Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) descriptionCite this page: Hamodat M. Acne vulgaris. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skinnontumoracne.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
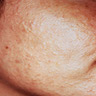
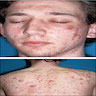
- Common skin disease of seborrhea (scaly red skin), comedones (blackheads and whiteheads), papules (pinheads), pustules (pimples), nodules (large papules) and possibly scarring
- Typically affects skin with densest sebaceous follicles: face, upper chest, back; uncommon in scalp for unknown reasons
Terminology
- Acne vulgaris is common acne, typically with comedones
- Acne rosacea is a different disorder
Etiology
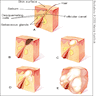
- Due to hormonal variations and alterations in hair follicle maturation
- Begins with abnormal follicular keratinization with retention of keratinous material in the follicle
- Then increased sebum production
- Then appearance of gram positive, anaerobic, diphtheroid Propionibacterium acnes
- May become inflammatory
Clinical features
- Usually teenagers of either sex, but often more severe in males
- Worsens with drugs (steroids, testosterone, contraceptives), oils / tars, heavy clothing and tropical climates
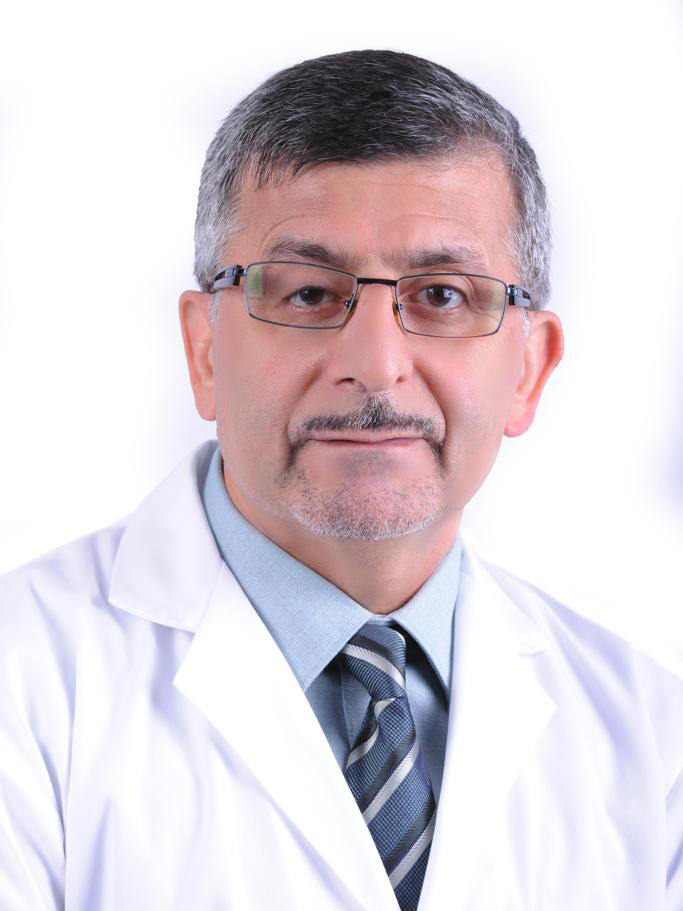
- Non-inflammatory acne is due to open and closed comedones
- Open comedones: small follicular papules with central, black keratin plug (due to oxidation of melanin)
- Closed comedones: follicular papules with a deeper plug below the surface
- Follicles may rupture and become inflamed
- Diverse lesions such as comedones, papules, pustules, cysts, sinuses and scars
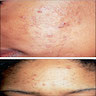
Treatment
- Antibiotics, isotretinoin, phototherapy (eMedicine, Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2011;4:41)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- 3 major components are comedones, inflammatory lesions and scars
- Comedones (open or closed) are cyst-like cavities filled with compact mass of keratinous material and numerous bacteria
- Closed comedo has 1 - 2 hairs trapped in lumen and atrophic, sebaceous acini
- Open comedo has 10 - 15 hairs in lumen and sebaceous acini are atrophic or absent
- Epithelial lining of comedones is usually thin