Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Immunofluorescence description | Negative stains | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Vaughan VC, Wisell J. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skinnontumoragep.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Pustular drug eruption
- May have superficial desquamation
Essential features
- Pustular drug eruption
- Most commonly associated with beta lactams and macrolides but also calcium channel blockers, acetaminophen, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, proton pump inhibitors, anticonvulsants (carbamazepine), cetirizine, antimalarials, antifungals and more rarely, enterovirus or mercury exposure (Int J Dermatol 2017;56:405)
- Short interval from exposure to eruption, < 4 days
- Quick improvement after withdrawal of offending agent
Terminology
- Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, AGEP, toxic pustuloderma
ICD coding
- ICD-10: L27.0 - Generalized skin eruption due to drugs taken internally
Epidemiology
- 1 - 5 cases per million population per year (Acute Med 2016;15:140)
Pathophysiology
- Unknown
- HLA B5, DR11 and DQ3 more frequent
- Theory: drug activated T lymphocytes migrate to skin and in conjunction with keratinocytes, recruit neutrophils (Am J Med 2018;131:639, Int J Mol Sci 2016;17:E1214)
Clinical features
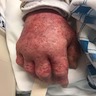
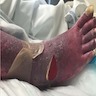
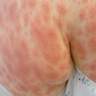
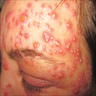
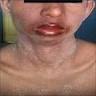
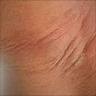
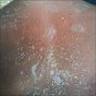
- Acute onset of nonfollicular based monomorphic sterile pustules on a background of edematous erythema with superficial desquamation in areas of confluence (J Am Acad Dermatol 2015;73:843)
- Spreads from the face and intertriginous areas
- Mucous membrane involvement may occur
- Fever, pruritus or burning sensation
- Resolves in 1 - 2 weeks
- 17% of cases have visceral involvement
- 1 - 2% mortality
Diagnosis
- Histological findings are nonspecific and a definitive diagnosis should only be rendered in the appropriate clinical context and after consideration of other entities with the same histological appearance
- Eruption should occur shortly after initiation of a new drug or, less commonly, with viral infection and should also convalesce after discontinuation of the drug
- Patch testing can be useful in confirming the patient's sensitivity to the drug in question
Laboratory
- Neutrophilia and leukocytosis
- Abnormal renal function and hepatic function tests may occur
- Immunofluorescence is negative (as opposed to IgA pemphigus and pemphigus foliaceus)
- 50 - 60% of cases have a positive patch test to offending agent
Case reports
- 6 year old boy with reaction to terbinafine (Int J Dermatol 2019;58:e42)
- 32 year old woman with otitis and reaction to oxacillin (Contact Dermatitis 2018;79:108)
- 34 year old woman with generalized pustular eruption after pantoprazole (Cutis 2018;101:E22)
- 34 year old man with reaction to ibuprofen, confirmed with patch testing (Contact Dermatitis 2018;79:40)
- 39 year old woman with reaction to lamotrigine, worsening after rechallenge (JAAD Case Rep 2018;4:645)
- 40 year old woman with pustular eruption on the face 1 week after starting flurbiprofen (Cutis 2016;98:E9)
- 50 year old woman with spreading stinging pustular eruption 2 weeks after starting hydroxychloroquine (Cutis 2016;97:212)
- 56 year old woman with diffuse erythema and micropustular eruption after antibiotics (Cutis 2014;93:E10)
- 63 year old woman with breast cancer and reaction to docetaxel and again after letrozole (Clin Breast Cancer 2018;18:e743)
Treatment
- Discontinue drug (J Immunol Res 2017;2017:1503709)
- Topical or systemic steroids (cautiously as steroids may provoke a pustular psoriasis flare)
- May pursue patch testing, especially in cases in which multiple drugs are suspected
Clinical images
Images hosted on other servers:
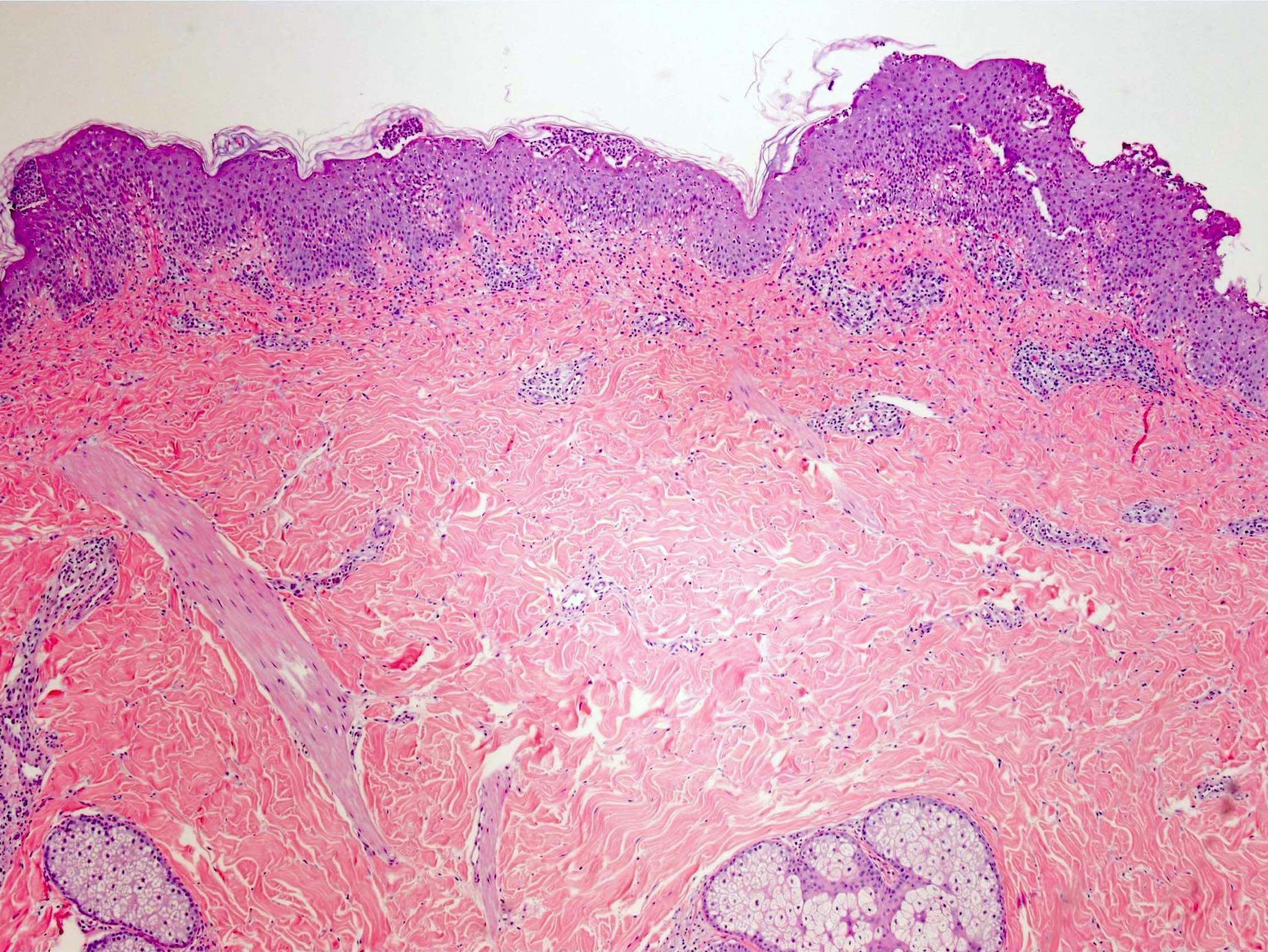
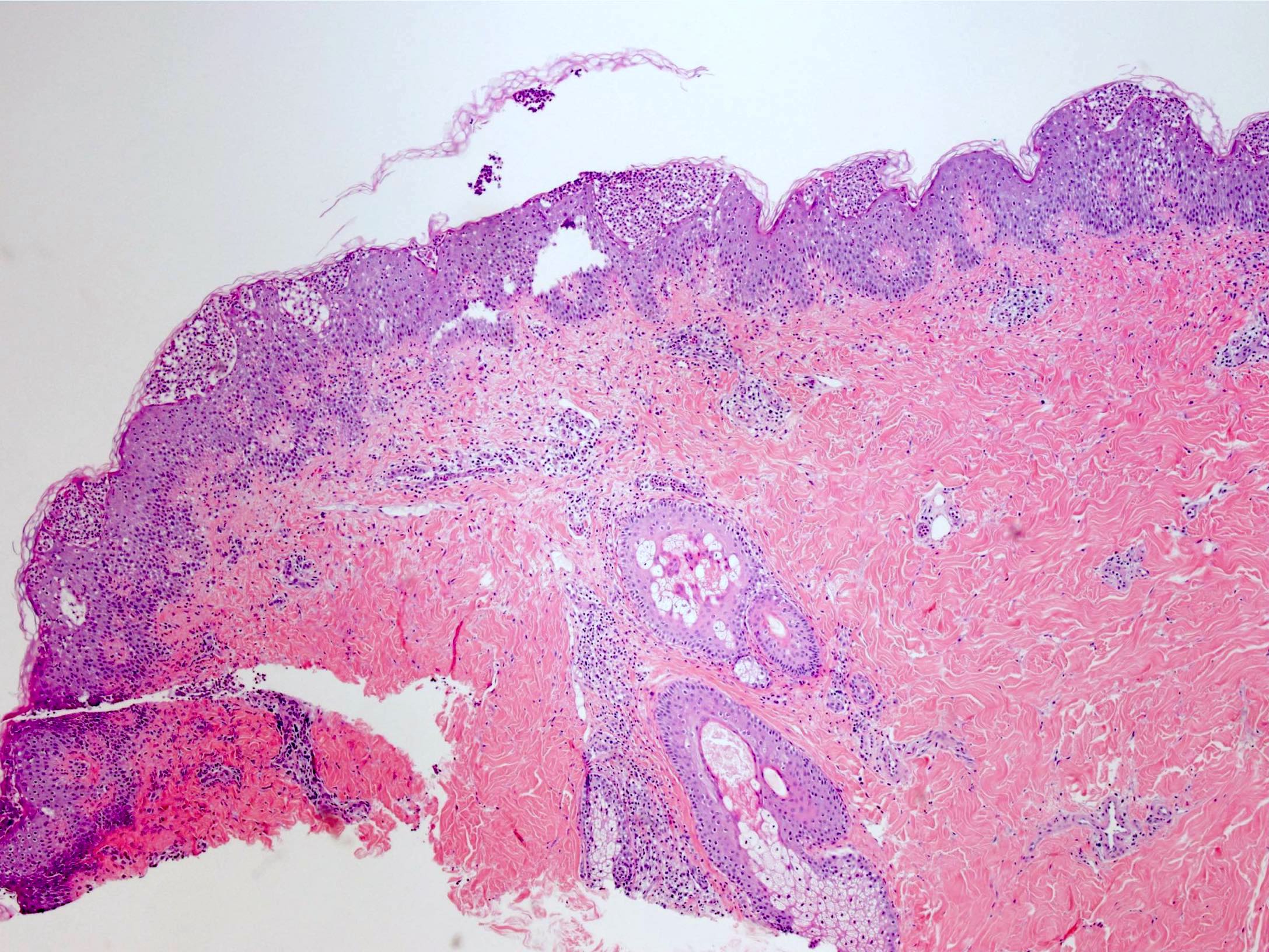
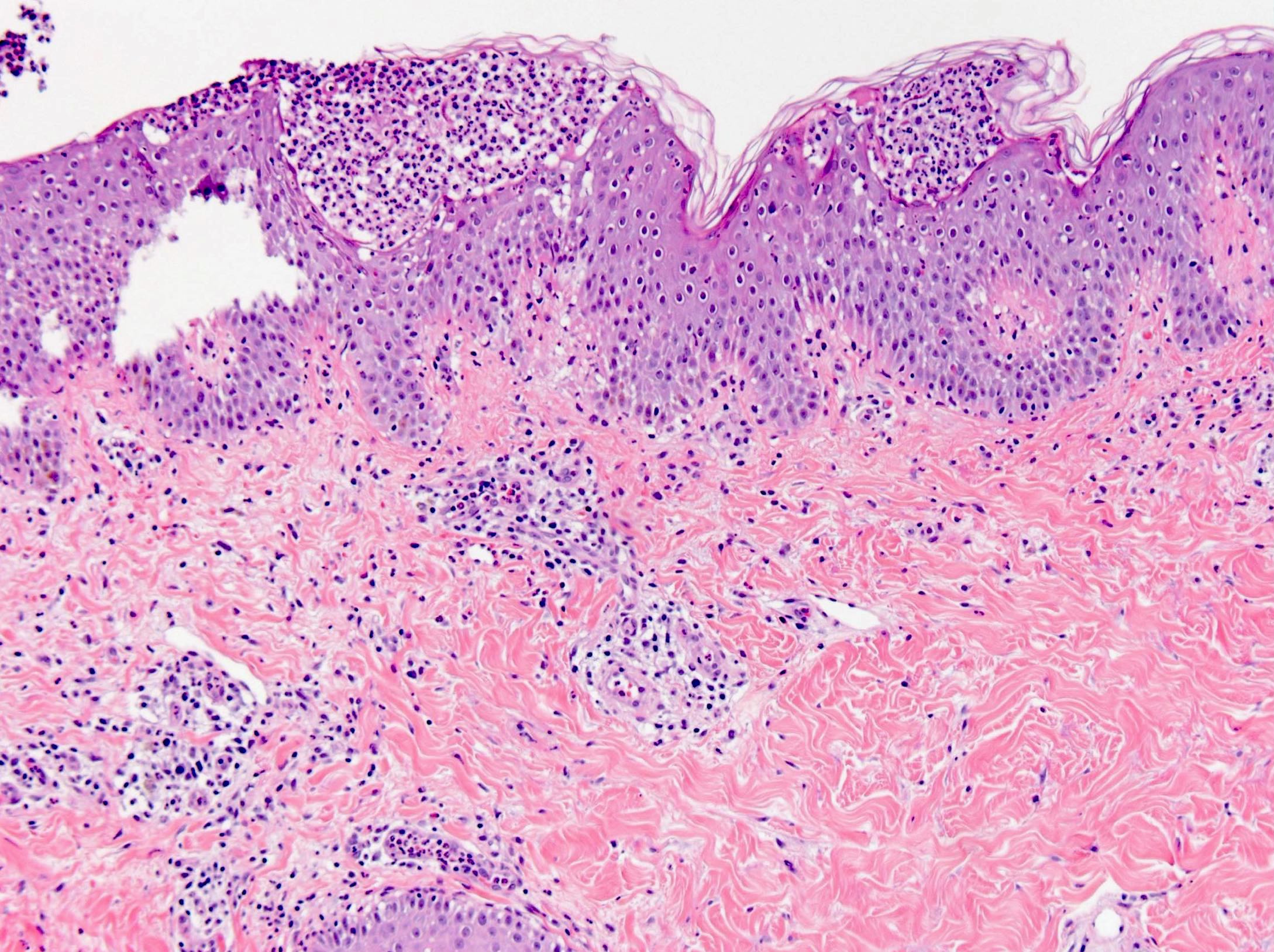
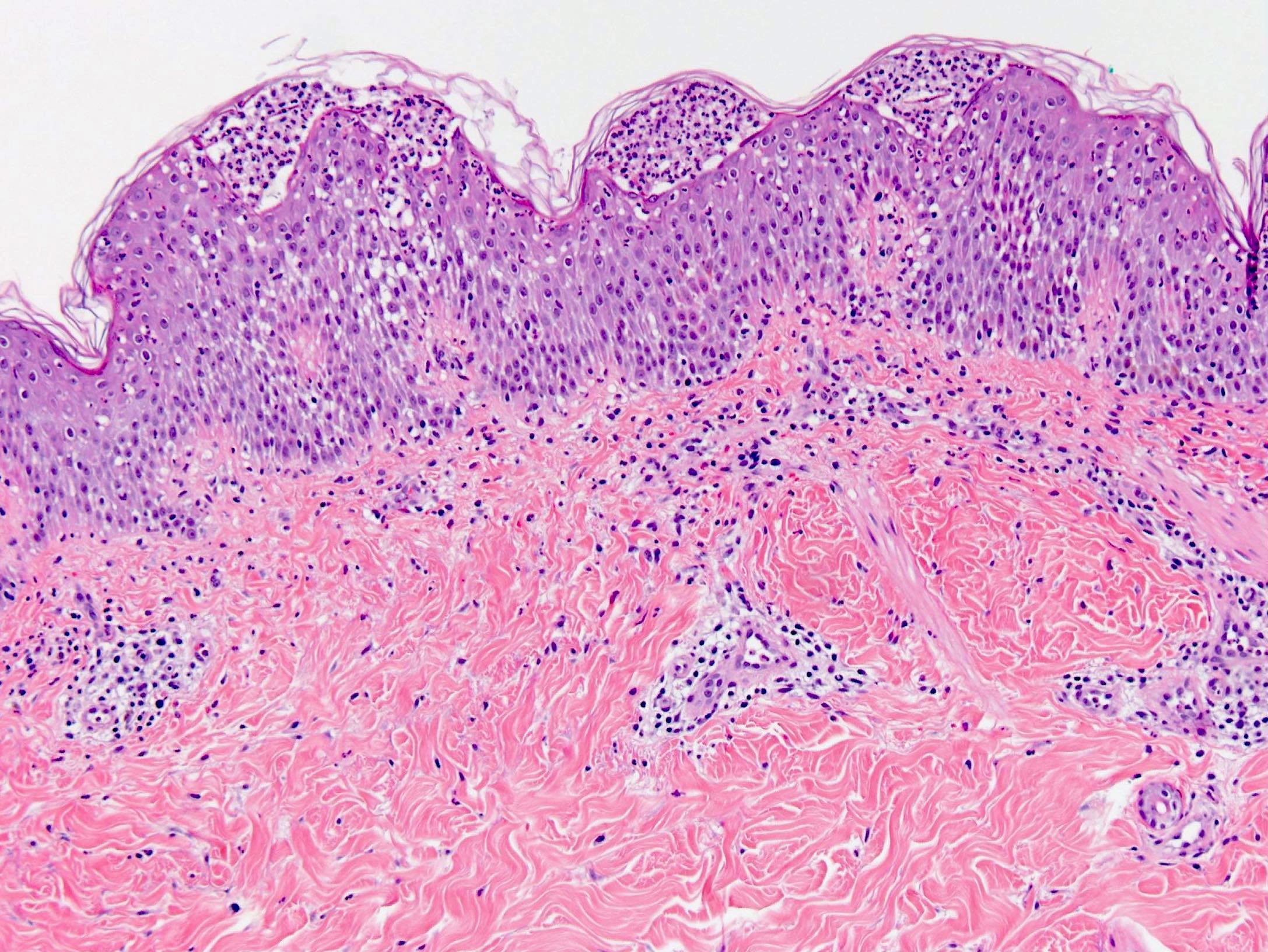
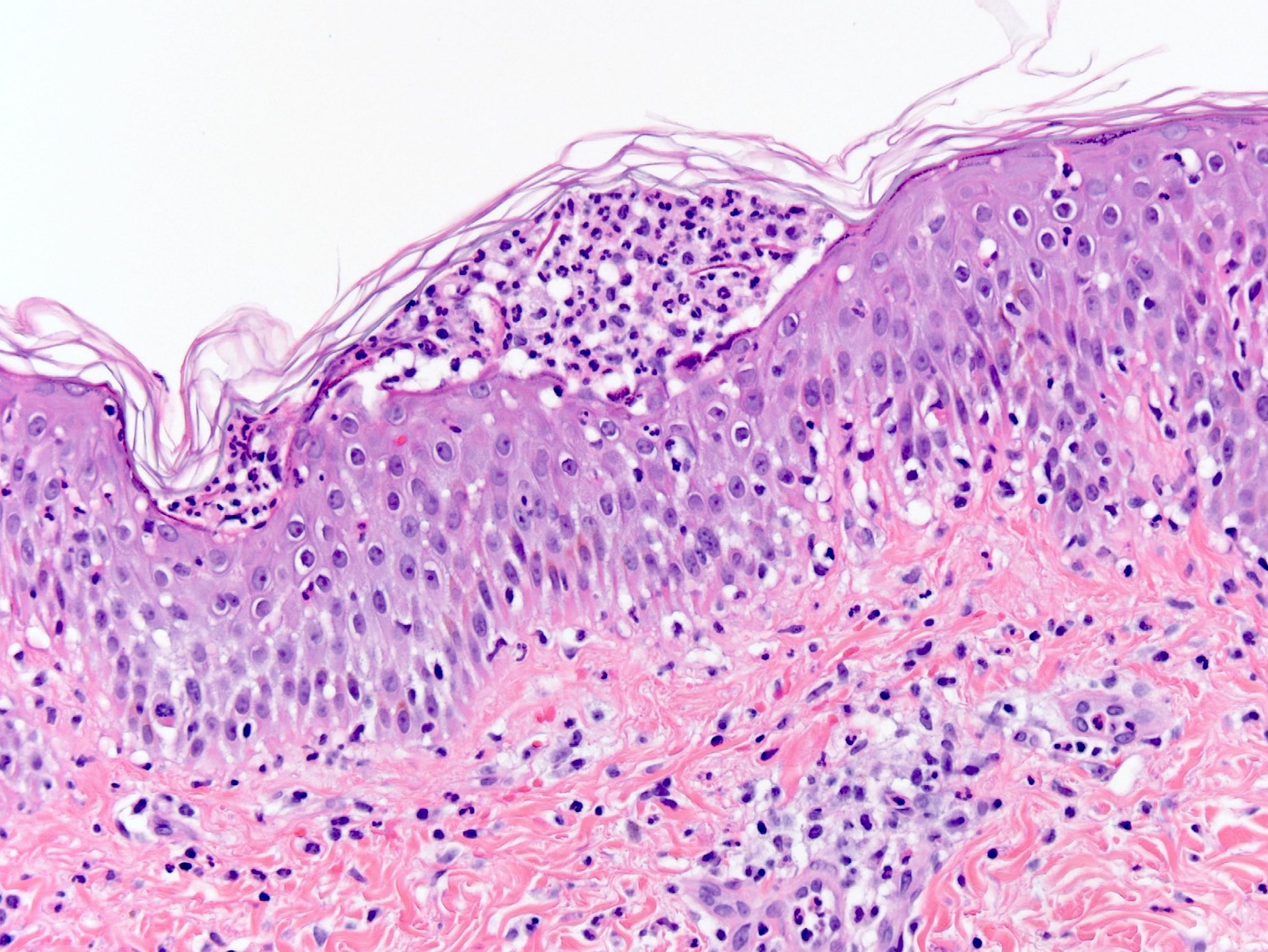
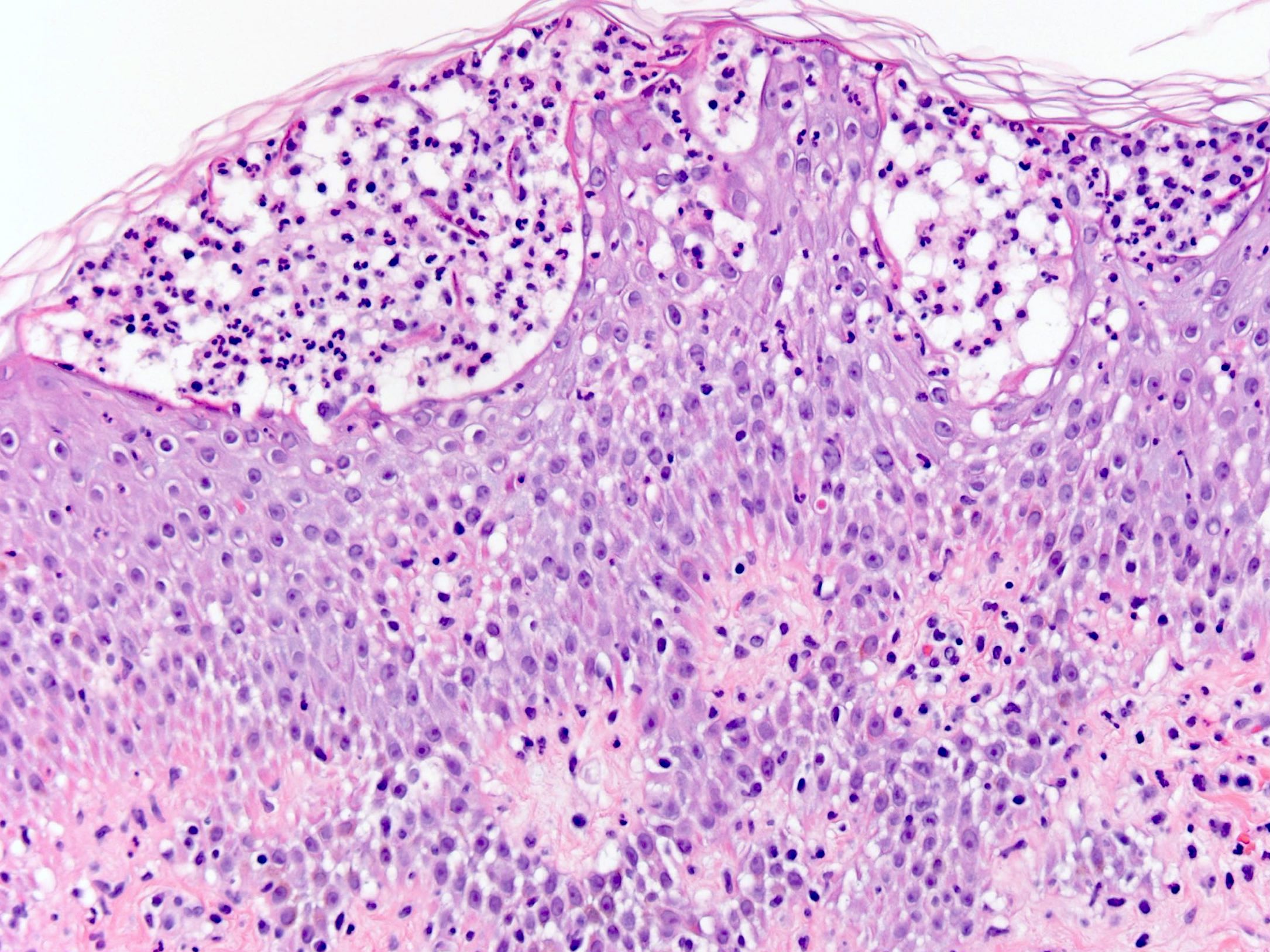
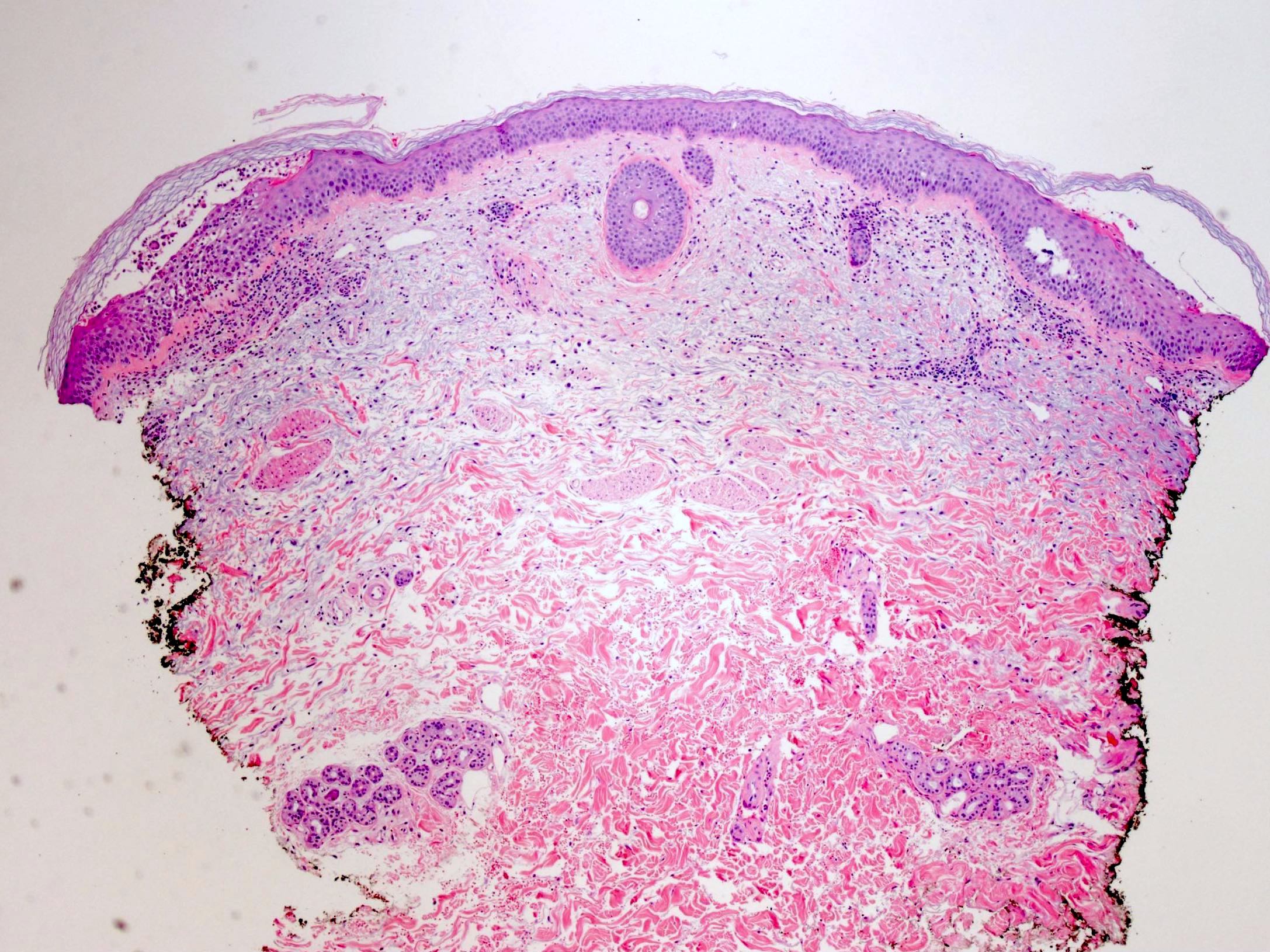
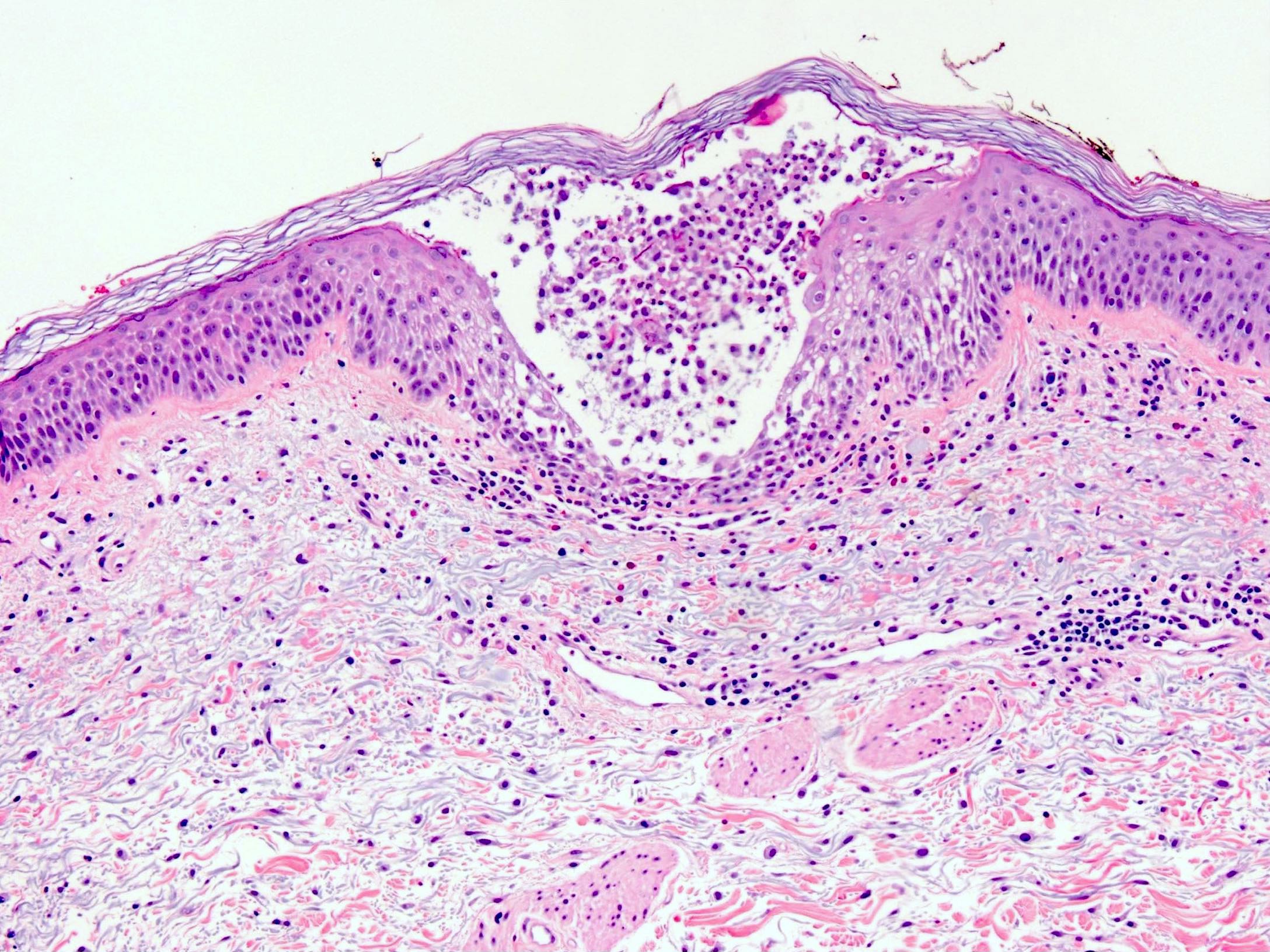
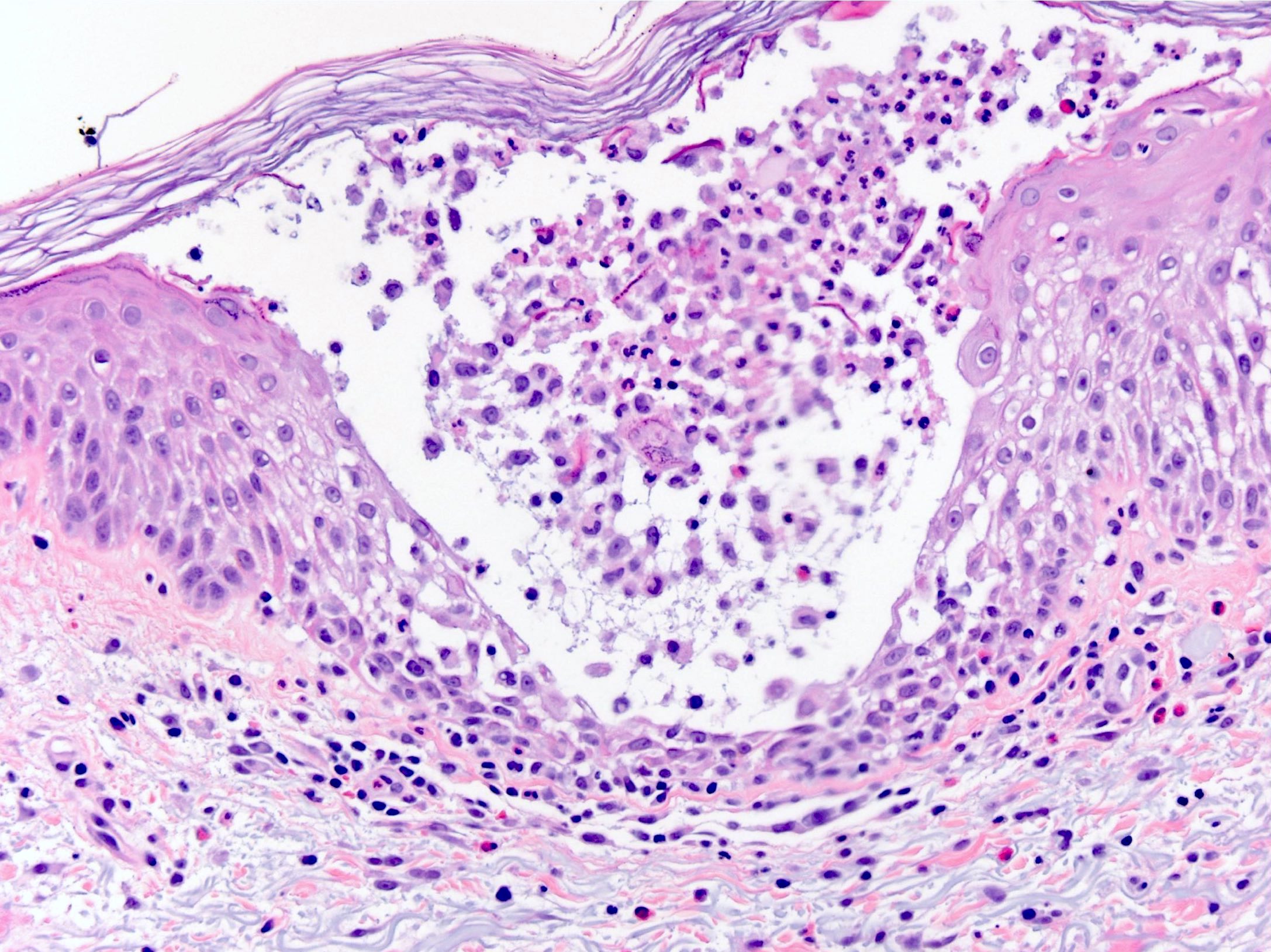
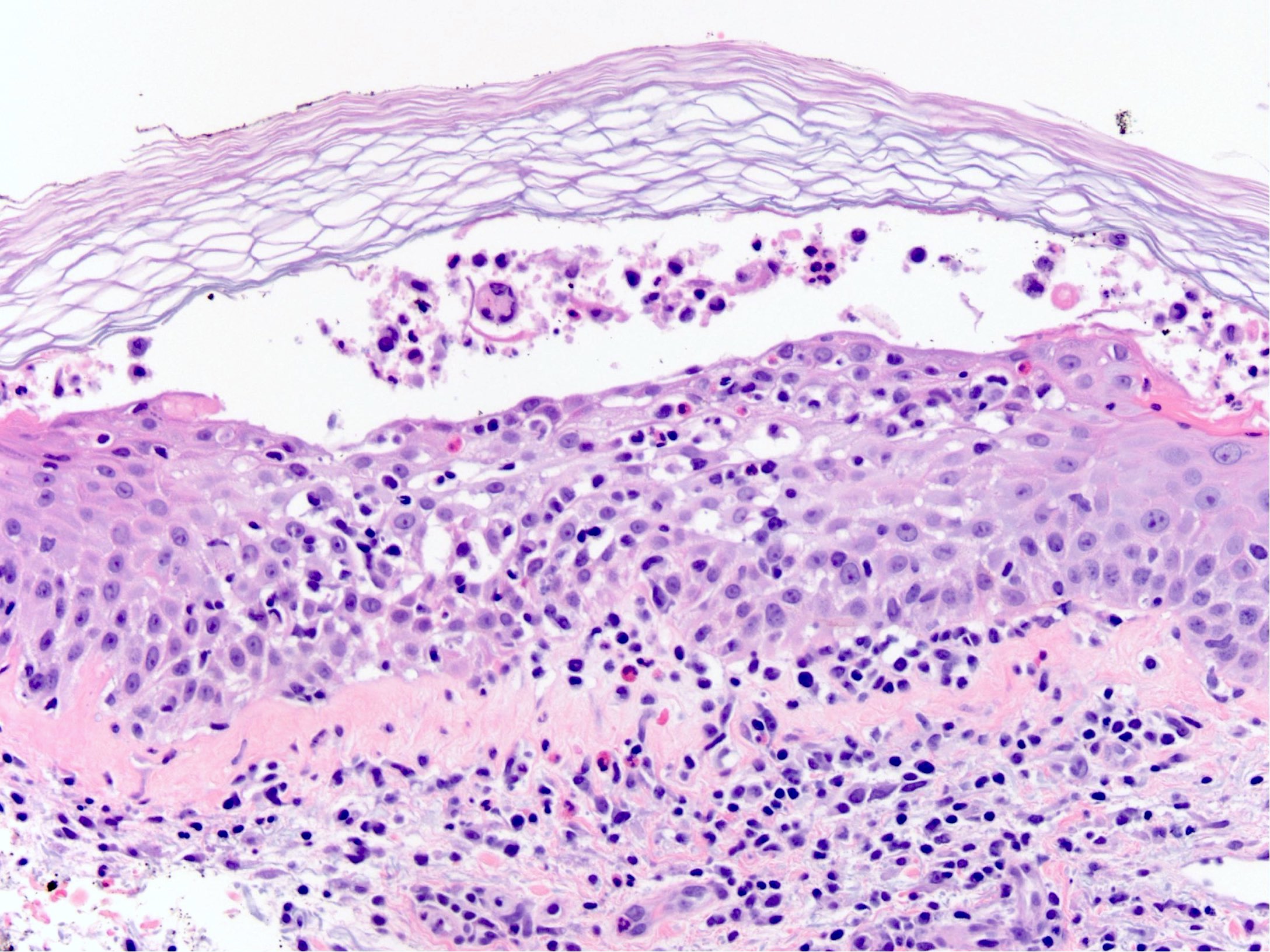
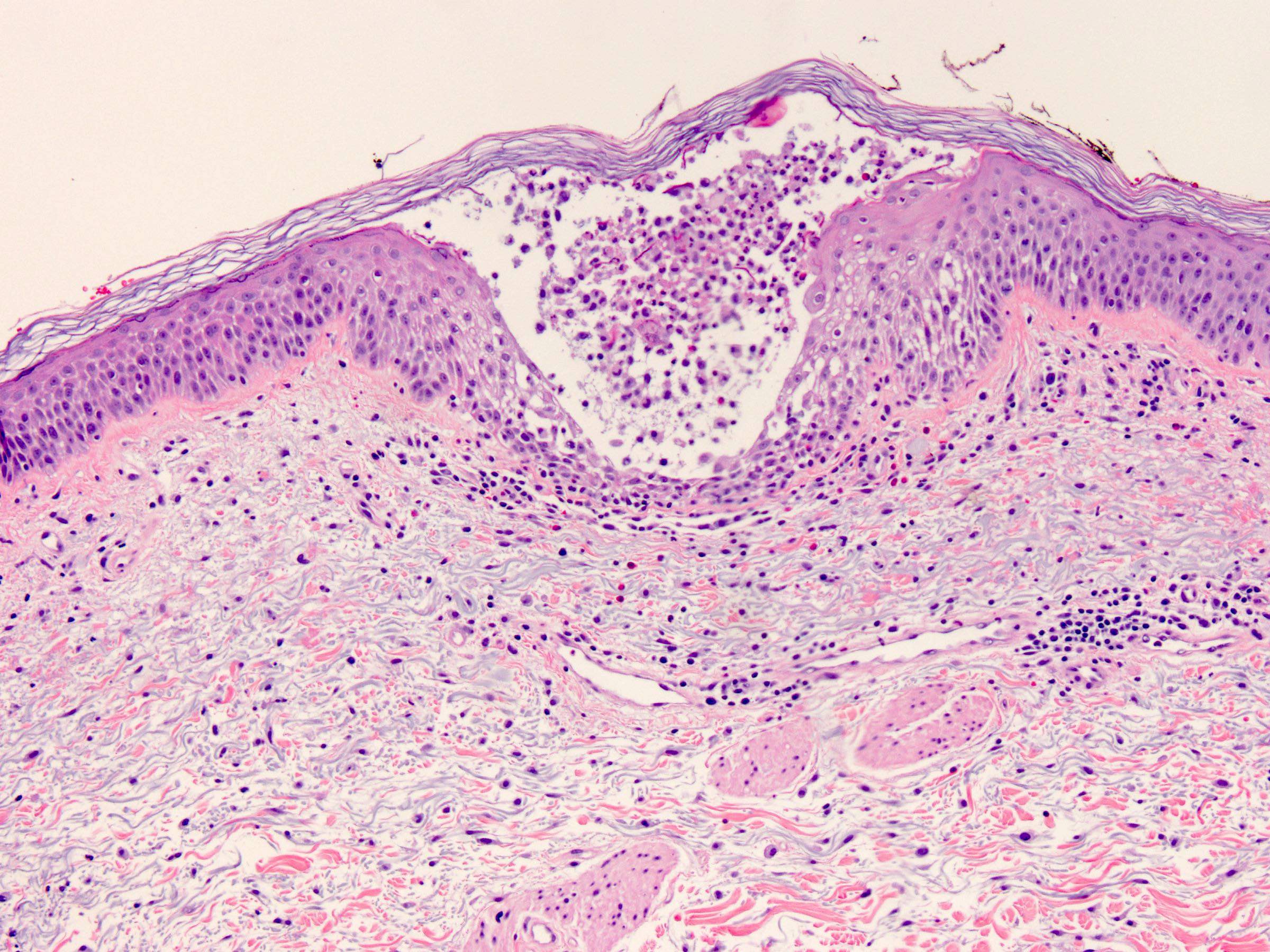
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Subcorneal pustules
- Spongiosis
- Histologically similar to pustular psoriasis but may have rare dermal eosinophils
- Scattered epidermal neutrophils
- Papillary dermal edema
- Perivascular mixed infiltrate, often with eosinophils and neutrophils
- Necrotic keratinocytes are sometimes seen
Microscopic (histologic) images
Immunofluorescence description
- Negative
Negative stains
- Special stains may be used to exclude mimickers (e.g. a Gram stain may be used to investigate the possibility of bullous impetigo)
Differential diagnosis
- Pustular psoriasis:
- Nearly identical histologically but lacks dermal eosinophils
- Subcorneal pustular dermatosis (Sneddon-Wilkinson disease):
- Nearly identical histologically
- IgA pemphigus:
- Both neutrophils and eosinophils within the blister cavity and intercellular IgA deposition on immunofluorescence
- Bullous impetigo:
- Presence of bacterial forms
- Pustular eruption in Kawasaki disease:
- Cervical lymphadenopathy, fever, conjunctivitis and strawberry tongue support Kawasaki disease (JAAD Case Rep 2018;4:558, Pediatr Dermatol 2015;32:547)
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A skin biopsy is received from a patient staying in the intensive care unit and undergoing antimicrobial therapy for bacterial pneumonia. On physical exam, there are innumerable minute monomorphic pustules over the trunk on a background of intense erythema with desquamation in the skin folds. The biopsy shows subcorneal clefting with neutrophilic pustules, spongiosis and scattered dermal eosinophils. Which of the following is most likely given the biopsy and clinical context?
- Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis
- Cellulitis
- Folliculitis
- Sneddon-Wilkinson disease
- Staphylococcal scalded skin disease
Board review style answer #1
A. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis
Comment Here
Reference: Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis
Comment Here
Reference: Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2
A. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis
Comment Here
Reference: Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis
Comment Here
Reference: Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis