Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Cox C, Zoumberos NA. Clear cell acanthoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticclearcellacanthoma.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign epidermal tumor, typically of the leg, with acanthosis and accumulation of glycogen in keratinocytes leading to pale staining cytoplasm
Essential features
- Benign intraepithelial tumor composed of pale staining, glycogen rich keratinocytes
- Pink to tan papule or plaque on the distal lower extremity of older adults
- Histologic features include bland, pale keratinocytes with abrupt transition to normal epidermis, often associated with psoriasiform hyperplasia with scattered neutrophils
Terminology
- Pale cell acanthoma (of Degos)
- Degos acanthoma
- Acanthome cellules claires of Degos and Civatte (StatPearls: Clear Cell Acanthoma [Accessed 21 July 2023])
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- 80% of cases on legs
- No gender proclivity
- Occurs most commonly between ages 50 and 70 (Dermatopathol 2020;7:26)
Sites
- Distal lower extremities of middle aged and older individuals
- Other sites reported, in order of frequency: trunk, especially back, abdomen, head, upper extremities (StatPearls: Clear Cell Acanthoma [Accessed 21 July 2023])
Pathophysiology
- Possible upregulation of KGF (keratinocyte growth factor)
- Defect in phosphorylase enzyme leads to intracellular glycogen accumulation
- Reference: Exp Dermatol 2006;15:762
Etiology
- Unknown
- Hypotheses
- Inflammatory epithelial hyperplasia (reactive)
- Produces similar cytokeratin as in psoriasis (Dermatopathol 2020;7:26)
- Associated with other inflammatory dermatoses, such as stasis dermatitis, bacterial and viral dermatoses, atopic dermatitis and insect bite reactions (Dermatopathol 2020;7:26)
- Variation of seborrheic keratosis
- Inflammatory epithelial hyperplasia (reactive)
Clinical features
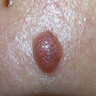
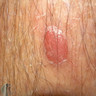
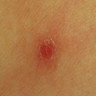
- Well demarcated, pink to brown papule or plaque
- Usually 0.5 - 2.0 cm in diameter
- Peripheral rim of scale and central erythema with puncta that bleed easily upon trauma
- Associated with crust from weeping
- Polypoid, pigmented and giant variants (up to 6 cm) have been described
- Dermoscopic findings
- Dotted blood vessels lined up in strings with white surrounding halo
- Vascular lines may be coiled (glomerular) or more rarely in a hairpin-like structure
- References: J Am Acad Dermatol 2015;72:S47, Dermatopathol 2020;7:26
Diagnosis
- Skin biopsy or excision
Case reports
- 22 year old woman with clear cell acanthoma with melanophages simulating a spitz nevus (Dermatol Pract Concept 2021;11:e2021089)
- 33 year old woman with clear cell acanthoma developing in epidermal nevus (J Dermatol 1997;24:601)
- 58 year old woman with erythematous lesion on the hard palate (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:535)
- 60 year old woman with clear cell acanthoma developing on a psoriatic plaque (Br J Dermatol 2000;142:842)
- 64 year old man with lower leg lesion and ichthyosis (Arch Dermatol 1972;105:371)
- 78 year old man with clear cell acanthoma with malignant cytologic features (Dermatopathol 2022;9:355)
Treatment
- Preferred management is with complete removal
- Location, size and number of lesions should be considered
- Methods
- Shave removal or curettage followed by electrofulguration
- Electrofulguration alone
- Surgical excision
- Cryotherapy or carbon dioxide laser (when there are multiple lesions)
- Reference: StatPearls: Clear Cell Acanthoma [Accessed 21 July 2023]
Gross description
- Well demarcated, pink to brown papule or small plaque
Microscopic (histologic) description
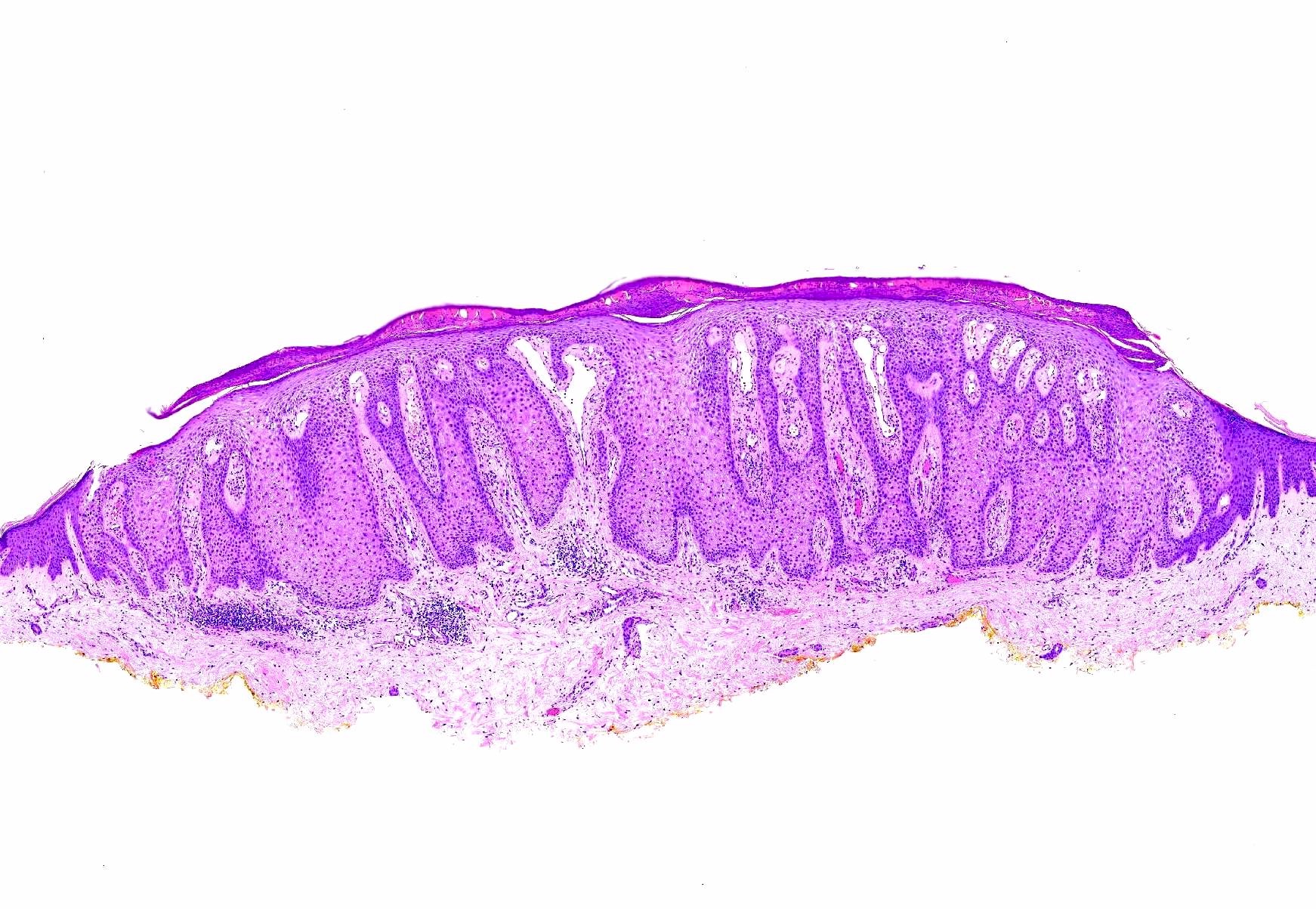
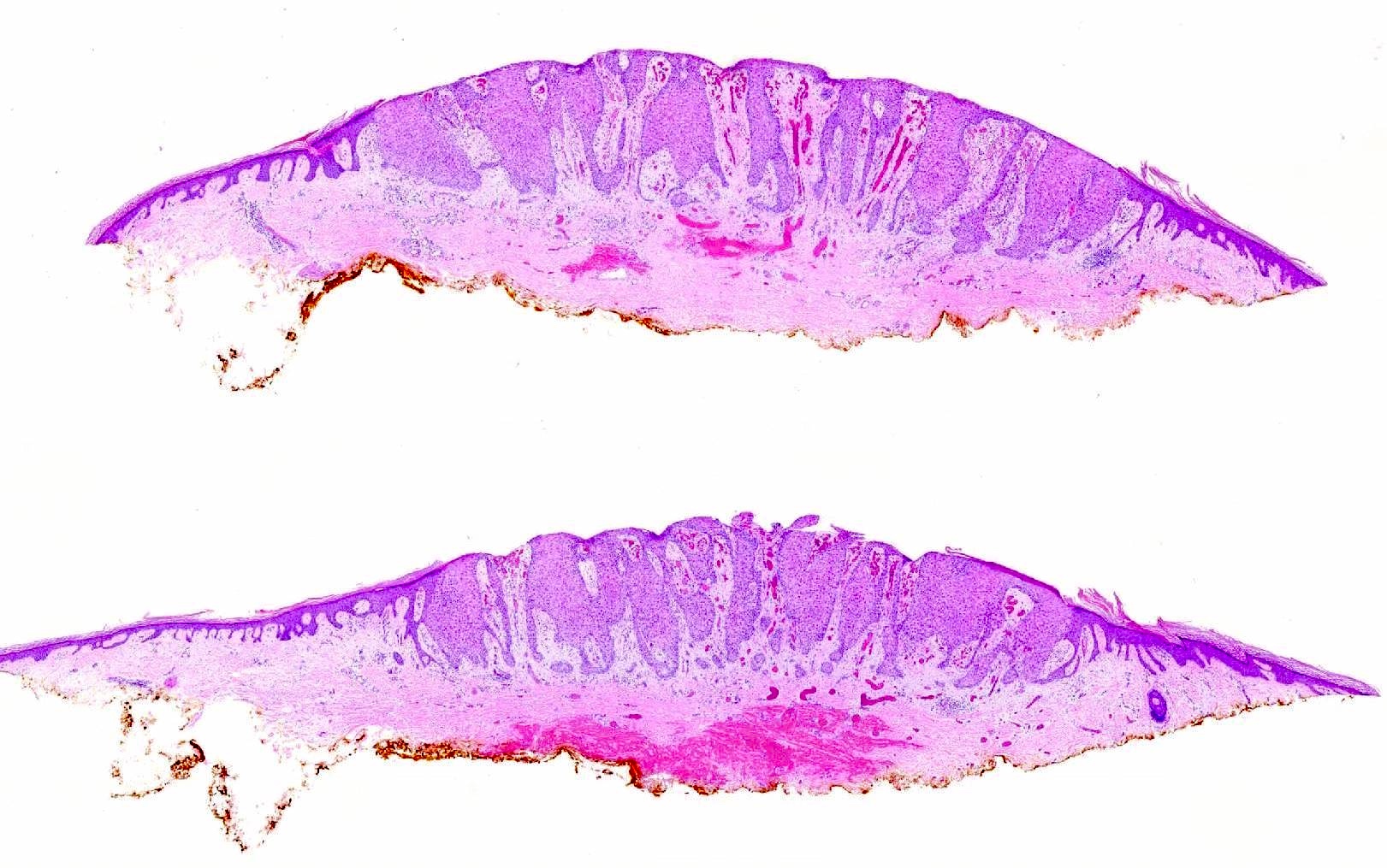
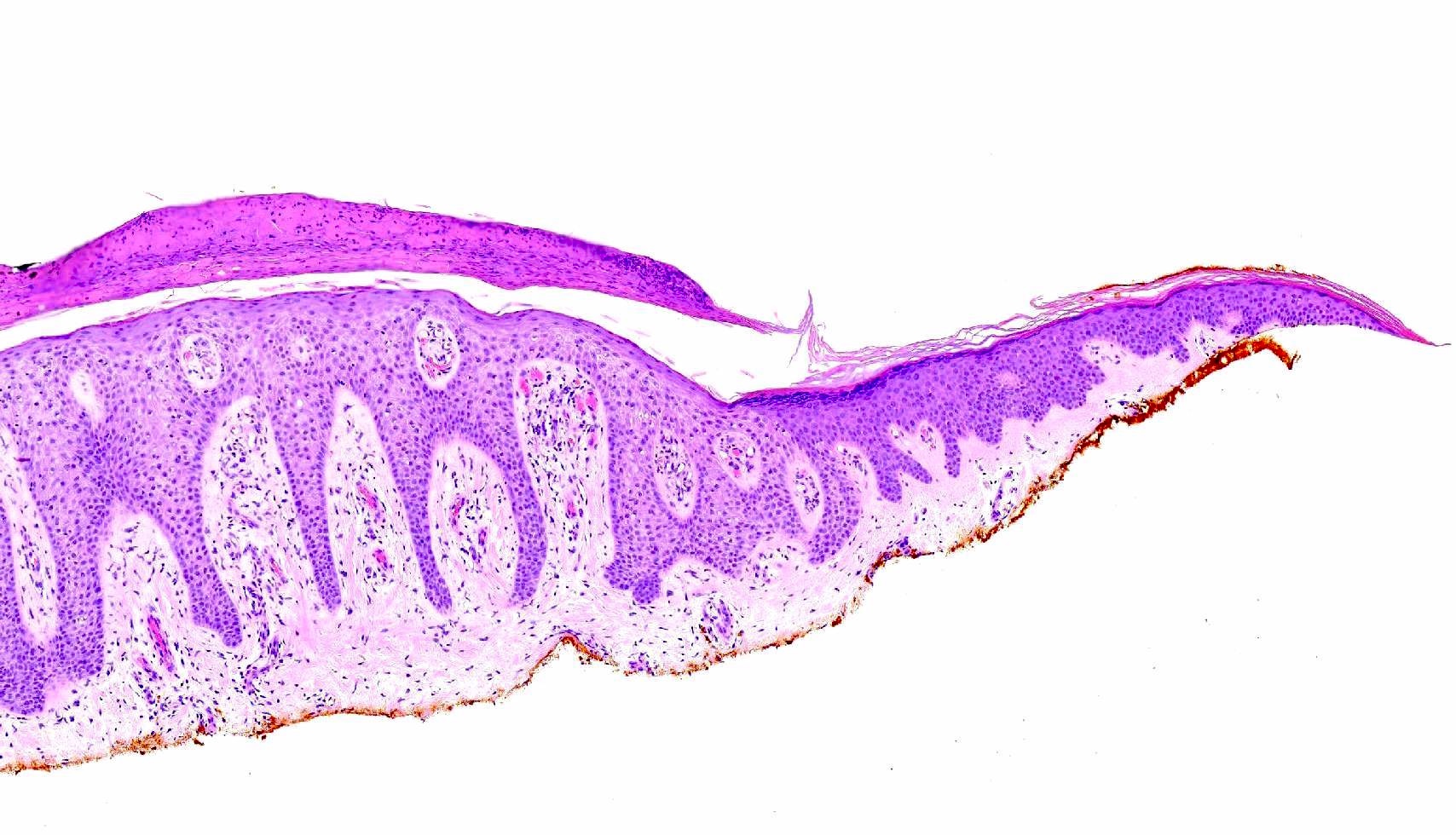
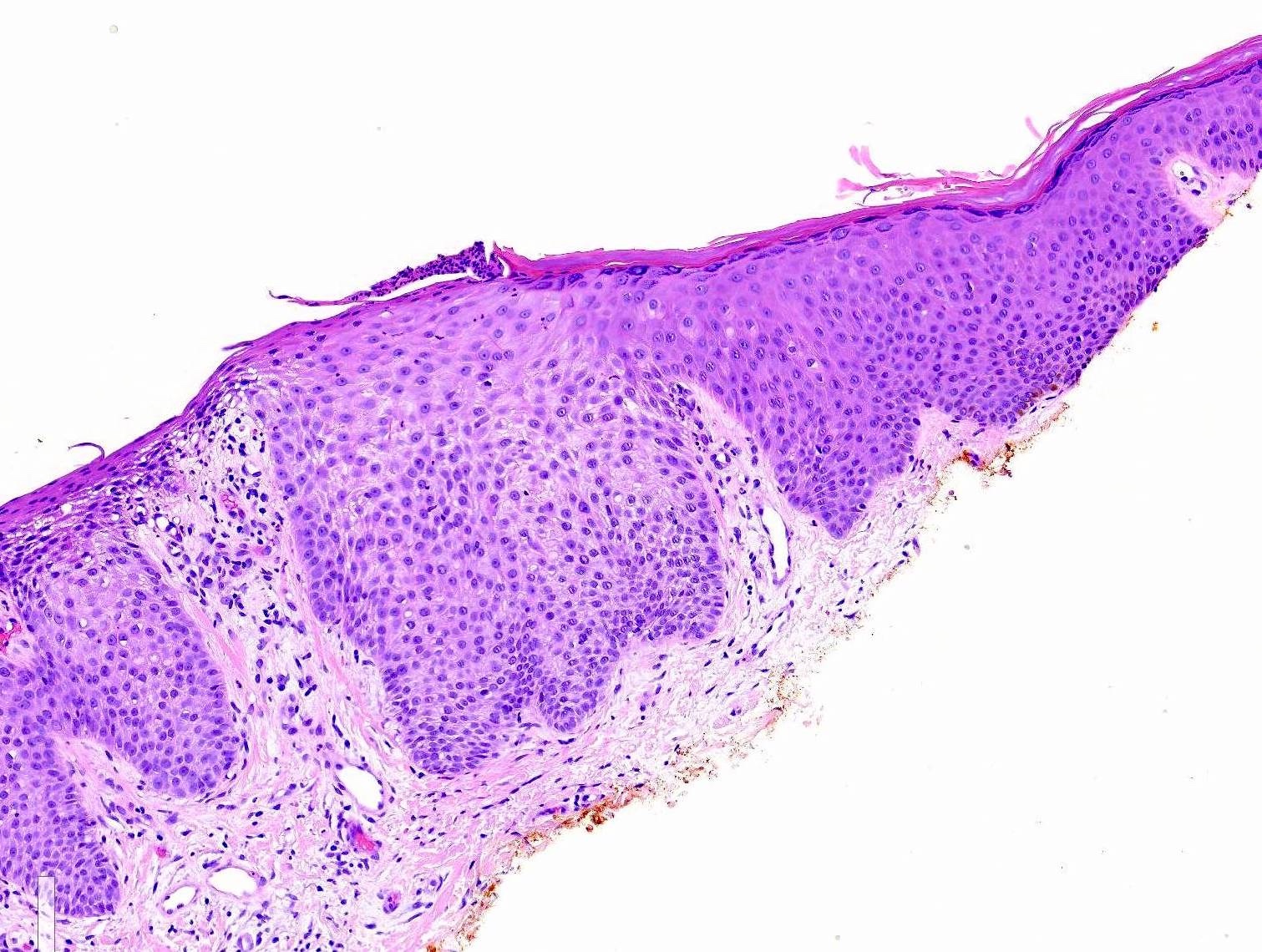
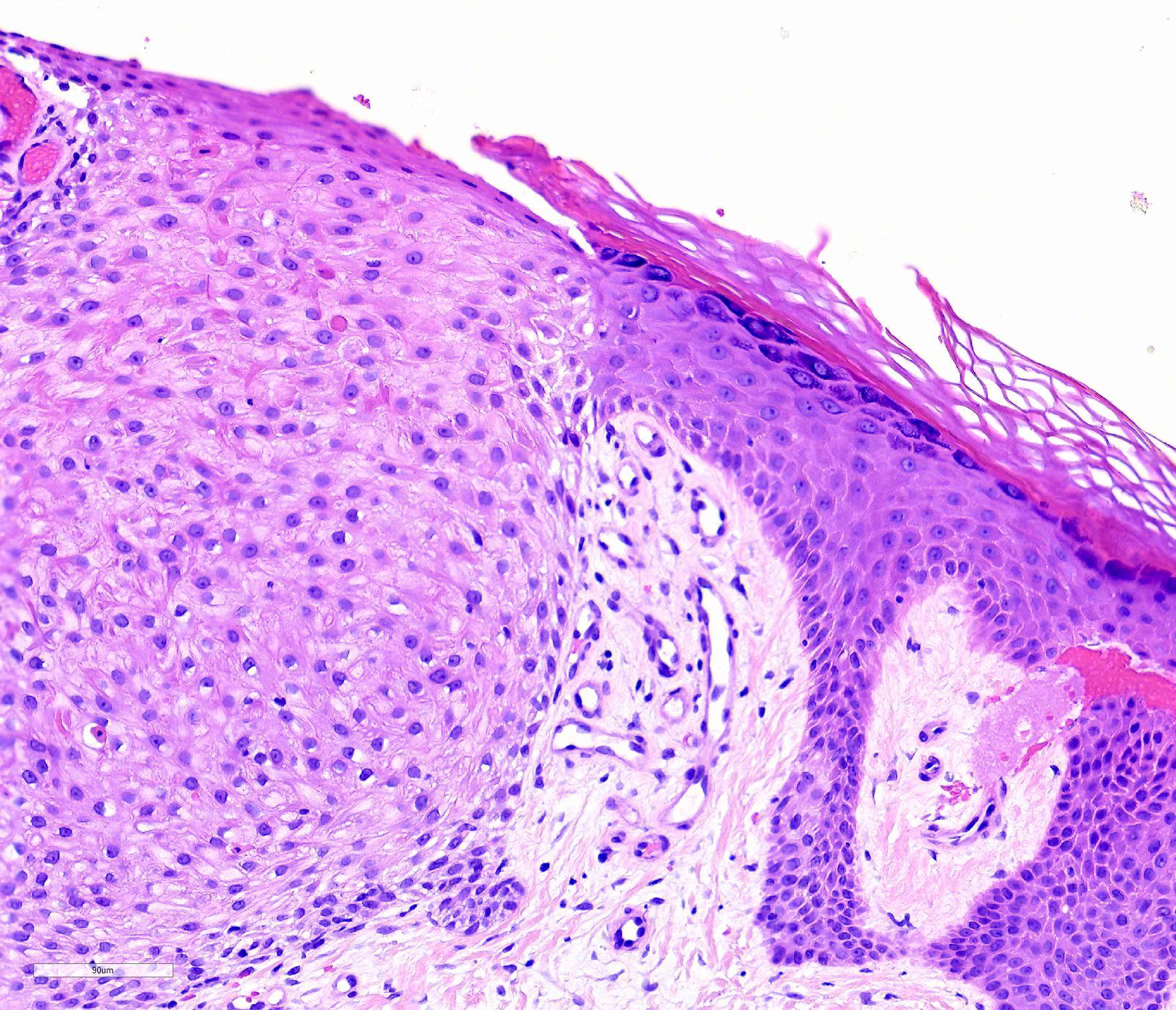
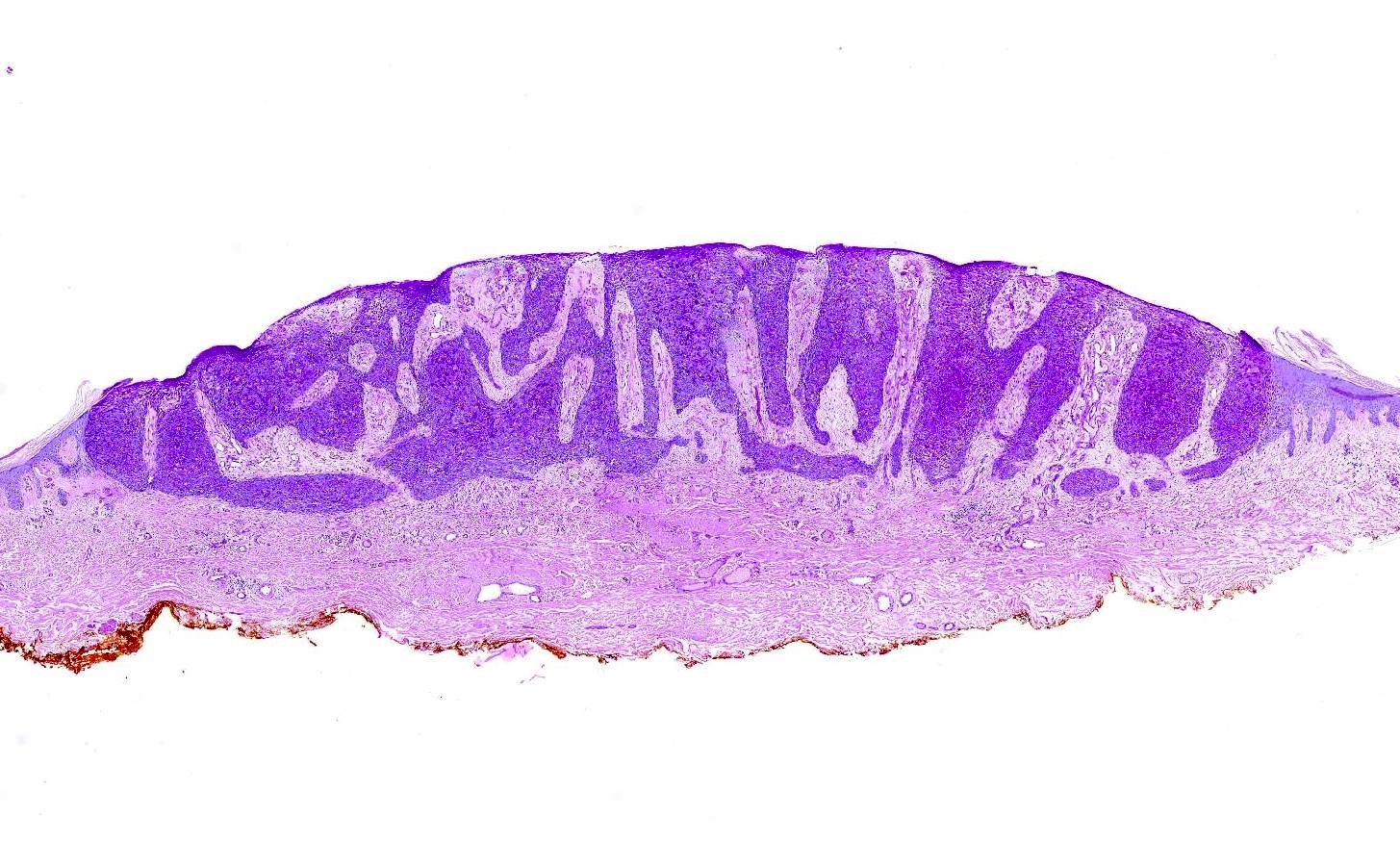
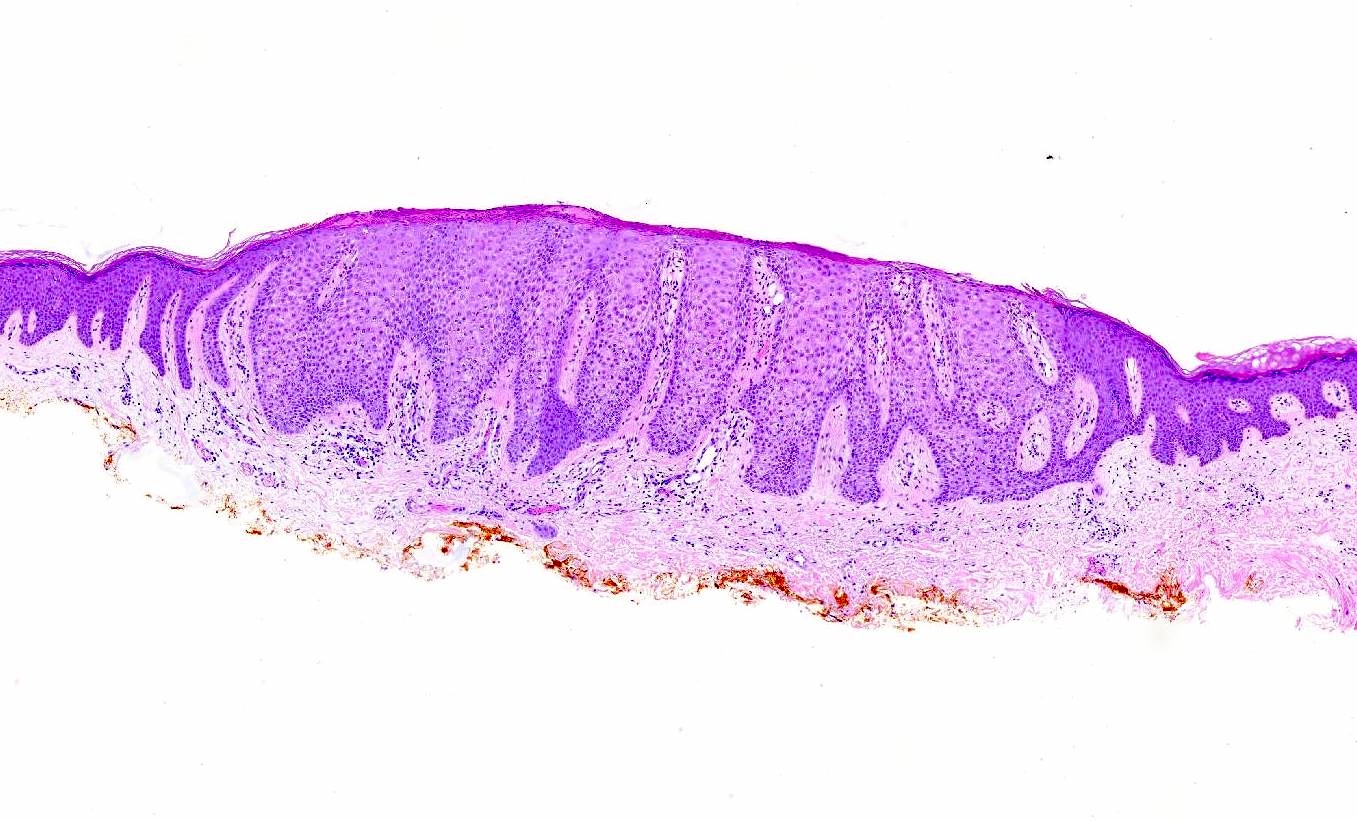
- Bland, intraepithelial tumor of clear, glycogen rich keratinocytes
- Abrupt transition to normal epidermis (Dermatopathology (Basel) 2020;7:26)
- Often in a pattern of psoriasiform hyperplasia
- Parakeratosis
- Typically lacks the thinning of the suprapapillary plate seen in psoriasis
- With or without colonization with melanocytes
- Often the vessels within the dermal papillae are dilated, tortuous and run vertically up the papillae
- Often spares hair follicles / adnexal structures
- Some cases have hyperplasia of underlying sweat ducts
- Reference: Dermatopathology (Basel) 2020;7:26
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- PAS (diastase sensitive due to glycogen accumulation)
- Keratin, filaggrin and involucrin
- Strong diffuse EMA (epithelial membrane antigen) positivity
- References: J Cutan Pathol 1988;15:27, Br J Dermatol 1967;79:249
Negative stains
- Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)
- Phosphorylase negative (cytochemical stain), except in the basal layer
- References: J Cutan Pathol 1988;15:27, Br J Dermatol 1967;79:249
Videos
Clear cell acanthoma
Sample pathology report
- Skin, right lower leg, biopsy:
- Clear cell acanthoma
Differential diagnosis
- Squamous cell carcinoma in situ:
- Squamous cell carcinoma in situ may have clear cell variant
- Cells are pleomorphic with increased N:C ratio
- Has full thickness atypia
- Psoriasis vulgaris:
- Elongation of rete ridges, thinning of suprapapillary plates
- Lymphocytic infiltrate in upper and middle portions of dermis
- Lacks the sharply demarcated lateral boundaries and glycogenation
- Lacks string-like arrangement of vessels on dermoscopy
- Seborrheic keratosis:
- Hyperkeratotic with horn pseudocysts
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
D. PAS. PAS stains glycogen in the keratinocytes. Answers A, B and C are incorrect because CEA, GMS and p16 are negative in clear cell acanthomas. p16 is often used as a surrogate for HPV, which is not identified in clear cell acanthomas. Answer E is incorrect because clear cell acanthomas are not of neural or melanocytic origin.
Comment Here
Reference: Clear cell acanthoma
Comment Here
Reference: Clear cell acanthoma