Table of Contents
Definition / general | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Tranesh GA, Qu H. Other cysts. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticcystadenoma.html. Accessed January 7th, 2025.
Definition / general
Bronchogenic cyst
Cutaneous ciliated cyst
- Bronchogenic cysts presenting in the skin are very rare, with fewer than 70 cases reported
Cutaneous ciliated cyst
- Also called cystadenoma, cutaneous Müllerian cyst
- Usually extremities of teenage girls
- May have Müllerian derivation in females, distinct fetal eccrine duct origin in males
Epidemiology
Cutaneous ciliated cyst
- Solitary lesion which presents shortly after menarche on limb of young females (12 - 42 years)
- Also described in males and at atypical sites including back, shoulder, scalp, cheek
Sites
Bronchogenic cyst
Cutaneous ciliated cyst
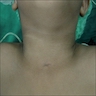
- Most are present at birth on the precordium or overlying the suprasternal notch
- Occasionally occur near shoulder, back, scapula, neck, abdomen or chin or present at a later age
Cutaneous ciliated cyst
- Thigh > buttock > calf > foot
Pathophysiology
Bronchogenic cyst
Cutaneous ciliated cyst
- Believed to form from buds or diverticula that separate from foregut during development of the tracheobronchial tree
- May be intrapulmonary or peripheral
- Cutaneous bronchogenic cysts may result from subsequent sequestration outside the chest cavity following fusion of the mesenchymal bars of the sternum or from active migration prior to fusion
Cutaneous ciliated cyst
- Lesions on limbs of young females are generally thought to be of Müllerian (paramesonephric) derivation, representing a migration abnormality of fetal development (heterotopia)
- Cysts arising at other sites and in males may represent metaplasia of lining of a pre-existent simple cyst of sweat duct derivation or have an entirely different histogenesis
Clinical features
Bronchogenic cyst
Cutaneous ciliated cyst
- 80% males
- Variable presentation as cutaneous cystic nodule, sinus or papillomatous growth
- Usually asymptomatic but may be tender or painful
- Rarely are multiple
- Treatment is surgical resection, if clinically indicated
Cutaneous ciliated cyst
- Located in deep dermis or subcutaneous tissue
- Usually asymptomatic
Case reports
Bronchogenic cyst
Cutaneous ciliated cyst
- 2 year old boy with scapular cyst (Dermatol Online J 2012;18:12)
- 21 year old woman with multiple cysts on neck and scalp (Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat 2008;17:69)
Cutaneous ciliated cyst
- 16 year old girl with cutaneous ciliated cyst on finger (Am J Dermatopathol 2012;34:335)
- 18 year old woman with cutaneous ciliated cyst over knee (J Cutan Aesthet Surg 2011;4:158)
- 48 year old woman with cystic lesion on right heel (Dermatol Online J 2011;17:6)
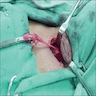
Treatment
Cutaneous ciliated cyst
- Surgical excision
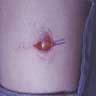
Clinical images
Gross description
Bronchogenic cyst
Cutaneous ciliated cyst
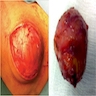
- Skin nodule
Cutaneous ciliated cyst
- Soft to cystic, solitary, movable, nontender, fluctuant swelling
Gross images
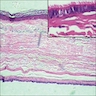
Microscopic (histologic) description
Bronchogenic cyst
Cutaneous ciliated cyst
- Cutaneous bronchogenic cyst occurs within dermis or subcutaneous tissue
- Lining is usually thrown into small folds
- Epithelium is invariably ciliated, pseudostratified cuboidal or columnar, with mucus secreting goblet cells in 50% of cases
- May have nonciliated cuboidal, columnar and stratified squamous epithelium
- Smooth muscle supports the mucosa in 8% of cases
- Lymphoid follicles are found in 25% of cases and appear to be part of a secondary inflammatory response
- Occasionally seromucinous glands or cartilage are present
- Cutaneous lung tissue heterotopia, in which fully developed bronchioles and alveoli are present, is considered a variant
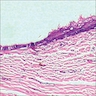
Cutaneous ciliated cyst
- Unilocular or multilocular cyst with intraluminal papillary projections of lining resembling fallopian tube
- Cuboidal to columnar ciliated epithelium with frequent pseudostratified foci
- Deep to the epithelium lie well vascularized parallel bundles of collagen but smooth muscle is not present
- Occasional: squamous metaplasia, intercalated dark cells
- Rare: mucin secreting cells, apocrine-like features
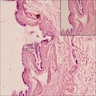
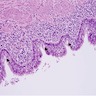
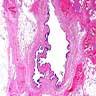
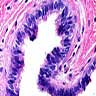
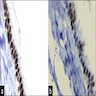
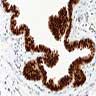
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Bronchogenic cyst
Cutaneous ciliated cyst
Cytology description
Bronchogenic cyst
- Ciliated columnar cells with abundant cytoplasm and eccentric nuclei in proteinaceous or clean background (J Cutan Aesthet Surg 2010;3:181)
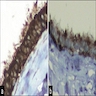
Positive stains
Negative stains
Bronchogenic cyst
Cutaneous ciliated cyst
Cutaneous ciliated cyst
Electron microscopy description
Cutaneous ciliated cyst
- Ultrastructurally, cilia have characteristic morphology with a central pair of microtubules, 9 radially orientated pairs of microtubules, basal bodies, cross striated rootlets
Differential diagnosis
Bronchogenic cyst
Cutaneous ciliated cyst
- Heterotopic rests
- Mature cystic teratoma
- Thyroglossal duct cyst
Cutaneous ciliated cyst
- Branchial and thymic cysts
- Bronchogenic cyst
- Mature cystic teratoma
- Thyroglossal duct
Additional references
Cutaneous ciliated cyst