Table of Contents
Definition / general | Clinical features | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Additional referencesCite this page: Hamodat M. Dermatomyositis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skinnontumordermatomyositis.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- See also Muscle chapter
- Autoimmune inflammatory disease of skeletal muscle and skin, usually affects women
- Symmetric proximal muscle weakness and skin lesions
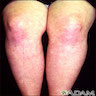
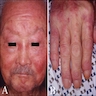
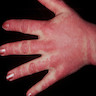
- Affects face, dorsal hands and feet, particularly knuckles
- 20% of cases lack muscle involvement (Arch Dermatol 2010;146:26)
- 15% have coexisting adenocarcinoma of stomach, breast, ovary, lung or colon, with remission of dermatomyositis following tumor resection; high risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Asian patients (Ann Acad Med Singapore 2010;39:843)
- Increased risk of thyroid disease, particularly hypothyroidism, especially in patients with interstitial lung disease
- Polymyositis: similar muscle changes without skin changes
Clinical features
- Poorly demarcated, scaly, erythematous patches
- Also heliotrope erythema of upper eyelids and extensor joint surfaces
Treatment
- Steroids, immunosuppressants (Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2010;62:219), tumor resection (if present)
Clinical images
Microscopic (histologic) description
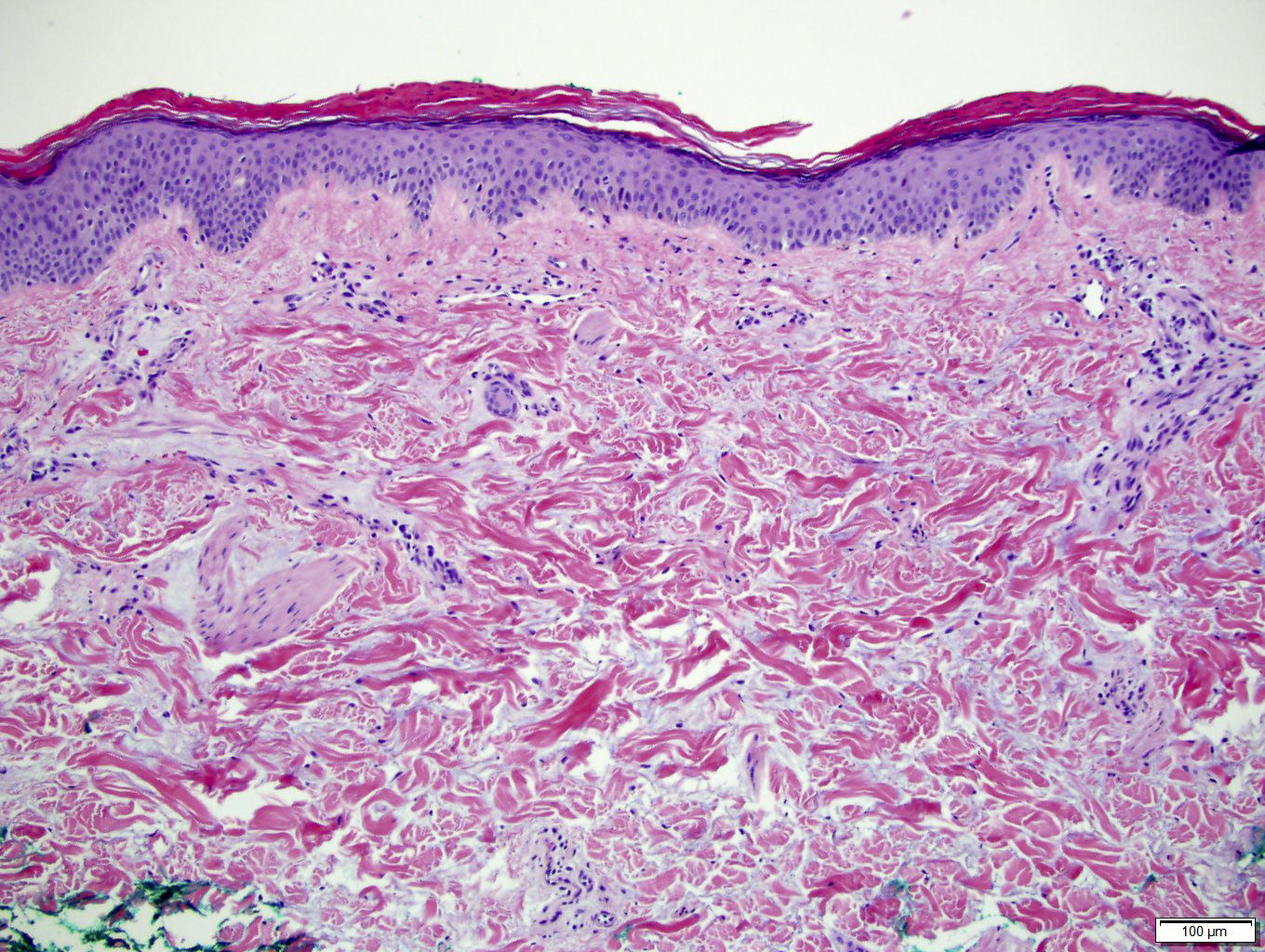
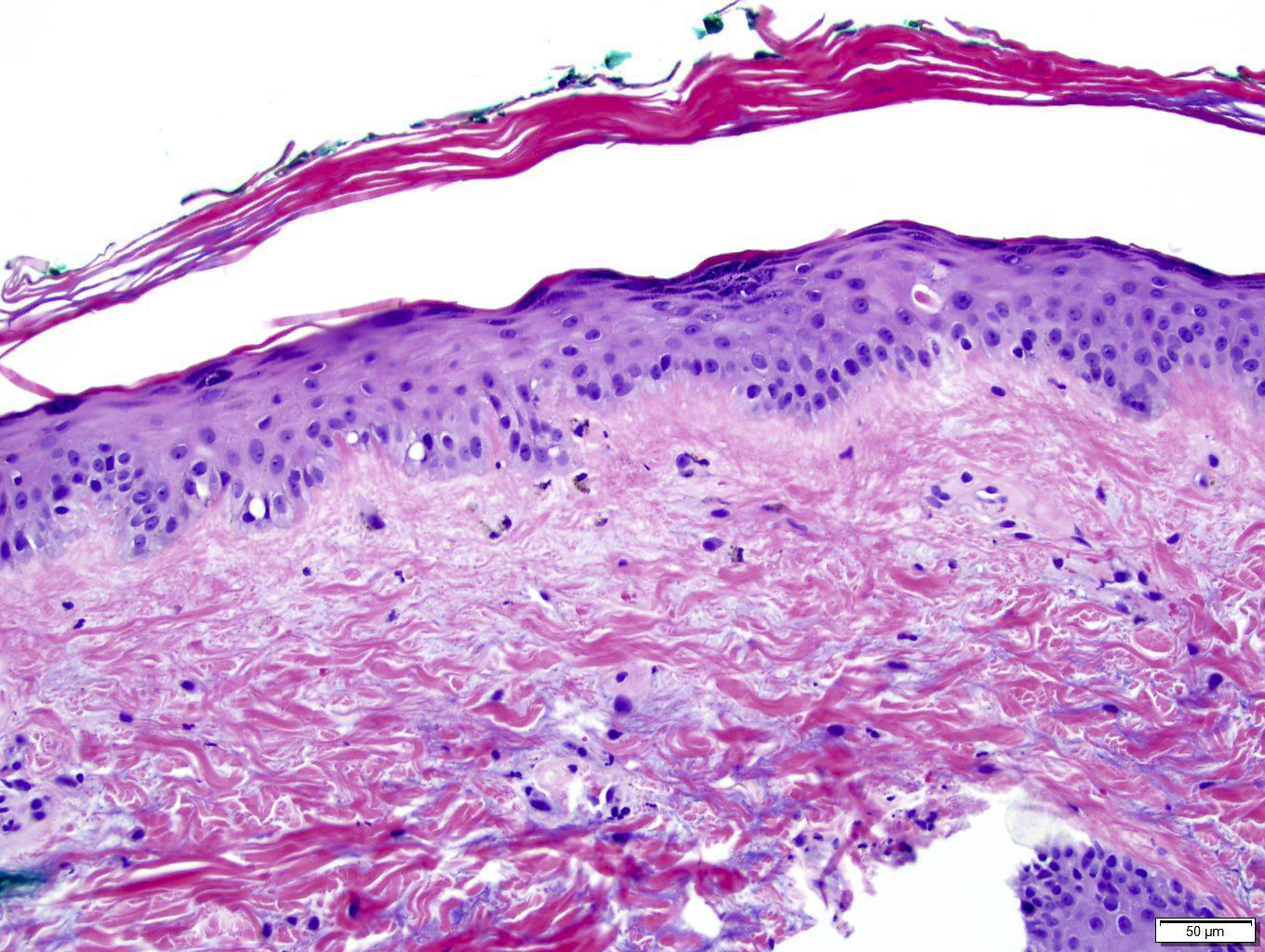
- Chronic nonspecific dermatitis or interface dermatitis resembling systemic lupus erythematosus
- Often atrophic epidermis with prominent vacuolar interface change
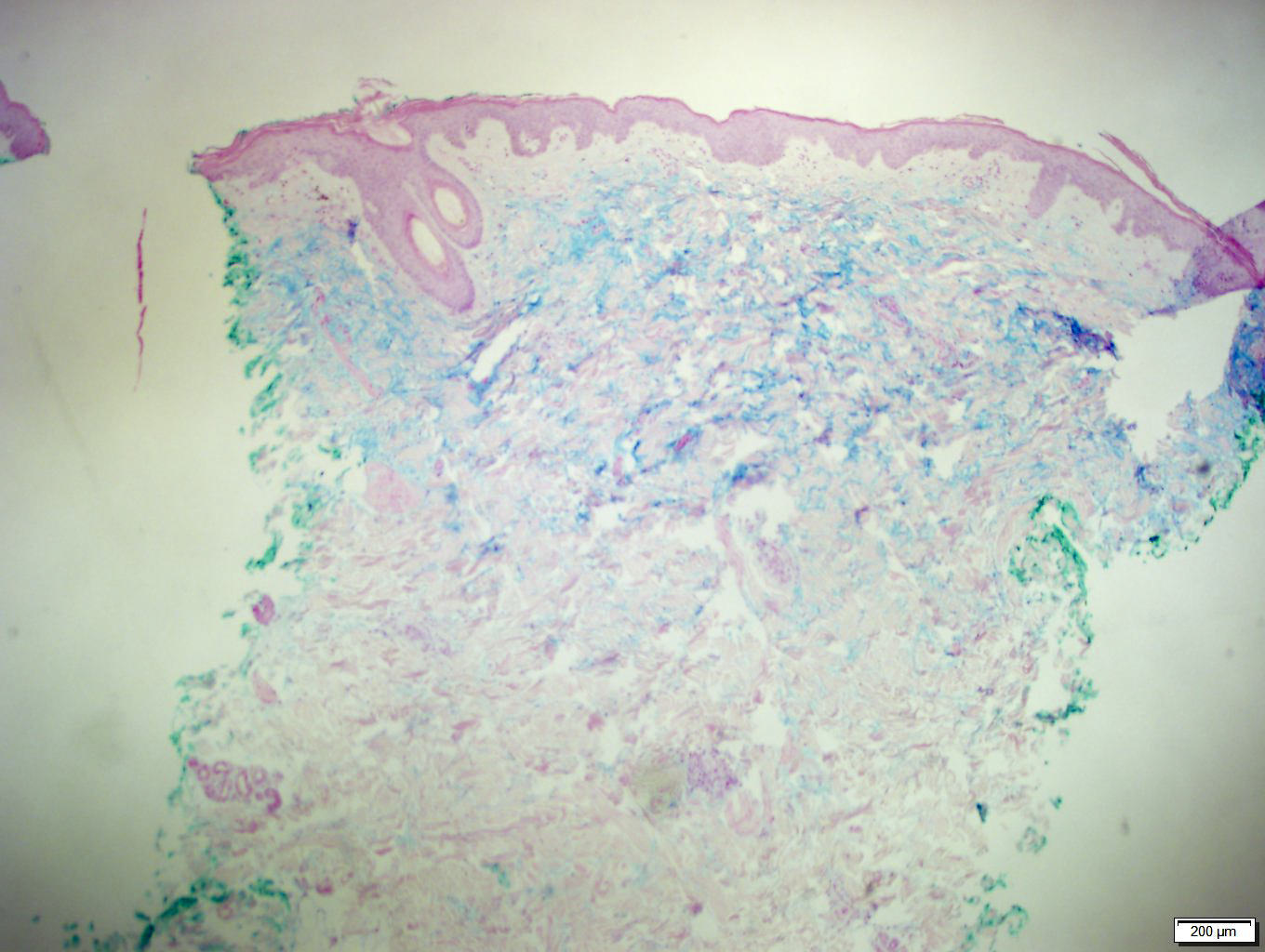
- Sparse perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate with markedly increased dermal mucin
- Muscles show myositis with myofiber necrosis, fragmentation and phagocytosis; late myofiber atrophy, fibrosis and fatty change
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- C5-9 (by immunofluorescence)
Negative stains
- IgG, IgA and IgM by immunofluorescence
Additional references