Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Zhao X, Wei S. Myoepithelioma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/salivaryglandsmyoepithelioma.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rare, benign tumor composed almost exclusively of myoepithelial cells
Essential features
- Epithelial component should be less than 5% (some consider even focal epithelial differentiation sufficient to label the tumor as pleomorphic adenoma) (J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2013;17:257)
- Monomorphic histology and rare or absent ductal structures in myoepithelioma differentiate it from pleomorphic adenoma
Terminology
- Formerly considered a variant of pleomorphic adenoma; recognized as a distinct entity by WHO in 1991 (Clin Pract 2014;4:628, Pathol Res Pract 1990;186:555)
- Not recommended: myoepithelial cell tumor, myoepithelial adenoma
Epidemiology
- 1% of all salivary gland neoplasms (Case Rep Oncol 2014;7:310)
- 2.2% of major and 5.7% of minor salivary gland neoplasms, respectively (Case Rep Oncol 2014;7:310)
- No sex predilection (Clin Pract 2014;4:628)
- Myoepithelioma of parotid occurs in older people and is composed more often of spindle and epithelial cells (Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:1183, Histopathology 1995;27:1)
- Myoepithelioma of minor glands occurs in slightly younger individuals and is composed of plasmacytoid cells (Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:1183, Histopathology 1995;27:1)
Sites
- Affects the parotid gland (~40%) and minor salivary gland sites (palate) (~21%) (Case Rep Oncol 2014;7:310, Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2003;129:359)
Pathophysiology
- Arising from neoplastic myoepithelial cells located between the basement membrane and the basal plasma membrane of acinar or ductal / luminal cells
- Accumulation of p53 and overexpression of KIT receptor have been implicated in malignant progression (J Clin Pathol 1998;51:552, Cancer Lett 2000;154:107)
Etiology
- Myoepithelial cells are contractile cells originating from the ectoderm, found in normal tissues with secretory function that aids in excreting glandular secretions (Ear Nose Throat J 2011;90:E9, Clin Pract 2014;4:628)
- Common stem cell with a bidirectional differentiation into epithelial or myoepithelial cell is hypothesized to be the cell of origin; the varied histological types (spindle, plasmacytoid, epithelioid, clear and oncocytic) exhibited by myoepitheliomas can be attributed to the various stages in the differentiation from a cell that has the potential to differentiate into epithelial cells (J Clin Diagn Res 2013;7:1165)
- Myoepitheliomas and pleomorphic adenomas are hypothesized to exist along a continuum, with a shared chromosome 12q cytogenetic abnormality (Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1999;113:49)
Clinical features
- No distinctive clinical features
- 1% of salivary gland tumors, more common in parotid (40%) and minor salivary gland (21%) (Case Rep Oncol 2014;7:310, Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2003;129:359)
- Usual age of presentation is 40 - 50 years (range: 9 - 85 years)
- No sex predilection (Clin Pract 2014;4:628)
- Slow growing, painless, well circumscribed mass
- Recurs locally if incomplete removal (Semin Diagn Pathol 1997;14:203)
- Clear cell variant may have unpredictable clinical course despite being histologically benign (Rosai: Ackerman's Surgical Pathology, 8th Edition, 1996)
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis is often rendered in resection specimen
Radiology description
- Located chiefly in the superficial lobe and abutted on the capsule of the gland
- CT: well circumscribed, enhancing mass lesion with smooth or lobulated margins (AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2008;29:1372)
- May contain enhancing nodules and nonenhancing areas of linear bands, slit-like shaped or of cystic configuration
- MRI: well circumscribed, lobulated, inhomogeneous enhancement, apparent diffusion coefficient, different from Warthin tumor and similar to pleomorphic adenoma (AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2009;30:591)
Prognostic factors
- Malignant transformation to myoepithelial carcinoma has been reported but seems to be extremely rare (Ultrastruct Pathol 1996;20:145, Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:761)
Case reports
- 29 year old woman with plasmacytoid myoepithelioma of palate (Head Neck Pathol 2011;5:154)
- 41 year old woman with myoepithelioma as a palatine nodule (J Oral Med Oral Surg 2018;24:81)
- 80 year old man with cystic clear cell myoepithelioma of parotid gland (Oral Maxillofac Surg 2009;13:45)
- 86 year old woman with a mucinous myoepithelioma (SAGE Open Med Case Rep 2020;8:2050313X20940567, Head Neck Pathol 2013;7:S85)
- 3 cases of myoepithelioma in minor salivary glands (J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2013;17:257)
- Oncocytic myoepithelioma of salivary gland (Virchows Arch 1999;434:537)
Treatment
- Complete surgical excision with free margin recommended (Clin Pract 2014;4:628)
- Regular follow up to evaluate for local recurrence
Gross description
- Up to 5 cm; encapsulated, may have cystic change
- Absence of grossly myxoid or chondroid areas
- Solid, tan or yellow-tan glistening cut surface
- Usually encapsulated in parotid gland and no capsule for those in minor salivary glands (Ear Nose Throat J 2001;80:155)
Frozen section description
- Nonspecific, may show atypical cells, usually need to defer to permanent for further characterization
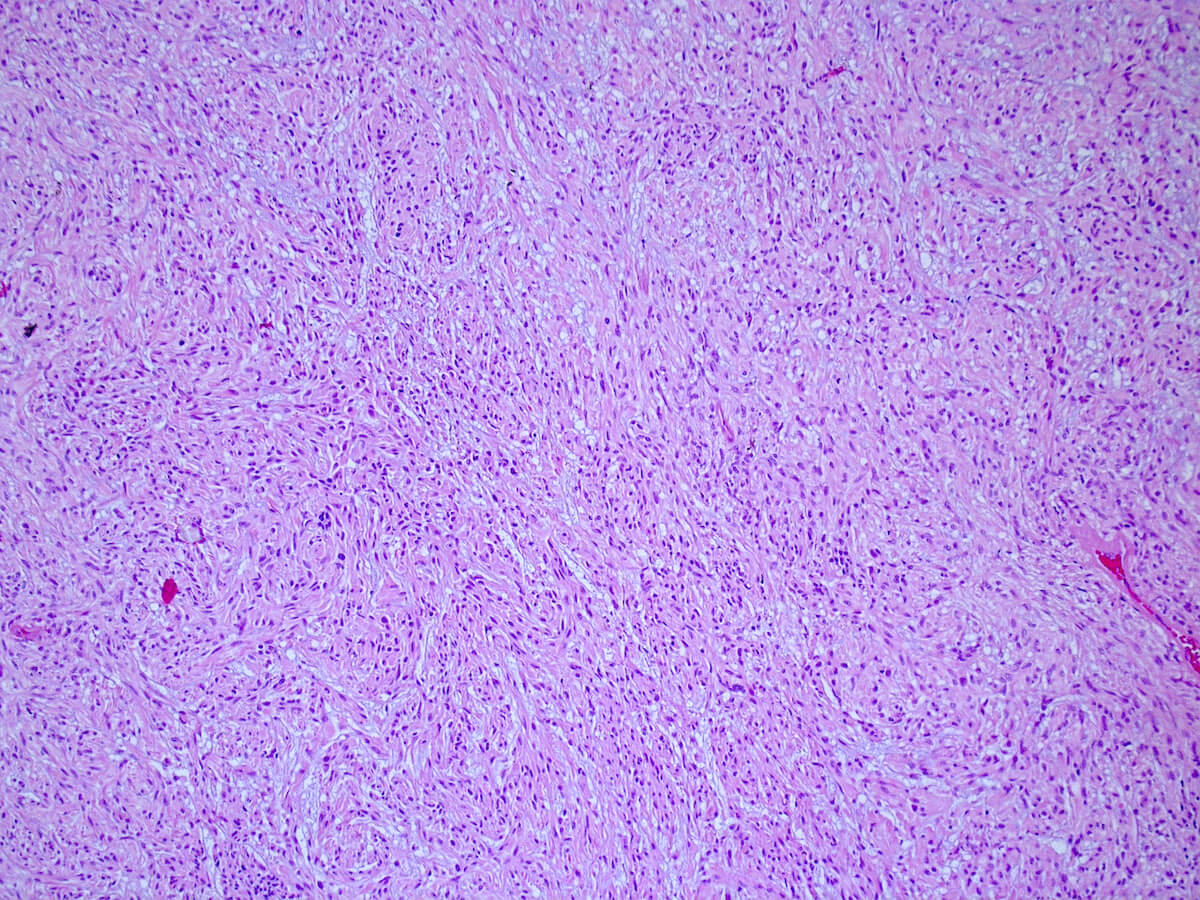
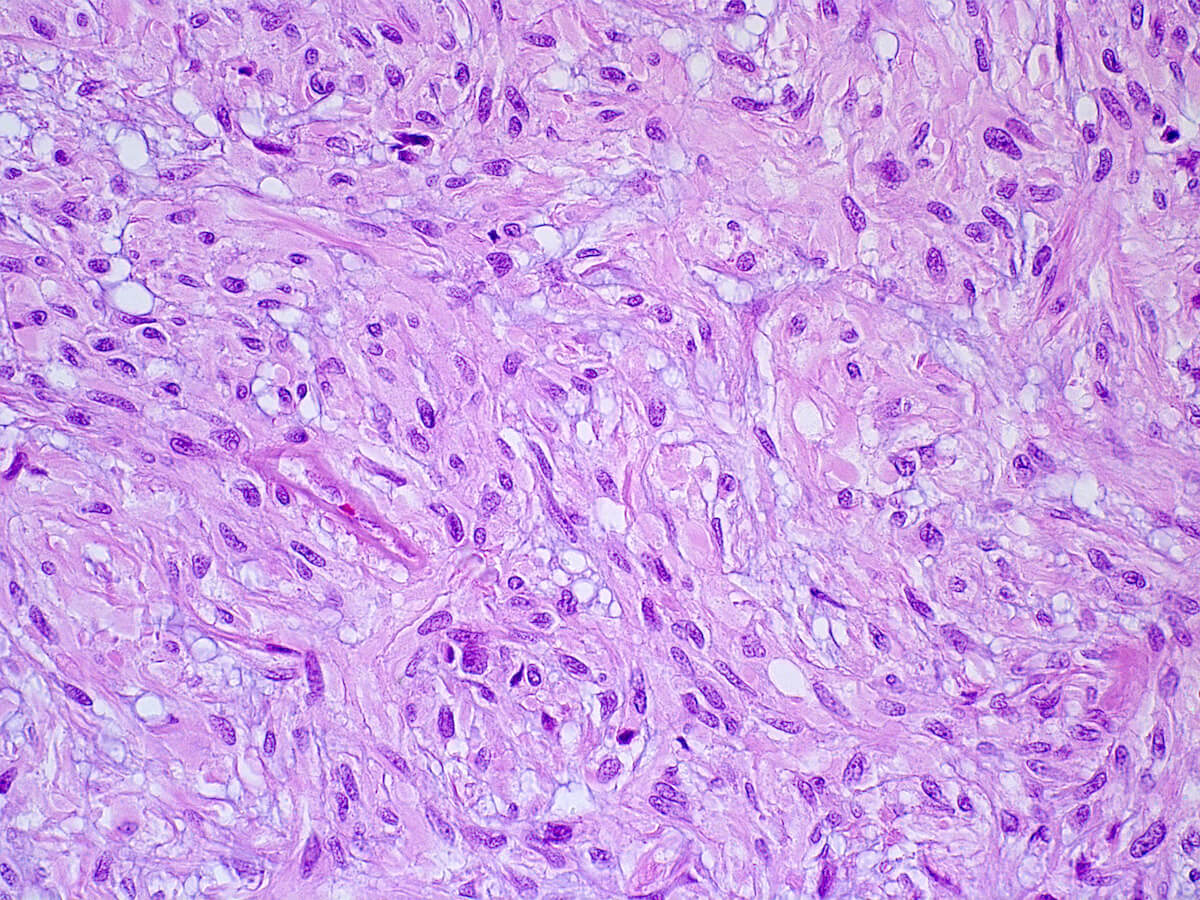
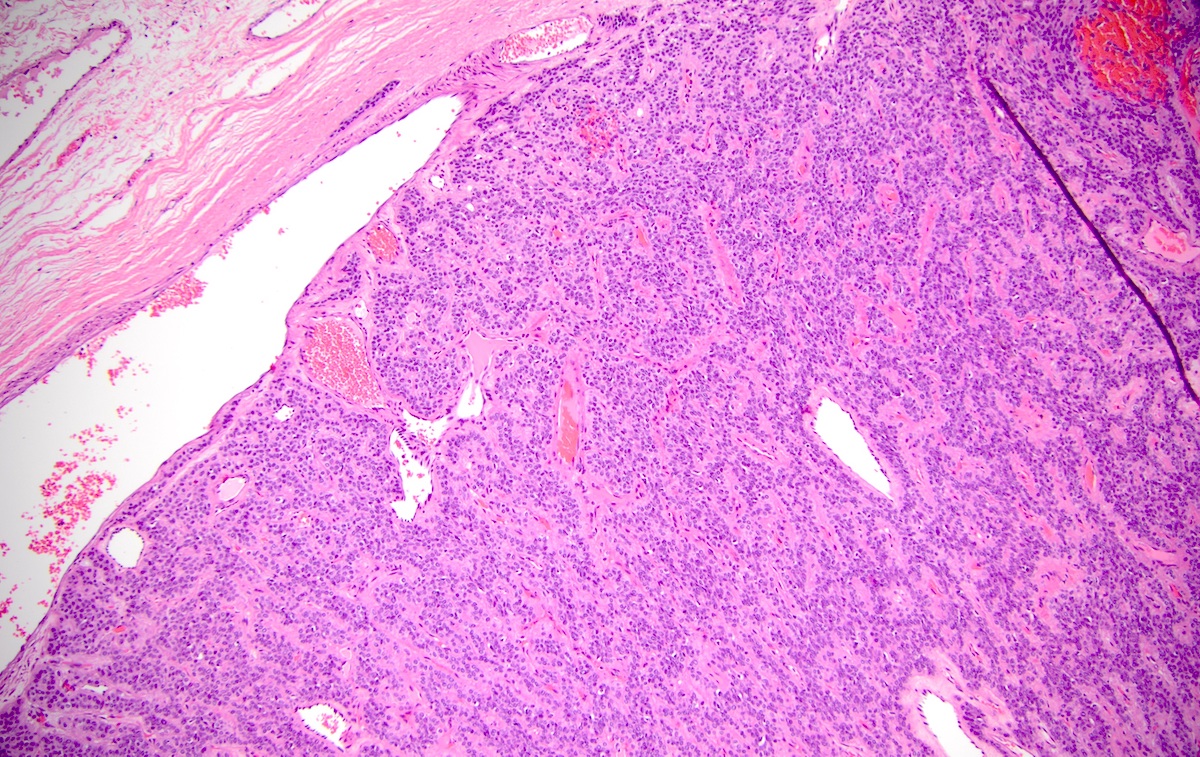
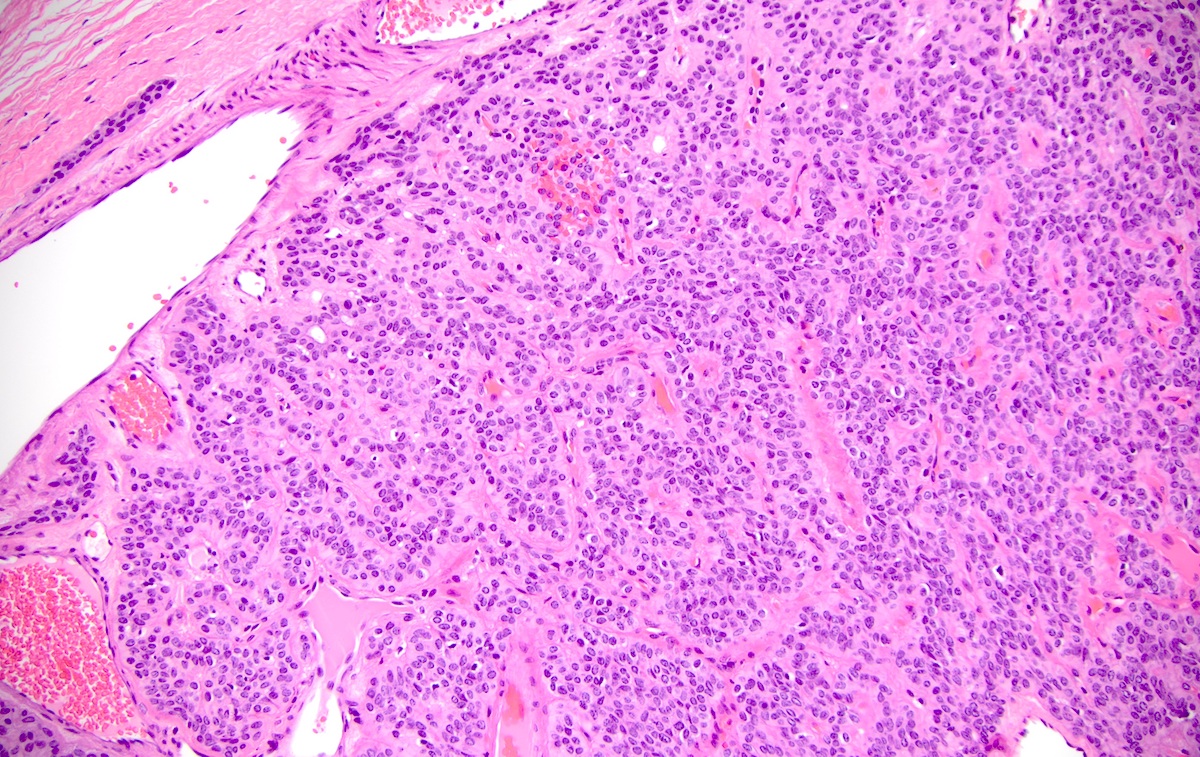
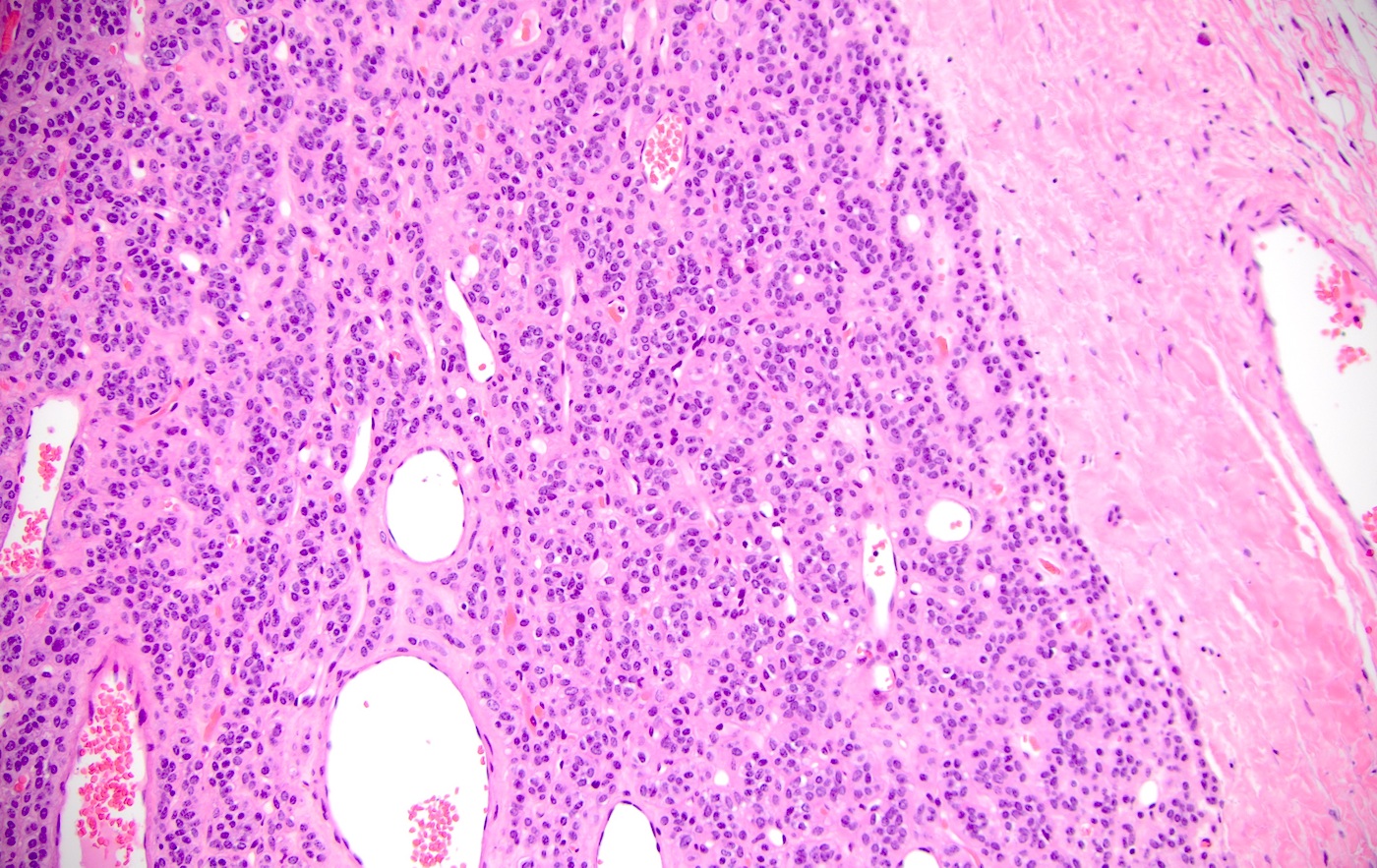
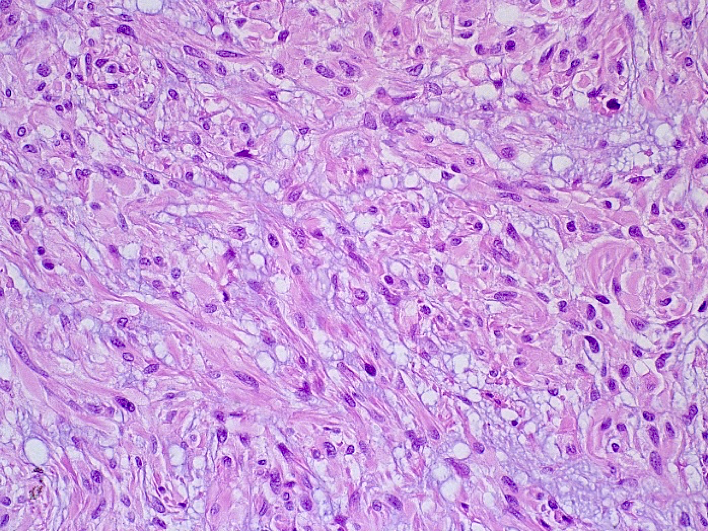
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Spindled, epithelioid, plasmacytoid, clear or oncocytic cells; most tumors are composed of a single cell type but combinations may occur (Clin Pract 2014;4:628)
- Well circumscribed or encapsulated with a thin capsule
- Stroma, when present, may be hyalinized, fibrous, myxoid or mucoid; lipomatous stroma may rarely been seen.
- Encapsulation uncommon in minor salivary gland tumors
- Architectural pattern: solid (non-myxoid), myxoid, reticular (canalicular-like) or mixed patterns of myoepithelial cells with no ductal differentiation
- Mucinous myoepithelioma is rarely reported; contains abundant intracellular mucin material, which may be mistaken for signet ring cell adenocarcinoma of salivary gland with positive myoepithelial markers and should be distinguished from secretory myoepithelial carcinoma (Head Neck Pathol 2013;7:S85)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
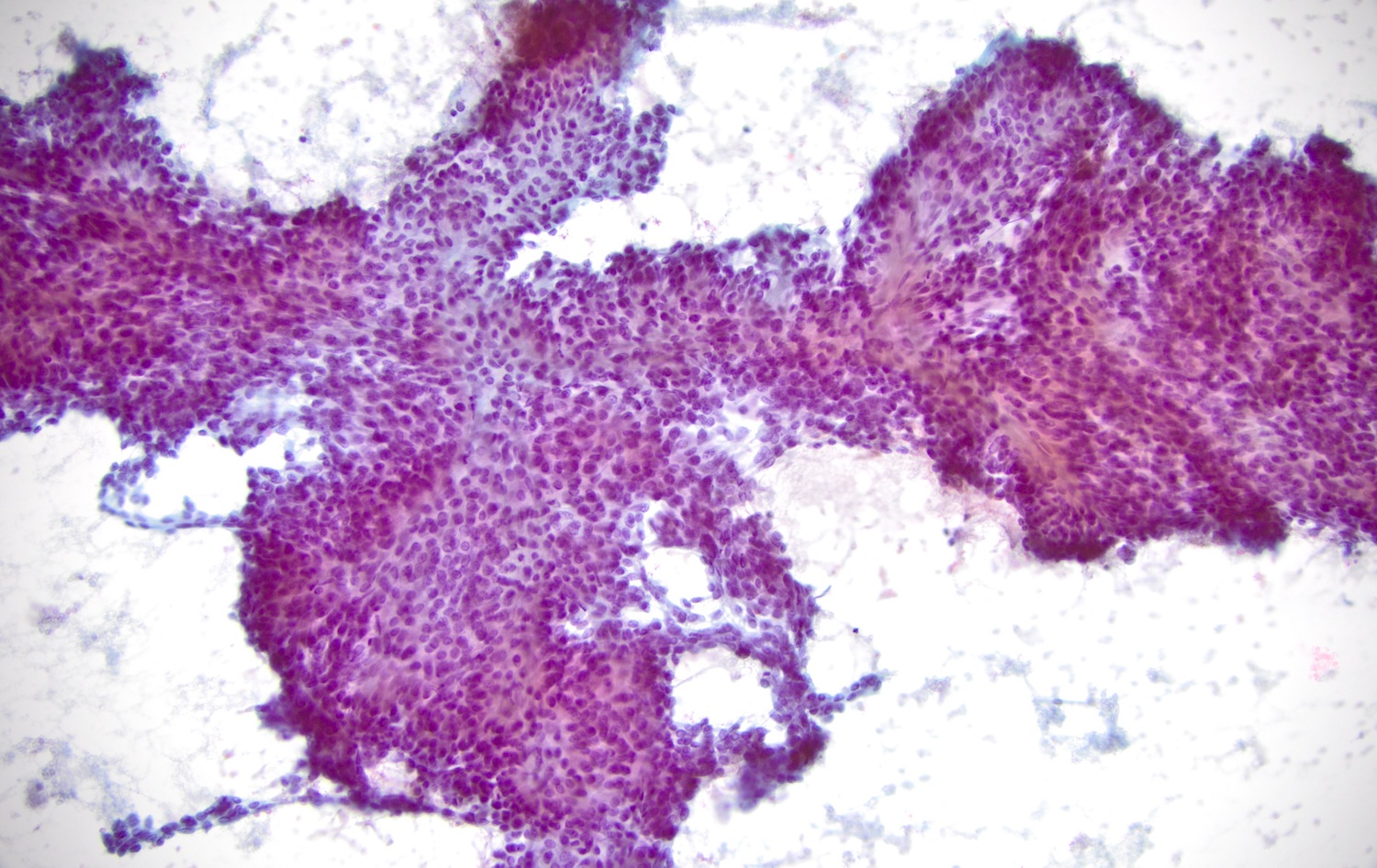
- Monotonous spindle cell, plasmacytoid cells or epithelioid cells (J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2014;18:131)
- No glandular / ductal cells
- Can have nuclear grooves, intranuclear cytoplasmic inclusions, no marked pleomorphism, no mitoses
Cytology images
Positive stains
- GFAP, S100, SMA, calponin, HHF35 / muscle specific actin, CD10, CK14, CEA (variable), p63 (J Cell Biol 1980;84:633, Acta Histochem Cytochem 2012;45:269)
Negative stains
- Plasmacytoid variant may be negative for all myoepithelial markers
Electron microscopy description
- Composed of a single cell population characterized by numerous cytoplasmic filaments, duplication of basement membrane material and characteristic cytoplasmic appearance of myoepithelial cells (Arch Pathol 1974;98:312, Oral Oncology Extra 2005;41;104)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Clear cell myoepithelial carcinoma can have EWSR1 rearrangement (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:338)
- NTF3-PLAG1, FBXO32-PLAG1 and GEM-PLAG1 fusions have been detected in oncocytic myoepithelioma (Hum Pathol 2020;103:52)
- Detection of PLAG1 rearrangement by cytogenetics or other methods can be helpful (Ann Diagn Pathol 2017;28:19, Hum Pathol 2020;103:52)
Sample pathology report
- Parotid, right, parotidectomy:
- Myoepithelioma, 3.6 cm, completely excised
Differential diagnosis
- Myoepithelial carcinoma:
- Invasive growth pattern
- Low recurrence rate
- For palatal myoepitheliomas, encapsulation is not a reliable criterion
- High cell proliferative activity (i.e. 7 mitosis instances per 10 high power fields or a Ki67 labeling index > 10%) may indicate malignancy (Cancer 1998;83:1292)
- Spindle morphologic characteristics were observed with nodal and distant metastasis (Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2010;136:702)
- Basal cell adenoma:
- Ductal (epithelial) cells present
- Pleomorphic adenoma:
- Fibromyxoid stroma and ductal structure present
- Spindle cell soft tissue neoplasm, nerve sheath tumor, fibrous histiocytoma, nodular fasciitis, synovial sarcoma, leiomyoma, leiomyosarcoma and hemangiopericytoma:
- Keratin negative
- Plasmacytoma:
- Perinuclear clearing (hof)
- Positive for plasma cell markers, such as CD138
Board review style question #1
A 46 year old man presents with swelling close to his right ear. Imaging reveals a well circumscribed 1.8 cm nodule in the parotid gland. Biopsy findings are shown in the picture above. Which of the following statements about this tumor is true?
- Monomorphic tumor cells and absence of ducts help to differentiate myoepithelioma from pleomorphic adenoma
- Mucinous features should rule out this entity
- Sometimes the epithelial component can be as high as 30%
- This lesion is most common in minor salivary glands of palate
- This tumor is completely benign and no malignant transformation has been reported
Board review style answer #1
A. Monomorphic tumor cells and absence of chondromyxoid stroma and ducts help to differentiate myoepithelioma from pleomorphic adenoma. The presence of chondromyxoid stroma is consistent with pleomorphic adenoma rather than myoepithelioma.
Comment Here
Reference: Myoepithelioma
Comment Here
Reference: Myoepithelioma
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is correct about myoepithelioma?
- Negative for keratin
- Negative for nuclear beta catenin
- Negative for S100
- Negative for SMA and HHF35
- Positive for PLAG1 translocation
Board review style answer #2
E. Positive for PLAG1 abnormalities. Detection of PLAG1 rearrangement by cytogenetics or other methods can be helpful. NTF3-PLAG1, FBXO32-PLAG1 and GEM-PLAG1 fusions have been detected in oncocytic myoepithelioma (Ann Diagn Pathol 2017;28:19, Hum Pathol 2020;103:52).
Comment Here
Reference: Myoepithelioma
Comment Here
Reference: Myoepithelioma