Table of Contents
Definition / general | Major updates | WHO (2022) | Microscopic (histologic) images | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Collie CJ, Ho JD. WHO classification. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumormelanocyticWHO.html. Accessed July 15th, 2024.
Definition / general
- WHO classification of melanocytic skin tumors
- Currently on 5th edition, published August 2022 (Epub ahead of print)
Major updates
- Advanced knowledge of molecular pathomechanisms have led to definition changes (Annu Rev Pathol 2014;9:239)
- Nevi: single initiating mutation, bland cytology and benign biology
- Melanocytomas: neoplasms with > 1 driver mutation with a second mutation affecting specific pathways resulting in distinct atypical microscopic features and increased risk of local recurrence; melanocytomas occur on a spectrum between nevi and melanoma
- Some nevi renamed as melanocytoma variants
- WNT activated deep penetrating / plexiform melanocytoma (previously deep penetrating nevus) (Clin Exp Dermatol 2024;49:356)
- Pigmented epithelioid melanocytoma (PEM, also known as PRKAR1A inactivated melanocytoma); previously epithelioid blue nevus (Surg Pathol Clin 2021;14:285)
- BAP1 inactivated melanocytoma (Pathol Res Pract 2024;259:155162)
- Spitz melanocytoma (Front Oncol 2022:12:889223)
- Microphthalmia associated transcription factor (MITF) pathway activated melanocytic tumors (melanocytomas)
- Clear cell tumor with melanocytic differentiation and ACTIN::MITF translocation (CCTMAM) (Am J Surg Pathol 2021;45:962)
- Clear cell tumor with melanocytic differentiation and MITF::CREM translocation (CCTMMC) (Virchows Arch 2021;479:841)
WHO (2022)
| Melanocytic neoplasms | ICD-O | ICD-11 |
| ||
| ||
| 8740/0, 8760/0, 8750/0 | 2F36.Y & XH1M79, XH27A6, XH2MQ5 | |
| 8742/0 | 2F20.0Y, 2F20.2Y |
| 8727/0 | 2F20.1 & XH9035, 2F72.2 | |
| 8720/0 | 2F20.Y & XH40S8 | |
| 2F20.1, 2F20.Y | ||
| 8723/0 | 2F20.Y & XH5971 | |
| 8720/0 | 2F20.Y & XH8NP4 | |
| 2F20.Y | ||
| 8720/0 | 2F20.Y & XH0DU8 | |
| ||
| 8720/1 | 2F20.Y & XH81Y1 | |
| 8780/1 | 2F20.1 & XH4VD0 | |
| 8720/1 | 2F20.1 | |
| 8727/0 | 2F20.1 |
| ||
| 8743/3 | 2C30.0 | |
| ||
| 8742/3 | 2C30.2 | |
| 8745/3 | 2C30.Y & XH1Z15 | |
| ||
| ||
| 8770/0 | 2F20.Y & XH2P88 | |
| 8770/0 | 2F20.Y & XH2HG8 | |
| ||
| 8770/1 | 2F20.Y & XH9WF4, 2F72.1 | |
| 8770/3 | 2C30.Y & XH8DS3 | |
| ||
| 8744/0 | 2F20.Y & XH9DB2 | |
| 8744/3 | 2C30.3 | |
| ||
| ED61.Y | ||
| 8720/0 | 2F20.Y & XH5EL4 | |
| 8720/3 | 2C70.1, 2C11.2 & XH4846 | |
| ||
| ||
| LC10 | ||
| LC10 | ||
| 8780 | 2F20.Y & XH7QJ7, XH3X84 | |
| 8780/3 | 2C30.Y & XH1G74 |
| ||
| ||
| 8761/0 | 2F20.2Z | |
| 8762/1 | 2F20.2 & XH6AH3 | |
| ||
| 8761/3 | 2C30.Y & XH5L25 | |
| ||
| ||
| 8740/0, 8760/0, 8750/0 | 2F36.Y & XH1M79, XH27A6, XH2MQ5 | |
| 8720/2 | 2E63.1 | |
| 8720/3 | 2D00.0 | |
| ||
| 8726/0 | 2F36.0 |
| 8770/3, 8771/3, 8772/3, 8773/3, 8774/3 | 2D07.2, 2D06.4, 2D05.0 | |
| ||
| 8728/0, 8728/3 | 2A01.0Y & XH8974, XH1BP7 |
| 8728/1, 8720/3 | 2A01.0Y & XH2RY7, XH3DN1 |
| ||
| ||
| 8721/3 | 2C30.1 | |
| 8720/3 | 2C30.Y & XH8681 | |
| 8780/3 | 2C30.Y |
| ||
| 8720/6 | 2E08 & XH4846 | |
| 8720/6 | 2E0Y & XH4846 |
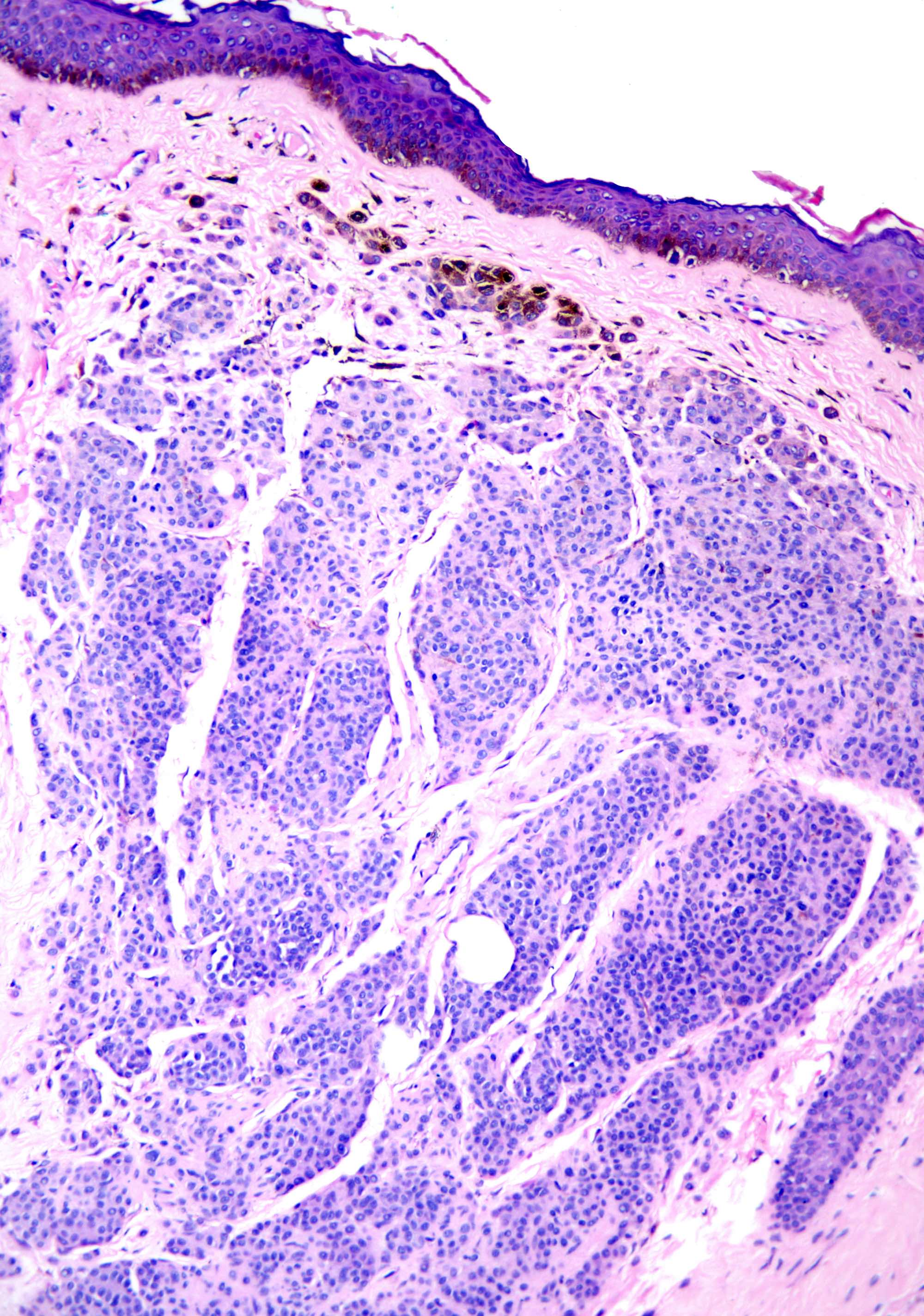
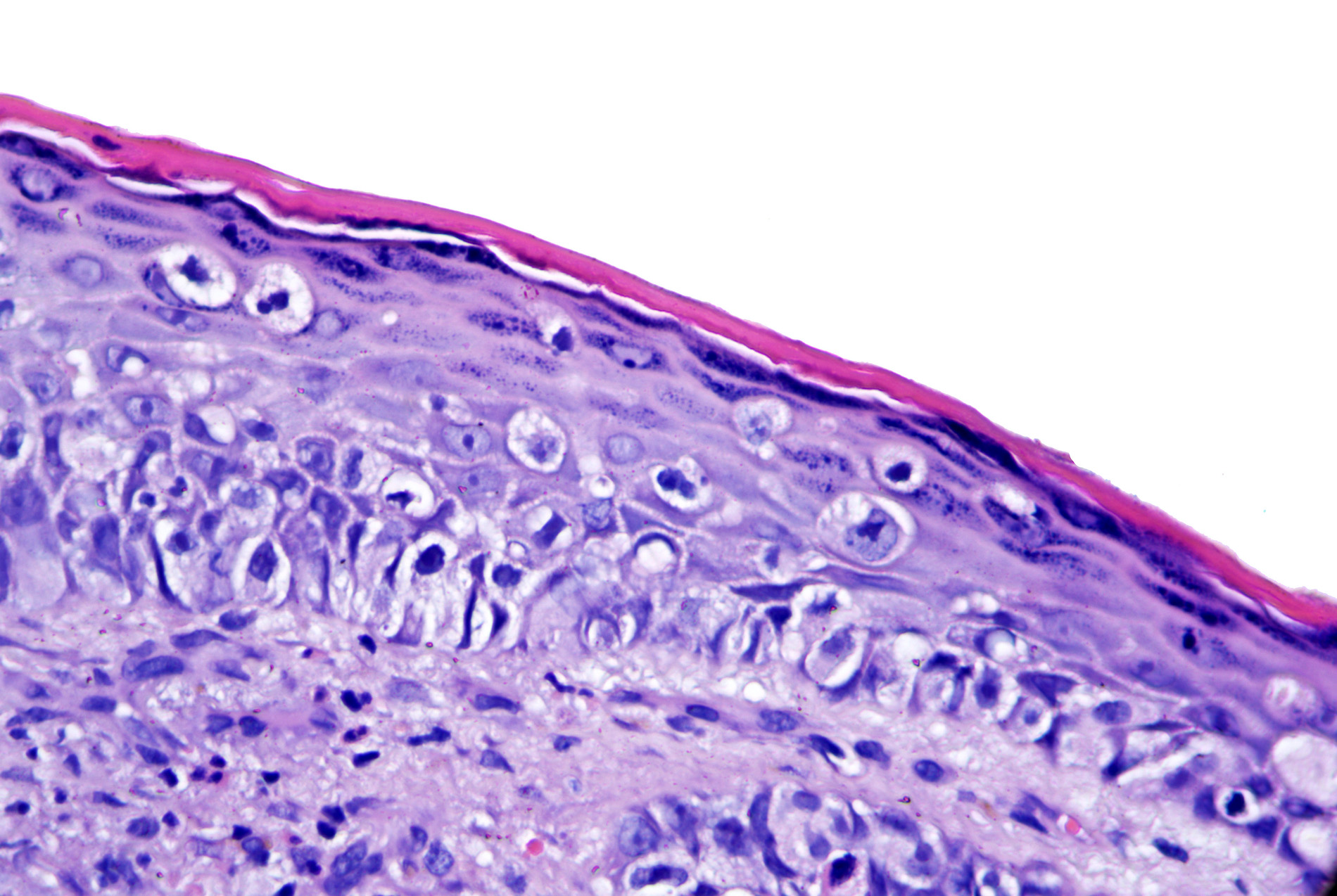
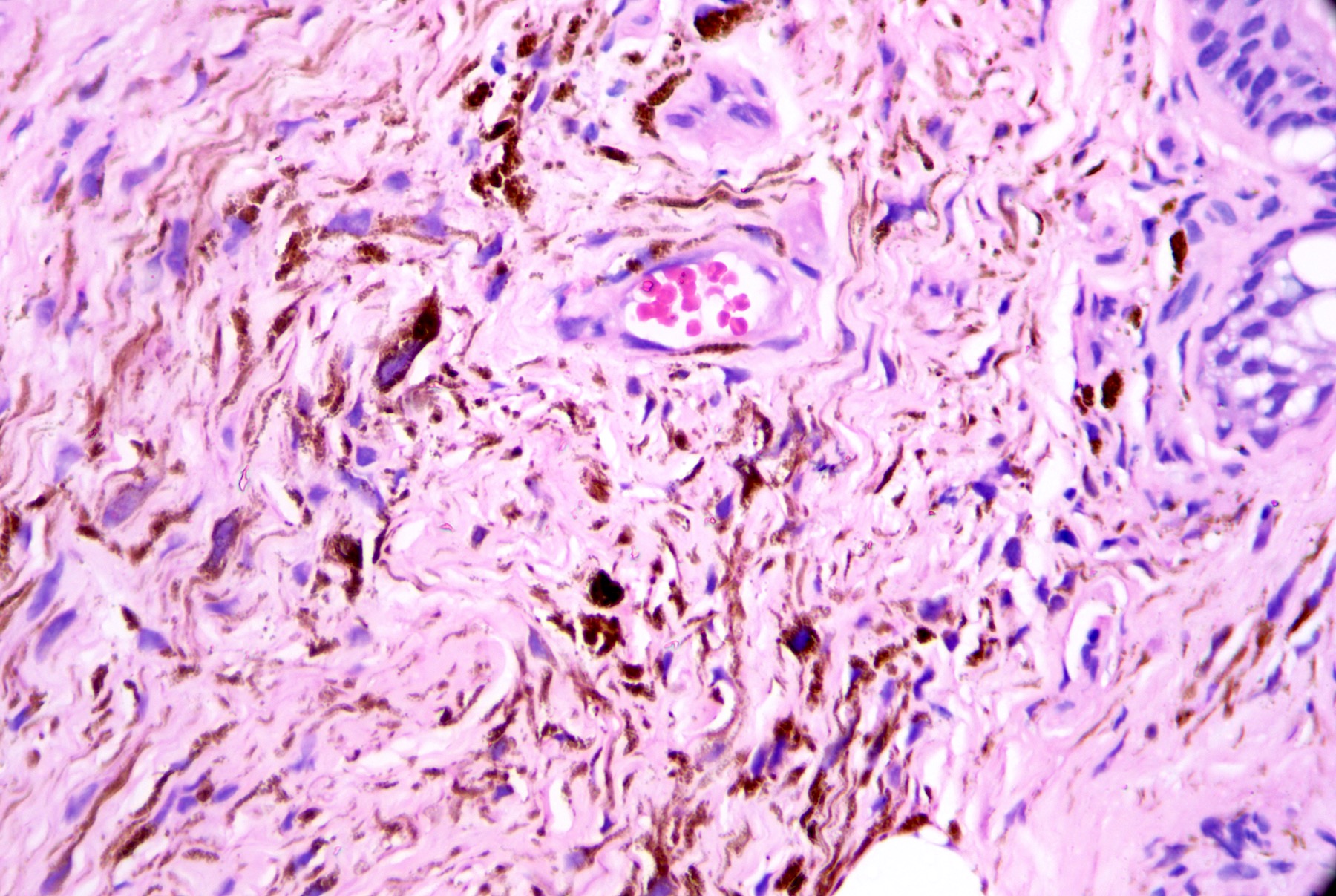
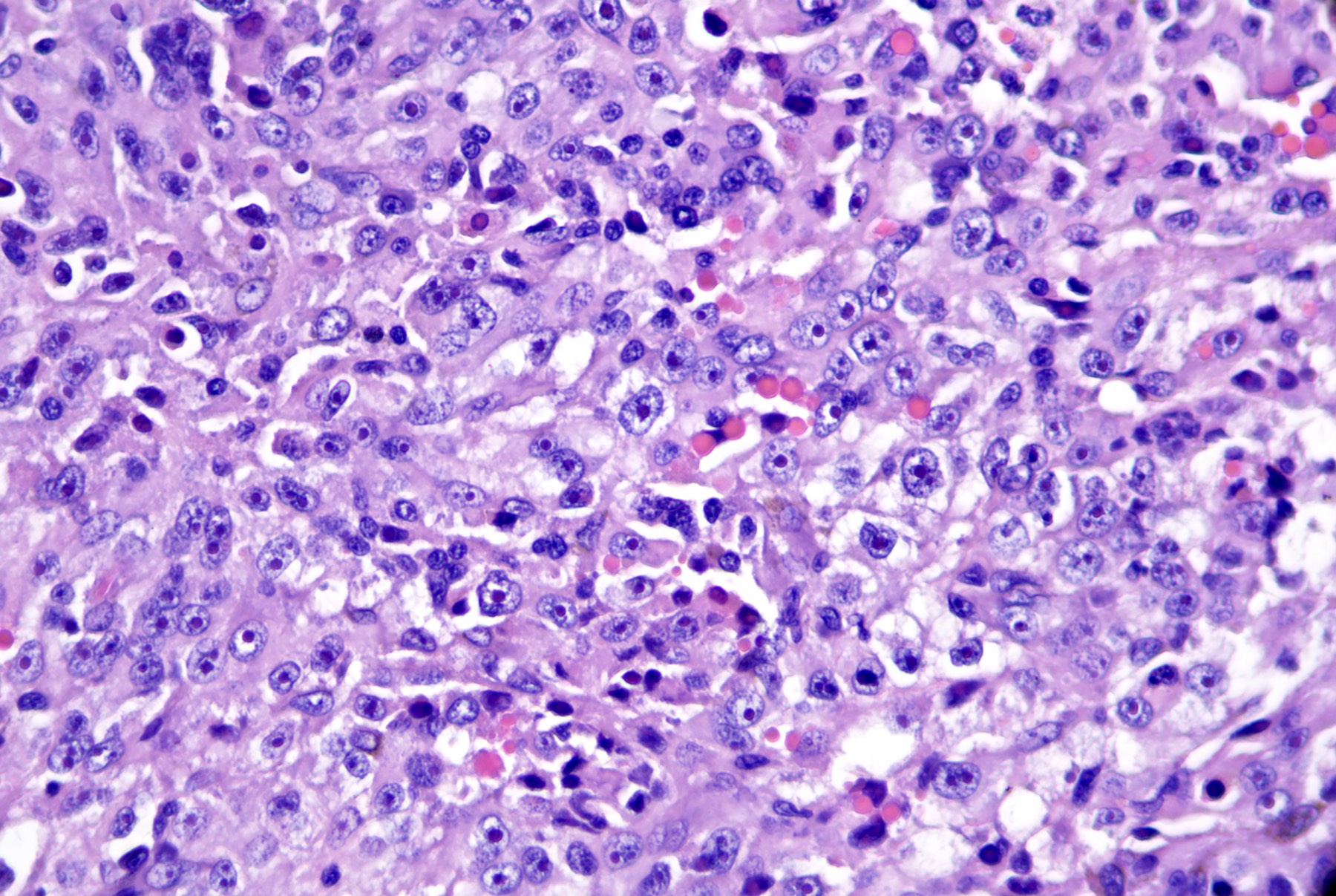
Microscopic (histologic) images
Additional references
Board review style question #1
What are melanocytic neoplasms with > 1 driver mutation with a second mutation affecting specific pathways resulting in distinct atypical microscopic features, increased risk of local recurrence and little risk of distant spread best defined as?
- Melanocytic hyperplasia
- Melanocytic tumors of uncertain metastatic potential
- Melanocytomas
- Melanomas
- Nevi
Board review style answer #1
C. Melanocytomas. Melanocytomas are neoplasms with > 1 driver mutation with a second mutation affecting specific pathways resulting in distinct atypical microscopic features and increased risk of local recurrence. Melanocytomas occur on a spectrum between nevi and melanoma. Examples include WNT activated deep penetrating / plexiform melanocytoma (previously deep penetrating nevus), pigmented epithelioid melanocytoma (PEM, also known as PRKAR1A inactivated melanocytoma) and BAP1 inactivated melanocytoma.
Answer D is incorrect because melanomas are malignant neoplasms that have accumulated mutations, allowing for unregulated growth and lack of response to tumor suppressor pathways. They have a risk of both local recurrence and distant metastasis. Answer E is incorrect because nevi are melanocytic tumors with a single initiating mutation, bland cytology and benign biology. Answer B is incorrect because melanocytic tumors of uncertain metastatic potential is reserved for neoplasms with atypical features that fall short of melanoma yet do not exhibit typical histopathologic, immunohistochemical and molecular features of well described melanocytomas. These are lesions with a prominent dermal component whose biologic behavior is unclear and in which melanoma is the main diagnostic consideration. Answer A is incorrect because melanocytic hyperplasia is a general term for an increase in epidermal melanocytes, which may be benign, atypical or frankly malignant.
Comment Here
Reference: Skin melanocytic tumor - WHO classification
Answer D is incorrect because melanomas are malignant neoplasms that have accumulated mutations, allowing for unregulated growth and lack of response to tumor suppressor pathways. They have a risk of both local recurrence and distant metastasis. Answer E is incorrect because nevi are melanocytic tumors with a single initiating mutation, bland cytology and benign biology. Answer B is incorrect because melanocytic tumors of uncertain metastatic potential is reserved for neoplasms with atypical features that fall short of melanoma yet do not exhibit typical histopathologic, immunohistochemical and molecular features of well described melanocytomas. These are lesions with a prominent dermal component whose biologic behavior is unclear and in which melanoma is the main diagnostic consideration. Answer A is incorrect because melanocytic hyperplasia is a general term for an increase in epidermal melanocytes, which may be benign, atypical or frankly malignant.
Comment Here
Reference: Skin melanocytic tumor - WHO classification