Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Ormandy A, Balgobind S. Sjögren syndrome. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/salivaryglandssjogren.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Chronic autoimmune disorder of the salivary and lacrimal exocrine glands
- Primary etiological events remain unknown (CMAJ 2014;186:E579)
- Characterized by lymphocytic infiltrates of the affected glands with subsequent dysfunction of these glands and the clinical picture of sicca syndrome
- Considered primary if not associated with other systemic disease or secondary if it occurs in association with another underlying autoimmune condition (Clin Exp Med 2022;22:9)
Essential features
- Chronic autoimmune disorder of uncertain etiology
- Characterized by focal lymphocytic sialadenitis with subsequent clinical sequela including keratoconjunctivitis sicca (dry eyes) and xerostomia (dry mouth)
- Diagnosed using a combination of subjective and objective measures as determined by the 2016 American College of Rheumatology / European League Against Rheumatism (ACR / EULAR) classification
- Salivary gland biopsy findings consistent with diagnosis are focal lymphocytic sialadenitis with a focus score (FS) ≥ 1
Terminology
- Not recommended: Mikulicz disease (Lancet 2005;366:321)
Epidemiology
- One of the 3 most common autoimmune disorders (Lancet 2005;366:321)
- F:M = 9:1 (Clin Exp Med 2022;22:9)
- Bimodal distribution
- Third and fourth decade
- Sixth decade (Lancet 2005;366:321)
- Incidence of 6.92 per 100,000 person-years (person-years is defined as the estimate of the actual time at risk in years that all persons contributed to a study) (95% confidence interval, 4.98 - 8.86)
- Prevalence of 60.82 cases per 100,000 inhabitants (Europe, South America, Asia) (95% confidence interval, 43.69 - 77.94) (Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74:1983)
Sites
- Exocrine glands
- Notably lacrimal and salivary glands (Eur J Oral Sci 2018;126:37)
Pathophysiology
- Pathological basis of the disease remains unknown
- Numerous theories have been proposed; however, a consensus has not been established (Immunol Lett 2011;141:1)
Etiology
- Etiology is unknown
- Likely multifactorial with potential genetic, environmental and hormonal factors suggested; however, no causal associations have been demonstrated (Clin Exp Rheumatol 2022;40:2211)
- Primary Sjögren syndrome
- 90% of patients with high anti-Ro and anti-La antibody titers are HLA DR3 positive (Clin Med (Lond) 2007;7:53)
- Secondary Sjögren syndrome
- Sjögren syndrome associated with rheumatoid arthritis has a different genetic background (HLA DR4) (Lancet 2005;366:321)
Diagrams / tables
Clinical features
- Keratoconjunctivitis sicca (dry eyes)
- Xerostomia (dry mouth)
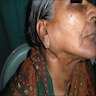
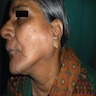
- Enlarged salivary glands
- Extraglandular manifestations include
- Musculoskeletal
- Myalgia, arthralgia and morning stiffness
- Dermatological
- Xerosis
- Respiratory tract
- Rhinosinusitis
- Vocal hoarseness
- Chronic cough (Clin Exp Med 2022;22:9)
- Musculoskeletal
Diagnosis
- 2016 ACR / EULAR classification system
- Score ≥ 4 is compatible with a diagnosis of primary Sjögren syndrome in patients experiencing ocular or oral dryness or with clinical suspicion due to systemic features (Arthritis Rheumatol 2017;69:35)
- Factors assessed include
- Labial salivary gland biopsy with lymphocytic sialadenitis and focus score ≥ 1 (3 points)
- Anti-SSA (Ro) positive serology (3 points)
- Ocular staining score ≥ 5 (1 point)
- Schirmer test ≤ 5 mm / 5 min (1 point)
- Unstimulated whole saliva flow rate ≤ 1 mL/min (1 point)
- Exclusion criteria
- History of head and neck radiation treatment
- Active hepatitis C infection
- Sarcoidosis, amyloidosis
- IgG4 related disease
- Graft versus host disease
- Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (Arthritis Rheumatol 2017;69:35)
Laboratory
- Positive anti-SSA (Ro) antibodies and anti-SSB (La) antibodies
- Emerging potential biomarkers: muscarinic type 3 receptor (M3R), salivary calprotectin and carbamylated proteins (homocitrulline) (Eur J Oral Sci 2018;126:37)
Radiology description
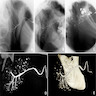
- Sialography
- Serial Xray projections taken following injection of contrast medium
- Imaging with computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has also been developed producing 3 dimensional images of the ductal system
- Dilatation of ducts and punctate collections of contrast medium (sialectasis)
- Sparsity of ductal branching
- Less commonly used (J Clin Med 2020;9:2492)
- Serial Xray projections taken following injection of contrast medium
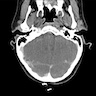
- MRI
- Heterogeneous signal intensity distribution on T1 and T2 weighted images conveying a salt and pepper appearance
- Cystic changes in advanced disease (J Clin Med 2020;9:2492)
- Ultrasound
- Hypoechogenic areas, hyperechogenic reflections and poorly defined salivary gland borders (J Clin Med 2020;9:2492)
- Ultrasound findings may be incorporated in the diagnostic features in the future; however, these require further validation (Clin Exp Rheumatol 2018;36:159)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- High focus score predicts greater decline in unstimulated salivary flow over time (Ann Rheum Dis 2008;67:949)
- Overall increased risk of lymphoma with an estimated risk of 5 - 15% of patients (Presse Med 2012;41:e511)
- Risk of lymphoma thought to be 40 times greater than the general population (Ann Intern Med 1978;89:888)
- Most commonly low grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma, specifically extranodal marginal zone of mucosa associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma
- Features thought to be associated with increased risk of transformation to lymphoma include
- High focus score
- Particularly focus score ≥ 3 has a positive predictive value of 16% and negative predictive value of 98% for non-Hodgkin lymphoma (Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73:1537)
- Detection of ectopic germinal centers, although some studies did not find these a predictive factor for MALT lymphoma (Rheumatology (Oxford) 2013;52:276)
- Usually correlate with a higher focus score (Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73:1537)
- High focus score
Case reports
- 22 year old woman with a diagnosis of ranula preceding a diagnosis of primary Sjögren syndrome (World J Clin Cases 2021;9:5701)
- 41 year old woman with a varied clinical presentation of primary Sjögren syndrome (BMJ Case Rep 2019;12:e231802)
- 55 year old woman with bilateral parotid gland enlargement and Sjögren syndrome (J Int Oral Health 2015;7:72)
- 60 year old woman with cutaneous mucosa associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma complicating Sjögren syndrome (World J Clin Cases 2022;10:4509)
Treatment
- Primarily symptomatic treatment, including
- Artificial tears
- Saliva replacement
- NSAIDs for musculoskeletal symptoms (Clin Med (Lond) 2007;7:53)
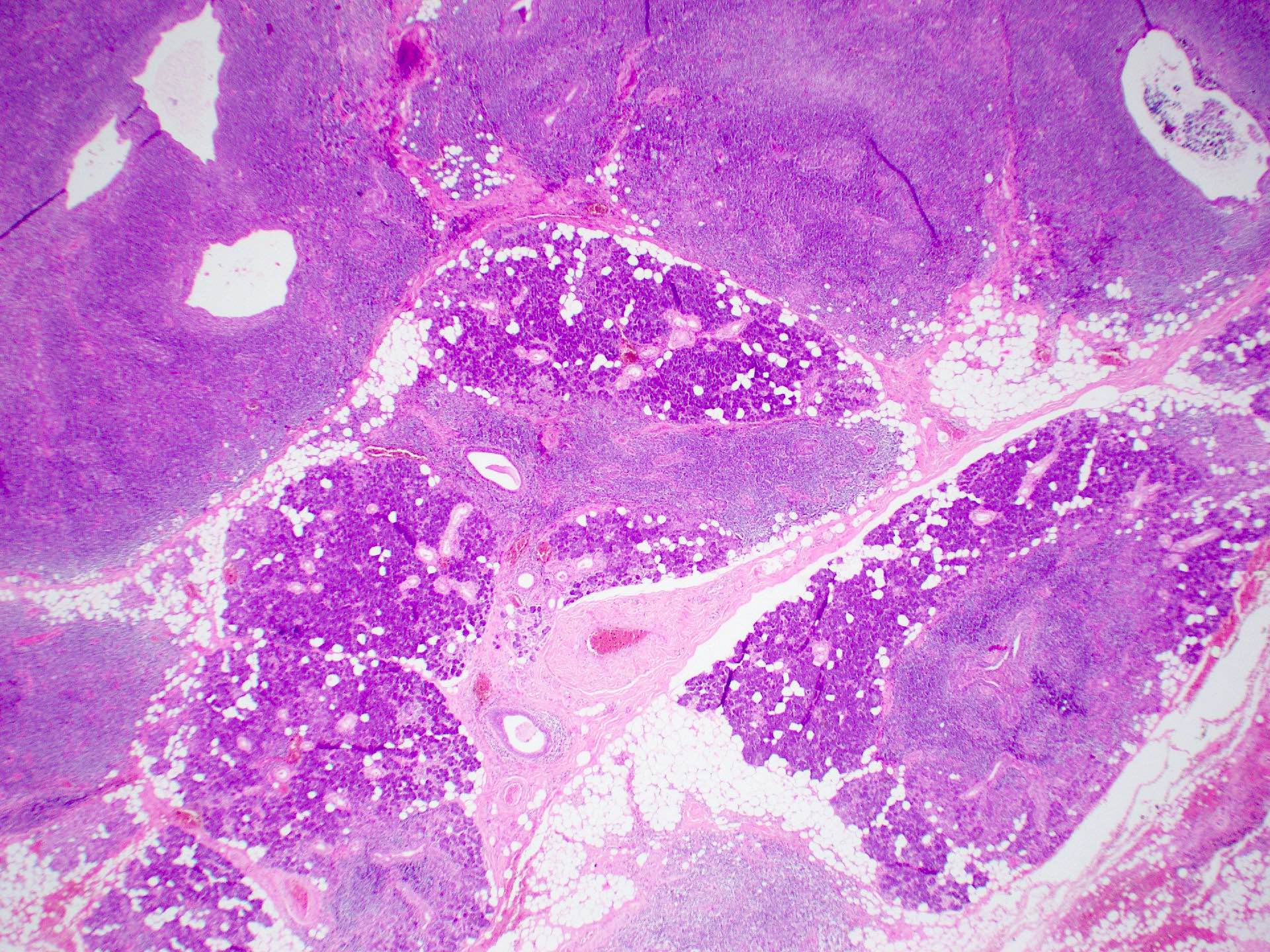
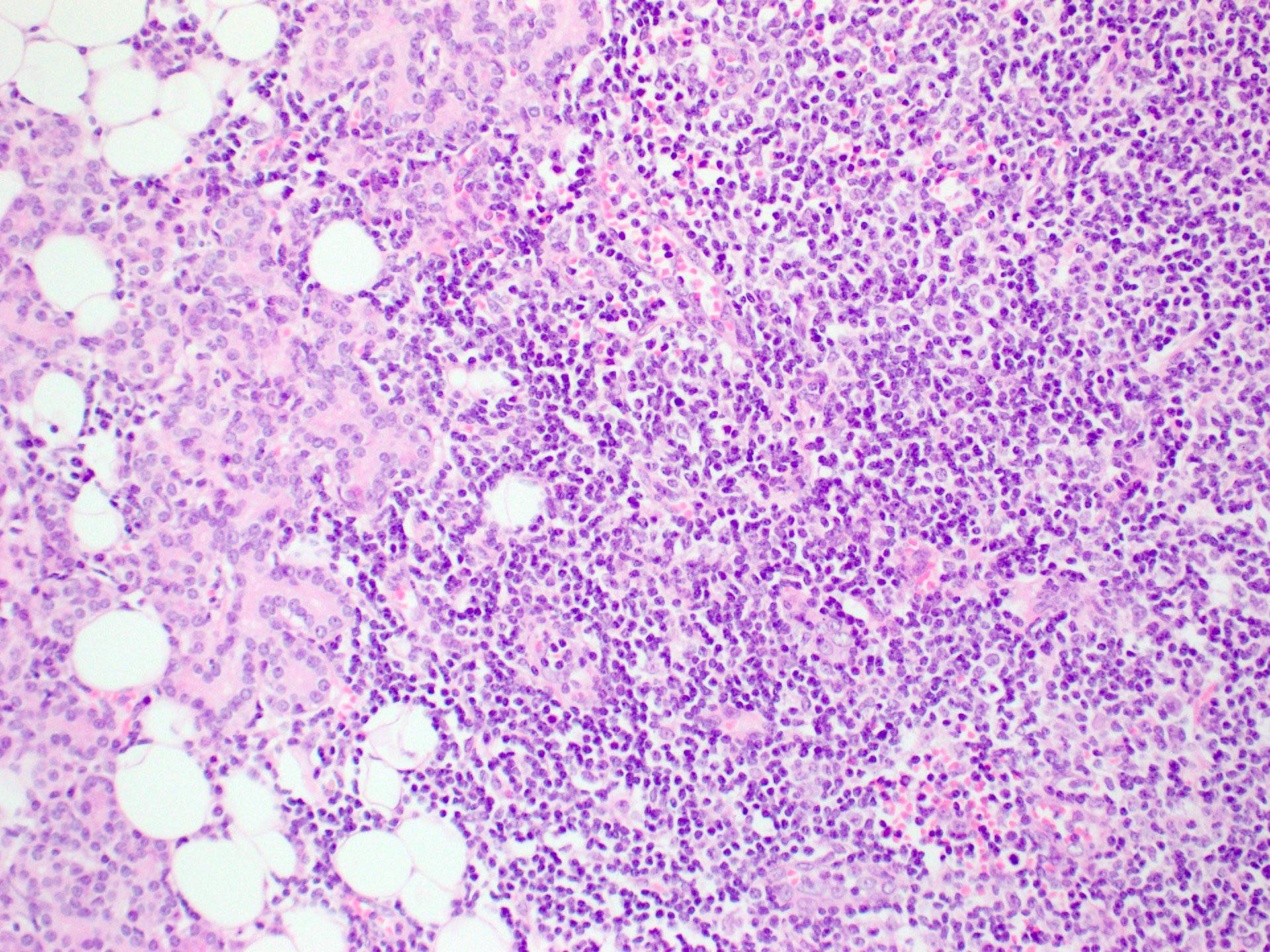
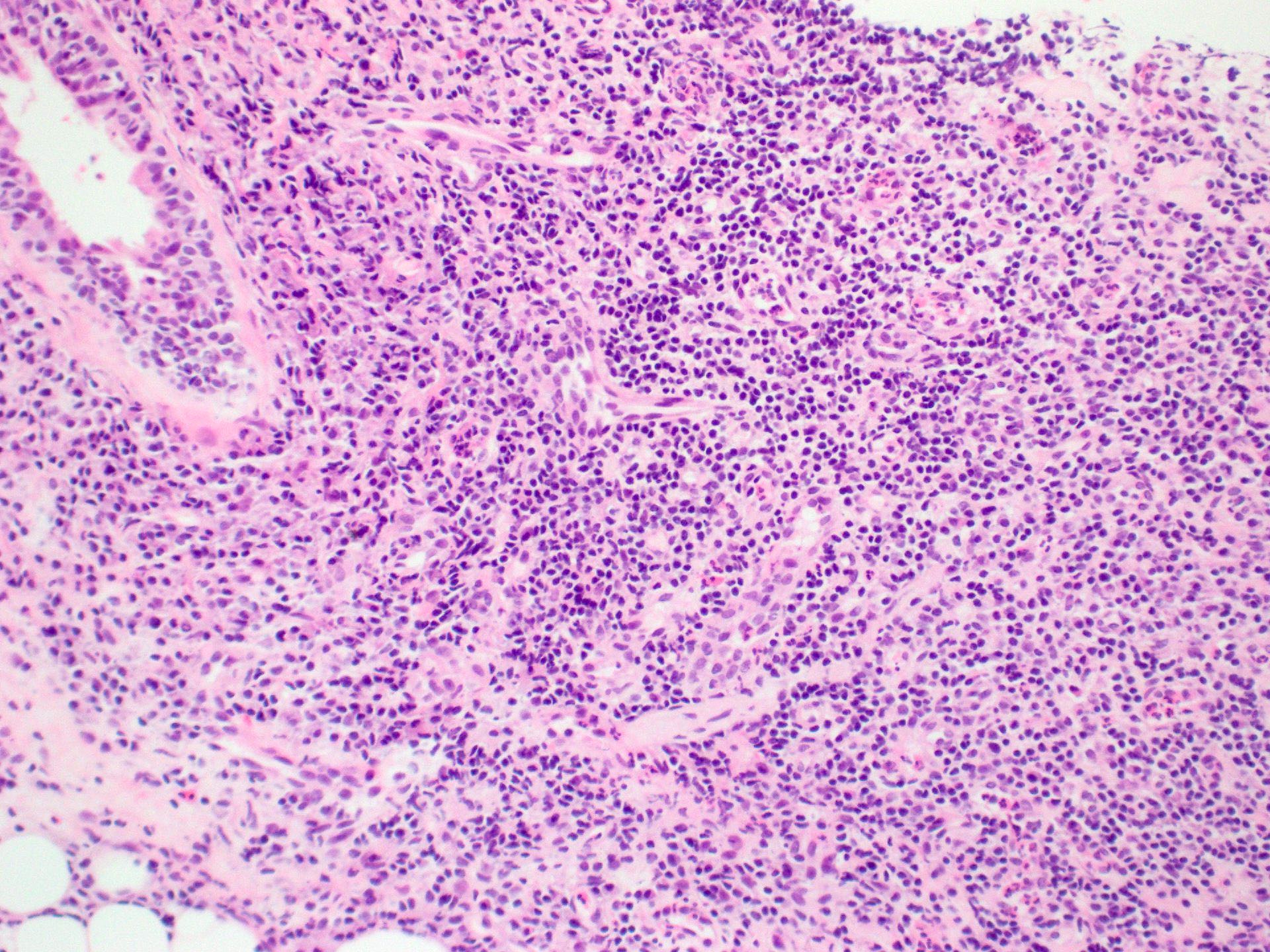
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Historically minor salivary gland biopsy has been assessed
- In a limited study, parotid gland biopsy was shown to have similar diagnostic sensitivity and specificity (Rheumatology (Oxford) 2007;46:335)
- Focal lymphocytic sialadenitis is the histological hallmark
- 1 or more dense aggregates with 50 or more lymphocytes
- Usually in perivascular or periductal areas
- Cannot be attributed if dominated by features of nonspecific chronic sialadenitis or chronic sclerosing sialadenitis (Reumatismo 2018;70:146)
- Other features are nonspecific and include
- Nonspecific chronic sialadenitis and chronic sclerosing sialadenitis
- Mild to diffuse lymphocytic infiltrates
- Progressive atrophy of normal salivary gland acini
- Duct dilatation
- Variable parenchymal fibrosis
- Lymphoepithelial lesions (seen in ~50% of patients with primary Sjögren syndrome) (Clin Exp Rheumatol 2022;40:2434)
- Lymphocytic infiltrate of ducts and basal cell hyperplasia
- Ectopic germinal centers
- Recommended that these always be reported if present (Ann Rheum Dis 2017;76:1161)
- Granulomatous inflammation
- Adiposis (Autoimmun Rev 2020;19:102690, Reumatismo 2018;70:146)
- Nonspecific chronic sialadenitis and chronic sclerosing sialadenitis
- ACR / EULAR classification criteria for labial salivary gland biopsy
- Focal lymphocytic sialadenitis
- If identified, a focus score should be recorded, with a focus score ≥ 1 suggestive of Sjögren syndrome (Arthritis Rheumatol 2017;69:35)
- Focus score 1 = 1 focus of 50 lymphocytes per 4 mm2 (Arthritis Rheum 2011;63:2021)
- Recommended at least 4 labial salivary glands with a surface area of at least 8 mm2 to allow for adequate assessment and focus scoring (Ann Rheum Dis 2017;76:1161)
- Focal lymphocytic sialadenitis
Microscopic (histologic) images
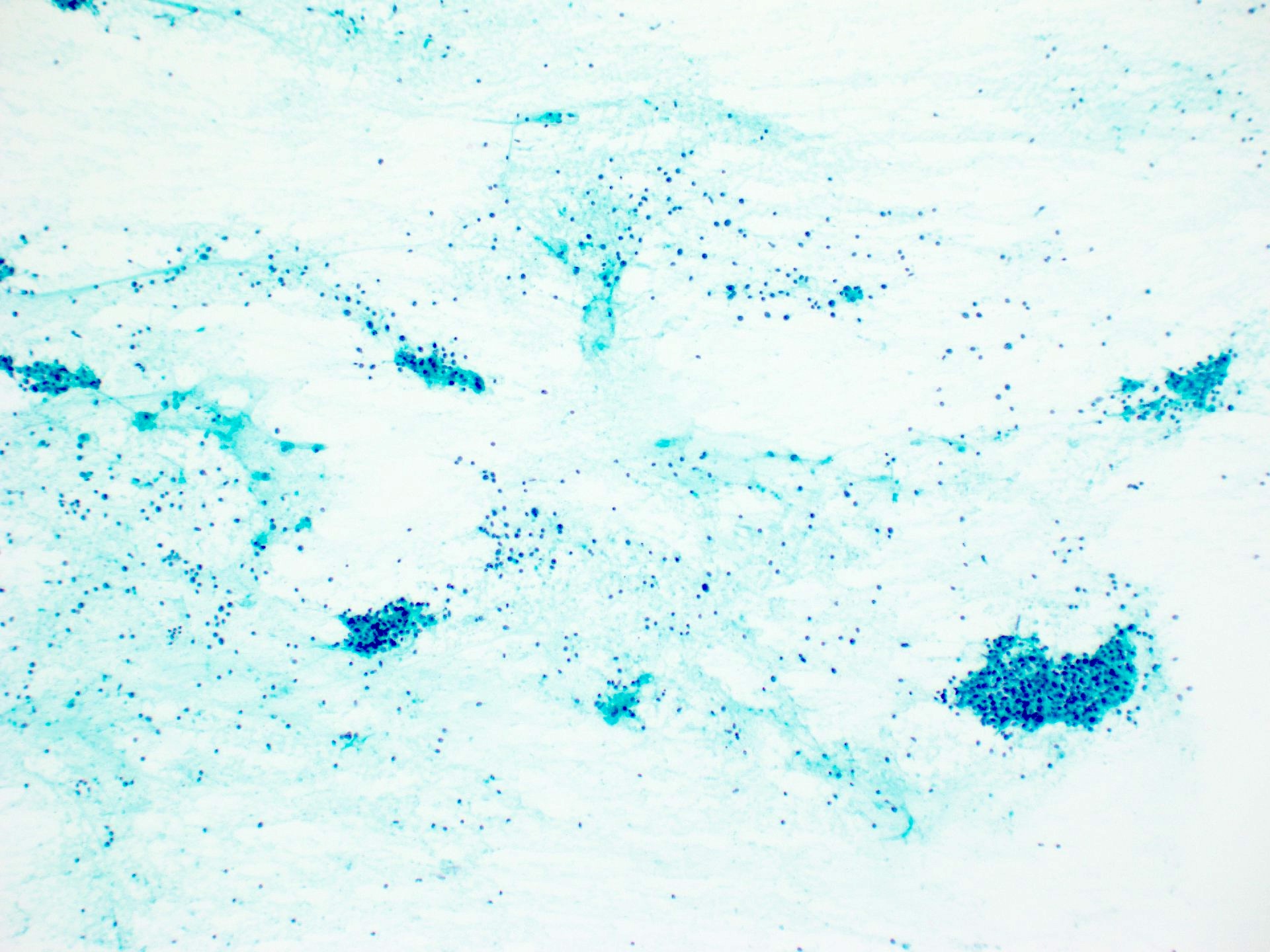
Cytology description
- Nonspecific findings
- May find benign myoepithelial and ductal epithelial cells interspersed with a lymphocytic infiltrate
- There may be macrophages in the background (Prog Health Sci 2013;3:178)
Cytology images
Positive stains
- BCL6 highlight germinal center B cells
- CD21 / CD23 can highlight follicular dendritic cells in germinal centers (Reumatismo 2018;70:146)
Sample pathology report
- Salivary gland, biopsy
- Focal lymphocytic sialadenitis with associated mild atrophy of the salivary acini (see comment)
- Comment: There is a single nodular lymphocytic aggregate (1 cluster of > 50 lymphocytes per 4 mm2, focus score = 1). There is no germinal center formation and no features to suggest malignancy. The finding of focal chronic sialadenitis with a focus score of 1 is compatible with the diagnosis of Sjögren syndrome in the correct clinical context. Correlation with clinical history, radiology, serology and flow cytometry is recommended.
Differential diagnosis
- Nonspecific chronic sialadenitis:
- Clinical pathological correlation required
- IgG4 disease:
- Plasma cell rich inflammatory infiltrate
- Increased ratio of IgG4 to IgG plasma cells
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
D. Focus score ≥ 3. A high focus score, particularly ≥ 3, has a positive predictive value of 16% and negative predictive value of 98% for non-Hodgkin lymphoma (Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73:1537). Answers A, B and C are incorrect because fat infiltration and fibrosis are all features that can be present in salivary gland biopsies of patients with Sjögren syndrome; however, they have not been associated with increased risk of lymphoma in these patients.
Comment Here
Reference: Sjögren syndrome
Comment Here
Reference: Sjögren syndrome
Board review style question #2
What is the most common salivary gland lymphoma occurring in patients with primary Sjögren syndrome?
- Diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- Extranodal marginal zone of mucosa associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma
- Follicular lymphoma
- Hodgkin lymphoma
Board review style answer #2
B. Extranodal marginal zone of mucosa associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma. Answers A and C are incorrect because diffuse large B cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma have been reported in salivary glands; however, they are not the most common lymphoma in this site. Answer D is incorrect because Hodgkin lymphoma is rare in salivary glands (Rheumatology (Oxford) 2022;61:3818).
Comment Here
Reference: Sjögren syndrome
Comment Here
Reference: Sjögren syndrome