Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Case reports | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Electron microscopy description | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Tjarks J. Angiokeratoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticangiokeratoma.html. Accessed March 29th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign vascular lesion characterized by superficial vascular ectasia and overlying epidermal hyperplasia (acanthosis or hyperkeratosis)
- Lesions may be solitary or multiple / diffuse
- Five types with similar histology:
- Angiokeratoma of Mibelli: seen in children and adolescents on dorsum of toes and fingers
- Angiokeratoma of Fordyce: scrotal skin of elderly
- Angiokeratoma corporis diffusum: clustered papules in a bathing suit distribution; associated with Anderson-Fabry disease (X-linked recessive lysosomal storage disease)
- Angiokeratoma circumscriptum: least common type, usually congenital, associated with nevus flammeus, cavernous hemangioma
- Idiopathic solitary or multiple angiokeratomas
Essential features
- Benign vascular lesion
- Characterized by superficial vascular ectasia and overlying epidermal hyperplasia
- May occur in a variety of clinical settings
- Associated with Anderson-Fabry disease (X-linked recessive lysosomal storage disease)
Case reports
- 17 year old boy and 21 year old woman with solitary tumors (J Clin Diagn Res 2015;9:WD01)
- 39 year old man with a family history of Fabry disease (Dermatol Online J 2011;17:5)
- 72 year old man with multiple penile shaft eruptions (An Bras Dermatol 2015;90:150)
Gross description
- Small red to brown / black papule or nodule with verrucous surface, can be clustered
Microscopic (histologic) description
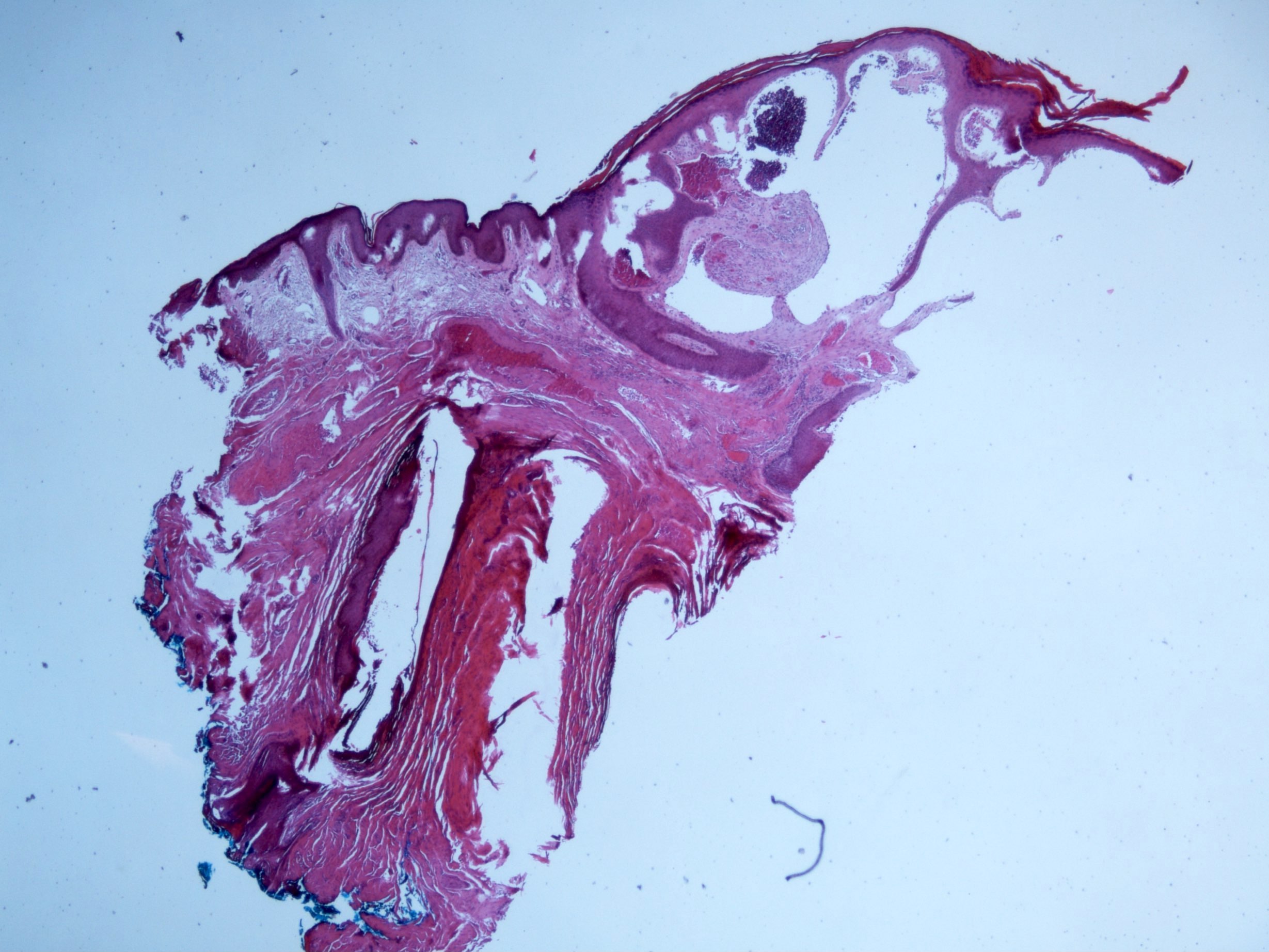
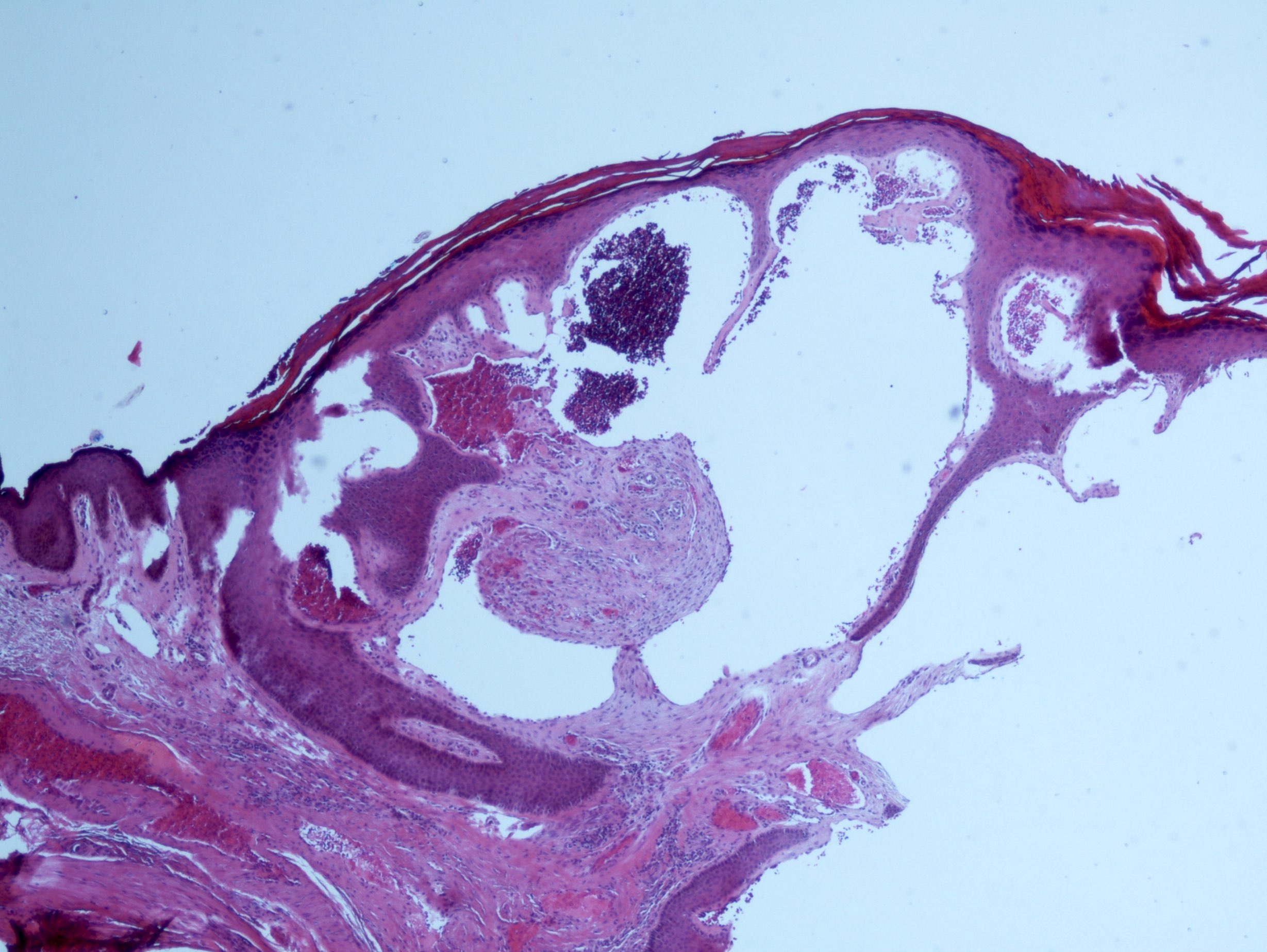
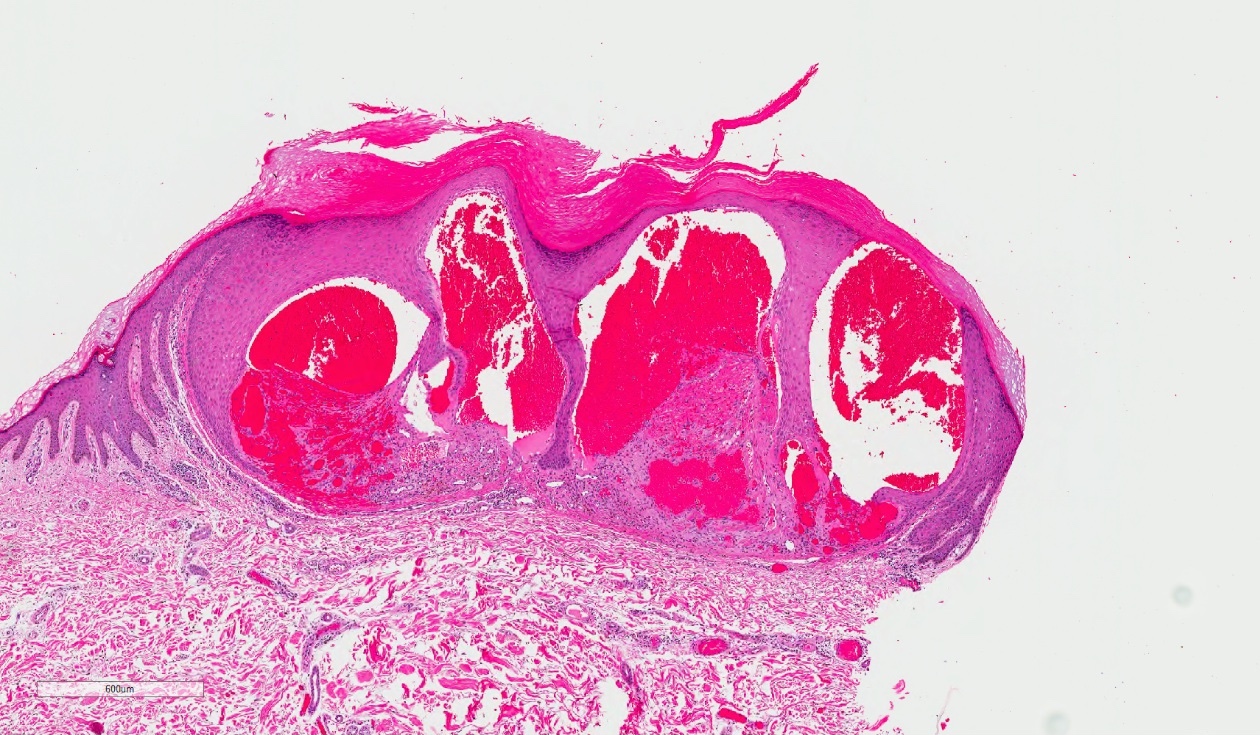
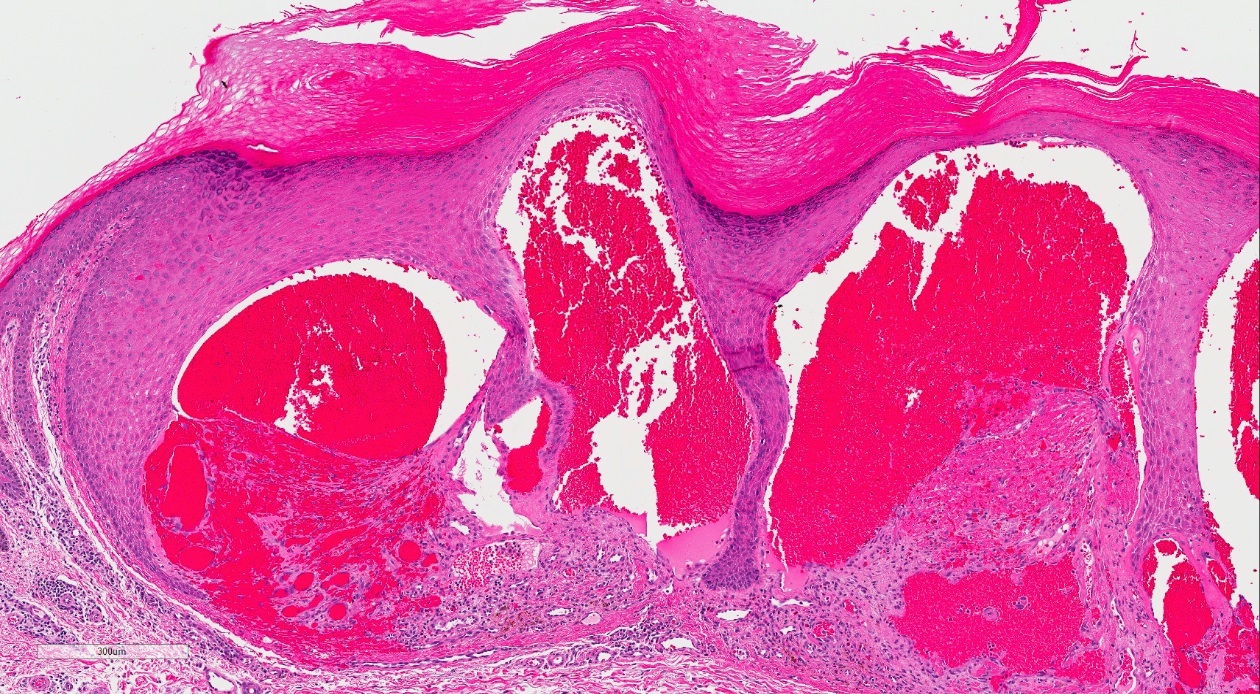
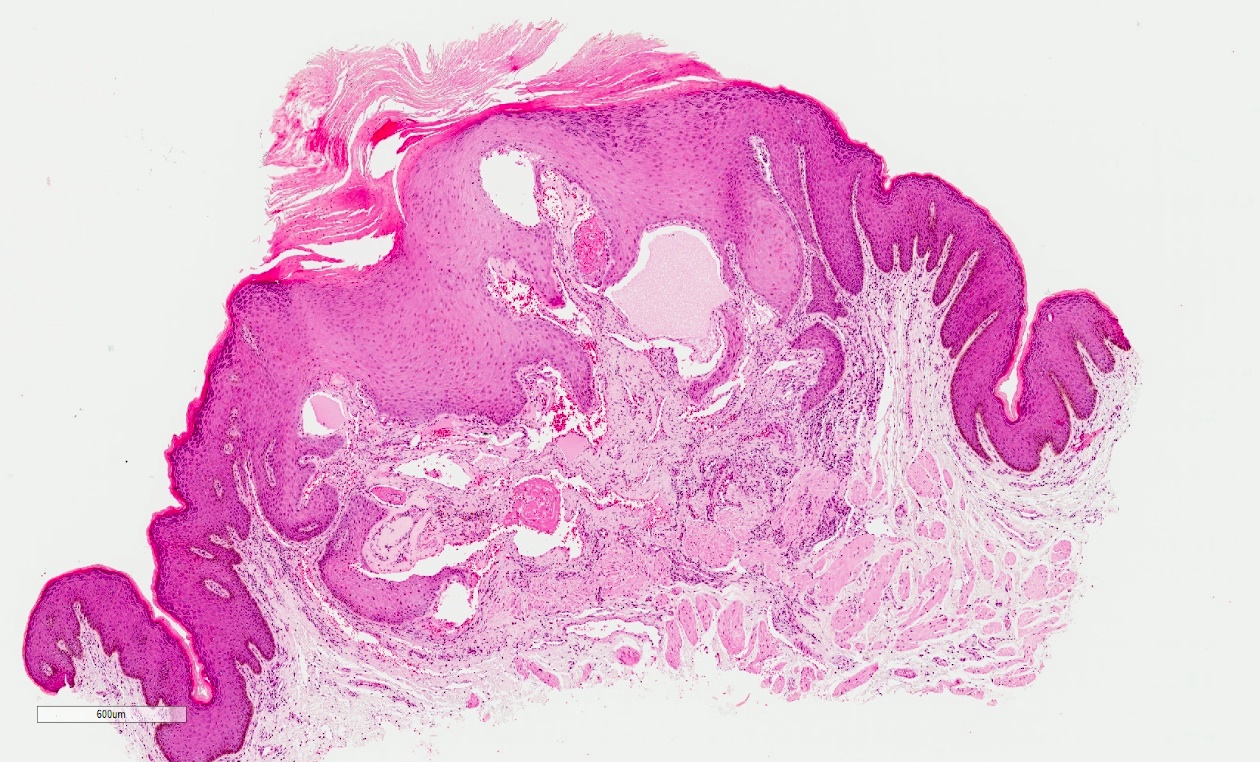
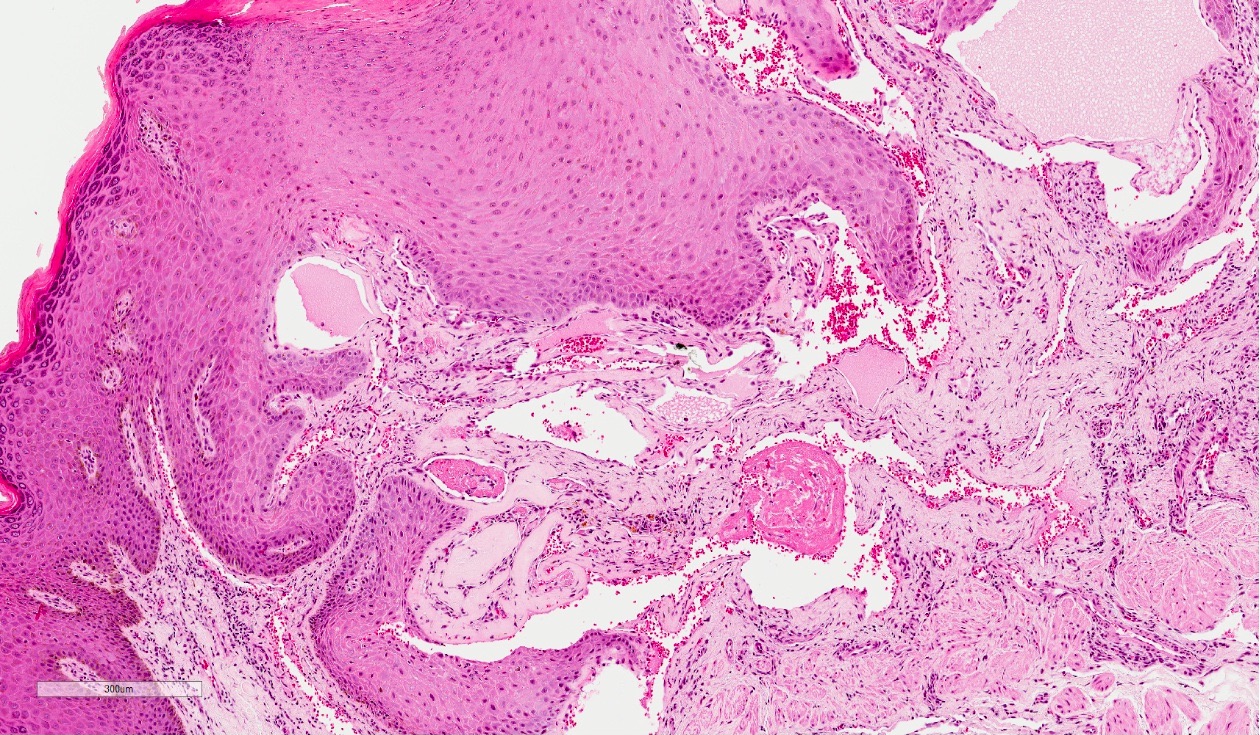
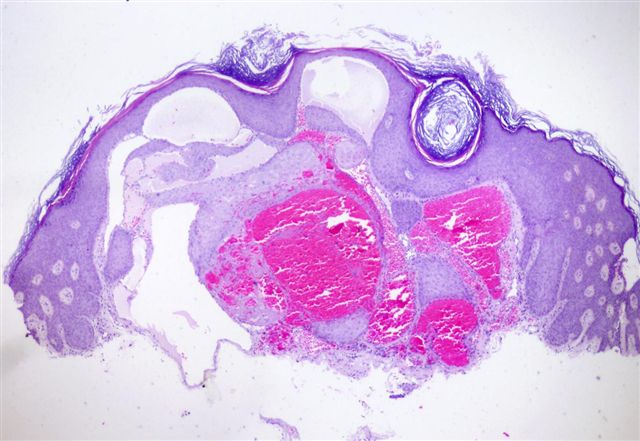
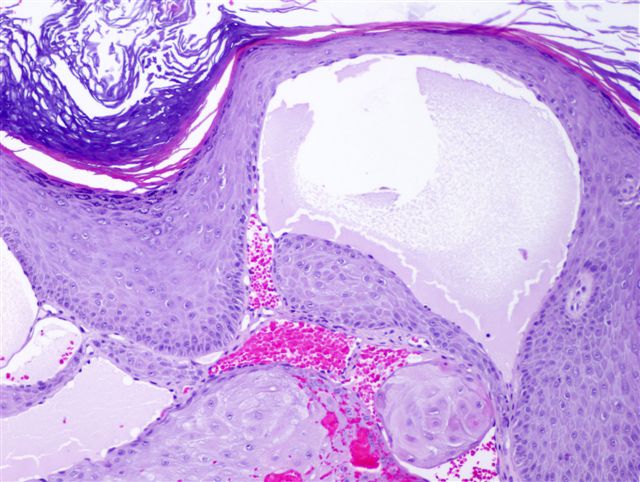
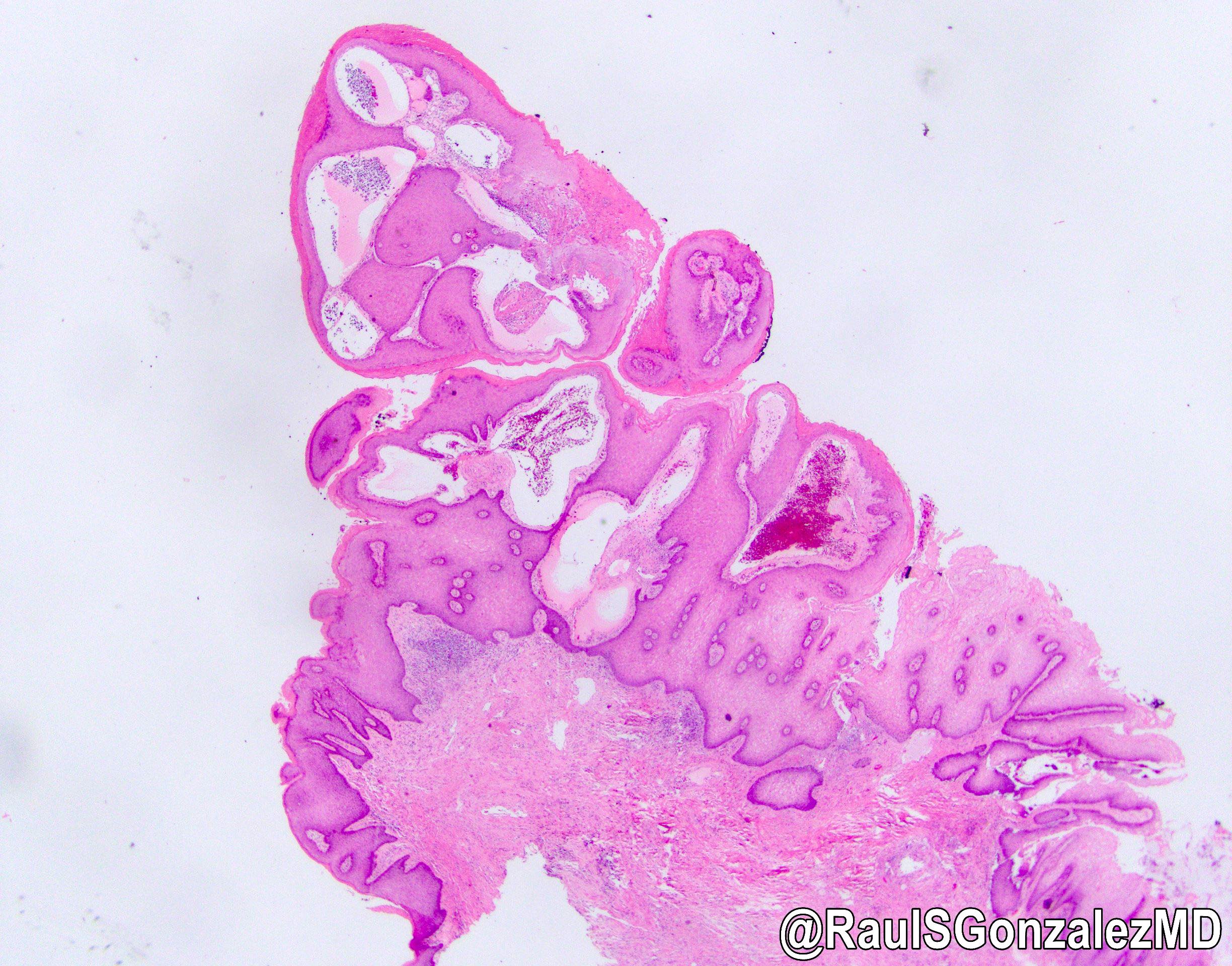
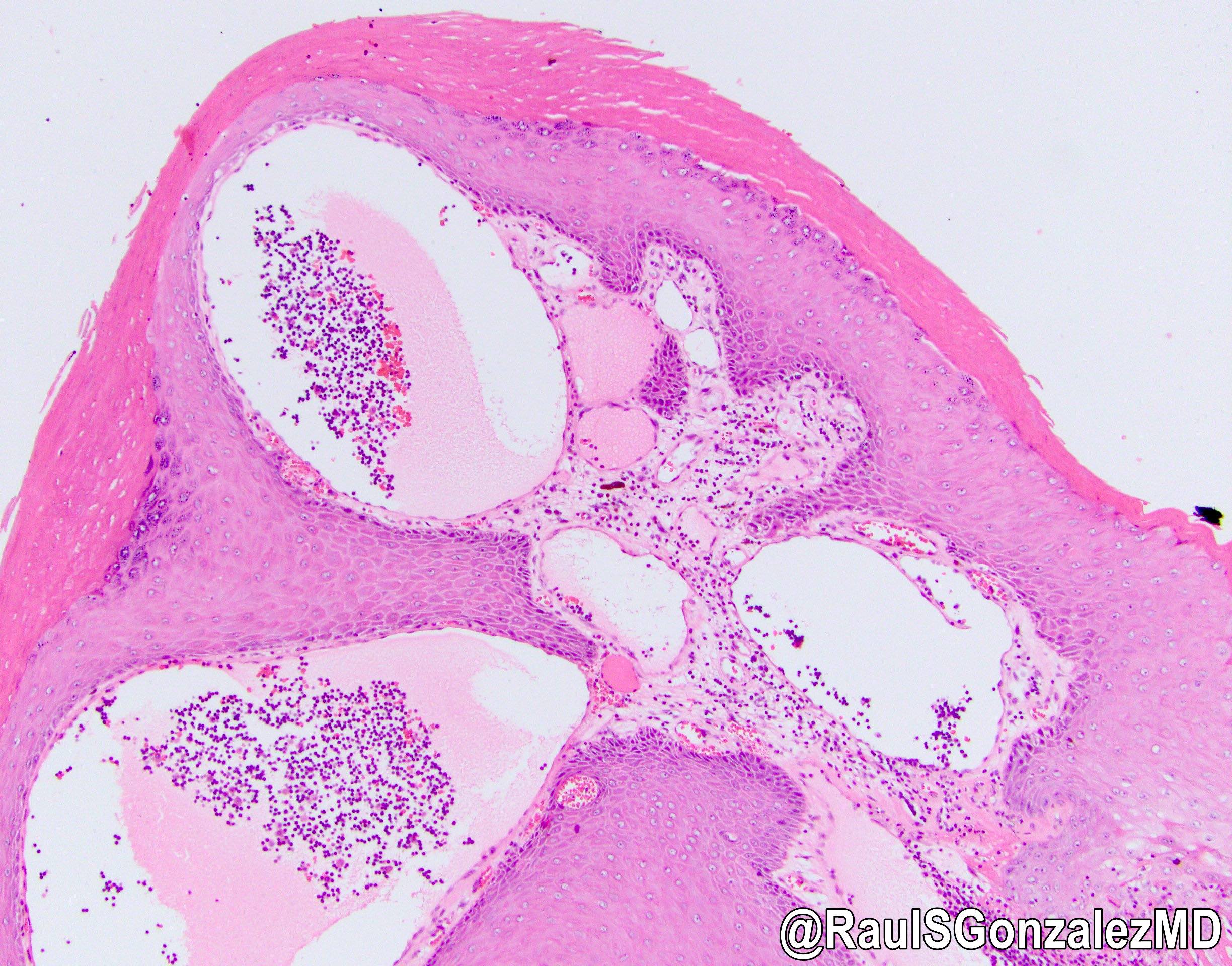
- Vascular ectasia of the papillary dermis which may appear to extend into the epidermis
- Overlying epidermal hyperplasia characterized by acanthosis, elongation of the rete and hyperkeratosis, with the epidermis encircling the dilated vascular spaces
- Often thrombosis within the vascular ectasia
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Sabrina C. Sopha, M.D, Joel Tjarks, M.D., Angel Fernandez-Flores, M.D., Ph.D. and @RaulSGonzalezMD on Twitter
Electron microscopy description
- In patients with Anderson-Fabry disease, see lipid bodies and lamellar inclusions in endothelial cells, pericytes and smooth muscle cells in angiokeratomas
Differential diagnosis
- Hemangioma (verrucous, lobular capillary, etc.)
- Lymphangioma
- Venous lake
- Clinical differential diagnosis may include pigmented / melanocytic lesions due to thrombosis