Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Clinical features | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Hamodat M. Erythema nodosum. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skinnontumorerythemanodosum.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
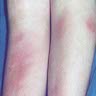
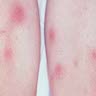
- Panniculitis with tender red nodules, usually on both shins
Terminology
- Erythema nodosum migrans (subacute nodular migratory panniculitis, migratory panniculitis): asymmetrical, unilateral and distributed solely on the legs; marked female predominance; older age group
- Chronic erythema nodosum: nodules appear over months / years; otherwise indistinguishable from typical condition
Clinical features
- Red, painful, bilateral, symmetrical nodules, elevated above the skin surface
- On anterior surface of legs, arms, face, calves and trunk
- Usually involutes in days / weeks, leaving depressed, pigmented lesions
- No ulceration
- Immune mediated but precise mechanism is unknown
- May be associated with streptococcus infection, tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, coccidioidomycosis, ulcerative colitis, Behçet disease, drug reactions or idiopathic; also Hodgkin lymphoma, renal cell carcinoma and carcinomas of colon, pancreas and uterine cervix
Microscopic (histologic) description
- A prototype of septal panniculitis, characterized by vascular changes, septal inflammation, hemorrhage and variable acute and chronic panniculitis
- Both septal and lobular panniculitis
- Marked septal fibrosis, infiltrated by lymphocytes, neutrophils, histiocytes and granulomas with giant cells
- Septal infiltrate spills over to affect the fat lobules
- Dermis shows perivascular and periadnexal chronic inflammatory cell infiltrate
- Early, the septal inflammation is acute and characterized by neutrophils, soon replaced by lymphocytes and histiocytes
- Variable eosinophils, variable vasculitis
- Miescher radial granuloma: characteristic finding of erythema nodosum; septal collection of histiocytes surrounding a cleft (appear to look like spaces); reported in Sweet syndrome, nodular vasculitis and necrobiotic lipodica
Differential diagnosis
- Nodular vasculitis or subacute nodular migratory panniculitis: usually septal
- Weber-Christian disease associated panniculitis: usually lobular inflammation
Additional references