Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Lee N, Ng T. Salivary duct cyst. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/oralcavitysalivaryductcyst.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Reactive lesion to salivary gland duct obstruction and buildup of trapped mucin within
Essential features
- Mucus trapped within lumen secondary to salivary gland duct obstruction
- Severe obstruction can lead to squamous or oncocytic metaplasia of duct epithelial bilayer
- Found on oral mucosal sites with minor salivary glands or parotid gland
- May become secondarily infected around sialolith, which acts as a nidus
Terminology
- Salivary retention cyst
- Mucus retention cyst
- Mucus duct cyst
- Sialocyst
- Reactive oncocytoid cyst (if epithelial lining has oncocytic metaplasia)
- Not to be confused with mucocele / mucus extravasation phenomenon / ranula / plunging rannula / mucus escape reaction
ICD coding
- ICD-10: K11.8 - other diseases of salivary glands
Epidemiology
- M = F (Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1987;113:51)
- Some reports have found a slight female predilection (Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1987;113:51)
- Adults with median age of 56 years from 177 cases (Head Neck Pathol 2017;11:469)
- Rarer than the oral cavity mucocele (Pediatr Dermatol 2008;25:308)
Sites
- Minor salivary glands of the floor of mouth, vestibule (mucobuccal fold), buccal mucosa, upper labial mucosa (Head Neck Pathol 2017;11:469)
- Parotid is the most commonly associated major salivary gland (J Oral Sci 2001;43:9)
- Rare in the lower lip (Pediatr Dermatol 2008;25:308)
Pathophysiology
- Salivary duct occlusion leading to reactive ductal ectasia (Diagn Cytopathol 2015;43:495)
- True developmental cyst with epithelial lining unlike the oral cavity mucocele (Head Neck Pathol 2017;11:469)
Etiology
- May be associated with sialoliths, mucus plugs, postoperative or postinflammatory stricture (J Oral Sci 2001;43:9)
- Distal obstruction of a salivary duct leads to retention of secretion within the duct (Diagn Cytopathol 2015;43:495)
Clinical features
- Dome shaped, sessile, slow growing but asymptomatic nodule (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1984;58:692)
- 1 - 3 cm but have been reported to grow up to 10 cm (J Oral Sci 2001;43:9)
- Fluctuant to palpation but usually painless, some may feel firmer especially if a sialolith is present (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1964;18:191)
- Mucus or pus may be expressed from dilated ductal orifices when palpated if secondarily infected (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1984;58:692)
- Blue tinge due to Tyndall effect
- Do not typically wax and wane over time (Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1987;113:51)
Diagnosis
- Based on patient reported history and clinical examination, definitive diagnosis made by histopathologic evaluation under light microscopy
Prognostic factors
- Benign with good prognosis
Case reports
- 15 year old boy with a 3 month history of a left lower labial mucosa swelling (J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2014;18:S151)
- 30 year old man with a left submandibular swelling only noticeable on swallowing and nose blowing (J Laryngol Otol. 2000;114:305)
- 56 year old man with an obstructive mass at the vallecula (Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1989;115:1254)
- 63 year old man presenting with an enlarging left preauricular swelling (J Clin Imaging Sci 2013;3:3)
- 78 year old man with a firm swelling at the left upper labial mucosal (Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2013;56:163)
Treatment
- Complete excision along with the feeding minor salivary gland is curative (Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1987;113:51)
- Iatrogenic intraoperative damage to neighboring salivary gland parenchyma may contribute to the development of postoperative mucocele (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1964;18:191)
- Partial or total removal of feeding major salivary glands may be required (Pediatr Dermatol 2008;25:308)
- Chlorhexidine mouth rinse or oral antibiotics for secondarily infected salivary duct cysts (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1984;58:692)
- Sialagogues may decrease the risk of salivary stasis within dilated ducts by stimulating salivary flow
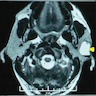
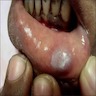
Clinical images
Gross description
- Nodular mass with soft texture
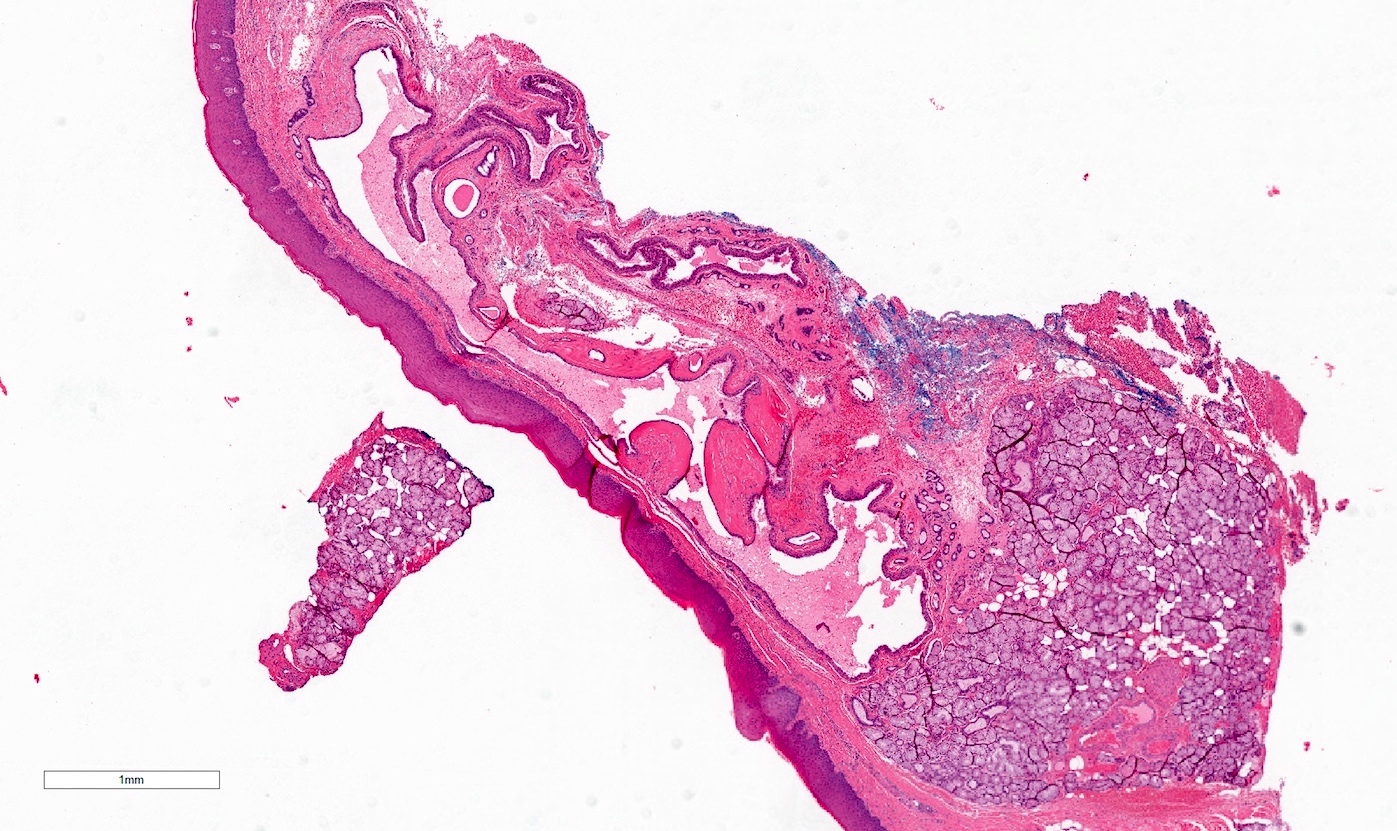
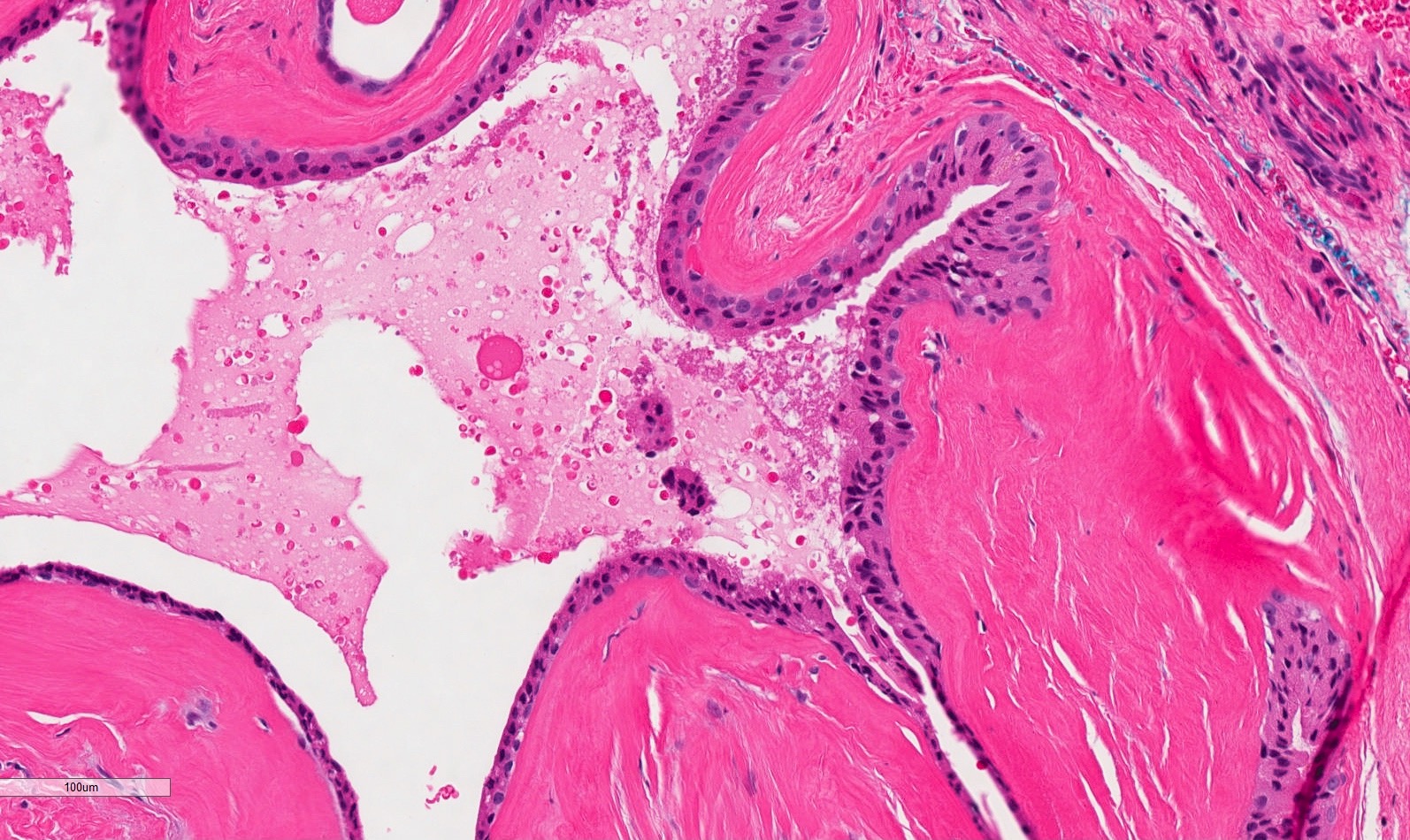
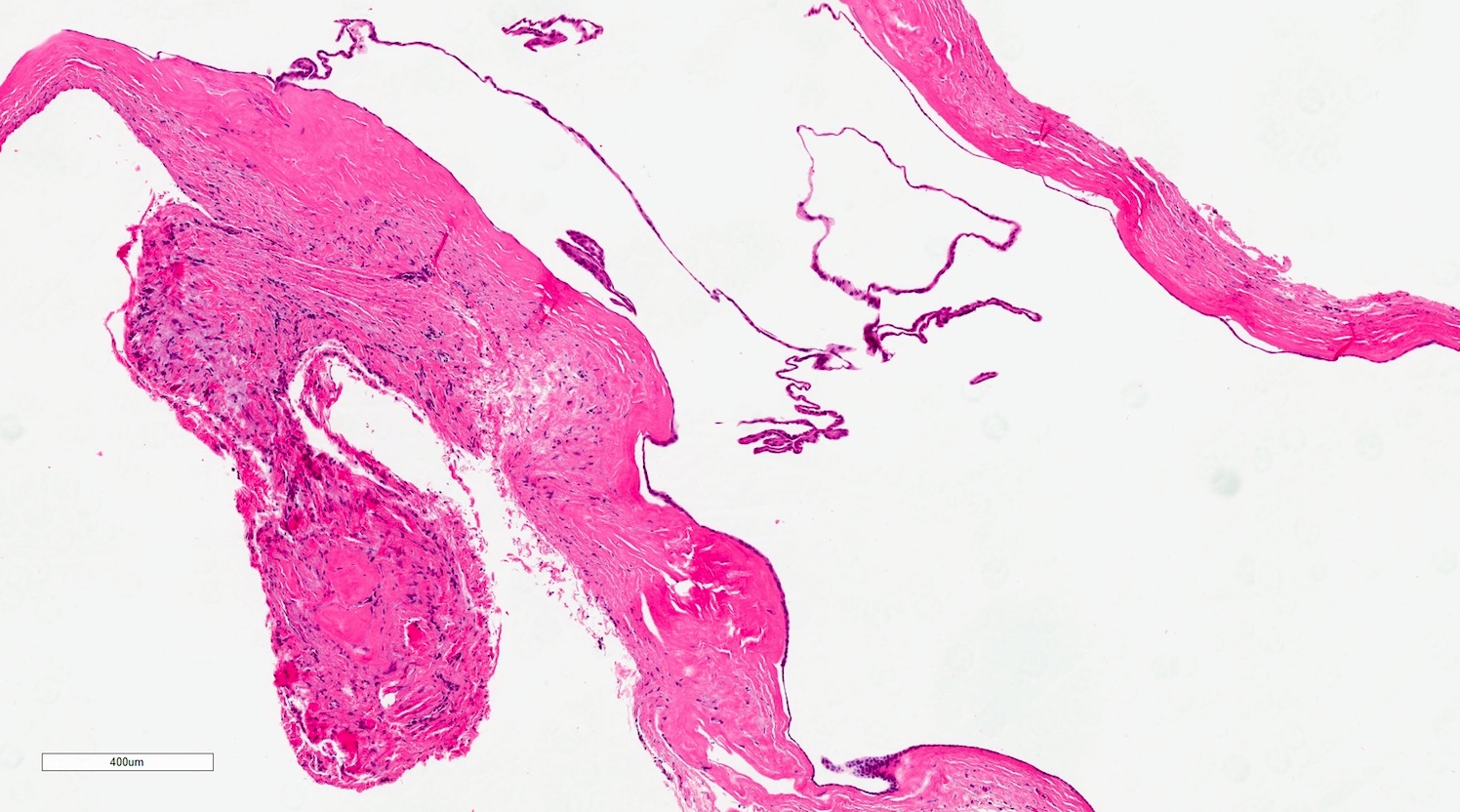
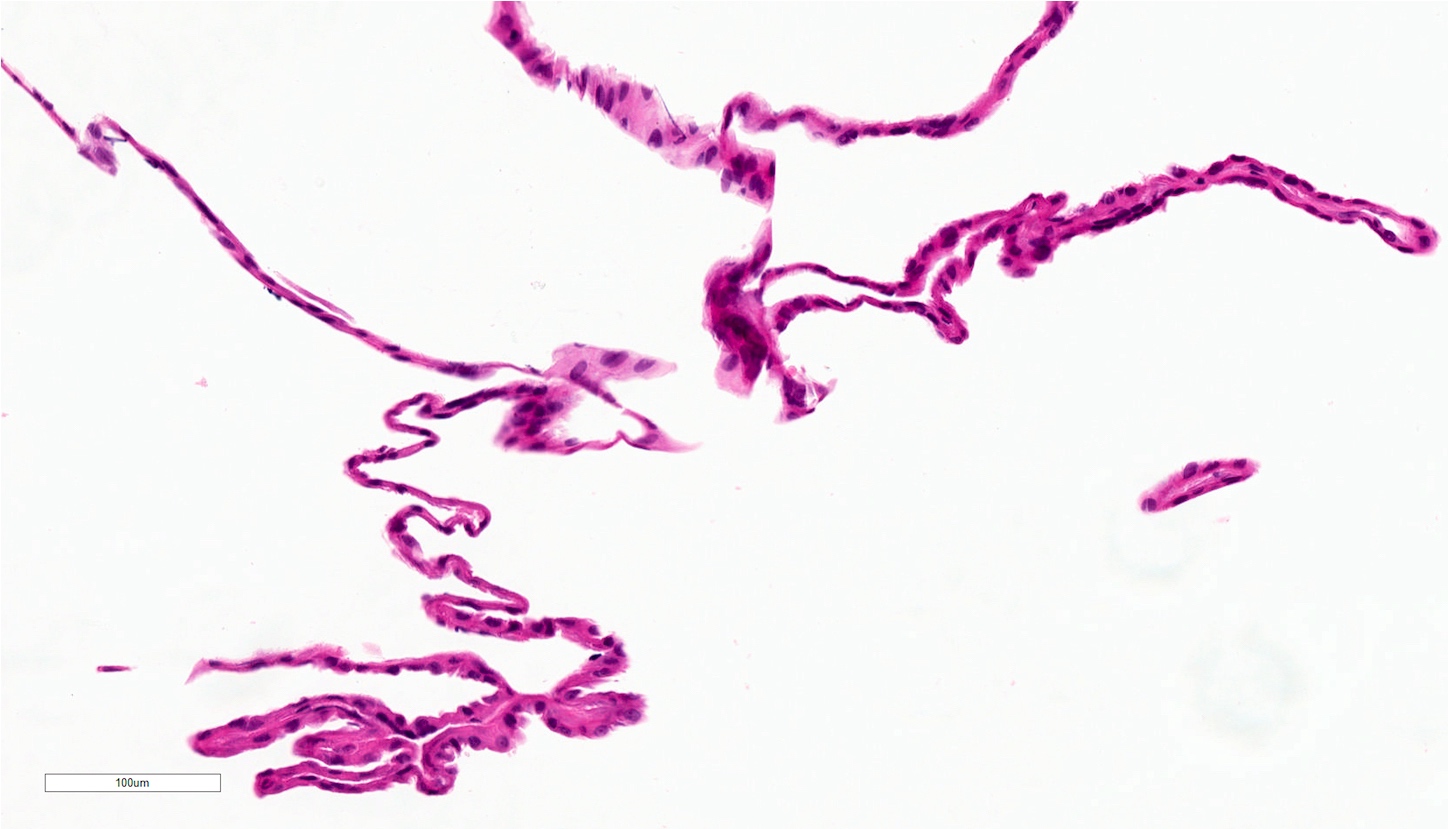
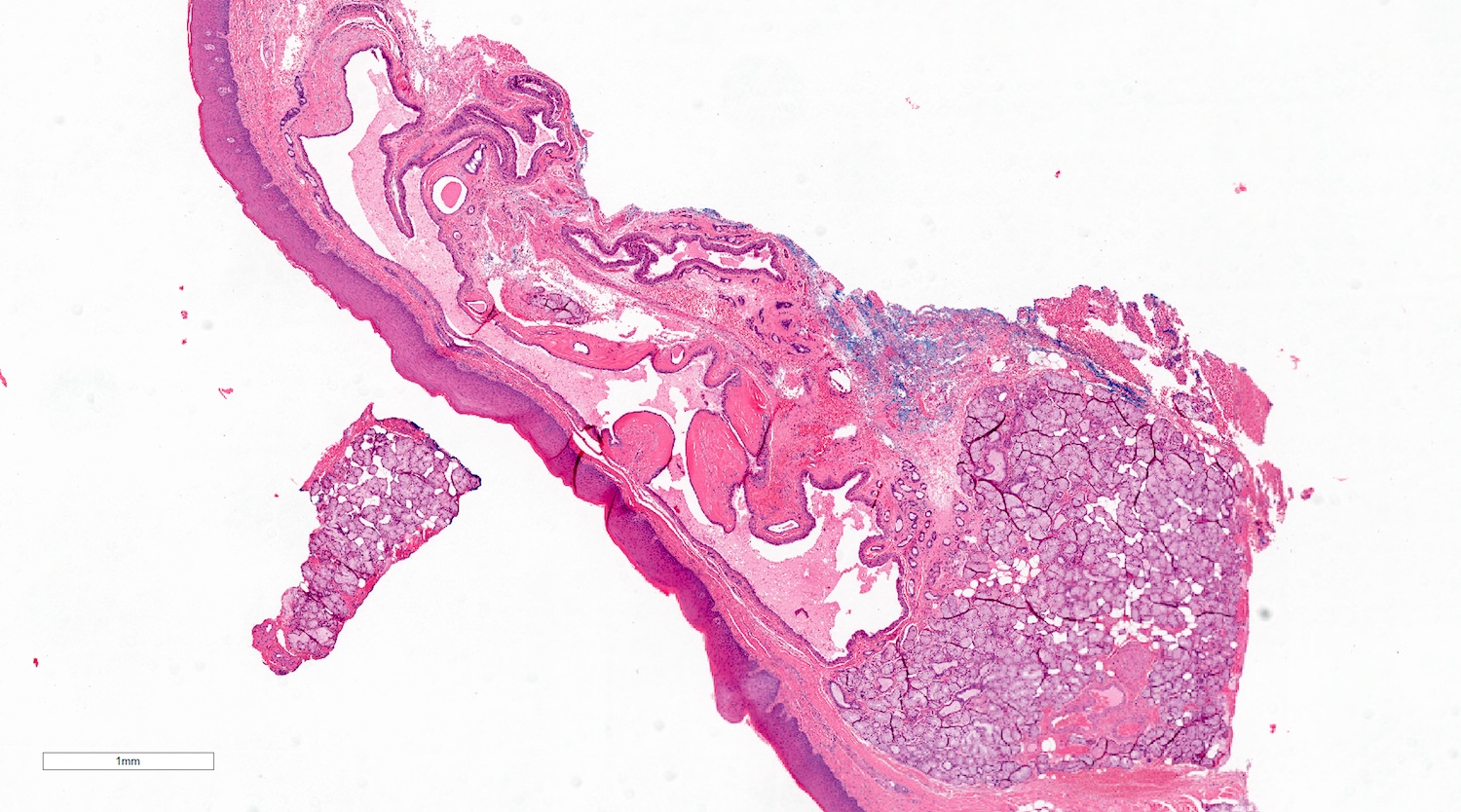
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Mucoid secretion surrounded by a bilayer of cuboidal or columnar stratified salivary duct epithelium (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1964;18:191)
- Cyst lining may have papillary folds into the lumen (Head Neck Pathol 2017;11:469)
- May have squamous or oncocytic metaplasia of cyst lining, especially with more severe obstruction (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1964;18:191)
- Sialolith and bacteria causing secondary infection may be present among the submitted tissue (Head Neck Pathol 2017;11:469)
- Feeding salivary gland, if included, has obstructive changes with variable ductal dilation, lymphocytic infiltrate with periductal pattern and fibrosis (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1984;58:692)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
Negative stains
Sample pathology report
- Right upper labial mucosa, exision:
- Salivary duct cyst (mucus retention cyst)
- Minor salivary gland parenchyma showing chronic sialoadenitis
Differential diagnosis
- Mucocele/mucus extravasation phenomenon/ranula/plunging rannula/mucus escape reaction
- There is no true salivary gland duct epithelial lining and instead this is mimicked by epithelioid macrophages (muciphages) at the periphery of the extravasated mucin
- Warthin tumor (papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum)
- Lymphoid stroma in the cyst wall and multiple papillary infoldings with a bilayer of columnar and oncocytic epithelial lining
- Papillary cystadenoma
- The lining epithelium has an adenomatous proliferation forming multilayered plaques of columnar or oncocytic salivary duct lining with papillary infoldings
- Gingival cyst of the adult
- These occur only on the gingiva which has no minor salivary glands
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
-
Among the choices below, what is the most common site for a salivary duct cyst?
- Dorsal tongue
- Gingiva
- Intrabony
- Maxillary sinus
- Parotid gland
Board review style answer #2