Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Gustafson DM, Chung CG. Dermatophytes / tinea. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skinnontumorfungisuperficialinfections.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Superficial cutaneous mycoses classified by location of infection
- Common genera involved (Trichophyton, Epidermophyton, Microsporum and others) (J Fungi (Basel) 2023;9:669)
- Dermatophytes typically reside in keratinized tissue (i.e., the stratum corneum, nails and hair shaft) and rarely show invasion (Mycoses 2021;64:340)
Essential features
- Tinea is diagnosed by identification of fungal organisms consistent with dermatophytes by microscopic examination of skin scrapings with KOH or by skin biopsy; periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) or Grocott-Gomori silver (GMS) special stains may be used on skin biopsies to help identify organisms
- Diagnosis classified by body site of infection
Terminology
- Classified by primary site of infection (Am Fam Physician 2014;90:702, JAAD Int 2023;13:104, Mycopathologia 2010;170:143)
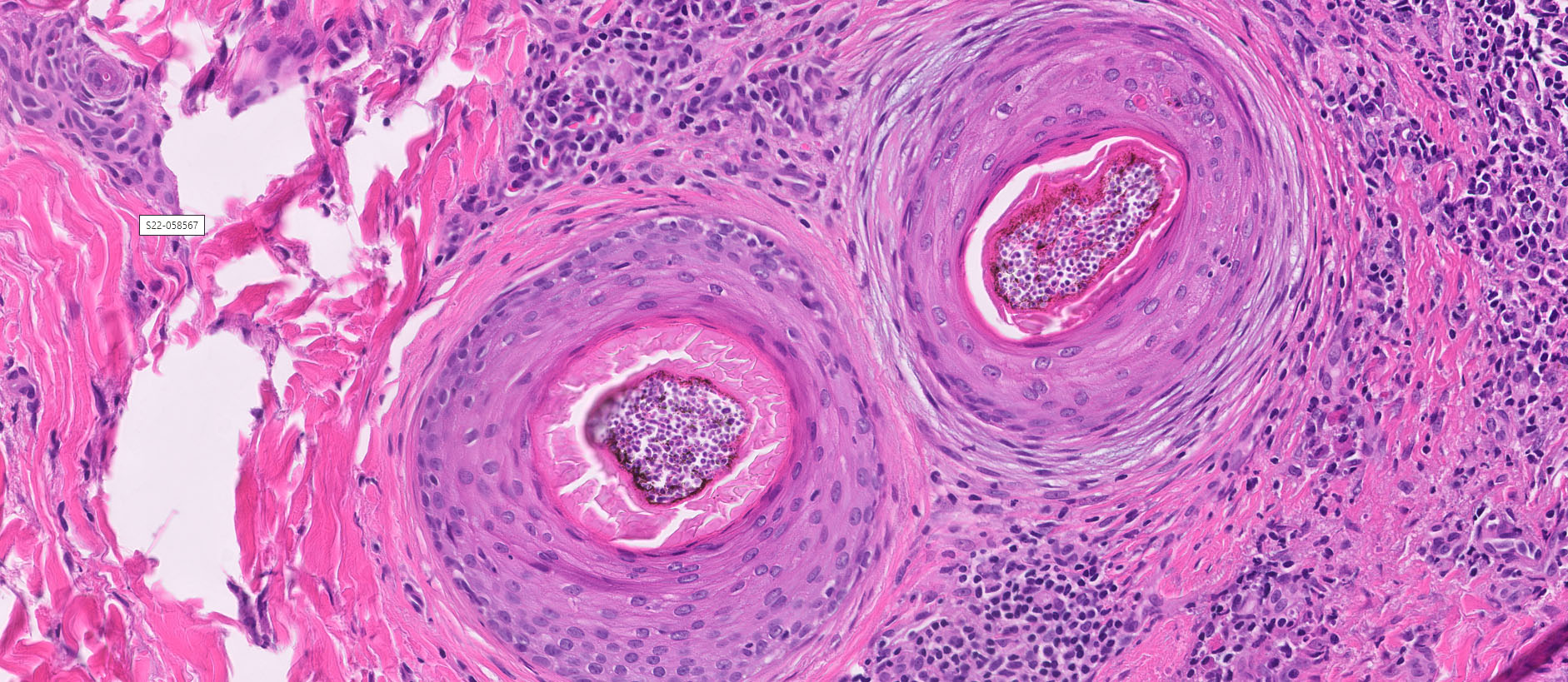
- Majocchi granuloma: dermatophytosis of hair follicles outside of the scalp and beard area
- Tinea barbae: dermatophytosis of the beard area, characteristically involving hair follicles
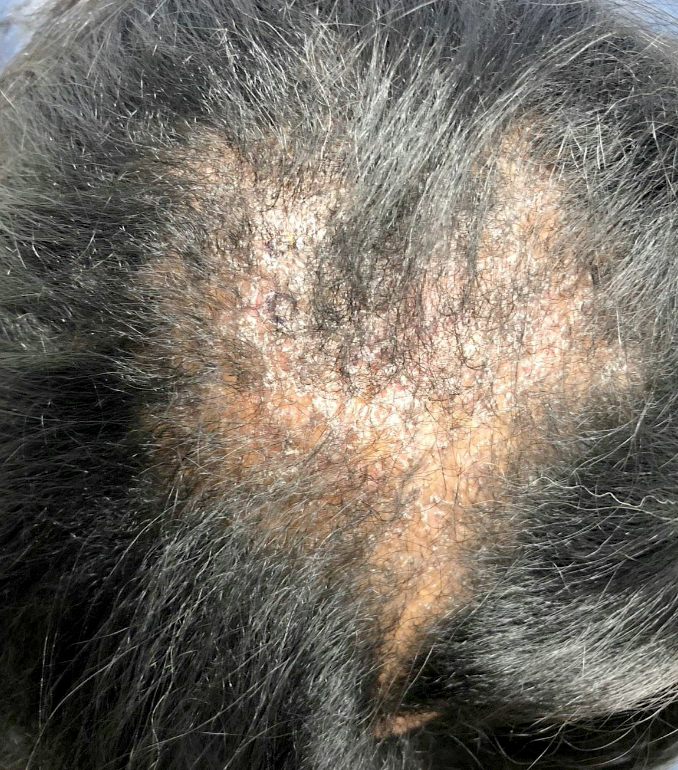
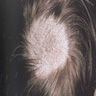
- Tinea capitis: dermatophytosis of the scalp, characteristically involving hair follicles
- Tinea corporis: dermatophytosis involving the trunk, neck, arms and legs
- Tinea cruris: dermatophytosis of the groin
- Tinea faciei: dermatophytosis of the face
- Tinea favosa: variant of tinea capitis; due to T. schoenleinii
- Tinea incognito: variant of tinea exacerbated by administration of topical / systemic corticosteroids
- Tinea manuum: dermatophytosis of the hands
- Tinea pedis: dermatophytosis of the feet
- Tinea unguium (onychomycosis): dermatophytosis of the nails
- Kerion: profound scalp inflammatory reaction associated with tinea capitis, especially by Microsporum canis infection
ICD coding
- ICD-10
- ICD-11
Epidemiology
- Affects 20 - 25% of the population worldwide (J Fungi (Basel) 2023;9:669)
- More common in subtropical regions (J Fungi (Basel) 2021;8:39)
- Most common organisms found in humans are Trichophyton, Microsporum, Epidermophyton and Nannizzia (J Fungi (Basel) 2023;9:669)
- Tinea capitis is more common in children
- Afro-Caribbean and Afro-American children in the United States have higher rates of infection; however, a host of epidemiologic factors can affect transmission (Am J Clin Dermatol 2005;6:203)
- Immunocompromised patients may have extensive / recurrent disease (J Fungi (Basel) 2021;8:39)
- Tinea favosa is endemic in Nigeria, Ethiopia, Western China, Iran and some regions in India (StatPearls: Favus [Accessed 26 September 2024)
- Trichophyton indotineae is an emerging dermatophyte that is sexually transmitted and extremely recalcitrant to therapy (J Am Acad Dermatol 2024;91:315, J Clin Med 2024;13:3558)
Sites
- See Terminology
Pathophysiology
- Fungal cell wall adhesins aid in inoculation and proteases digest host keratin (J Fungi (Basel) 2021;8:39)
- Host immune responses include innate, humoral and cell mediated (J Fungi (Basel) 2021;8:39)
Etiology
- Involves a group of closely related fungi that infect keratinized tissues such as the skin, hair and nails
- Spreads via direct contact with infected individuals, animals or contaminated surfaces
Clinical features
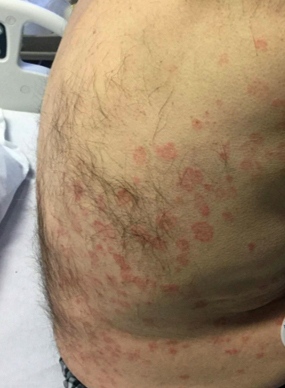
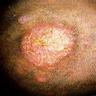
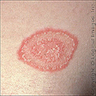
- Scaly, erythematous patches / plaques, often with an annular morphology (J Fungi (Basel) 2023;9:669)
- May present with pustules / vesicles (J Fungi (Basel) 2023;9:669)
- Onychomycosis may affect 1 or more nails and is characterized by onycholysis, hyperkeratosis, accumulation of subungual debris and nail discoloration (J Fungi (Basel) 2023;9:669)
Diagnosis
- Common methodologies
- Wood lamp fluorescence (Pathogens 2022;11:957)
- Potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation
- Skin biopsy
- Other methodologies
- Culture on dermatophyte test medium and Sabouraud dextrose agar (SDA)
- Various other media can be used to differentiate Trichophyton species (Pathogens 2022;11:957)
- Polymerase chain reaction may be used for diagnosis (Pathogens 2022;11:957)
Prognostic factors
- Most localized infections are treated effectively with topical or oral antifungal medications (J Am Acad Dermatol 2000;43:S104)
- Half of patients with invasive dermatophytosis are immunosuppressed (Mycoses 2021;64:340)
- Overall mortality rate is ~8% in invasive dermatophytosis and is higher in disseminated infection (Mycoses 2021;64:340)
Case reports
- 8 year old boy with tinea capitis and alopecia (CMAJ 2024;196:E526)
- 18 year old man with tattoo associated tinea corporis (Cureus 2022;14:e21210)
- 23 year old woman with ulcerative tinea manuum caused by N. gypsea (Cureus 2024;16:e55576)
- 27 year old man with T. indotineae (Med Mycol Case Rep 2022;36:37)
- 28 and 47 year old woman with T. indotineae, first reported U.S. cases (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2023;72:536)
- 57 year old man with tinea incognito (J Fungi (Basel) 2022;8:312)
- 78 year old woman with tinea capitis due to T. rubrum (Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 2021 Apr 24 [Epub ahead of print])
Treatment
- Topical antifungal therapy for most localized infections (J Fungi (Basel) 2021;8:39)
- Oral antifungal medications may be required for more extensive infections, including (J Fungi (Basel) 2021;8:39, Indian Dermatol Online J 2016;7:77)
- Large body surface area of involvement or overlapping body regions (e.g., tinea cruris, tinea corporis and tinea pedis)
- Infection failing to respond to repeated and different topical agents
- Tinea capitis
- Tinea affecting the nails
- Tinea pedis with extensive sole, heel or dorsal involvement or blistering
Clinical images
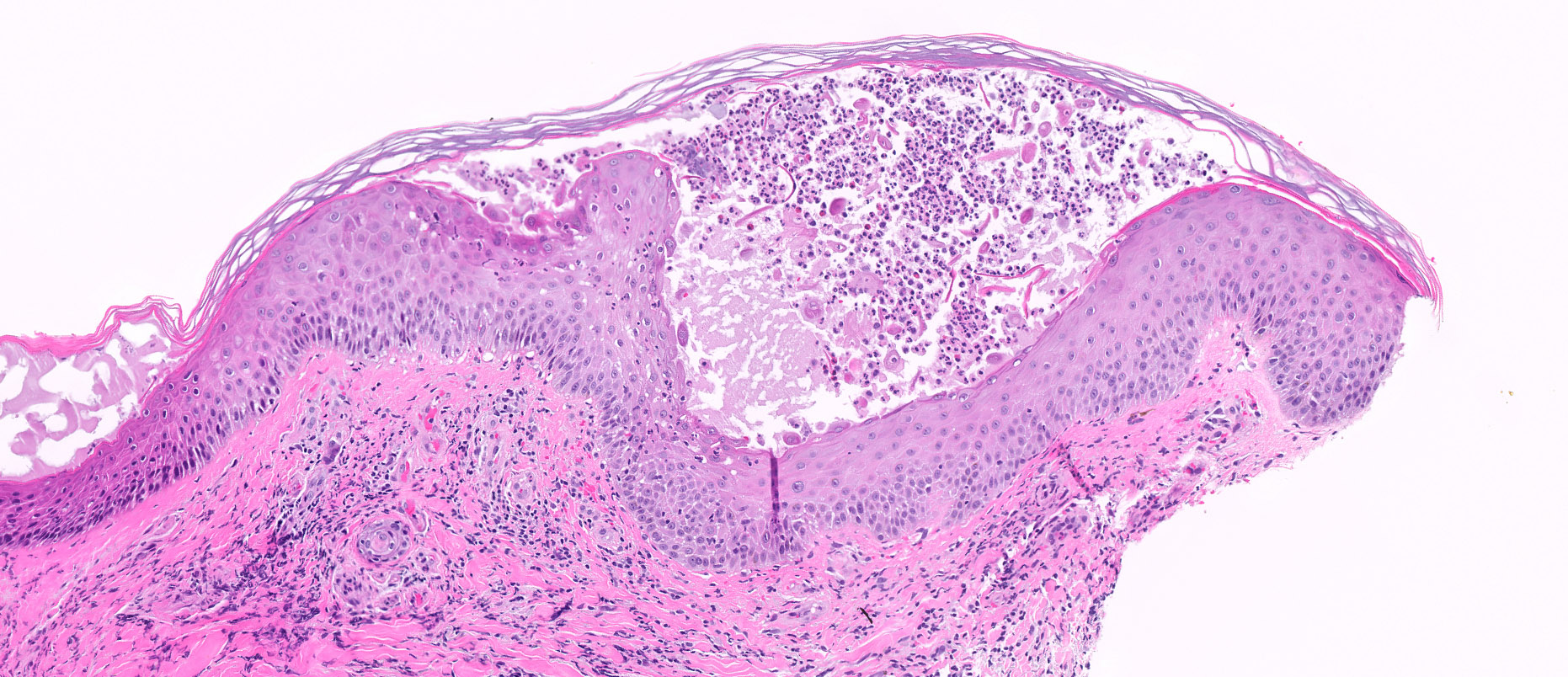
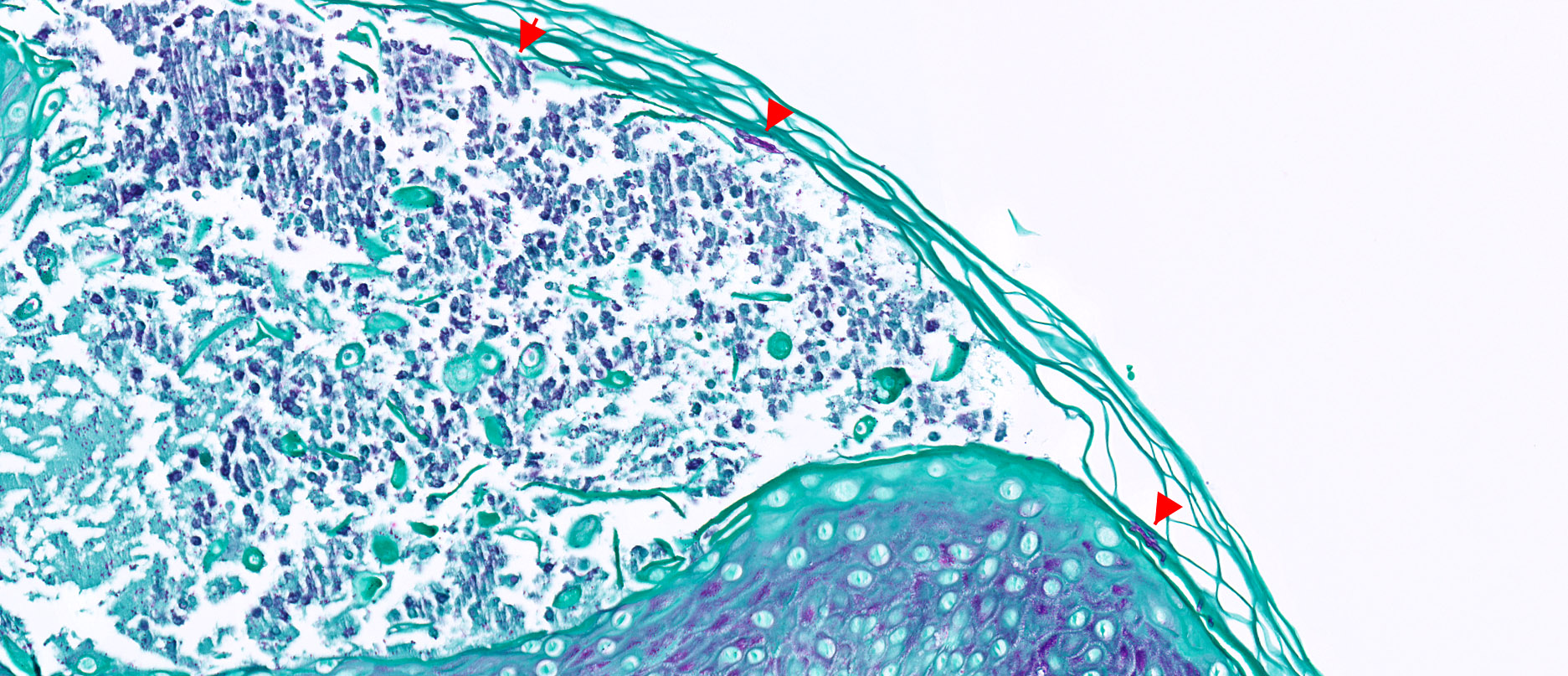
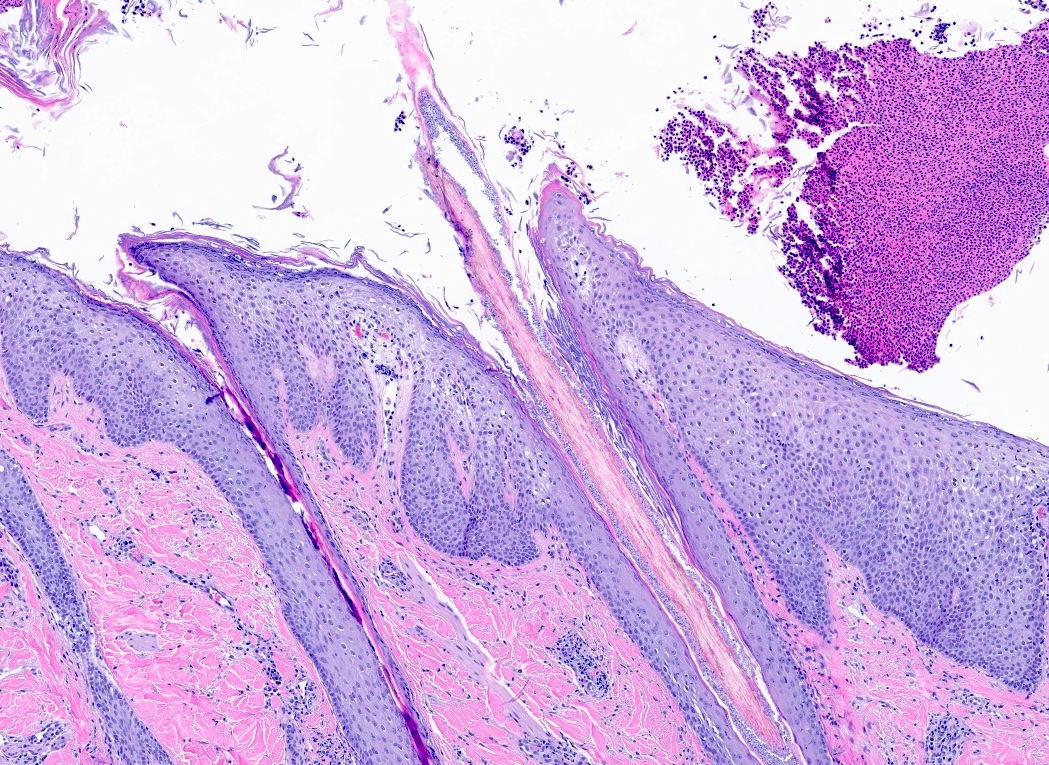
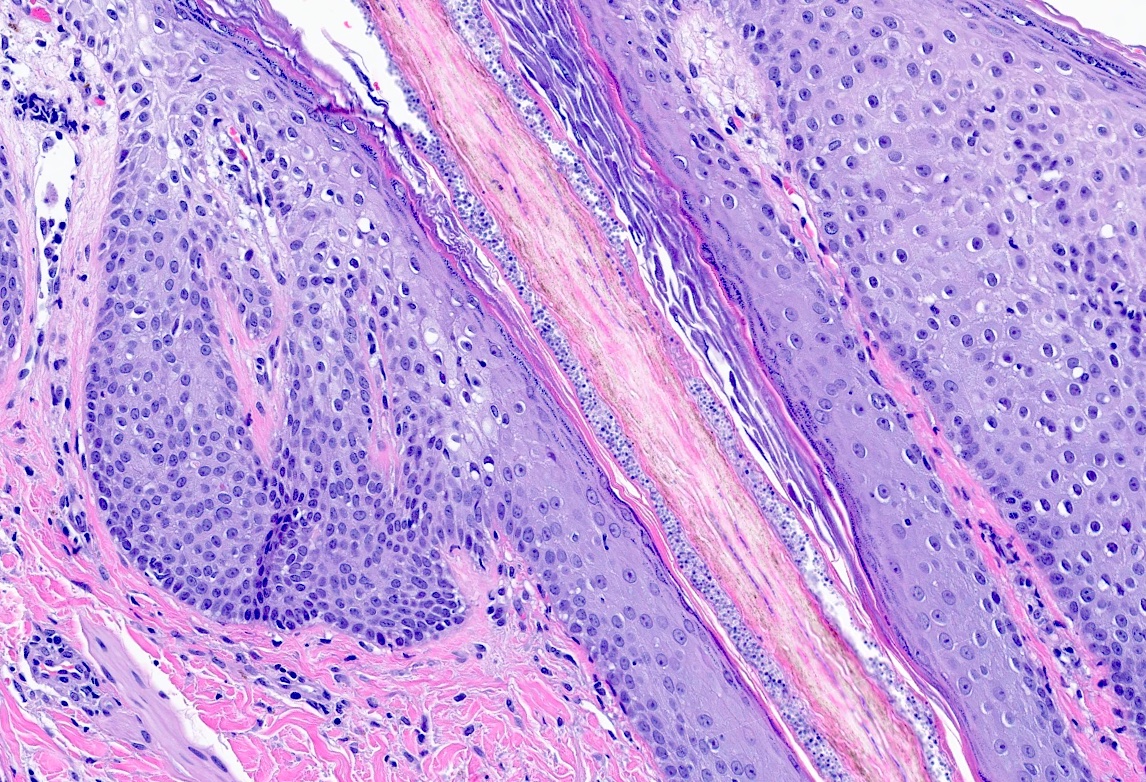
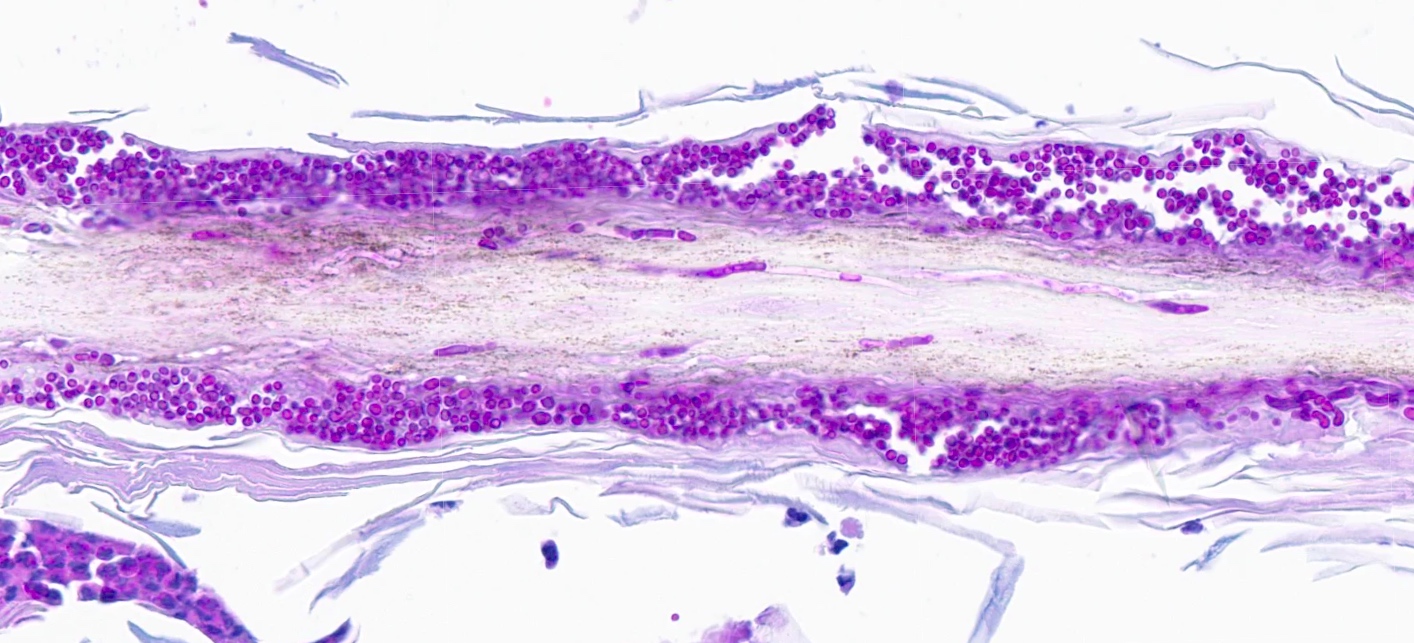
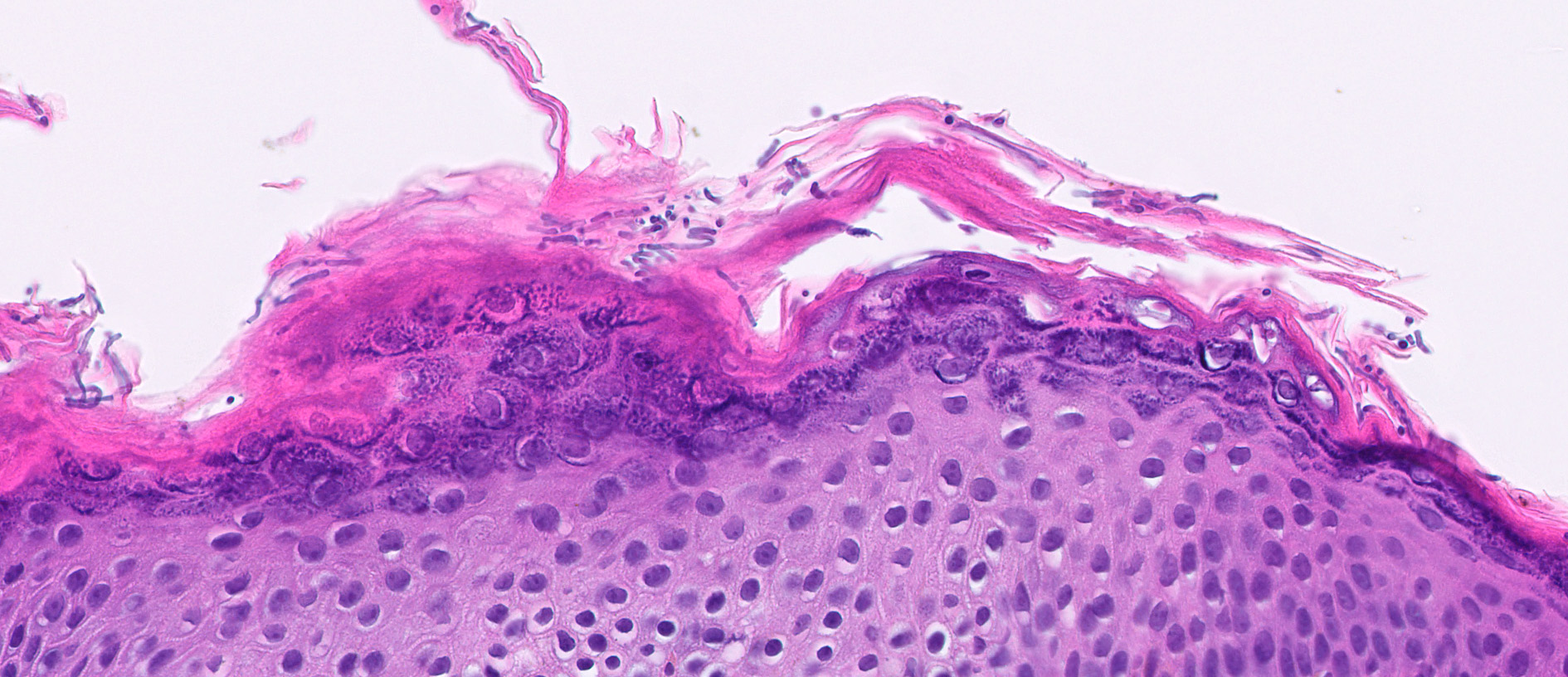
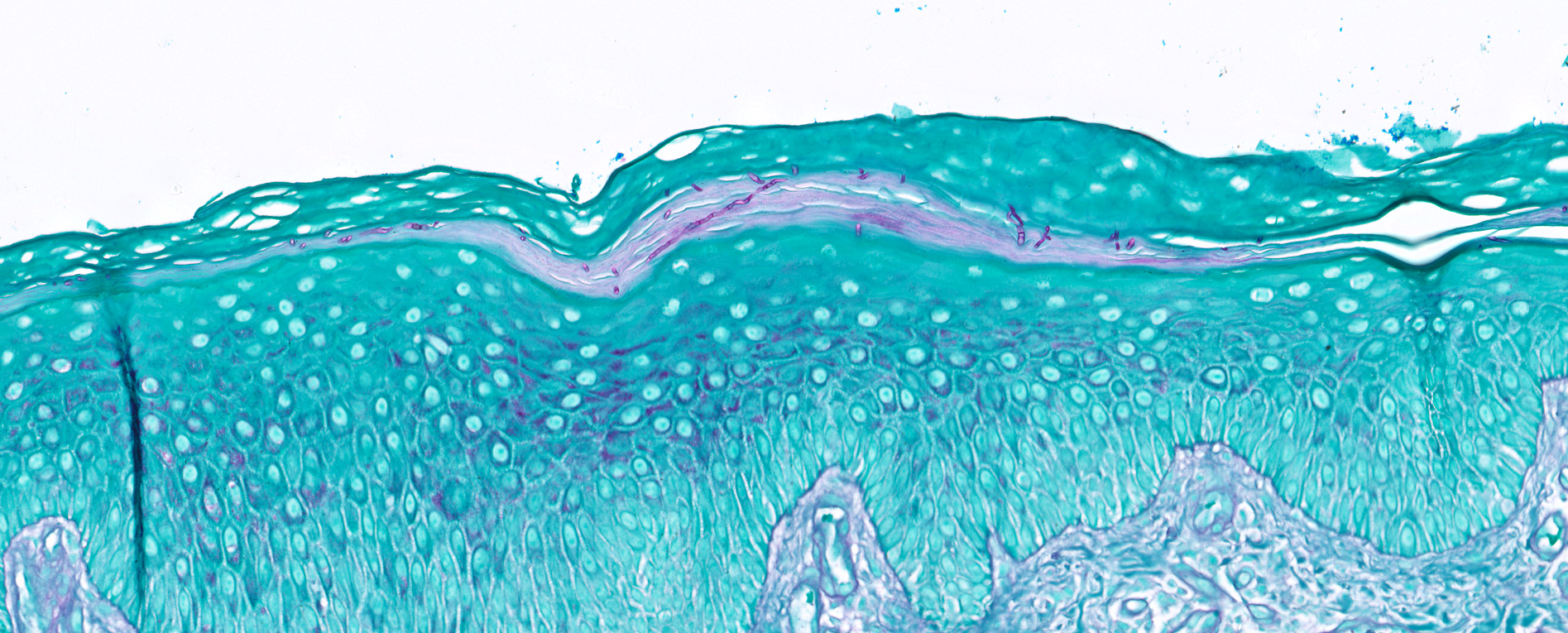
Microscopic (histologic) description
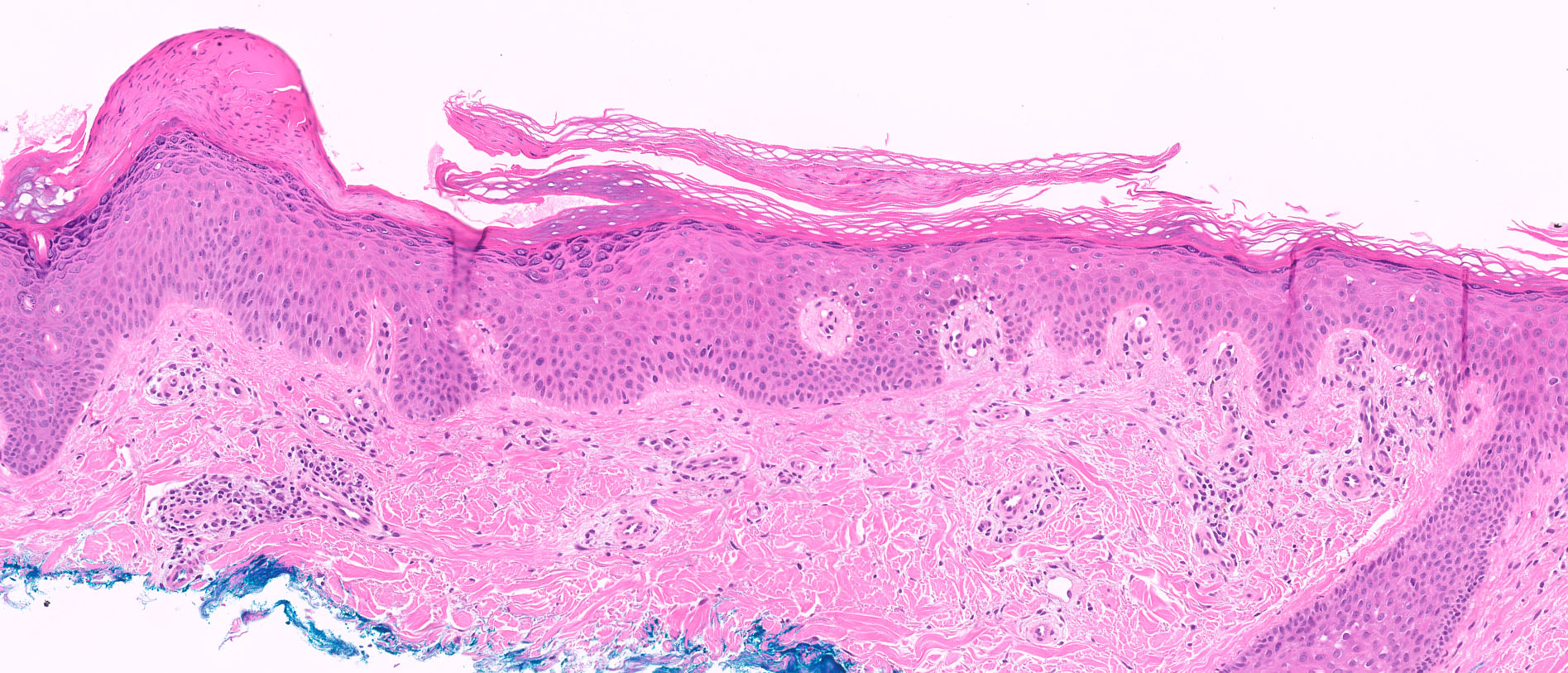
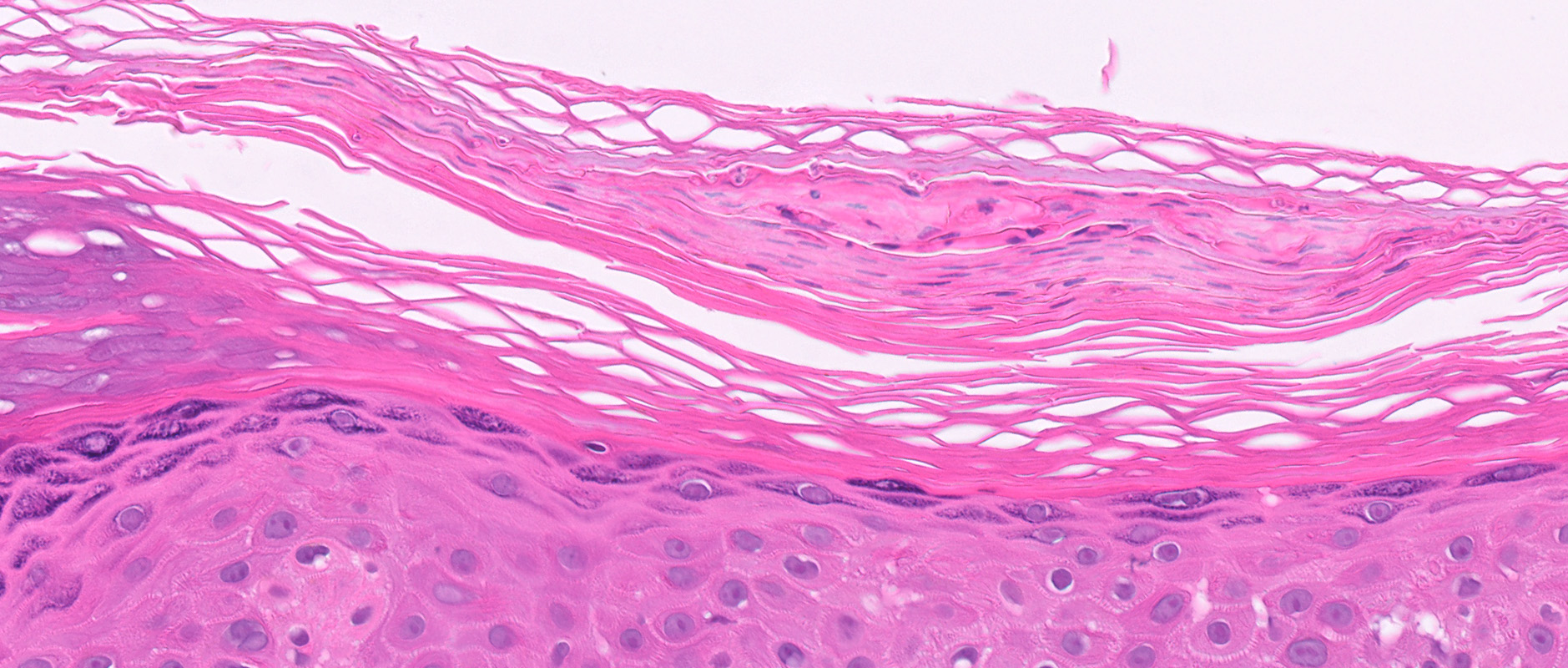
- Fungal hyphae and spores (1 - 2 microns in size) within the stratum corneum or within follicles
- In tinea capitis
- Endothrix: fungi invade the hair shaft and grow within it
- Ectothrix: hyphae do not invade the hair shaft but degrade the cuticle and grow on the surface of the hair
- Soft clues (Ann Dermatol 2014;26:286)
- Neutrophils within the stratum corneum and epidermis with parakeratosis
- Compact orthokeratosis
- Sandwich sign: orthokeratosis or parakeratosis alternating in layers with basketweave stratum corneum
- Epidermal spongiosis
- Variable inflammatory response (lymphocytic, neutrophilic, histiocytic)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Potassium hydroxide preparation of skin scrapings may show hyphae and spores (Am Fam Physician 2014;90:702)
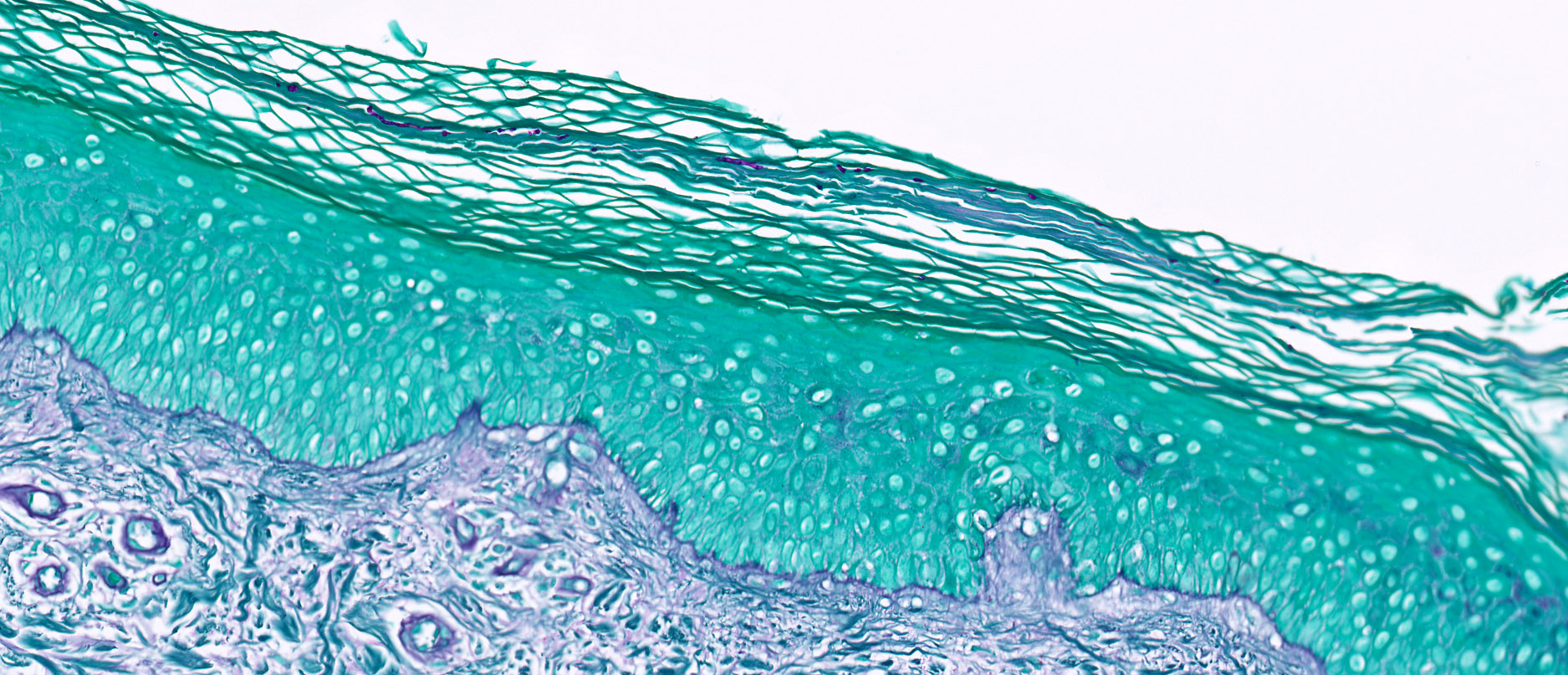
Positive stains
- Special stains: period acid-Schiff (PAS), Grocott-Gomori methenamine silver (GMS)
Sample pathology report
- Skin, biopsy:
- Dermatophytosis (tinea) (see comment)
- Comment: The sections show a biopsy of skin with spongiosis and a superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate. Special stains (PAS) highlight fungal organisms in the stratum corneum.
Differential diagnosis
- Clinical differential will vary widely depending on location and will include other annular and scaly eruptions (Am Fam Physician 2014;90:702)
- Atopic dermatitis, nummular dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis:
- Spongiosis, superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate; may have eosinophils
- Negative fungal special stains
- Psoriasis:
- Psoriasiform hyperplasia, confluent parakeratosis, diminished granular layer and collections of neutrophils in the stratum corneum
- Negative fungal special stains
- Pityriasis rosea:
- Spongiotic dermatitis with superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate
- Few extravasated red blood cells
- Negative fungal special stains
- Granuloma annulare:
- Palisading granulomas in the dermis surrounding degenerated collagen and central mucin deposition
- Mild perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate
- Annular / gyrate erythemas:
- Superficial and deep perivascular dermatitis with a coat sleeve appearance of lymphocytes hugging vessels
- Negative fungal special stains
- Syphilis:
- Psoriasiform and lichenoid dermatitis with increased collections of plasma cells
- Positive treponema immunohistochemical stain or Warthin-Starry silver stain
- If pustular, one may consider the following
- Impetigo:
- Subcorneal neutrophils
- May have acantholysis
- Gram stain may show bacterial organisms
- Pustular psoriasis:
- Subcorneal neutrophils, in addition to the features of psoriasis
- Arthropod bites:
- Superficial and deep, wedge shaped mixed inflammatory infiltrate (lymphocytes, histiocytes, and eosinophils)
- Candidiasis:
- See below
- Impetigo:
- Atopic dermatitis, nummular dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis:
- In cases where fungal organisms are identified, the differential diagnosis includes
- Pityrosporum (tinea) versicolor:
- Organisms present in basketweave stratum corneum usually without inflammatory reaction and will have shorter hyphae with numerous yeast forms that are readily identifiable on routine H&E slides
- Candidiasis:
- Nonseptate pseudohyphae
- Infection often in intertriginous areas or mucous membranes
- Pityrosporum (tinea) versicolor:
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
B. Tinea corporis. The sections show PAS positive hyphae in the stratum corneum, without yeast. Answer A is incorrect because candidiasis will have nonseptate pseudohyphae. Answer C is incorrect because while the etiology / morphology of organisms is the same, tinea cruris is classified as a superficial infection involving the groin. Answer D is incorrect because tinea versicolor is a superficial mycosis due to Malessezia spp. and morphologically will have short hyphae and yeast organisms.
Comment Here
Reference: Dermatophytes / tinea
Comment Here
Reference: Dermatophytes / tinea
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is true regarding dermatophyte infections?
- Candida is most frequently identified in cases of tinea cruris
- Invasive spread of organisms is impossible due to the superficial nature of cutaneous dermatophyte infections
- Morphologic features include abundant budding yeast
- Most commonly due to Trichophyton, Epidermophyton, Microsporum and Nannizzia organisms
Board review style answer #2
D. Most commonly due to Trichophyton, Epidermophyton, Microsporum and Nannizzia organisms. These are the most common organisms to cause dermatophytosis. Answer A is incorrect because Candida is not a dermatophyte. Answer B is incorrect because invasive dermatophytosis has been reported in immunosuppressed patients. Answer C is incorrect because tinea is not characterized by budding yeast.
Comment Here
Reference: Dermatophytes / tinea
Comment Here
Reference: Dermatophytes / tinea