Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Albahra S, Hosler GA. Desmoplastic melanoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumormelanocyticdesmoplasticmelanoma.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rare desmoplastic / fibrosing variant of spindle cell melanoma with > 90% stroma / collagen
Essential features
- Often amelanotic and mistaken for nonmelanocytic lesion, such as scar
- Prognosis variable, dependent on presence of conventional melanoma
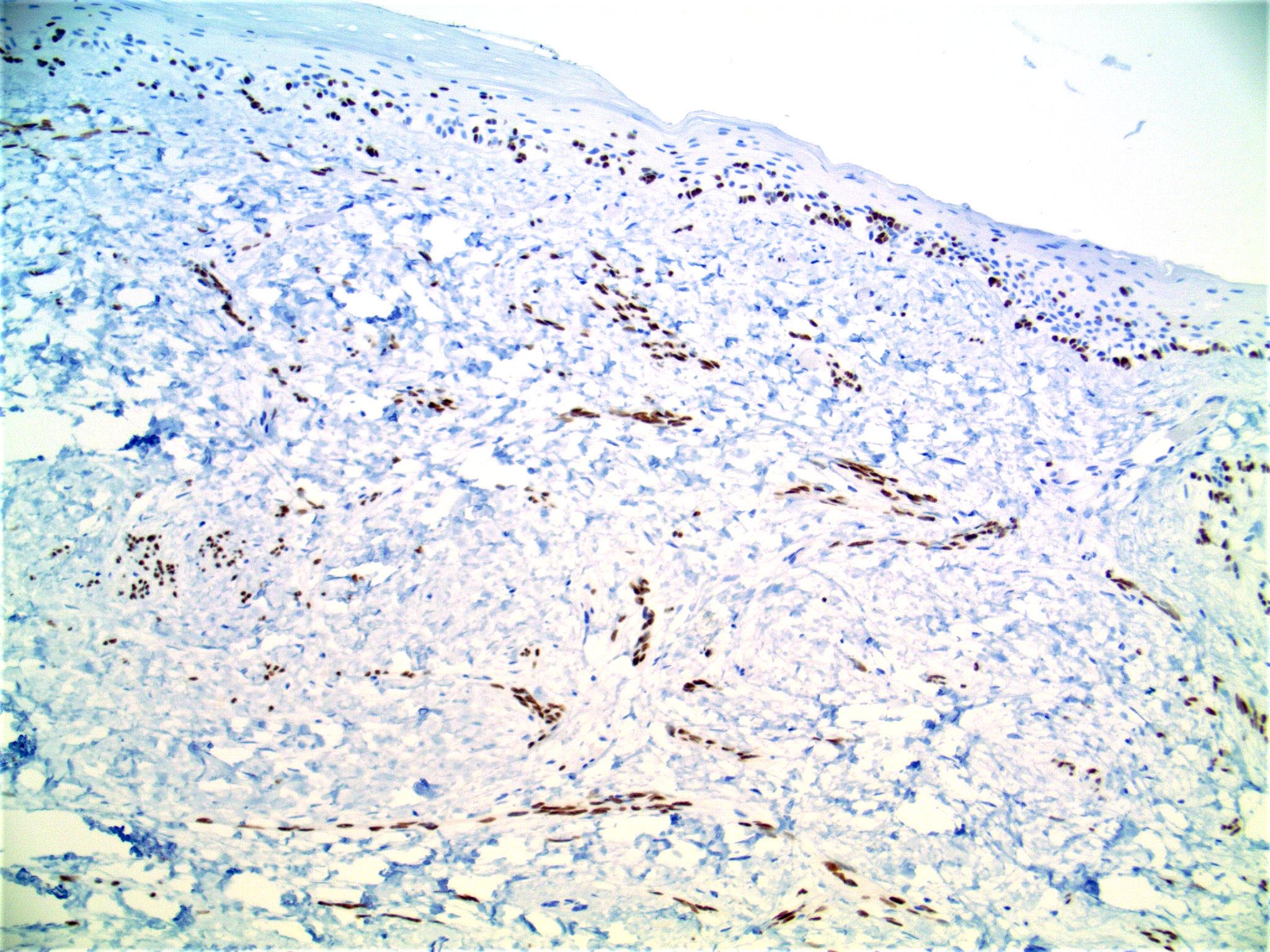
- Positive for SOX10 and S100 but often negative for other melanocytic markers
- Nodular lymphoid aggregates are a useful clue
Terminology
- Pure form: tumor predominantly / entirely desmoplastic (≥ 90%)
- Mixed form: significant component of conventional melanoma (> 10%)
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- < 1% of all melanomas
- Mean age: 61 (Cancer 1998;83:1128)
- M > F (2:1) (J Am Acad Dermatol 2013;68:825)
Sites
- Head and neck region most common
Pathophysiology
- Unclear
- Many have NF1 loss of function mutations (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1357)
- NFKBIE promoter mutations common (Nat Genet 2015;47:1194)
Etiology
- Unclear
- Mostly arises in a background of severe sun damage
Clinical features
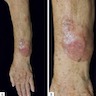
- Often nonpigmented and misdiagnosed as scar
- Usually advanced thickness at presentation (Br J Dermatol 2005;152:673)
- Dermoscopy is difficult due to absence of pigmented network
- Can have features of regression and melanoma associated vascular patterns (Br J Dermatol 2008;159:360)
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis can be made on biopsy but paucicellular variant is easily misdiagnosed
Prognostic factors
- 5 year disease free survival: 68% (J Am Acad Dermatol 1995;32:717)
- Lymph node metastasis: 12% (Cancer 2004;100:598)
- Prognosis related to
- Neurotropism: presence linked to significantly reduced survival
- Histologic type
- Pure form biologically behaves as sarcoma with frequent local recurrence and metastasis to lung
- Mixed form akin to conventional melanoma with metastasis to lymph node
Case reports
- 46 year old man with collision tumor with squamous cell carcinoma on lip (J Cutan Pathol 2008;35:473)
- 59 year old and 66 year old women presented with small scalp lesions clinically suggestive of alopecia (J Cutan Pathol 2016;43:872)
- 75 year old man presented with an ulceroproliferative growth on the foot (J Cutan Aesthet Surg 2015;8:60)
Treatment
- Wide local excision
- Adjuvant radiotherapy can be considered for pure form with perineural invasion, Breslow thickness > 4 mm or positive surgical margins (Melanoma Res 2016;26:35)
Gross description
- Pigmented or scar-like skin surface with ill defined induration (JAMA Dermatol 2013;149:413)
- Cross sections with white, poorly demarcated tumor
Microscopic (histologic) description
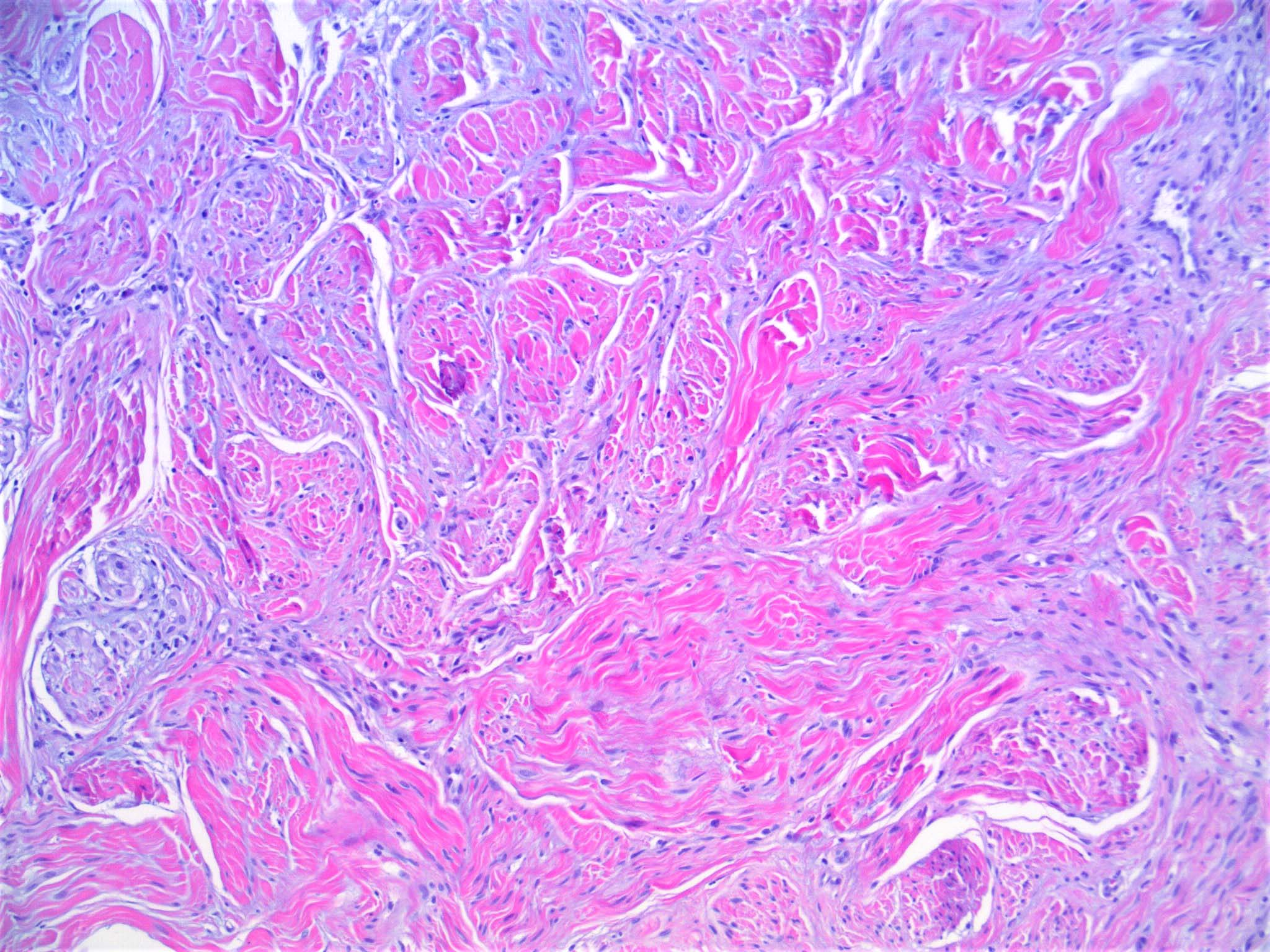
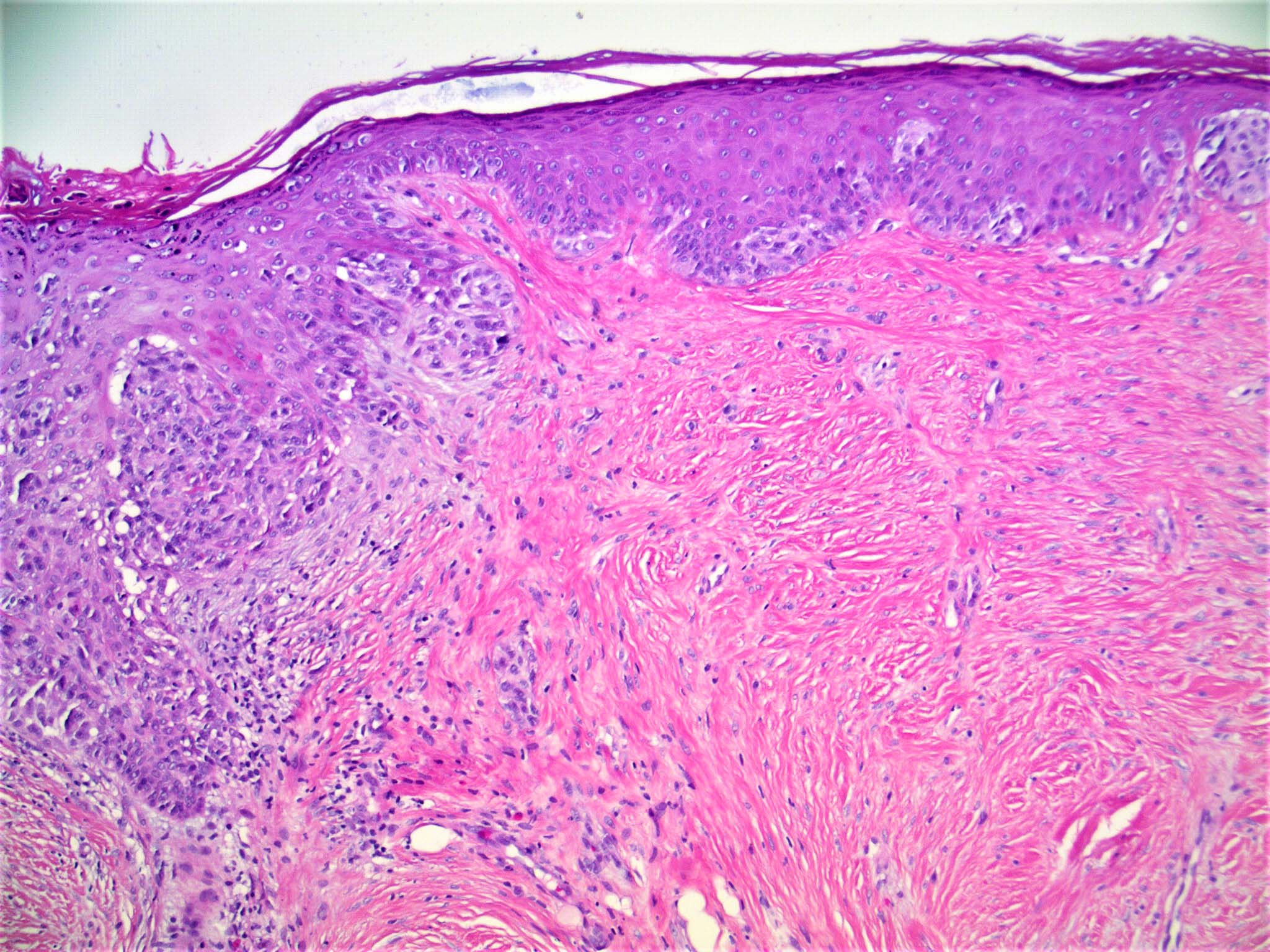
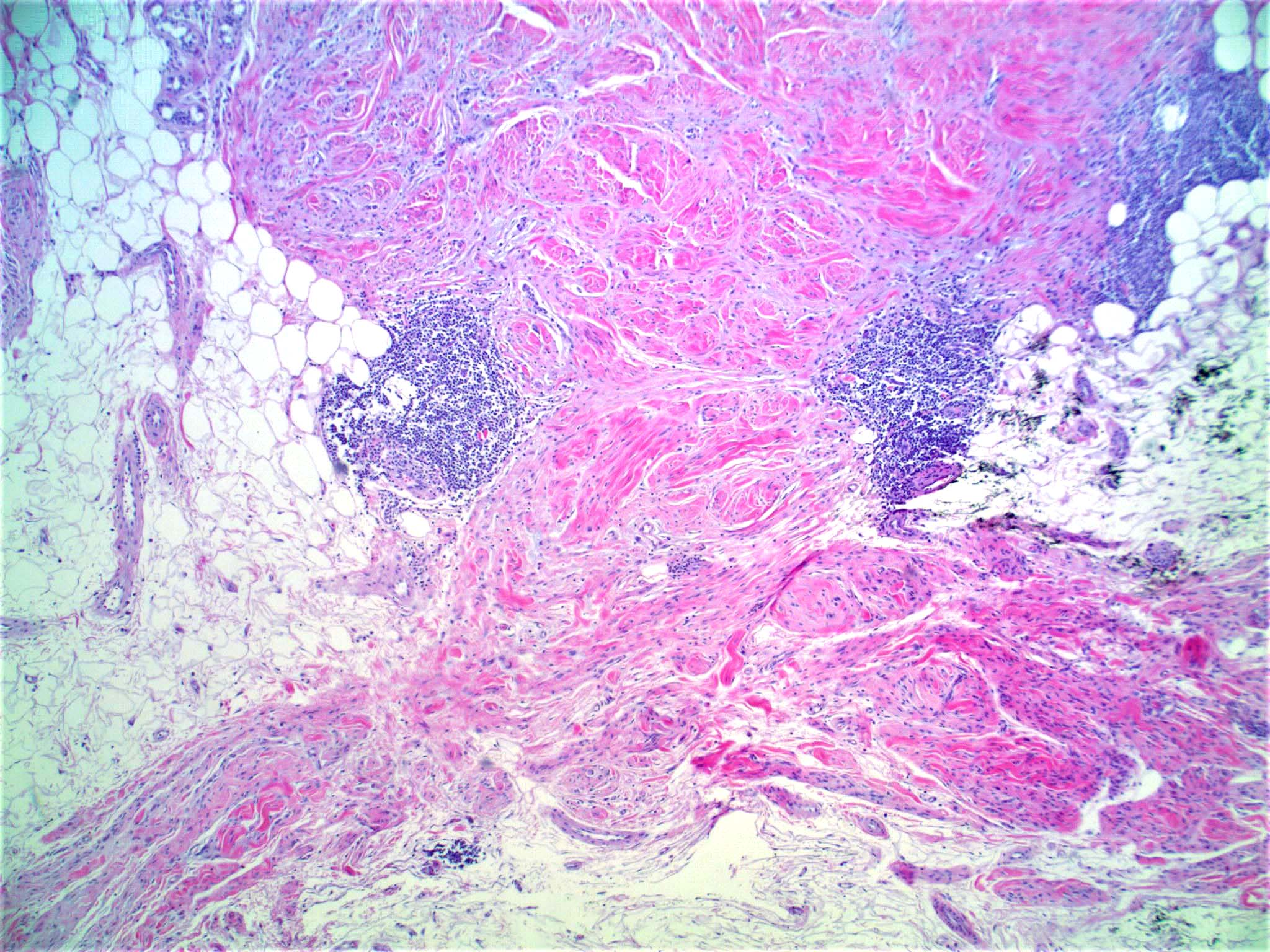
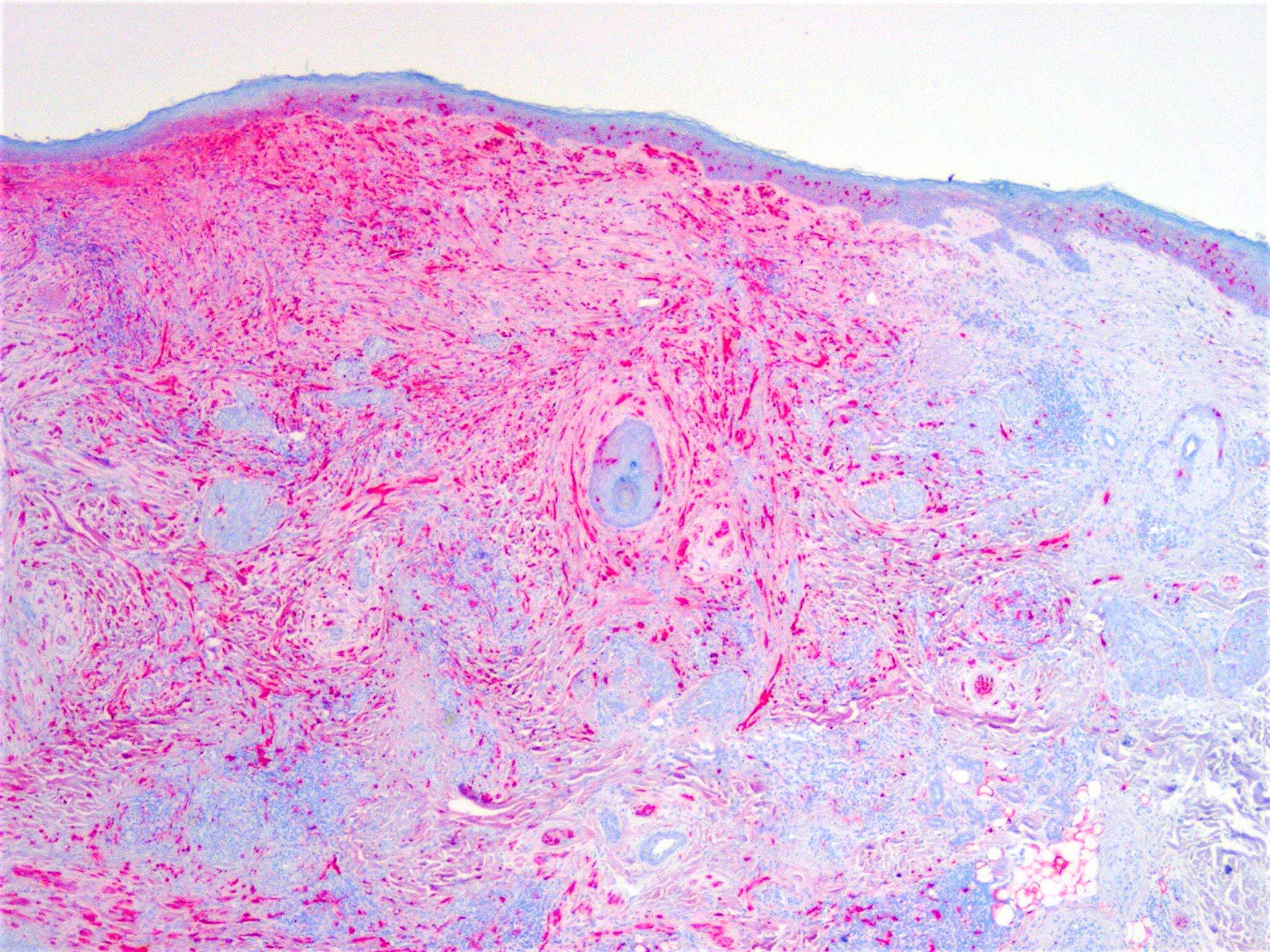
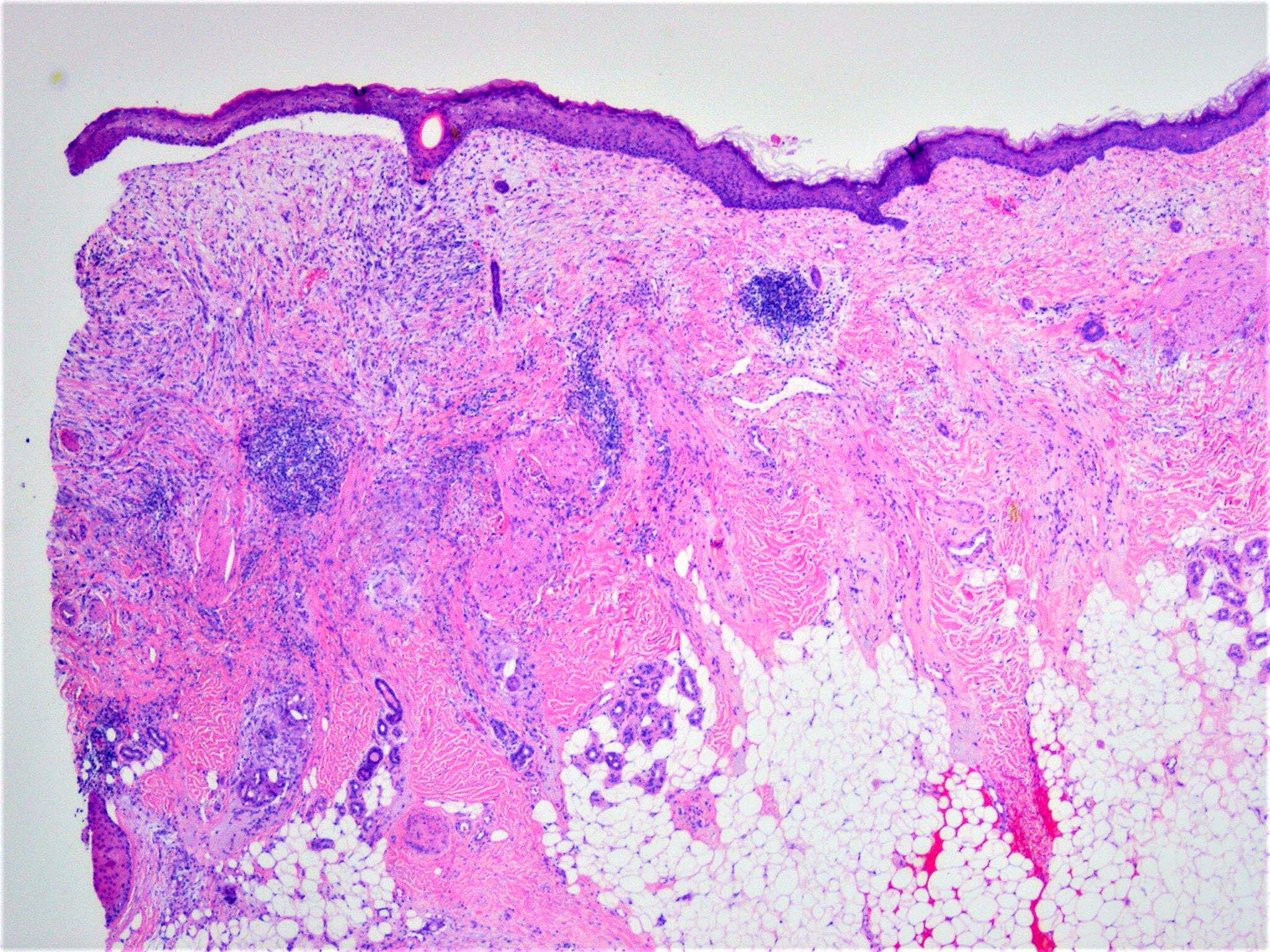
- Poorly circumscribed with deep infiltration
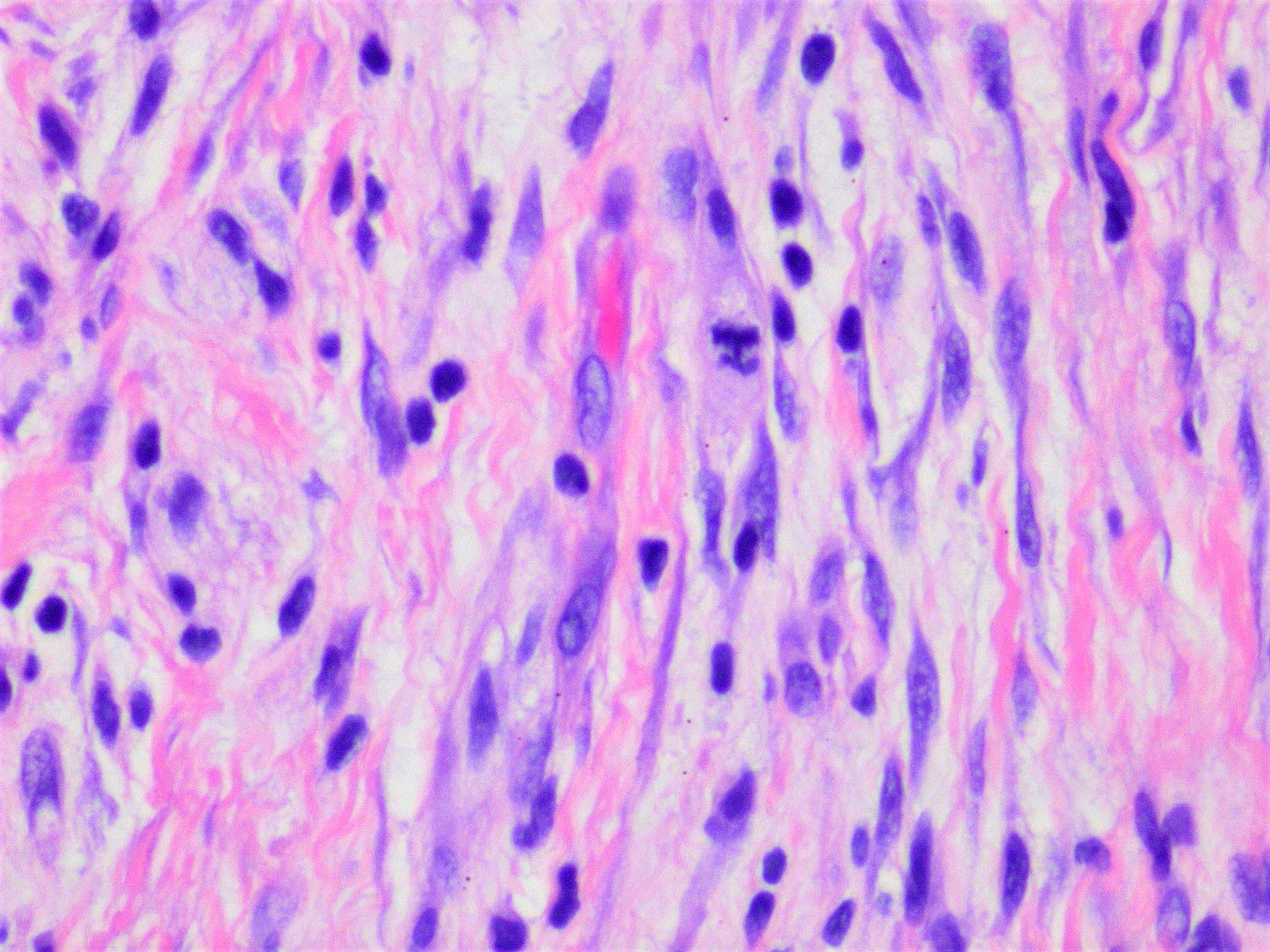
- Elongated spindle cell surrounded by collagen bundles (Hum Pathol 1983;14:1072)
- Can resemble fibroblasts
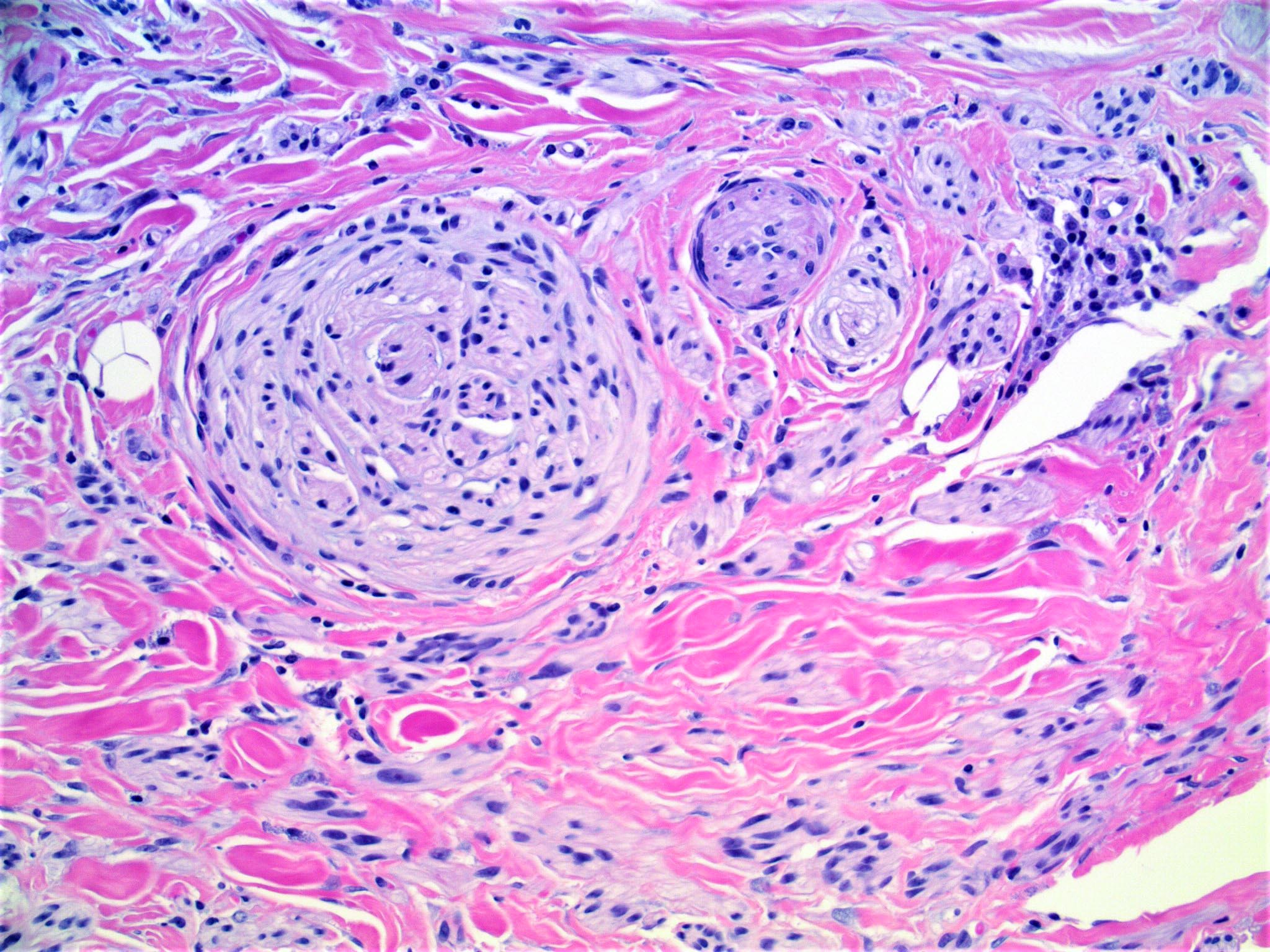
- Scattered cells show hyperchromasia and bizarre nuclei
- Multinucleated cells often present
- Stromal component varies in different tumors (Mod Pathol 2014;27:524)
- Some tumors with scattered spindle cells and abundant collagen
- Others with high cellularity and little stroma (best classified as spindle cell melanoma)
- Small foci of lymphoid aggregates is a useful clue to the diagnosis on scanning
- May be pure or combined with classic melanoma
- Desmoplastic neurotropic melanoma considered a variant (33% of all cases of desmoplastic melanoma) (Am J Dermatopathol 2008;30:207)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Clean background; aggregates of pleomorphic spindle cells mixed with fibrous stroma and single cells
- Fine, wispy and delicate cytoplasm at nuclear poles; elongated and plump nuclei with irregular contours; deep grooves and folds and dark coarse chromatin with variably prominent nucleoli (Cytojournal 2007;4:18)
- Less cellular with fewer intranuclear cytoplasmic inclusions and mitoses relative to conventional melanoma (Am J Clin Pathol 2008;130:715)
Positive stains
- S100 and SOX10 (J Cutan Pathol 2016;43:313)
- Ki67: usually high
- WT1, p75
- H3K27me3 retained
- May be helpful when differentiating from a malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:479)
- p53 (95%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:372)
- Helpful when differentiating from neurofibroma
Negative stains
- MelanA / MART1, tyrosinase, CD63, MITF
- HMB45 (can stain small clusters of cells in up to 20% of nonpure type cases)
- PRAME (approximately 30% positive) (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1456)
Electron microscopy description
- Shows only modest evidence of melanocytic origin
- Stage II melanosomes considered the hallmark of melanoma and melanin synthesis
- Some cases with nonmembrane bound melanin granules and premelanosomes (Hum Pathol 1983;14:1072)
- Cells have abundant rough endoplasmic reticulum and sometimes intracytoplasmic collagen and macular desmosomes
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- NF1 loss of function mutations common
- Numerous point mutations
- In contrast, other melanomas have genetic copy number alternations
- NFKBIE (NFκB inhibitor, epsilon; 6p21.1) promoter mutations appear to play a role in development (Nat Genet 2015;47:1194)
- BRAF mutations unusual
- Sensitivity of FISH assay ~ 50% (using a 4 probe FISH assay targeting RREB1, MYB, CEP6 and CCND1 (J Cutan Pathol 2011;38:329)
- Sensitivity of both single nucleotide polymorphism array and gene expression profiling 50 - 80% (Hum Pathol 2017;70:113)
Videos
Desmoplastic melanoma: 5 minute pathology pearls
Sample pathology report
- Skin, scalp, shave biopsy:
- Desmoplastic melanoma (pure type), level IV, 1.3 mm tumor thickness, nonulcerated
Differential diagnosis
- Scarring process:
- Horizontal orientation of fibroblasts with vertically oriented blood vessels and absence of adnexa
- S100 and SOX10 typically negative but may display positivity (Pathology 2016;48:626)
- Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor:
- Uniform spindle cells with hyperchromatic, thin and wavy, buckled or comma shaped nuclei
- Often arranged in sweeping fascicles
- May be associated with precursor lesion, such as neurofibroma
- Patchy S100 and SOX10 expression with lower rate of immunoreactivity (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2012;20:445)
- Neurofibroma:
- No or very low mitotic activity
- Spindled squamous cell carcinoma:
- Cytokeratin positive (may be weak or spotty)
- Atypical fibroxanthoma:
- Diagnosis of exclusion (negative for cytokeratins, S100, desmin and vascular markers)
- CD10 and procollagen 1 positive
- Dermatofibroma:
- Haphazard pattern of bland spindle cells with peripheral collagen trapping
- Often with overlying epidermal acanthosis and follicular induction
- Factor XIIIa positive in tumor cells
- Fibromatosis:
- Bland spindle cells arranged in sweeping bundles in a highly collagenized background
- Nodular fasciitis (superficial portion):
- Spindle stellate cells with a loose fascicular to storiform pattern (tissue culture-like growth)
- SMA positive
- Majority contain MYH9-USP6 fusion
- Cutaneous angiosarcoma:
- Cutaneous leiomyosarcoma:
- Fascicular growth pattern
- Desmin positive
Board review style question #1
A 65 year old man presents with a lesion on the scalp. Biopsy shows a spindle cell neoplasm centered in the dermis. The tumor cells express S100 and are negative for CD34, desmin, CD10 and cytokeratins. Regarding this entity, which of the following statements is true?
- Frequently metastasizes to lymph node
- MART1 is always positive
- Nodular lymphoid aggregates are a useful clue to the diagnosis
- Often clinically suspected at the time of biopsy
- Site of predilection is the trunk
Board review style answer #1
C. Nodular lymphoid aggregates are a useful clue to the diagnosis. This is a desmoplastic melanoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Desmoplastic melanoma
Comment Here
Reference: Desmoplastic melanoma
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2