Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Nishinda H. Digital papillary adenocarcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticaggressivedigital.html. Accessed March 29th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Malignant adnexal tumor with a marked predilection of acral sites
- Helwig first described as eccrine acrospiroma in 1979 (J Cutan Pathol 1987;14:129)
Essential features
- Malignant adnexal tumor with a marked predilection of acral sites
- Usually fingers and toes, rarely palm and sole
- Clinically confused with a cystic lesion
- Tumor cells are basaloid / cuboidal to low columnar epithelial cells and myoepithelial cells with mild to moderate cytologic atypia
- Rarely, metastasis to lung and lymph node
Terminology
- Also called digital papillary eccrine adenoma, aggressive digital papillary adenoma, digital adenocarcinoma
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8408/3 - Digital papillary adenocarcinoma
Epidemiology
- About 200 cases reported (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1883, Dermatol Surg 2018;44:911, Ann Diagn Pathol 2015;19:381, J Am Acad Dermatol 2017;77:549, Br J Dermatol 2019;180:1150)
- 0.08 cases/1,000,000 (Dermatol Surg 2018;44:911)
- M:F = 74:20 (~4:1) (Dermatol Surg 2018;44:911)
- 14 - 83 years (average 52 years)
- Most common in Caucasians (Dermatol Surg 2018;44:911)
- Mortality in 2.1% (Dermatol Surg 2018;44:911)
Sites
- Usually digits (fingers and toes), rarely palm and sole, hands are more common (> 80%) than feet
- Rarely, face (2 cases), thigh (1 case) (Dermatol Surg 2018;44:911, Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95:e4110)
Pathophysiology
- Ultrastructural finding (see below) and eccrine glands are abundant in acral sites
- This is because digital papillary adenocarcinoma is an eccrine tumor
Etiology
- Some patients have trauma
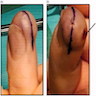
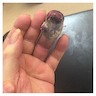
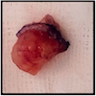
Clinical features
- Slow growing, asymptomatic nodule (average 1.7 cm, range: 0.4 - 4.3 cm)
- Clinically confused with a cystic lesion, ulceration is rare
- Pain may occur if the tumor involves the underlying bone, joint, nerves
- Rarely, metastatic disease (lung, lymph node) (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1883, J Am Acad Dermatol 2017;77:549)
Diagnosis
- Clinically, may be suspected from the site of origin and clinical course
- Histologic examination of tissue provides a definitive diagnosis
Prognostic factors
- Local recurrence and metastasis are 5 - 21% and 26 - 50%
- Histopathological features appear not to be predictive
- Delayed occurrence of metastases and a protracted course, long term follow up is necessary (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1883)
Case reports
- A man in his 20s (Dermatol Online J 2018;24)
- 53 and 65 year old men (Int J Dermatol 2017;56:1061)
- 54 year old Indian man with heel tumor (Clin Med Insights Case Rep 2019;12:1179547619828723)
- 67 year old right hand dominant man (Case Reports Plast Surg Hand Surg 2019;6:29)
- 89 year old Caucasian man (Dermatol Surg 2019 Sep 26 [Epub ahead of print])
Treatment
- Complete excision or amputation of the affected digit
- Sentinel lymph node biopsy may translate into decreased local recurrence and metastasis (S Afr Med J 1989;76:593)
- The role of chemotherapy remains unclear (J Clin Oncol 2013;31:e386)
- Radiation can be used effectively at conventional palliative doses (J Clin Oncol 2013;31:e386)
- FGFR or BRAF targeted therapy may be useful (Br J Dermatol 2019;180:1150, Ann Diagn Pathol 2015;19:381)
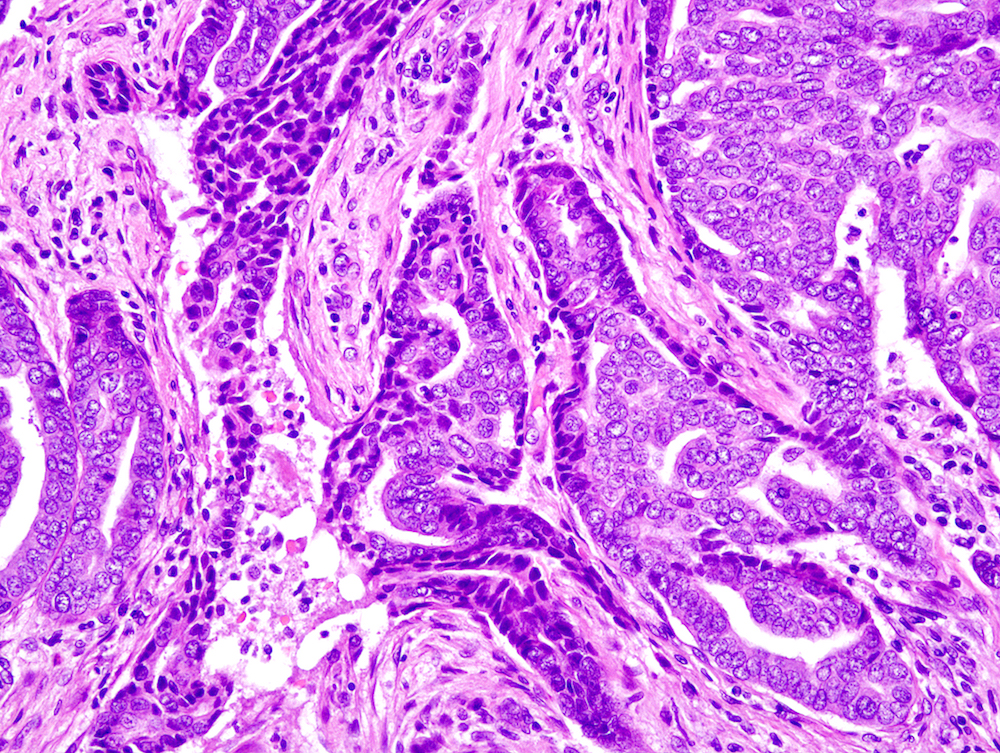
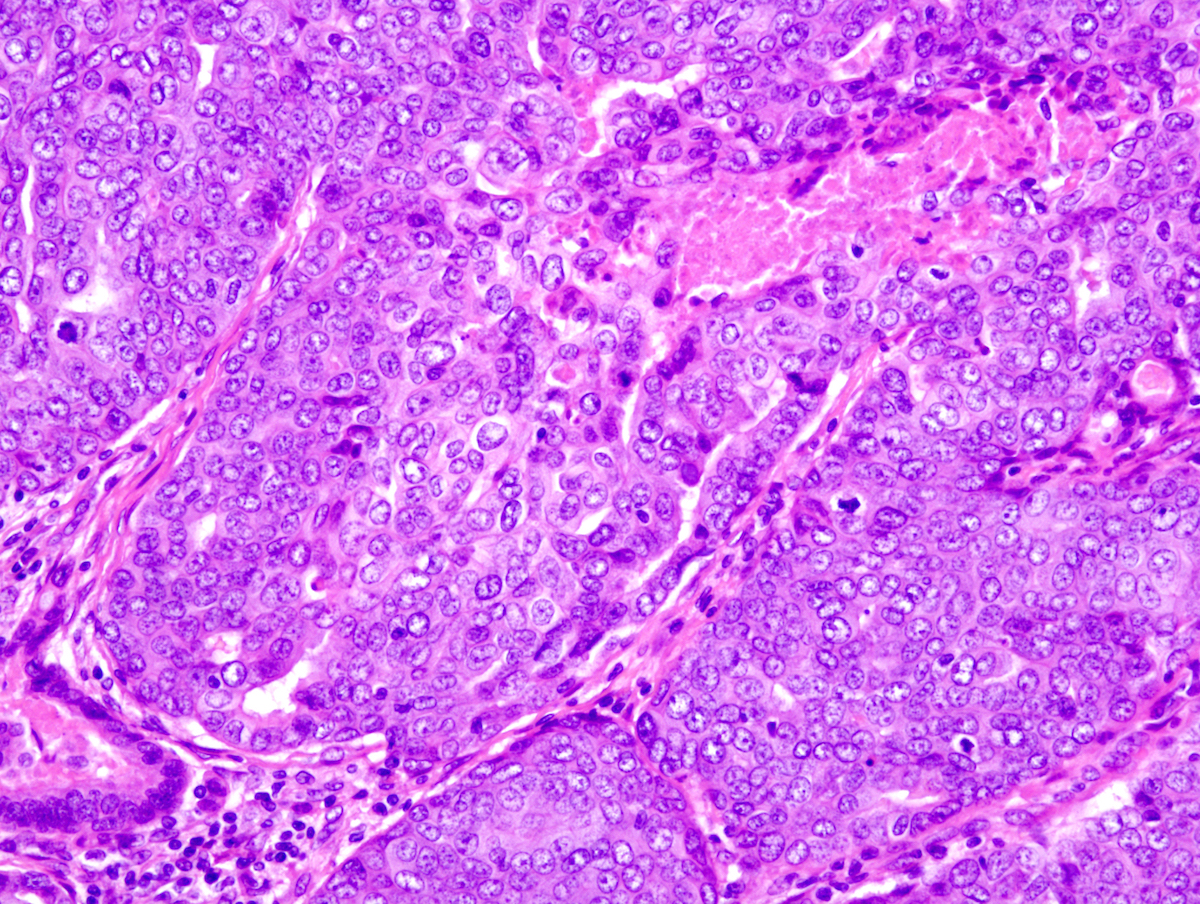
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Well circumscribed multinodular tumors within dermis and superficial subcutis
- Solid and cystic portions, papillary projections, tubular or ductal structures (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1883)
- Occasionally show infiltrative margin
- Uncommonly epidermal hyperplasia (3/31), ulceration (2/31), focal epidermal connection (1/31) (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1883)
- Tumor cells are basaloid, cuboidal to low columnar epithelial cells and myoepithelial cells with mild to moderate cytologic atypia
- Severe cytologic atypia (3/31) and tumor necrosis (6/31) is noted in a small subset of tumors (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1883)
- Mitoses may be inconspicuous or frequent (1 - 15 mm2) (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1883)
- Spindle cell, squamoid differentiation, clear cell changes may be encountered (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1883)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Pancytokeratin, CK7 diffusely positive
- S100 protein, ER, PR, AR in 50% of cases (J Am Acad Dermatol 2017;77:549)
- Inner cell layer: EMA, CEA (highlights luminal border of tubules) (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1883)
- Myoepithelial cell (outer cell) layer: SMA, calponin, p63, focally D2-40, CK14
Electron microscopy description
- Ultrastructural studies demonstrated three types of neoplastic cells: clear cells, dark cells and myoepithelial cells
- Some dark cells have dense granules (J Cutan Pathol 1987;14:129)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- BRAFV600E (1/9) (Ann Diagn Pathol 2015;19:381)
- Tumor overexpression of FGFR2 (6/6) (Br J Dermatol 2019;180:1150)
Sample pathology report
- Skin, left ring finger, punch biopsy:
- Digital papillary adenocarcinoma (see comment)
- Comment: The histopathological examination shows a well circumscribed multinodular tumor within the dermis to superficial subcutis. It shows solid and cystic portions with focal papillary projections and tubular structures. Two cell layers are present; inner cells are cuboidal epithelial cells with mild to moderate cytologic atypia and outer cells are myoepithelial cells. Some mitoses are seen (1 - 3 mm2). The inner layer is immunoreactive for EMA and CEA which highlighted the luminal border of tubules. The myoepithelial cell (outer cell) layer is positive for SMA, calponin and p63. These histologic features are consistent with digital papillary adenocarcinoma.
Differential diagnosis
- Hidradenoma:
- Lack of papillary structures and cytologic atypia
- Diffuse immunohistochemical positivity for p40 and p63; absence of S100 and SMA
- Fusion gene CRTC1/MAML2 detected in 50% (particularly in those with clear cell features) or CRTC3/MAML2 (Am J Surg Pathol 2019 Dec 23 [Epub ahead of print], Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2007;46:559, Hum Pathol 2017;70:55)
- Papillary eccrine adenoma:
- Rare or absent solid areas
- Absence of infiltrative growth pattern, significant cytologic atypia and pleomorphism
- Mitoses are usually absent but can be scant (Am J Surg Pathol 2019 Dec 23 [Epub ahead of print])
- Apocrine hidrocystoma / apocrine cystadenoma:
- Exceptionally rare on the distal extremities
- Cytologic atypia in cystic and papillary tumors on the distal extremities exclude this diagnosis (Surg Pathol Clin 2017;10:383)
- Microcystic adnexal carcinoma:
- infiltrative growth in a desmoplastic stroma
- Predominantly duct differentiation (Surg Pathol Clin 2017;10:383)
- Hidradenocarcinoma:
- Lack of two cell layers (Surg Pathol Clin 2017;10:383)
- Epithelial myoepithelial carcinoma / adenomyoepithelial carcinoma (tumor):
- Controversial; past reported cases might include epithelial myoepithelial carcinoma or adenomyoepithelial carcinoma
- These tumors are very rare; there are not enough cases to distinguish them
- Further examination is needed by correcting many cases (Dermatol Pract Concept 2014;4:33, J Dermatol 2018;45:357)
- Controversial; past reported cases might include epithelial myoepithelial carcinoma or adenomyoepithelial carcinoma
- Metastatic adenocarcinoma:
- Lack of two cell layers (especially myoepithelial cell) (Pathology 2013;45:55)
Additional references
Board review style question #1
- A 56 year old man presented with a tumor on his middle finger. The tumor shows solid and cystic areas with focal papillary projections and tubular structures. Which of the following is most likely the correct diagnosis?
- Apocrine hidrocystoma
- Bowen disease
- Digital papillary adenocarcinoma
- Hidradenoma
- Papillary eccrine adenoma
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
- Which of the following is true about digital papillary adenocarcinoma?
- Dual layered cystic structures are characteristic
- It arises only in digits
- It does not occur in young people
- Tumor does not show metastasis
Board review style answer #2
A. Dual layered cystic structures are characteristic
Reference: Digital papillary adenocarcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Digital papillary adenocarcinoma
Comment Here