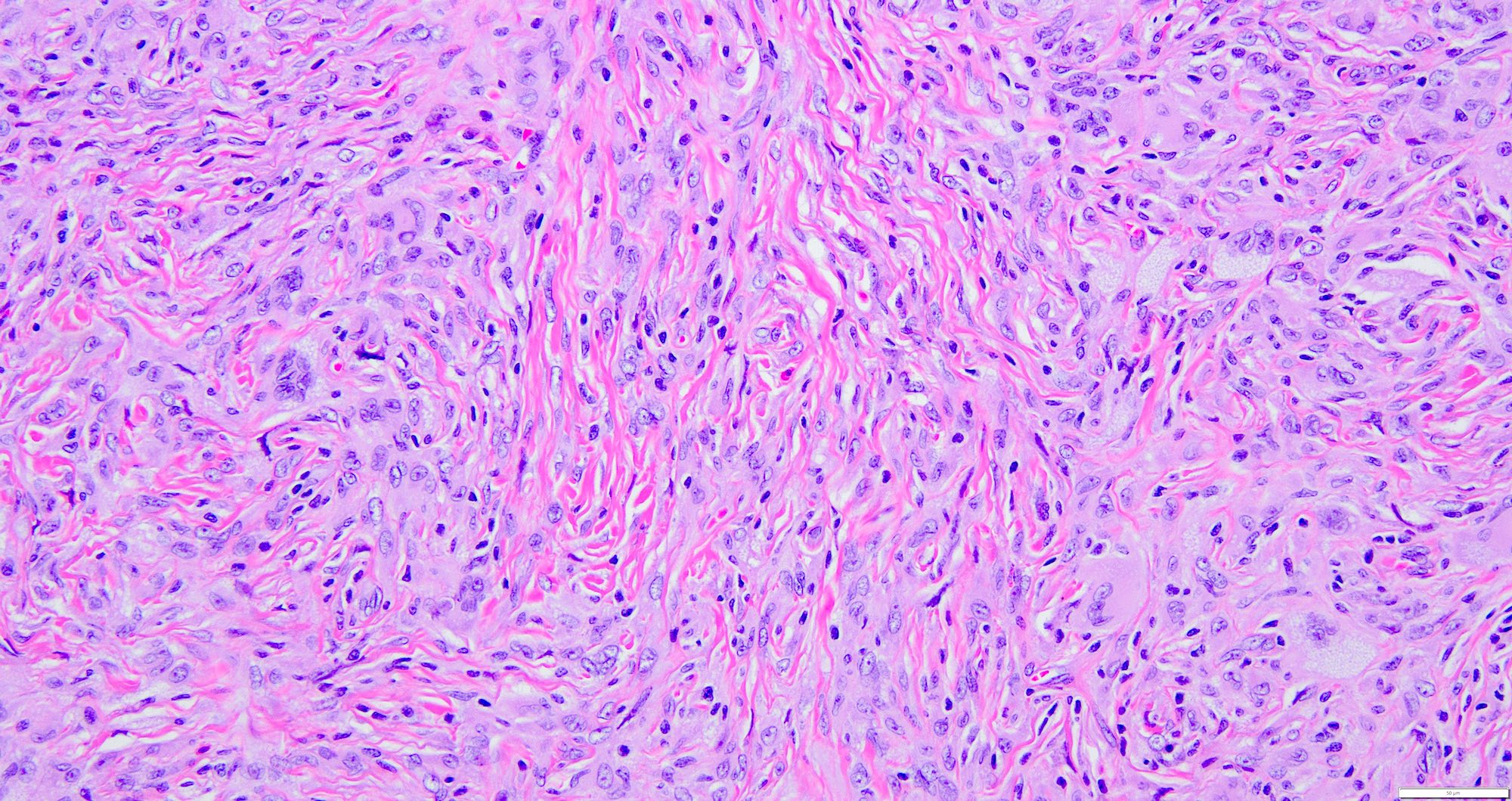
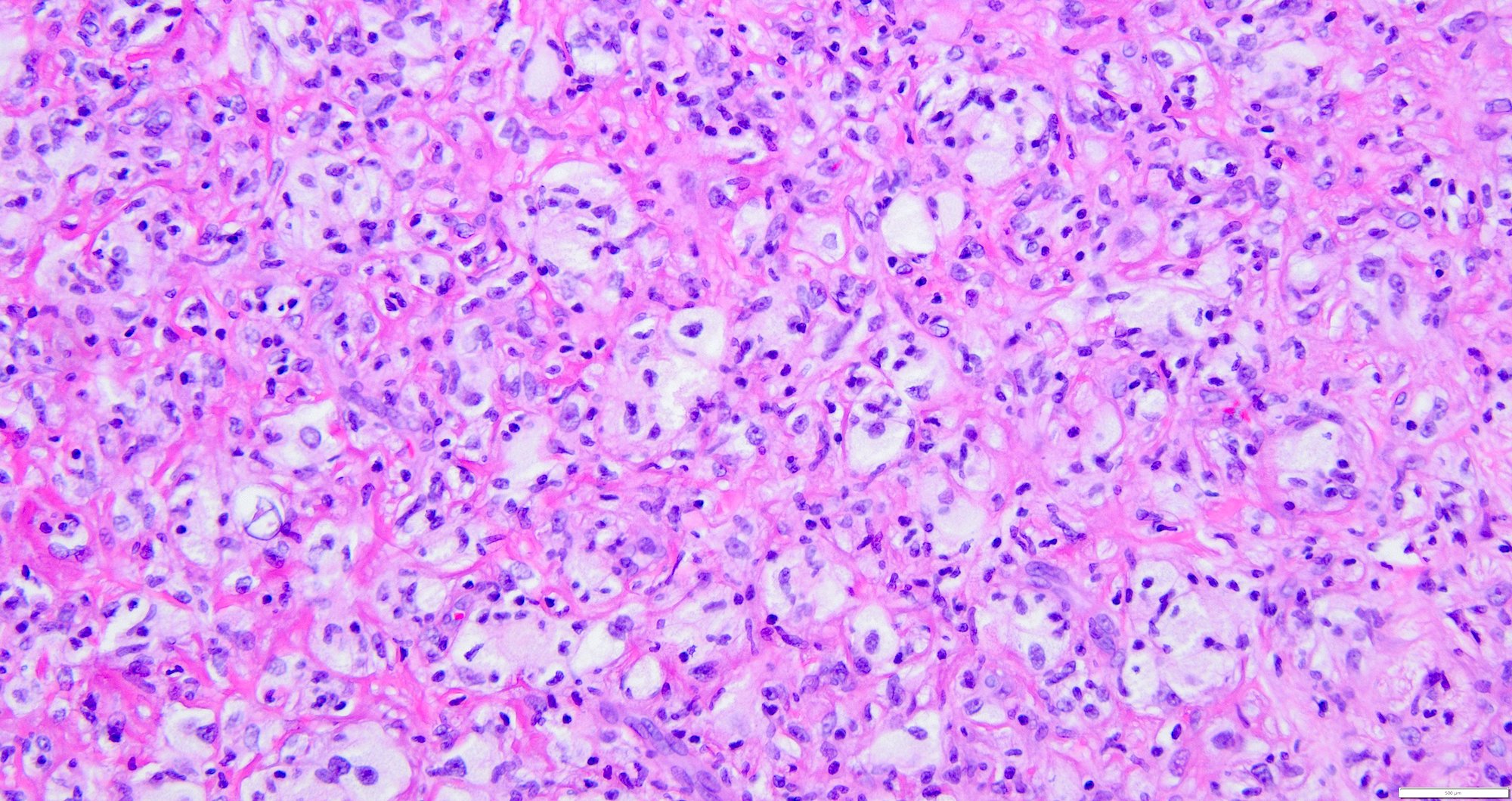
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Deep fibrous histiocytomas are well circumscribed
- Nodular cellular proliferation with collagen trapping (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019)
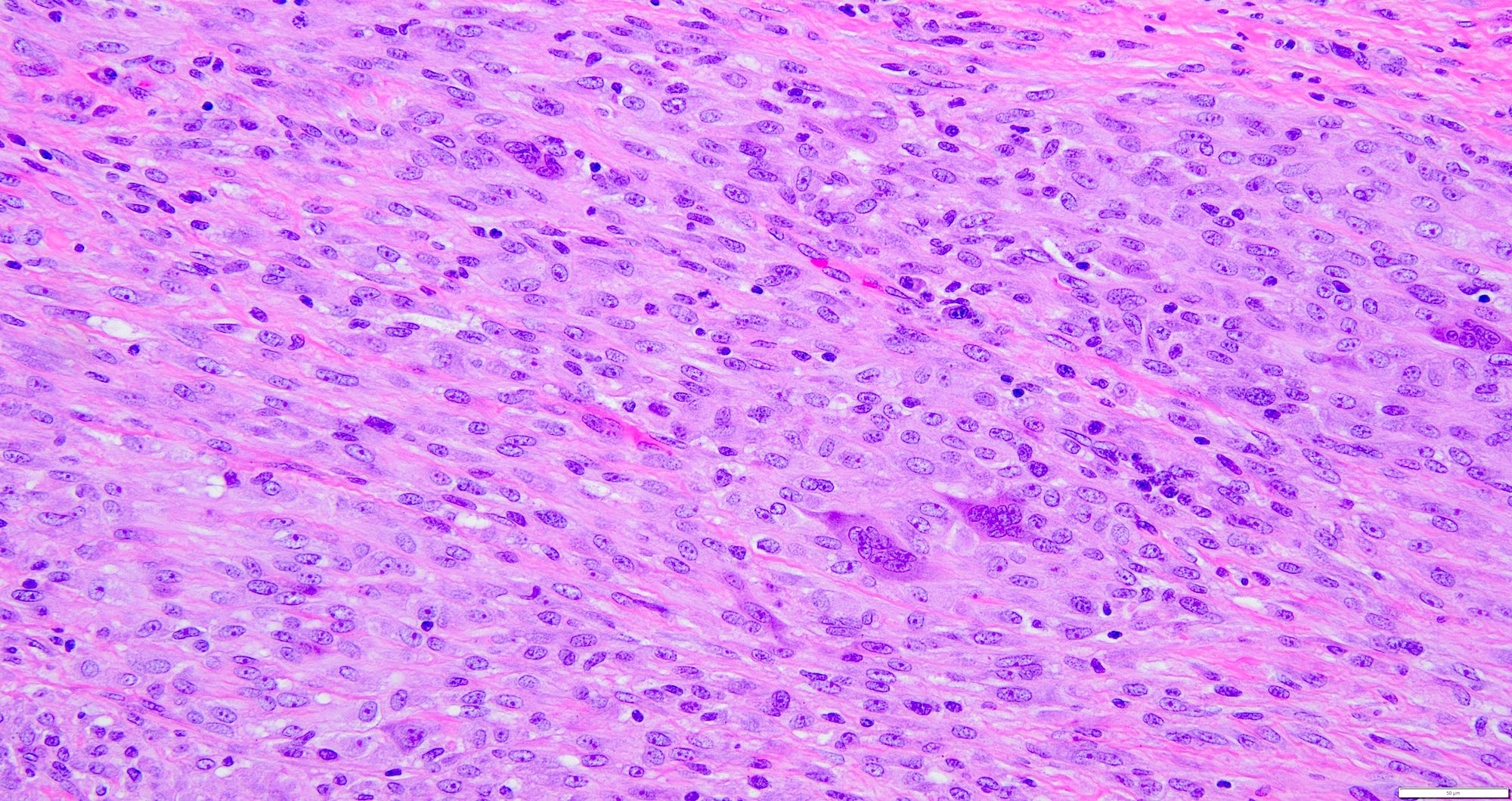
- Cells have minimal pleomorphism and atypia with no mitotic activity (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019)
- Tumor cells are spindled in shape with plump ovoid vesicular nuclei and pale eosinophilic cytoplasm, bland nuclei with vesicular chromatin and small single nucleoli (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354)
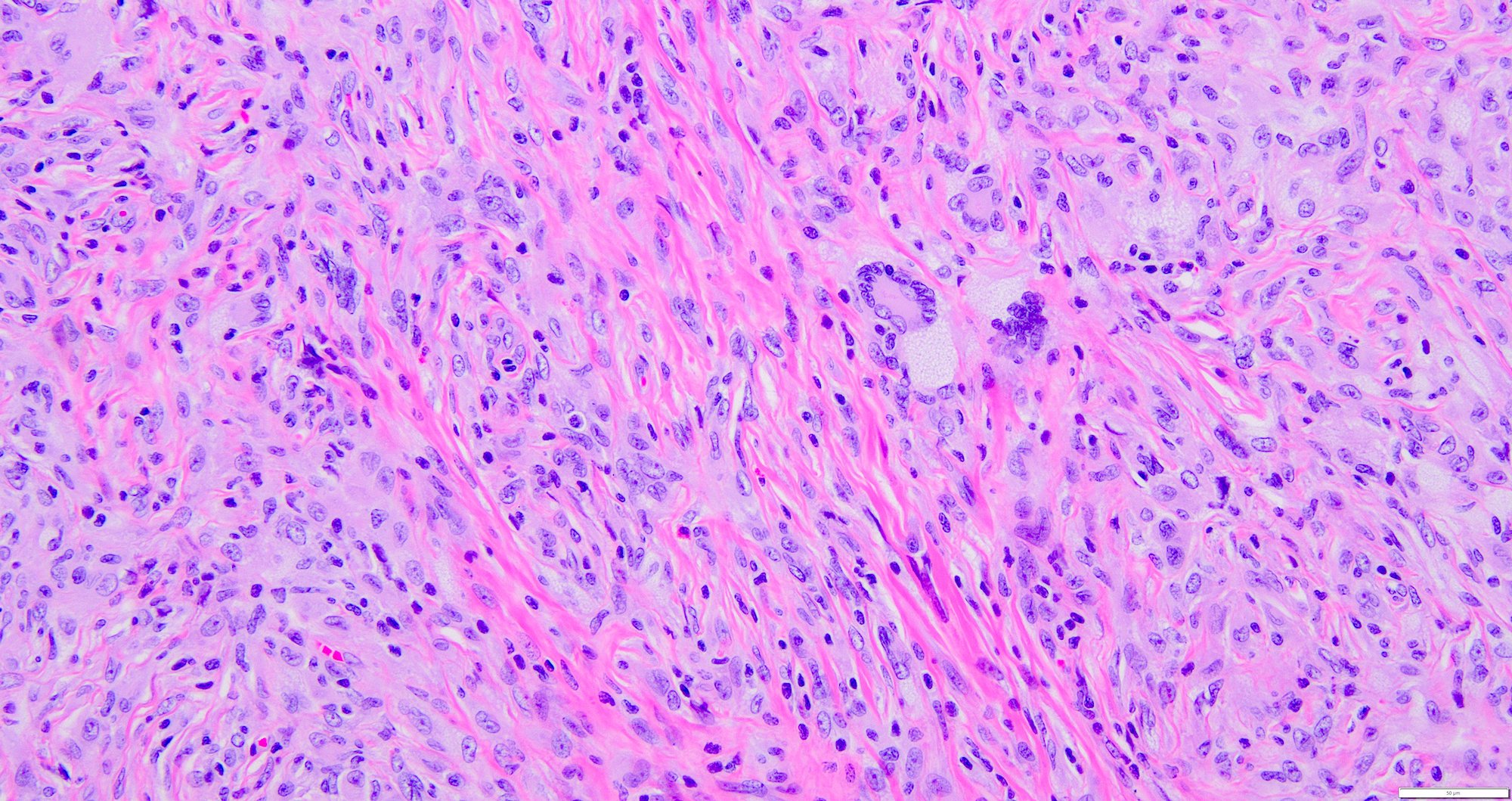
- Consists of monomorphic spindle cells in short intersecting fascicles arranged in a storiform pattern (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019, Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354)
- Branching, hemangiopericytoma-like vascular pattern can be seen (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354)
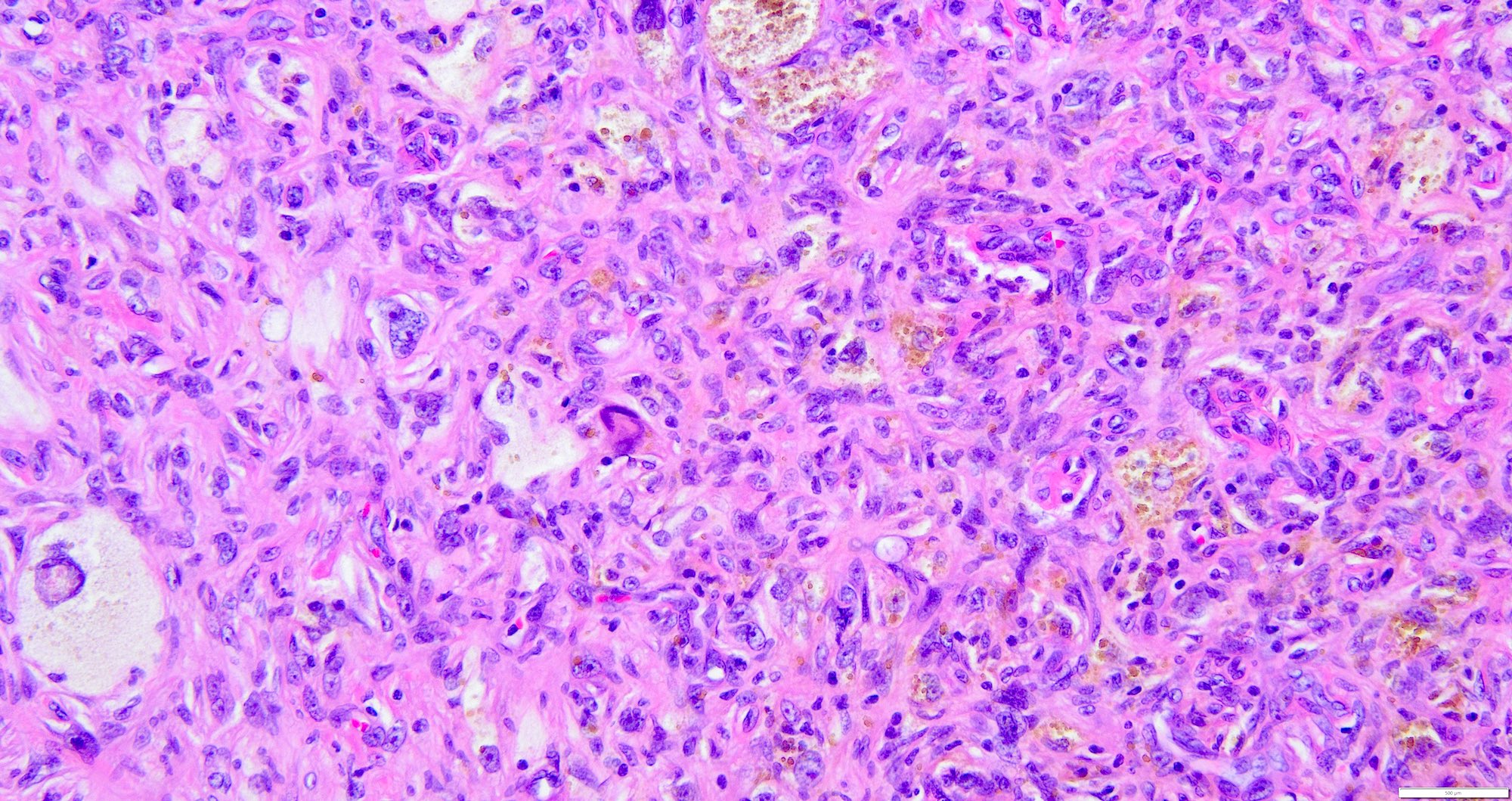
- Touton type giant cells with phagocytosed lipid and hemosiderin may be seen; however, nearly half of all deep fibrous histiocytomas are cytologically monomorphic, lacking the foamy histiocytes and giant cells that are often seen in cutaneous lesions (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019, Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354)
- Lymphocytes and a few xanthoma cells are dispersed throughout the lesion (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019)
- Hemorrhage, myxoid changes, cystic degeneration, central infarction is less frequent
- Interstitial or perivascular hyalinization is seen (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019, Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354)
- Median mitosis of 3/10 high power fields (HPF) is seen; lymphovascular invasion and tumor necrosis are rare (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354)
- Combined pericytic and fibrous histiocytic areas are seen in fibrous histiocytoma of the orbit (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019)
- Degenerative fibrous histiocytoma has pleomorphic cells with hyperchromatic nuclei, which are called monster cells (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019)
- Pleomorphism and increased mitosis may indicate an aggressive lesion, atypical fibrous histiocytoma or a superficial pleomorphic sarcoma (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019)
- Despite having increased cellularity and mitotic activity, cellular fibrous histiocytoma is still considered benign (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- No specific stains
- Factor XIIIa (81%)
- CD34 (positive in ~40% of cases, which is far more common compared to the cutaneous variant) (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354)
- SMA (69%) is occasionally positive
- CD68 (66%), CD163 (61%), S100 (3%) may be positive
- Podoplanin (D2-40) (100%), HMGA1 and HMGA2 (88%)
- Reference: Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019
Negative stains
- S100, SOX10 (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019)
- ApoD1 (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019)
- STAT6
- EMA (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354)
- Desmin (4%) is occasionally positive
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- PRKCB or PRKCD rearrangements
- Gains of chromosome 7 and 8q and loss of Xq in metastasizing fibrous histiocytomas and loss of 9 and 22 in atypical fibrous histiocytomas
- Cellular fibrous histiocytomas show rare gains in chromosome 20
- Metastasizing fibrous histiocytomas have CGH aberrations
- Reference: Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019
Videos
Cellular dermatofibroma and aneurysmal dermatofibroma
Sample pathology report
- Right thigh, excision:
- Deep fibrous histiocytoma (see comment)
- Comment: These are benign tumors with increased risk for local recurrence. Complete excision and clinical follow up is recommended.
Differential diagnosis
- Solitary fibrous tumor (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354):
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019, Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354):
- Small, slender nuclei, highly infiltrative margins, lymphocytes are not present scattered within the lesion
- CD34 diffusely positive
- Presence of PDGFB gene rearrangements
- Nodular fasciitis (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019):
- Loosely arranged bundles of proliferating myofibroblasts alternating with myxoid zones containing extravasated red blood cells (RBC) and inflammatory cells
- USP6 gene rearrangements
- Often positive for SMA
- Neurofibroma (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019):
- Sclerotic leiomyoma (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019):
- Storiform collagenoma (sclerotic fibroma) (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019):
- Hypocellular lesion
- Multifocal lesions are associated with Cowden syndrome
- Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (Weiss: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th Edition, 2019):
- Pleomorphic tumor cells
- Marked cytologic atypia
- Numerous mitoses
- Hemorrhage
- Necrosis
- IHC shows no specific line of differentiation
- Desmoplastic / spindle cell melanoma:
- Giant cell tumor of tendon sheath / giant cell tumor of soft tissue:
- Abundant giant cells, metaplastic bone may be seen (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354)
- Perineurioma (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354):
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 50 year old woman presents with a painless, gradually enlarging mass on her upper arm. Physical examination reveals a well circumscribed, firm, deeply located lesion. Histopathological examination of the excised lesion reveals spindle cell proliferation as depicted in the images above. Immunohistochemical staining is positive for CD34 (weak) and factor XIIIa, while negative for S100 and cytokeratins. Which of the following statements is correct regarding this type of lesion?
- Metastasis has been reported in 5% of cases in some series
- STAT6 is diagnostic for this entity
- These tumors only involve extremities
- These tumors rarely recur (< 1%)
Board review style answer #1
A. Metastasis has been reported in 5% of cases in some series, as this is a deep fibrous histiocytoma. Answer C is incorrect because in addition to extremities, these tumors can involve the head and neck, trunk and visceral soft tissue. Answer B is incorrect because STAT6 is not positive in fibrous histiocytoma. It is typically positive in solitary fibrous tumors. Answer D is incorrect because these tumors, when deep, recur in up to 20% of cases in some series.
Comment Here
Reference: Deep fibrous histiocytoma
Comment Here
Reference: Deep fibrous histiocytoma