Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Polster N, Dehner C. BAP1 inactivated nevus / melanocytoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumormelanocyticbap1nevus.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- BAP1 inactivated nevi / melanocytomas are benign melanocytic tumors with distinctive epithelioid morphology
- They are the result of germline or somatic inactivating mutations in the tumor suppressor gene BAP1
Essential features
- Benign melanocytic tumors with distinctive epithelioid morphology
- Result of biallelic inactivation of the BAP1 gene accompanied by an activating mutation, typically in BRAF
- Germline mutations of BAP1 are also associated with additional malignancies such as malignant mesothelioma, uveal melanoma and cutaneous melanoma
- BAP1 inactivated nevus refers to tumors with benign appearing histology, while melanocytoma refers to tumors with at least moderate cytologic atypia
Terminology
- First described in 2011 by Wiesner et al. (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:818)
- Synonyms: BAPoma, Wiesner nevus, atypical Spitz tumor with BAP1 loss, nevoid melanoma-like melanocytic proliferation (NEMMP) (J Cutan Pathol 2019;46:965)
- WHO categorizes BAP1 inactivated nevus and BAP1 melanocytoma under BAP1 inactivated melanocytic tumor (BIMT) (Mod Pathol 2022;35:664)
- Benign appearing BIMTs classified as BAP1 inactivated nevi and highly atypical appearing variants as BAP1 melanocytomas (Mod Pathol 2022;35:664)
- Listed as combined nevus due to remnants of a conventional nevus with retained expression of BAP1 within nevi that are histologically and molecularly consistent with BIMTs (Mod Pathol 2022;35:664)
- BAP1 is an acronym for BRCA1 associated protein 1 (J Cutan Pathol 2019;46:965)
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Equal sex distribution
- Occurs at any age but typically begins appearing in second decade of life
- Carrier frequency for the BAP1 tumor predisposition syndrome in the general population is 1:26,837 (GeneReviews: BAP1 Tumor Predisposition Syndrome [Accessed 20 December 2023])
Sites
- Anywhere on the skin
- Greatest predilection for the head and neck, followed by the trunk and upper extremities
- Less commonly occurs on lower extremities (J Am Acad Dermatol 2019;80:1585)
Pathophysiology
- BAP1 is a tumor suppressor gene located on chromosome 3p21.1 (Nat Rev Cancer 2013;13:153)
- Encoded BAP1 protein is a nuclear protein that is involved in many processes, including regulation of the cell cycle, cell growth and the DNA damage response (J Clin Oncol 2012;30:e337)
Etiology
- Can be sporadic or inherited
- Inherited form results from autosomal dominant inactivating mutation in BAP1 gene; the second wild type allele is subsequently lost by somatic mutation (Nat Genet 2011;43:1018)
Clinical features
- Transformation risk of BAP1 inactivated melanocytic nevus into melanoma is low
- Additional germline BAP1 mutation associations (Nat Rev Cancer 2013;13:153)
- Malignant mesothelioma (40.0%)
- Uveal melanoma (38.4%)
- Cutaneous melanoma (24.8%)
- Renal cell carcinoma (6.1%)
- BIMTs most commonly develop in second decade of life (Nat Genet 2011;43:1018)
- Typically solitary but multiple papules can be seen with germline mutation (J Cutan Pathol 2019;46:965)
- Size usually between 2 and 10 mm, average of 5 mm (Nat Genet 2011;43:1018, Nat Rev Cancer 2013;13:153)
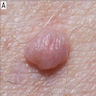
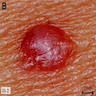
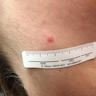
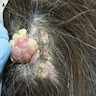
- Papules are flesh colored to orange or red-brown (Nat Genet 2011;43:1018, J Am Acad Dermatol 2019;80:1585)
- Dome shaped to pedunculated (Nat Genet 2011;43:1018)
- Can clinically resemble fibromas or intradermal nevi (J Am Acad Dermatol 2019;80:1585)
- Varied dermoscopic findings, most commonly presenting as irregular dots / globules located eccentrically (29.8%), structureless pink to tan (14.9%) and network with raised, structureless, pink to tan areas (14.9%) (J Am Acad Dermatol 2019;80:1585)
Diagnosis
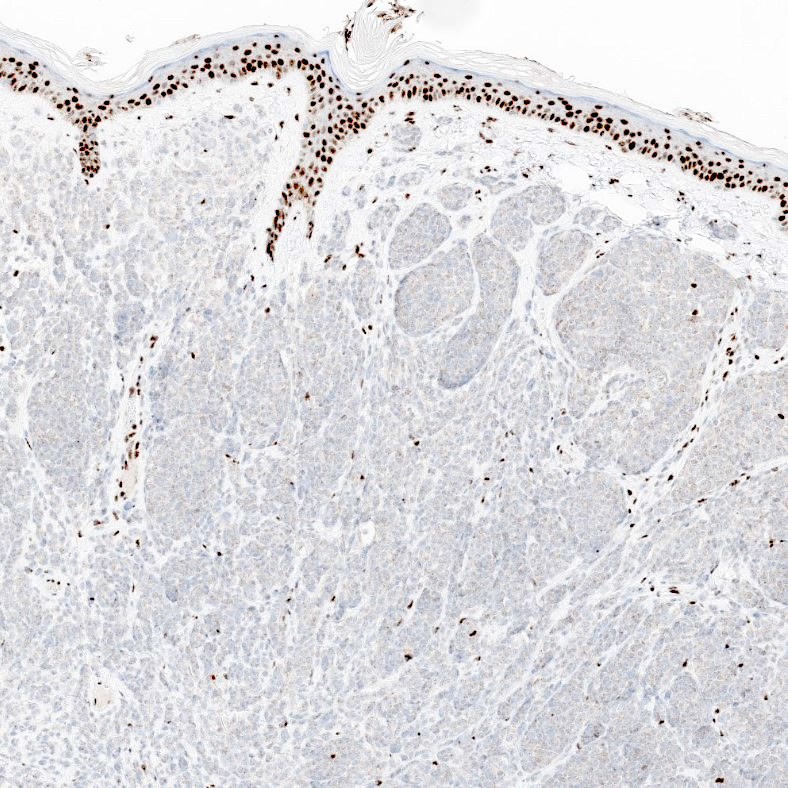
- Diagnosis of BAP1 inactivated tumors is typically rendered by observing loss of nuclear expression of BAP1 on immunohistochemical staining of specimens that histologically demonstrate the characteristic features of the entity on H&E (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:818)
- Internal control is mandatory; strong nuclear expression of BAP1 should be present in nearby keratinocytes and nonlesional melanocytes
- Recommend direct sequencing of saliva or blood to determine if germline mutation present
Prognostic factors
- Not well studied
- On rare occasion, has been seen to progress to melanoma (J Clin Oncol 2012;30:e337)
- Germline BAP1 mutation associated with the development of cutaneous melanomas without progression from BAP1 inactivated nevi / melanocytomas
Case reports
- 15 year old girl with uveal melanoma found to have BAP1 tumor predisposition syndrome (JAAD Case Rep 2020;6:563)
- 35 year old woman with melanocytic lesion with 3 distinct melanocyte populations (Am J Dermatopathol 2023;45:117)
- 49 year old woman with dome shaped papule on digit of right foot (BMC Dermatol 2017;17:13)
Treatment
- Complete excision is recommended; margins must be negative
- Reflex screening for germline BAP1 mutations not usually recommended but can be performed in patients with a high clinical suspicion for BAP1 tumor predisposition such as in younger patients (under 40) and in patients with family history of BAP1 tumor predisposition syndrome related malignancies (Eur J Hum Genet 2023;31:1261)
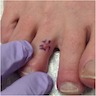
Clinical images
Gross description
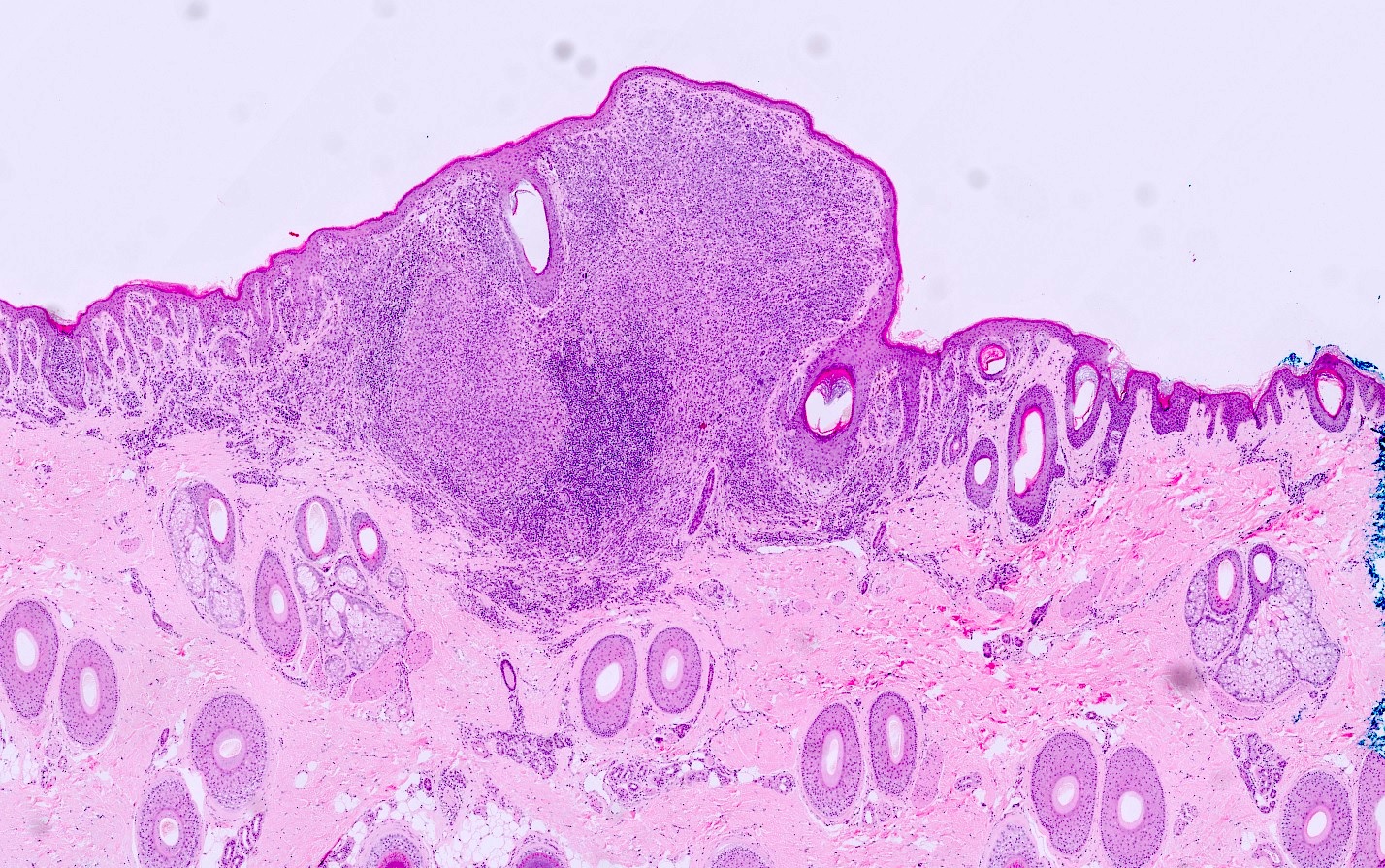
- Typically a well circumscribed, dome shaped, flesh colored 3 - 10 mm papule
Microscopic (histologic) description
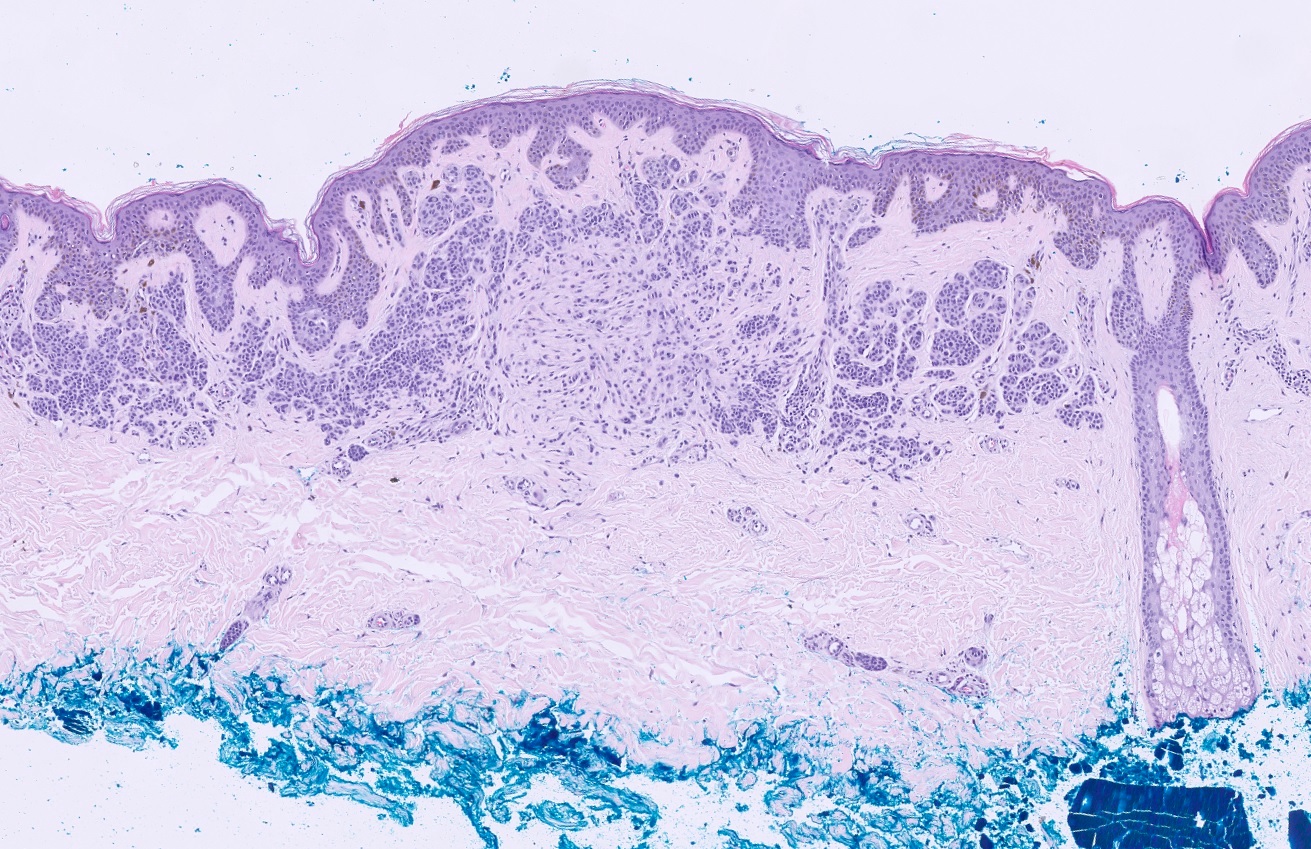
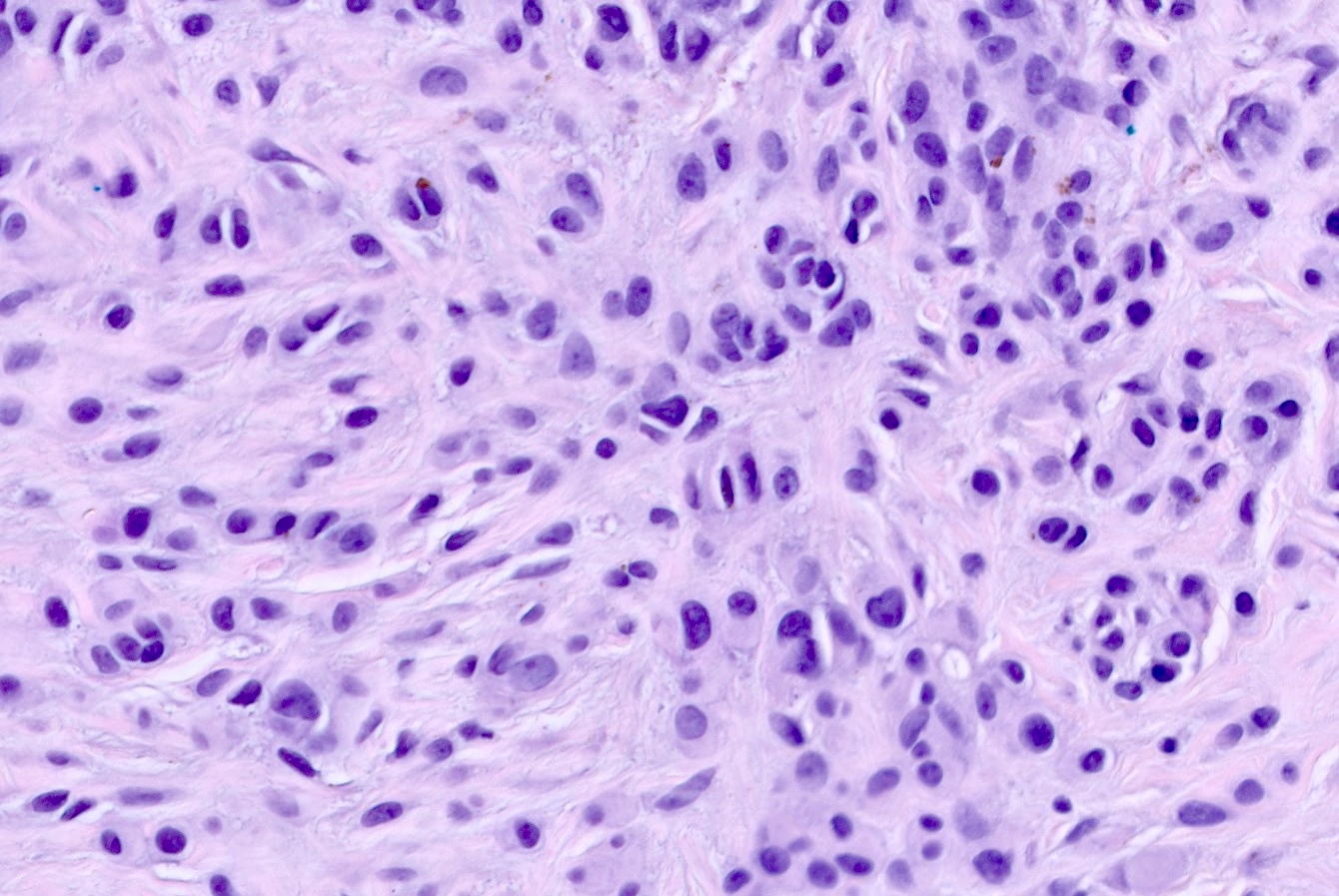
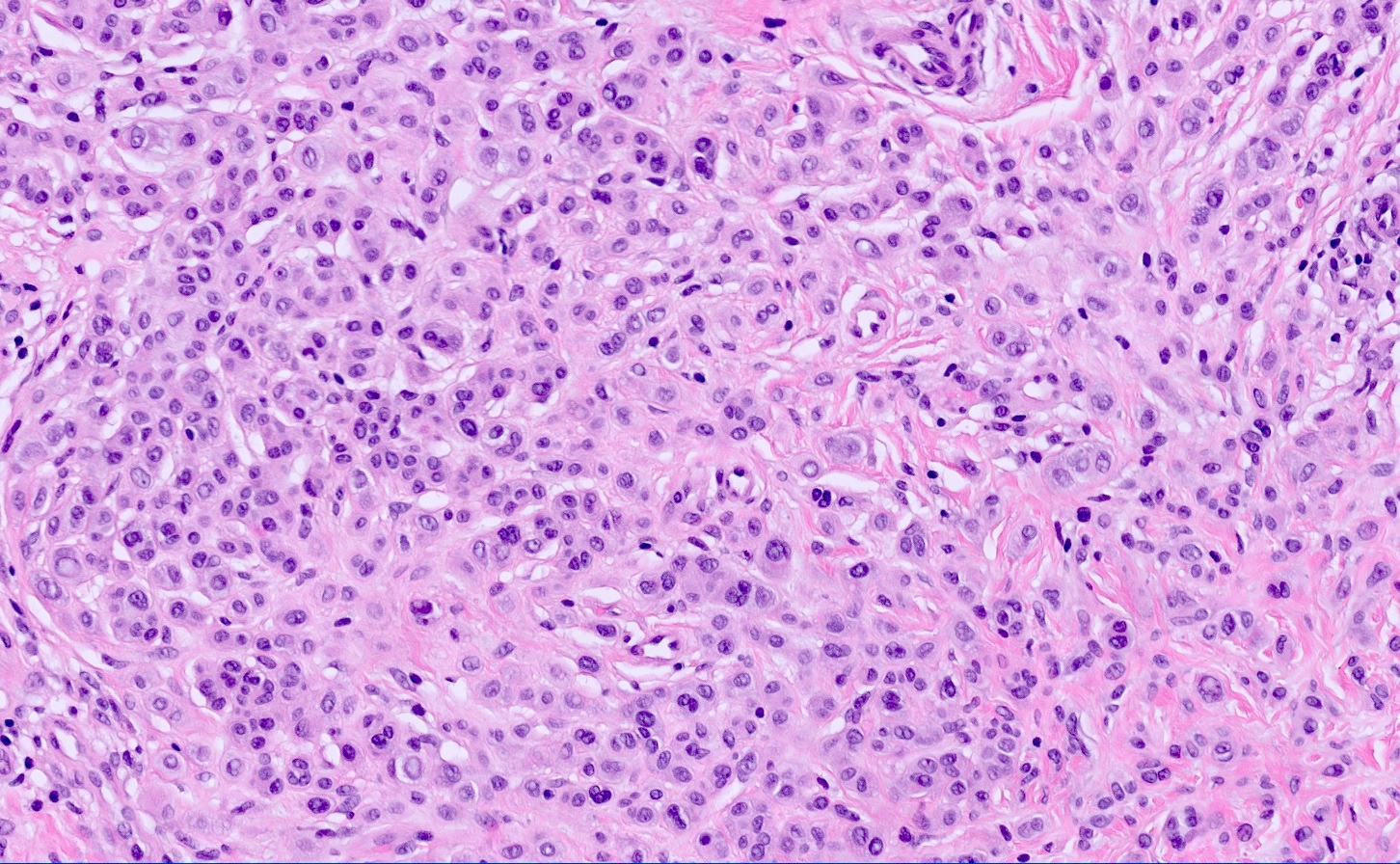
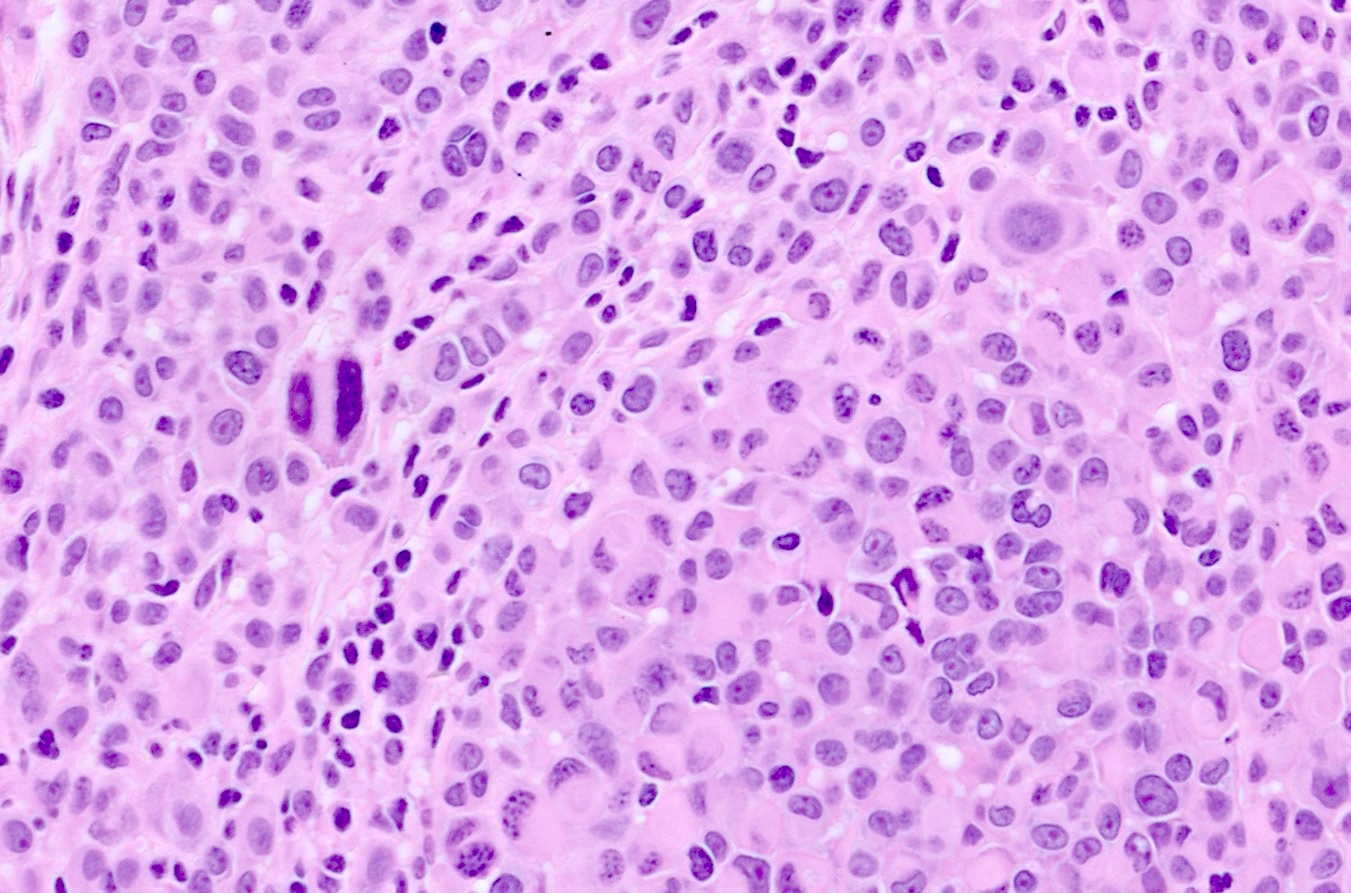
- Predominately dermal based proliferation of large epithelioid melanocytes, typically minimal junctional component
- Large vesicular nuclei and eosinophilic cytoplasm
- Often polypoid profile
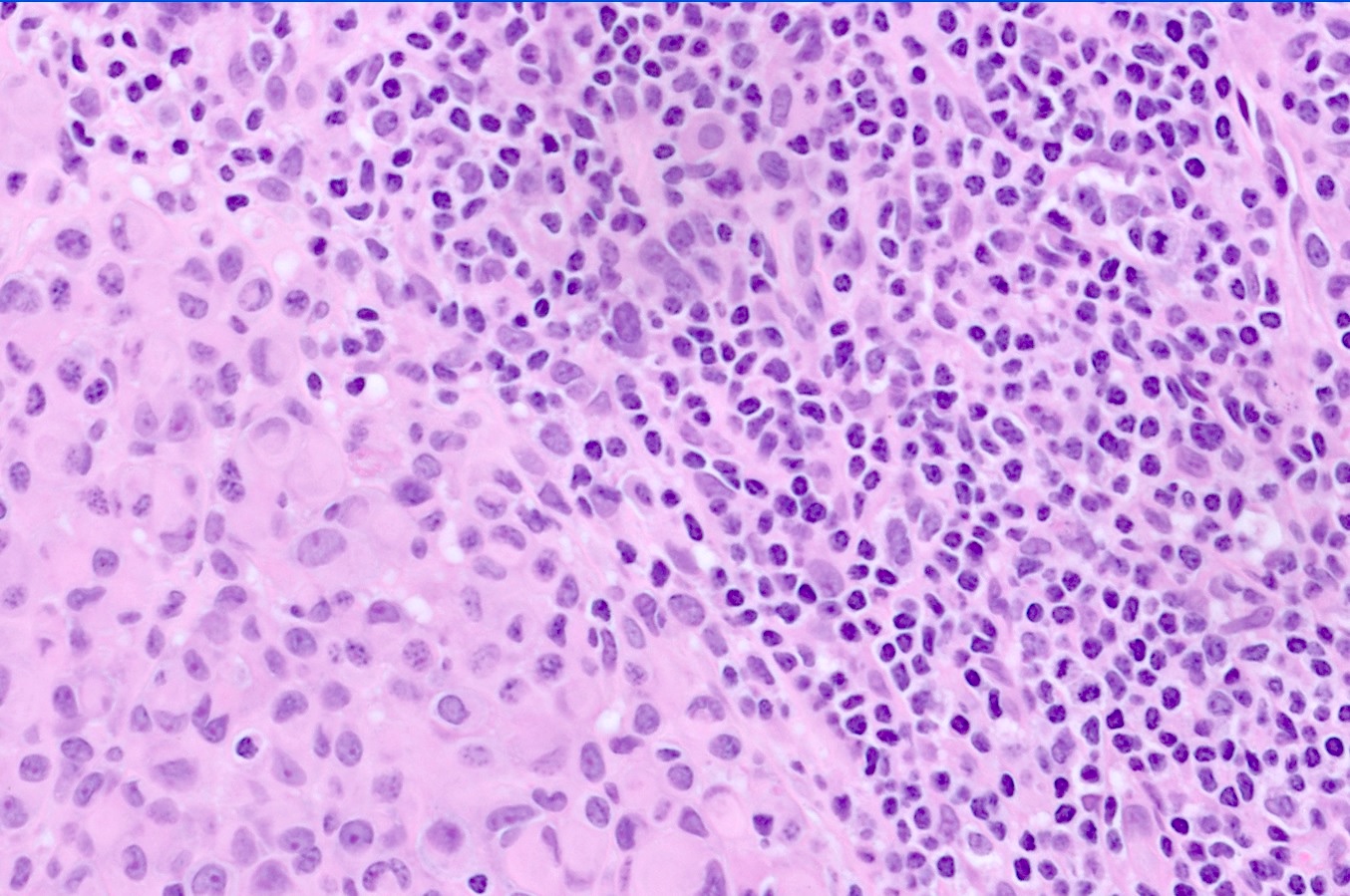
- Lymphocytic infiltrate with associated regression can be seen
- 2 predominant growth patterns (J Cutan Pathol 2019;46:965)
- Sheet-like growth of uniformly large epithelioid cells with distinct cytoplasmic borders
- Large epithelioid cells admixed with small nevoid cells
- BAP1 inactivated nevus
- Minimal atypia with rare to few mitotic figures
- BAP1 inactivated melanocytoma
- Can have pronounced cytologic atypia with high mitotic rate
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Cytology is not part of the work up for BAP1 inactivated tumors
Positive stains
- SOX10
- MelanA
- S100
- Reference: J Cutan Pathol 2023;50:349
Negative stains
- BAP1
- HMB45 with gradient (66%)
- PRAME
- Reference: J Cutan Pathol 2023;50:349; Am J Dermatopathol 2023;45:733
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Characteristic biallelic inactivation of BAP1
- Accompanied by a separate activating mutation, usually BRAF V600E but also rarely in RAS1 (Mod Pathol 2022;35:664)
- In combined nevi, the BRAF V600E mutation is found in all lesional melanocytes while only the epithelioid melanocytes have loss of BAP1
Videos
BAPoma - BAP1 inactivated nevus / melanocytoma - mimic of nevoid melanoma
Sample pathology report
- Skin, biopsy, right scalp:
- Intradermal melanocytic proliferation with BAP1 loss, consistent with BAP1 inactivated nevus (see comment)
- Complete excision is indicated
- Comment: The findings are those of a compound melanocytic proliferation with 2 distinct populations of cells. Toward the center of the biopsy specimen, there is sheet-like nodular proliferation of large epithelioid melanocytes with abundant cytoplasm, prominent nucleoli and no significant mitotic activity. Outside of this nodular proliferation, there is a compound proliferation of more conventional melanocytes. Immunohistochemical staining shows preferential BAP1 loss in the central sheet-like nodule with preserved expression in the background nevus. These findings are consistent with a BAP1 inactivated nevus.
Differential diagnosis
- Atypical Spitz nevus:
- Spindle shaped melanocytes, epidermal hyperplasia, Kamino bodies, clefting around junctional melanocytes (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:818)
- No loss of BAP1 in IHC / molecular
- Do not have BRAF V600E mutations, which BAP1 inactivated tumors almost always have (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:818)
- Invasive melanoma:
- Typically does not have loss of BAP1 in IHC / molecular
- Some cutaneous melanomas are part of BAP1 tumor predisposition syndrome
- Melanomas typically larger, > 1 cm compared to BAP1 inactivated nevi average of 0.5 cm and typically present as irregular pigmented lesions compared to the circumscribed flesh colored papules of BAP1 inactivated nevi
- Can display marked atypia depending on subtype
- Certain subtypes of melanoma such as spitzoid and nevoid melanomas can have lesional epithelioid cells, which may make differential without BAP1 IHC / molecular challenging (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2020;144:500)
Board review style question #1
Which of the following describes BAP1 inactivated nevi?
- Can be associated with malignant mesothelioma and uveal melanoma
- Found almost exclusively on the legs of older men
- Frequently undergo malignant transformation
- Histologically present as large spindled cells with Kamino bodies
- Typically present as large, ulcerative lesions
Board review style answer #1
A. Can be associated with malignant mesothelioma and uveal melanoma. Germline BAP1 mutations are associated with melanocytic nevi, malignant mesothelioma, uveal melanoma, cutaneous melanoma and renal cell carcinoma. Answer B is incorrect as BAP1 inactivated nevi have an equal sex distribution, can occur at any age but mostly are seen in the second decade of life and have a predilection for the head, neck and upper extremities. Answer C is incorrect as BAP1 inactivated nevi have only in very rare cases been seen to metastasize. Answer D is incorrect because it describes Spitz nevi. Histologically, BAP1 inactivated nevi present as large, epithelioid cells with defined cell borders and do not present with Kamino bodies. Answer E is incorrect because BAP1 inactivated nevi typically present as flesh to red-brown colored papules < 1 cm in diameter.
Comment Here
Reference: BAP1 inactivated nevus / melanocytoma
Comment Here
Reference: BAP1 inactivated nevus / melanocytoma
Board review style question #2
BAP1 inactivated melanocytic nevi are most often associated with activating mutation in which gene?
- BRAF
- EGFR
- HRAS
- KRAS
- NRAS
Board review style answer #2
A. BRAF. While BAP1 inactivated melanocytic nevi are characterized by biallelic inactivation of BAP1, they are accompanied by a separate mutation in a mitotic driver, usually BRAF V600E. Answers B, C, D and E are incorrect because mutations in the other listed genes are not known to be involved with the development of BAP1 inactivated melanocytic nevi.
Comment Here
Reference: BAP1 inactivated nevus / melanocytoma
Comment Here
Reference: BAP1 inactivated nevus / melanocytoma