Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Grove N. Familial benign chronic pemphigus (Hailey-Hailey disease). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skinnontumorhaileyhailey.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Autosomal dominant genodermatosis characterized by intraepidermal vesicles located predominately in intertriginous area
- Vesicles may progress to bullae, then rupture, forming a crust
- Histology shows intraepidermal acantholysis due to nonfunctional desmosomal protein complexes
Essential features
- Genodermatosis with autosomal dominant inheritance pattern (mutation in ATPC1 gene), 33% of cases are sporadic
- Presents in second to forth decades, improves with age
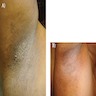
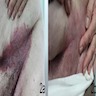
- Vesicles / bullae in intertriginous areas (axillae, groin, perianal and inframammary areas). exacerbated by perspiration
- Rarely involves other areas
- Relapsing remitting clinical course
- Secondary infection (bacterial, herpetic) can be problematic and serious
- Main treatment is topical steroids and topical antimicrobials
Terminology
- Also called benign familial pemphigus
- Papular acantholytic dermatosis in genitocrural region may be a localized form of H-H disease
ICD coding
- ICD-10: Q82.8 - Other specified congenital malformations of skin
Epidemiology
- Presents in second to fourth decades, improves with age
- 1/50,000 (Indian Dermatol Online J 2016;7:147)
- No sex predilection
Sites
- Axillae, groin, perianal and inframammary areas
- Rarely involves other sites
Pathophysiology
- Mutation in ATP2C1, a calcium pump important in normal function of desmosomal protein complex
- Dissociation of intracellular and extracellular domains of desmosomal cadherin and E-cadherin (adherens junction associated protein)
- Faulty calcium pump action leads to disorganized function of desmogleins, which are calcium dependent adherence proteins (cadherins) (Indian Dermatol Online J 2016;7:147)
- Hailey-Hailey and Darier disease share similar pathogenesis, as opposed to pemphigus vulgaris, in which autoantibodies develop against desmosomal proteins
Etiology
- Blistering lesions in affected individuals may be induced by trauma, heat, UV light, perspiration
- May be complicated by secondary infection with scabies, bacteria, herpes or yeast
Clinical features
- Pruritic / burning, often malodorous lesions
- Papular, verrucous, annular and vesiculopustular variants are rare
- Nikolski sign may be positive
- 33% of cases are sporadic
- Healing accompanied by hyperpigmentation, but scarring is rare
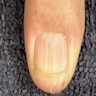
- Longitudinal leukonychia (asymptomatic white longitudinal bands on the fingernails in 70% of patients)
- Superinfection by Candida albicans, herpes virus and Staphylococcus aureus are frequent complications
- Cases of complication by squamous cell carcinoma have been reported
- Symptoms worsen during summer, often disappear during winter
Case reports
- 25 year old woman and her 51 year old mother with bullous variant of Darier disease mimicking Hailey-Hailey disease (Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) 2011;1:31)
- 26 year old man with papular acantholytic dyskeratosis localized to the perineal and perianal area (Indian J Dermatol 2013;58:393)
- 38 year old woman with coexisting Darier disease and Hailey-Hailey disease (Postepy Dermatol Alergol 2017;34:180)
- 44 year old woman with squamous cell carcinoma arising from a localized vulval lesion of Hailey-Hailey disease after tacrolimus therapy (Am J Obstet Gynecol 2010;203:e5)
- 57 year old woman and her 61 year old brother with Hailey-Hailey disease showing atypical clinical features (JAMA Dermatol 2014;150:97)
Treatment
- Topical steroids and topical antimicrobials are the first line treatments
- Botulinum toxin A injections
- Cryotherapy
- Photodynamic therapy
- Oral magnesium chloride
- Laser ablation
- Electron beam radiotherapy
- Dermabrasion
- Glycopyrrolate
- Afamelanotide
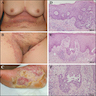
Clinical images
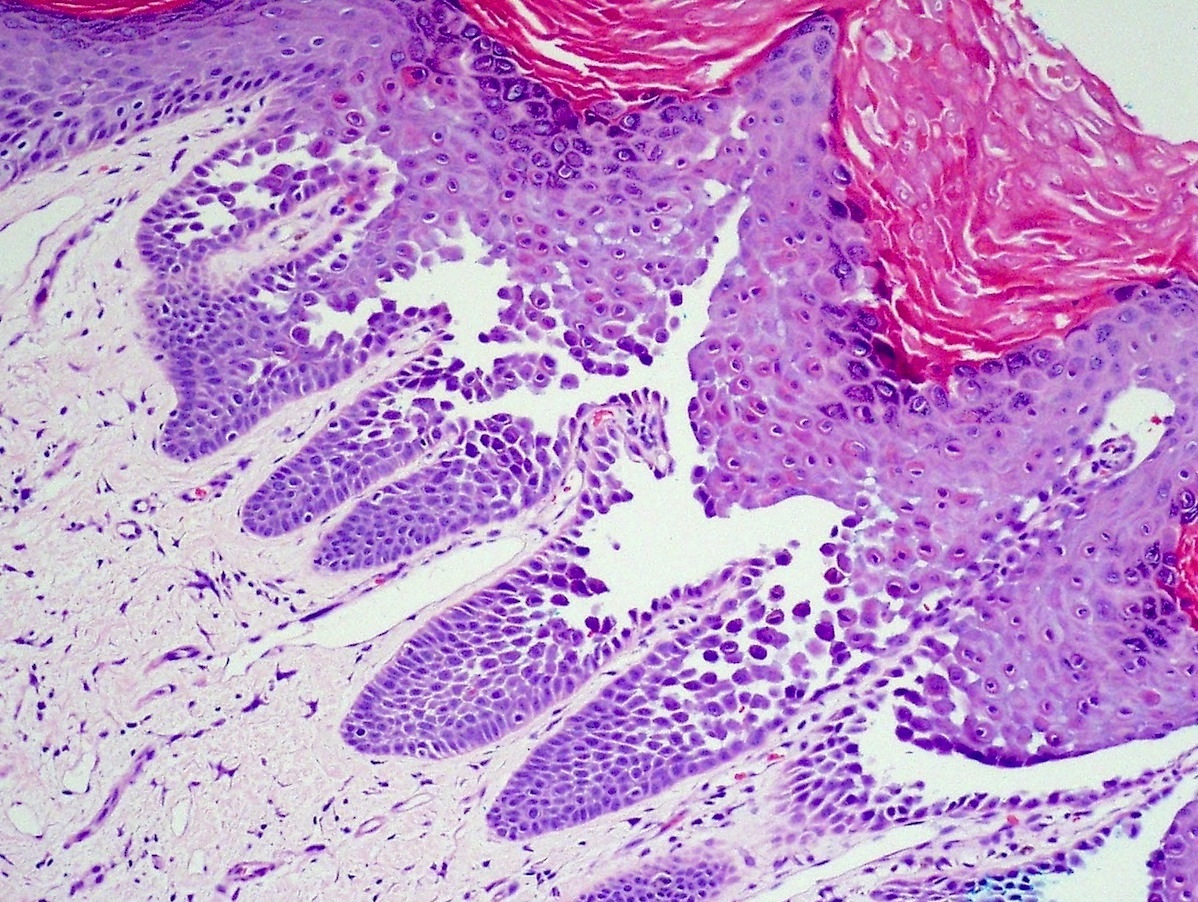
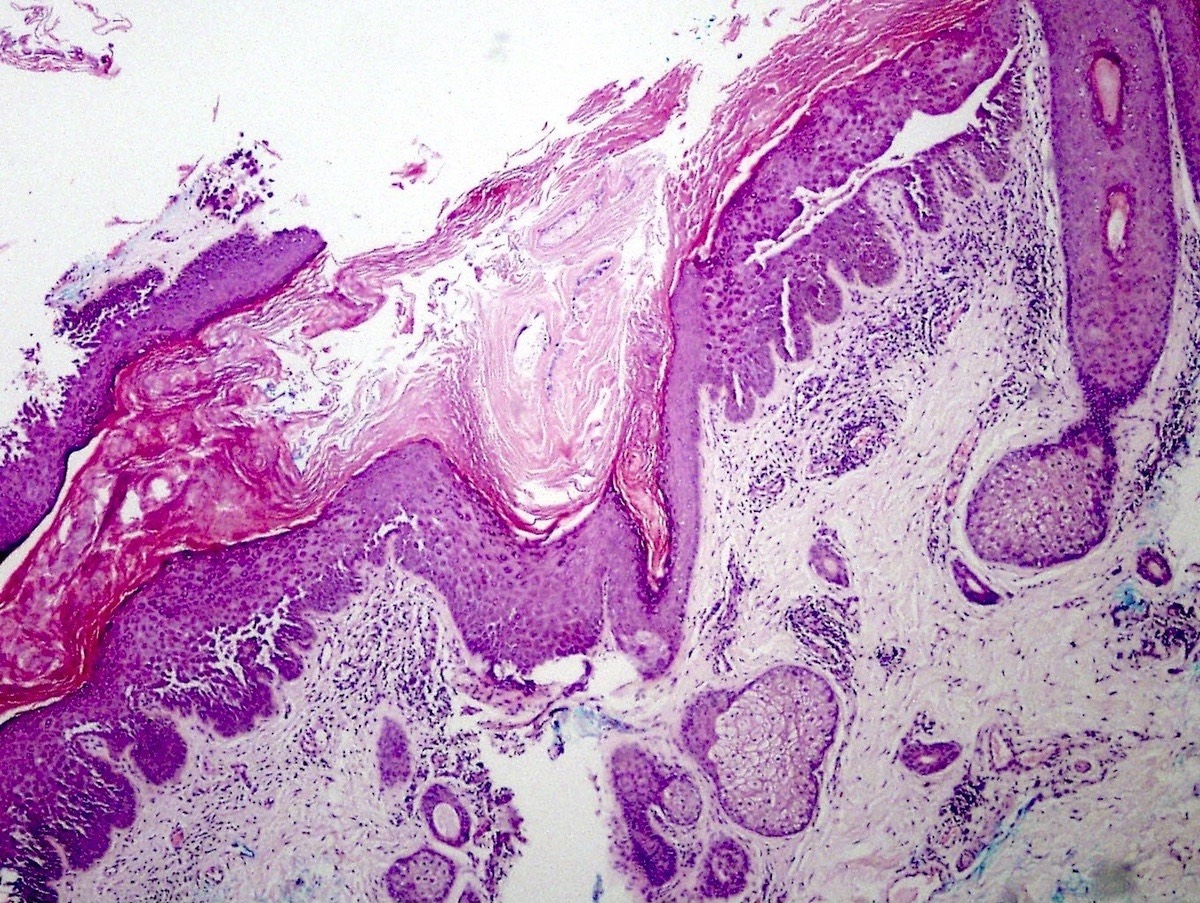
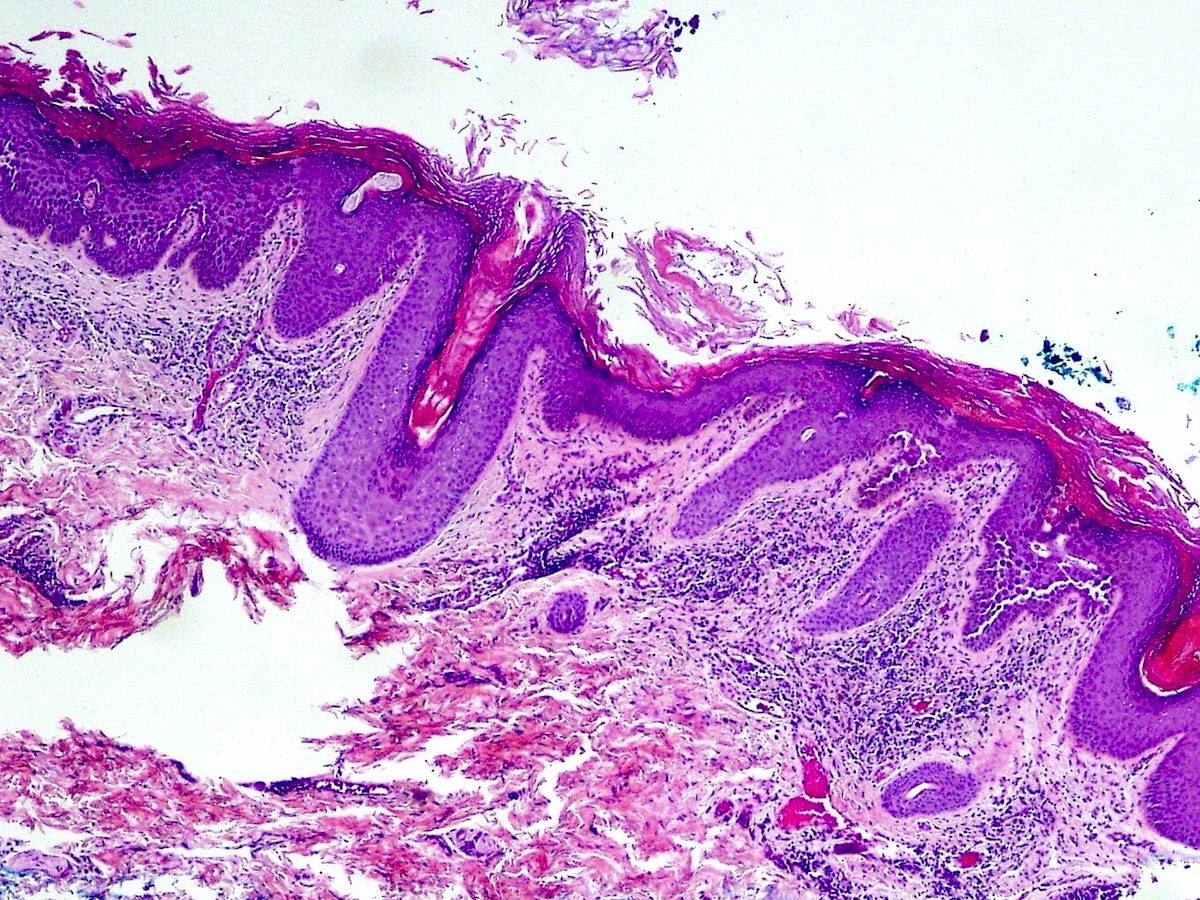
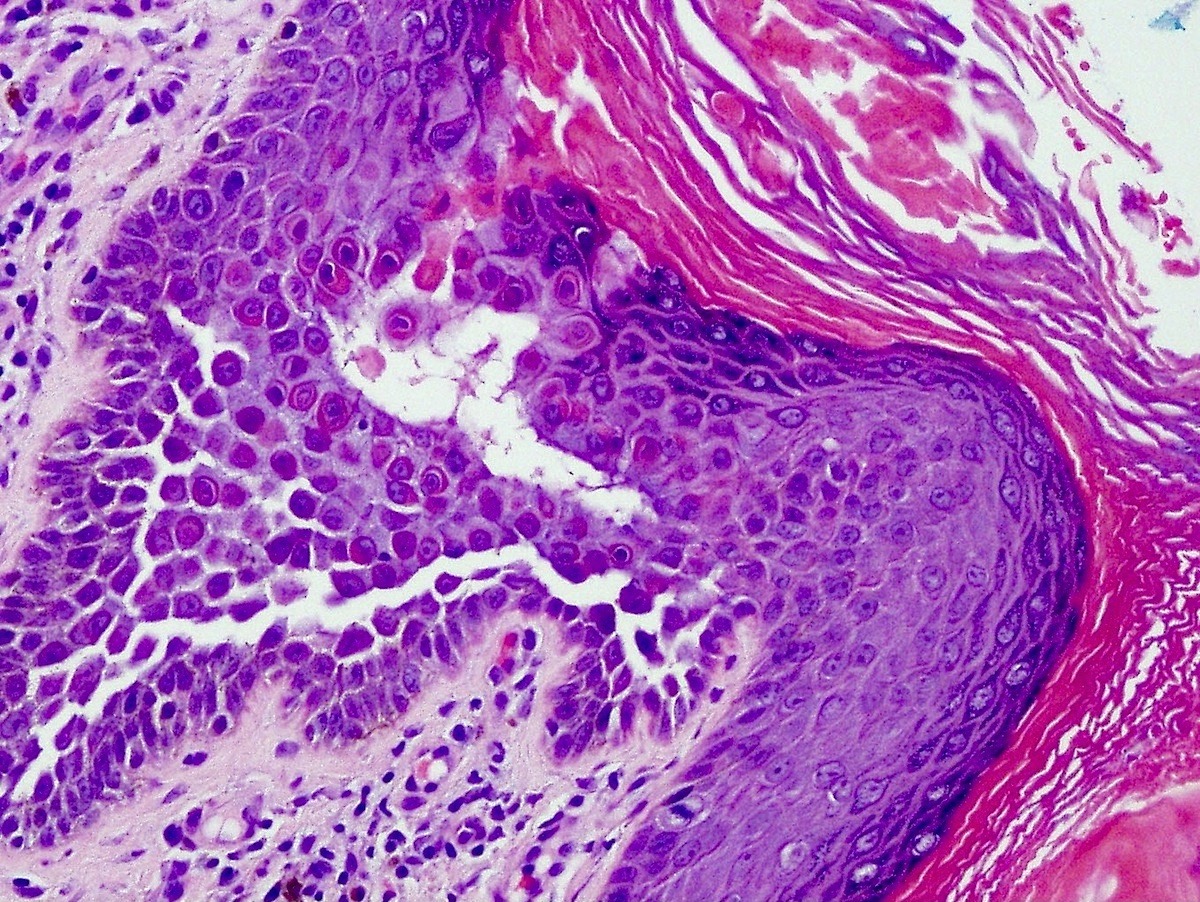
Microscopic (histologic) description
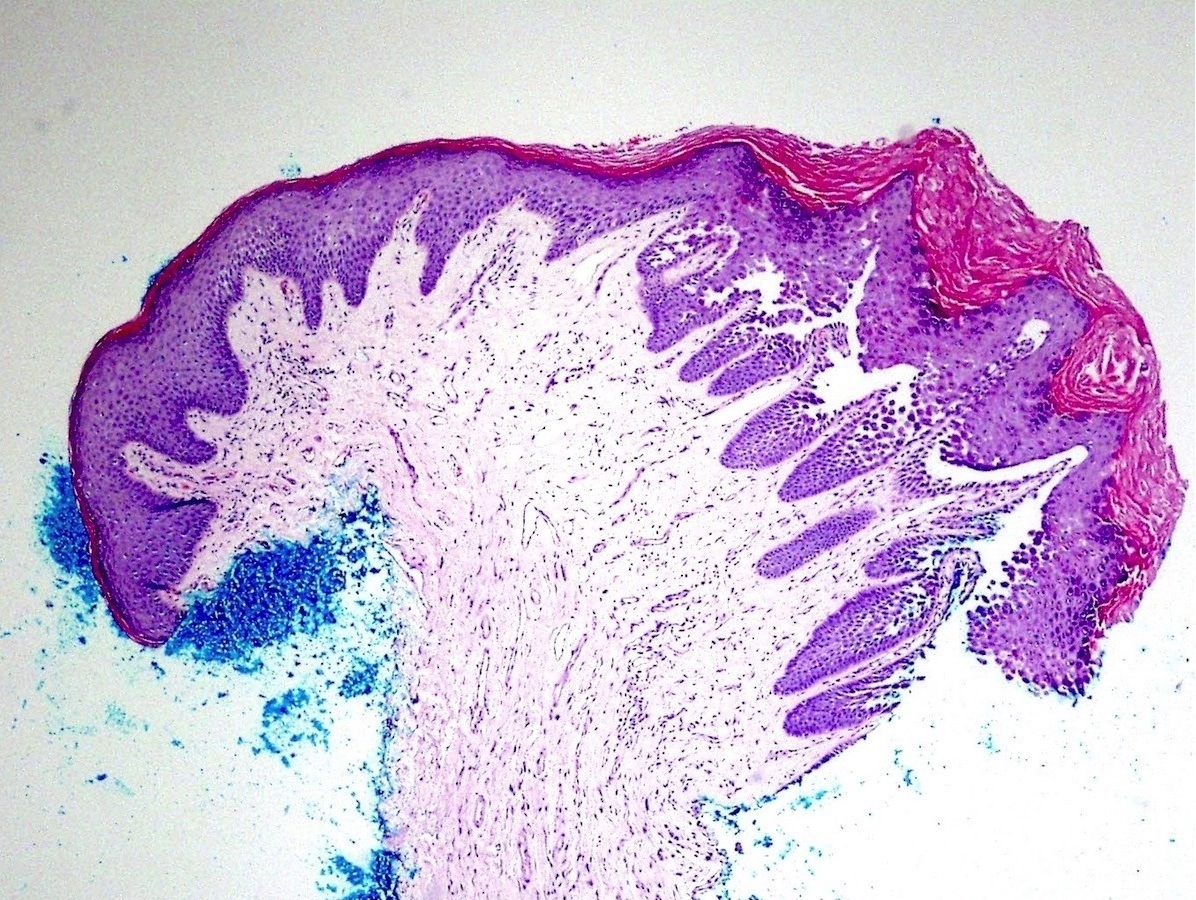
- Suprabasilar and intraepidermal clefting
- Acantholysis of keratinocytes resembling dilapidated brick wall
- Epidermal hyperplasia
- No pronounced dyskeratosis but dyskeratotic keratinocytes have well defined nucleus and preserved cytoplasm (unlike pemphigus vulgaris)
- Corps ronds and grains are rare
- Adnexal structures are spared
- Dermis shows variable chronic inflammatory infiltrate
- Parakeratotic crust may contain neutrophils and bacteria
- Immunofluorescence negative
Microscopic (histologic) images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Autosomal dominant condition with incomplete penetrance
- ATPase calcium transporting type 2C member 1 gene (ATP2C1) on chromosome 3q21-q24 encodes a CA2+/ Mn2+ ATPase channel pump SPCA1
Differential diagnosis
- Darier disease:
- ATP2A2 mutation
- Less acantholysis, more dyskeratosis
- Involves "seborrheic" areas of the body, including scalp, face, upper chest, back
- Acantholytic zones involve adnexal structures (particularly hair follicles)
- Numerous corps ronds and grains
- Grover disease:
- Narrow vesicles involving only a few rete ridges but may be histologically identical to Hailey-Hailey disease
- Different clinical distribution of lesions
- Acquired rather than inherited (no family history)
- Papular acantholytic dermatosis of the genitocrural region:
- Localized variant of Hailey-Hailey or Darier disease involving only the perigenital areas
- Pemphigus vulgaris:
- No predilection for intertriginous areas
- Intact epithelium in adjacent epidermis
- Involvement of adnexal structures
- Eosinophils on histology
- Less acantholysis, more dyskeratosis
- Autoimmune mediated direct immunofluorescence is positive
- Relapsing linear acantholytic dermatosis:
- Vesicles follow the lines of Blaschko
Additional references
Board review style question #1
- What is the underlying pathogenesis of Hailey-Hailey disease?
- ATP2A2 mutation
- ATP2C1 mutation
- Autoantibodies against desmosomal proteins
- Autoantibodies against non collagenous domain of type VII collagen
- Autoantibodies against the hemidesmosomal antigens bullous pemphigoid antigen 1 (BP1) and 2 (BP2)
Board review style answer #1
B. Hailey-Hailey is caused by an autosomal dominant mutation in ATP2C1, a calcium pump important in normal function of desmosomal protein complex. This mutation causes dissociation of intracellular and extracellular domains of desmosomal cadherin and E-cadherin (adherens junction associated protein), and a faulty calcium pump action leads to disorganized function of desmogleins, which are calcium dependent adherence proteins (cadherins).
Comment Here
Reference: Hailey-Hailey disease
Comment Here
Reference: Hailey-Hailey disease
Board review style question #2
- What differential diagnosis of Hailey-Hailey is also inherited in an autosomal dominant manner?
- Darier disease
- Grover disease
- Papular acantholytic dermatosis of the genitocrural region
- Pemphigus vulgaris
- Relapsing linear acantholytic dermatosis
Board review style answer #2
A. Darier disease is the only other genodermatosis transmitted in an autosomal dominant manner. The disease is due to the mutation in ATP2A2 that encodes sarco / endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) ATPase isoform 2 (SERCA2).
Comment Here
Reference: Hailey-Hailey disease
Comment Here
Reference: Hailey-Hailey disease