Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Immunofluorescence description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Motaparthi K. Granuloma faciale. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skinnontumorgranulomafaciale.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Chronic fibrosing vasculitis with eosinophils
- Facial plaque or plaques
- Often refractory to treatment (An Bras Dermatol 2016;91:803)
Essential features
- Solitary or multiple asymptomatic red-brown plaques on the face
- Persistent and refractory to treatment
- Mixed infiltrate with neutrophils, plasma cells and eosinophils
- Fibrosing vasculitis: leukocytoclasia with perivascular and often storiform fibrosis
ICD coding
- ICD-10: L92.2 - Granuloma faciale (eosinophilic granuloma of skin)
Epidemiology
- Rare
- M > F
- Mean age 53 years (J Am Acad Dermatol 2005;53:1002)
Sites
- Face - forehead, cheeks and nose - most common
- Extrafacial - trunk or extremities - not uncommon
Pathophysiology
- Immune complex mediated vasculitis (J Cutan Pathol 2006;33:508)
- IL5 production by clonal CD4+ T cells leads to eosinophil recruitment (Br J Dermatol 2005;153:454)
Etiology
- Unknown at this time
Clinical features
- Usually solitary but multiple lesions observed in > 30% of cases
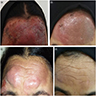
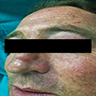
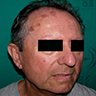
- Red-brown or violaceous plaque (An Bras Dermatol 2016;91:803)
- Asymptomatic with occasional pruritus (An Bras Dermatol 2016;91:803)
- Associated with eosinophilic angiocentric fibrosis
- Rare, progressive fibrosing disorder of sinonasal mucosal surfaces
- Same histopathology as granuloma faciale
- Same populations of T cells as granuloma faciale (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2017;25:213)
Diagnosis
- Dermoscopy: prominent follicular orifices, whitish streaks, telangiectasia and yellow-brown areas (An Bras Dermatol 2018;93:587)
Prognostic factors
- Persists indefinitely and frequently refractory to treatment
- Spontaneous resolution is rare
Case reports
- 25 year old woman with plaques on the forehead and around the mouth (Dermatol Ther 2020;33:e13162)
- 41 year old man with a plaque on the nose (Int J Dermatol 2020;59:e29)
- 47 year old woman with multiple facial plaques, epistaxis and saddle nose (Br J Dermatol 2018;178:e395)
- 54 year old man with multiple plaques and nodules on the forehead (Clin Exp Dermatol 2017;42:799)
- 63 year old woman with a painful plaque on the cheek (Acta Derm Venereol 2019;99:833)
Treatment
- First line
- Topical tacrolimus
- Second line
- Intralesional corticosteroids
- Cryotherapy
- Refractory cases
- Pulsed dye laser
- Dapsone (Acta Derm Venereol 2018;98:14)
Clinical images
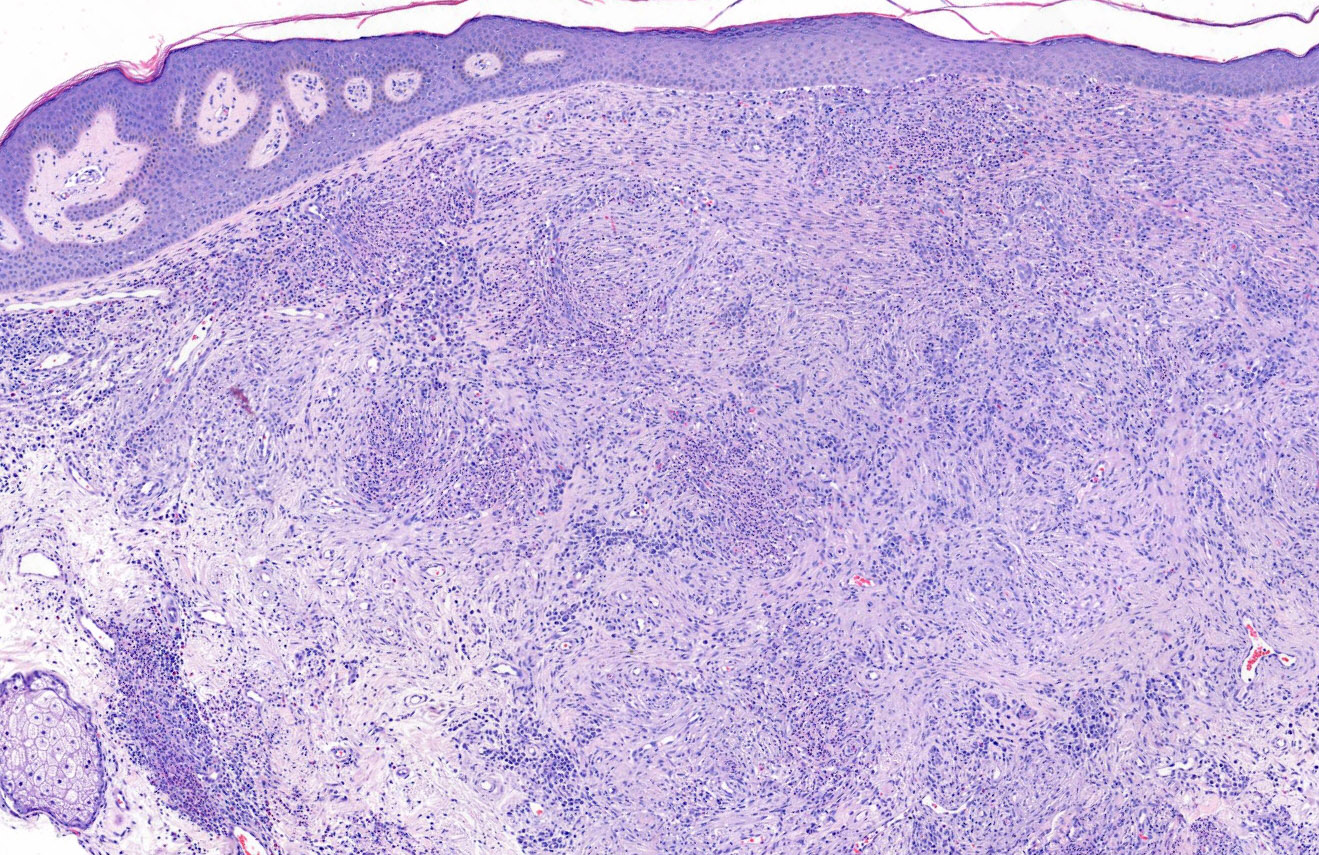
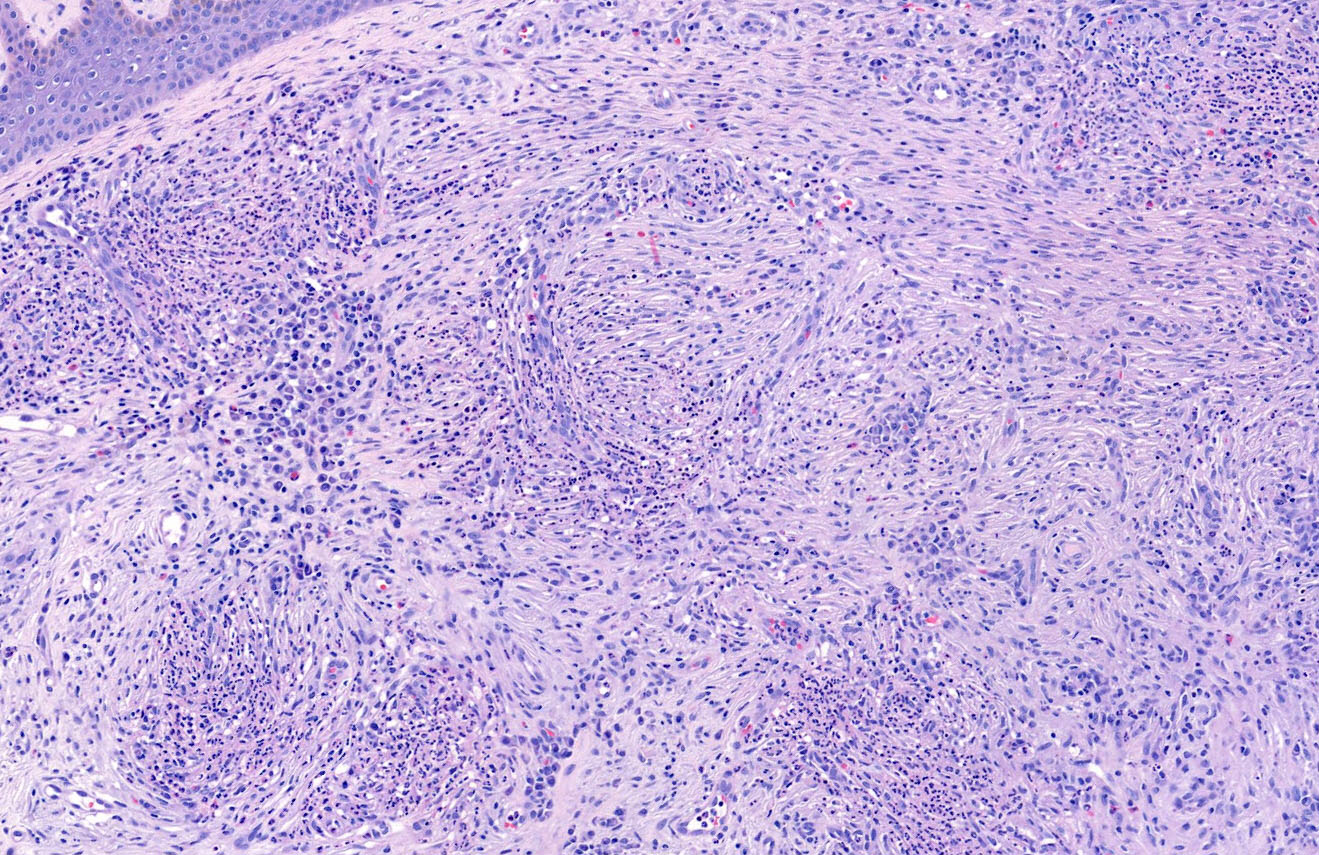
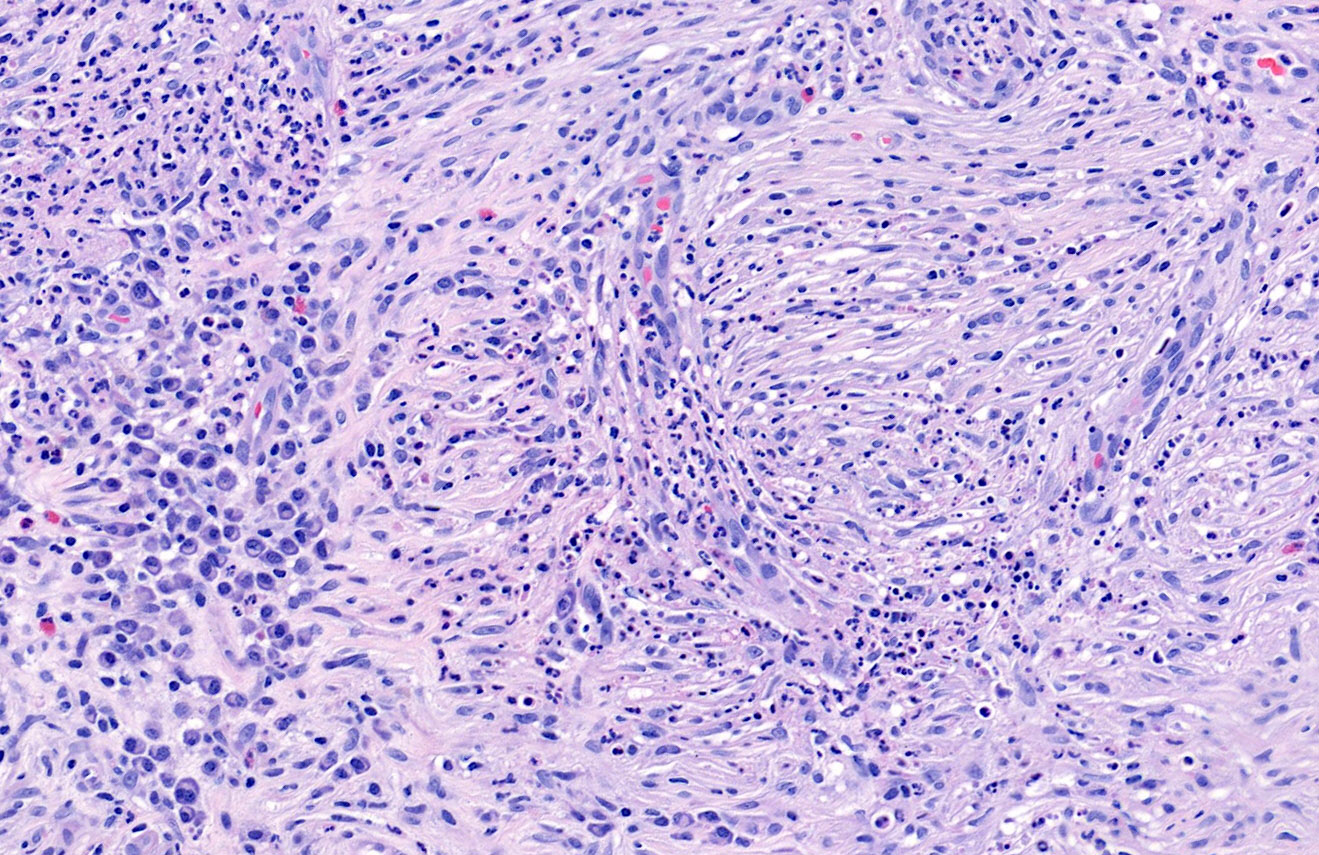
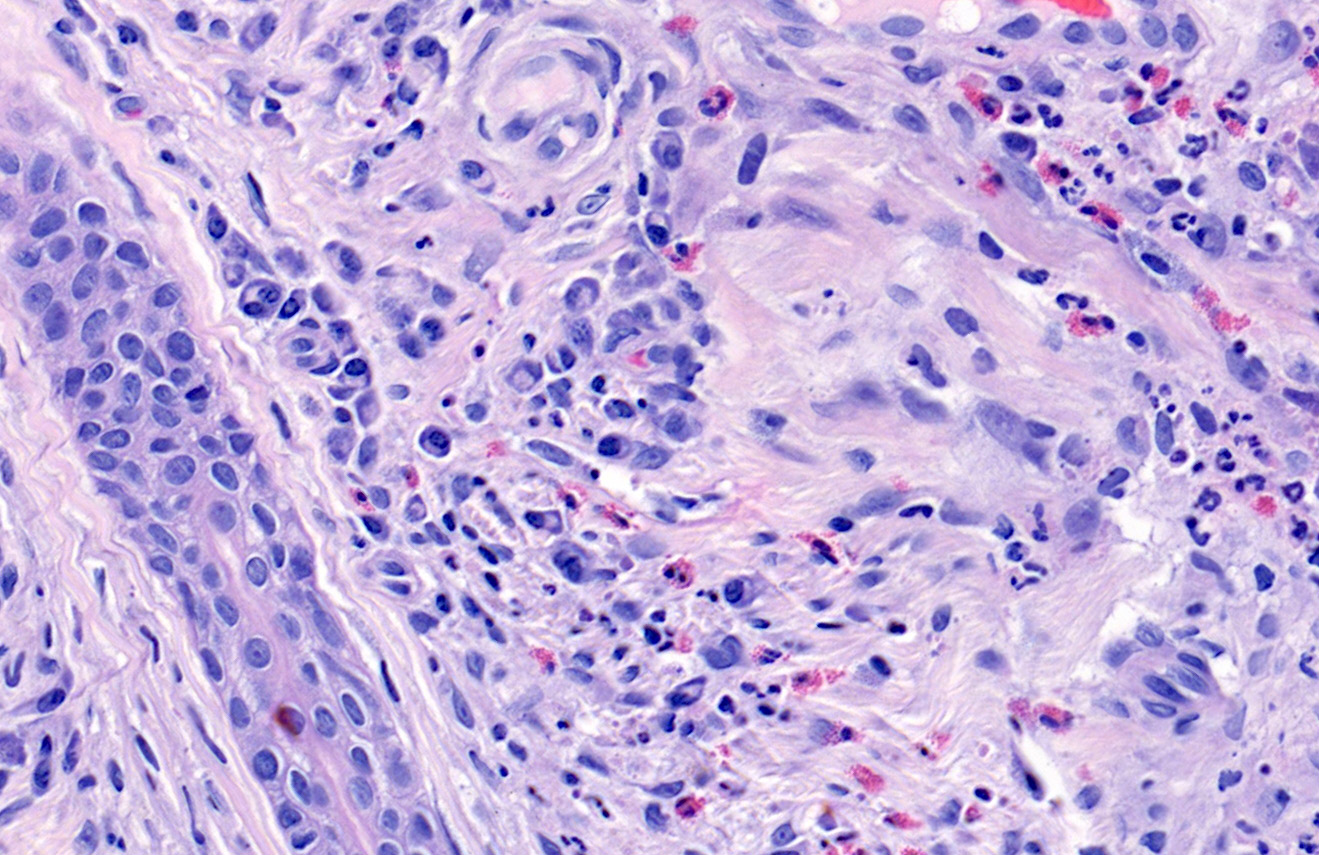
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Grenz zone
- Diffuse, polymorphous inflammatory infiltrate involves the upper half of the dermis
- Neutrophils, plasma cells, eosinophils, lymphocytes and histiocytes
- Leukocytoclasia (karryorrhexis), extravasated red blood cells and hemosiderin
- Fibrinoid necrosis of small vessels is variable
- Perivascular fibrosis with clefting between collagen bundles results in storiform fibrosis
- Fibrosing vasculitis pattern also observed in erythema elevatum diutinum (Am J Clin Pathol 2016;145:401)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Immunofluorescence description
- Immunoglobulin and complement deposition within vessel walls and at the dermoepidermal junction are variable (J Cutan Pathol 2006;33:508)
Sample pathology report
- Skin, nasal dorsum, punch biopsy:
- Granuloma faciale
Differential diagnosis
- Erythema elevatum diutinum:
- More prominent fibrosis in late lesions
- Often paucicellular inflammatory infiltrate in late lesions
- Few plasma cells
- Fewer eosinophils (J Cutan Pathol 2011;38:876)
- Generally papules and nodules on backs of hands, extensor surfaces of extremities, buttock and trunk
- Cutaneous IgG4 related disease:
- > 200 IgG4 positive plasma cells per high power field
- IgG4/IgG ratio > 40% within plasmacellular infiltrate (Am J Clin Pathol 2016;145:401)
- Lymphocytoma cutis (pseudolymphoma, cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia):
- No vasculitis
- Few neutrophils and no leukocytoclasia
- Often germinal centers with tingible body macrophages
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Compared with granuloma faciale, which of the following disorders demonstrates nearly identical histopathologic features?
- Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia
- Eosinophilic angiocentric fibrosis
- Eosinophilic cellulitis
- Eosinophilic folliculitis
- Eosinophilic fasciitis
Board review style answer #2