Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Etiology | Treatment | Cytology description | Cytology images | Sample pathology report | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Hang JF. Nondiagnostic. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/salivaryglandsmilannondiagnostic.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Fine needle aspiration (FNA) with insufficient diagnostic material to provide an informative interpretation
- 18.2% of all salivary gland FNA (Cancer Cytopathol 2022;130:800)
- Estimated risk of malignancy (ROM) by the Milan system: 25% (Faquin: The Milan System for Reporting Salivary Gland Cytopathology, 1st Edition, 2018)
- Real world risk of malignancy: 15.7% (FNA with surgical follow up), 4.1% (overall) (Cancer Cytopathol 2022;130:800)
Essential features
- FNA with insufficient amount of lesional cells to provide an informative interpretation (ideally > 60 lesional cells for adequate evaluation)
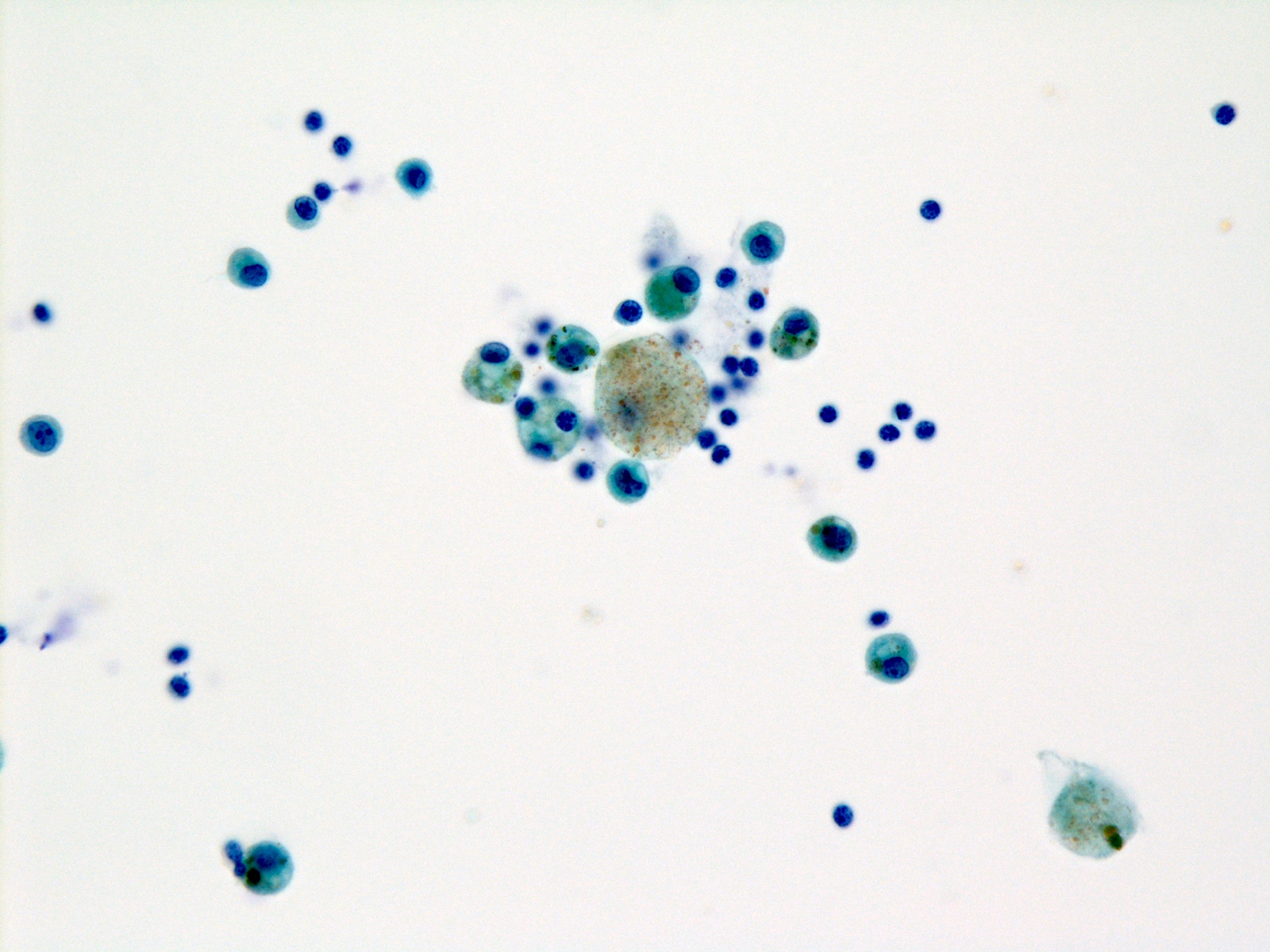
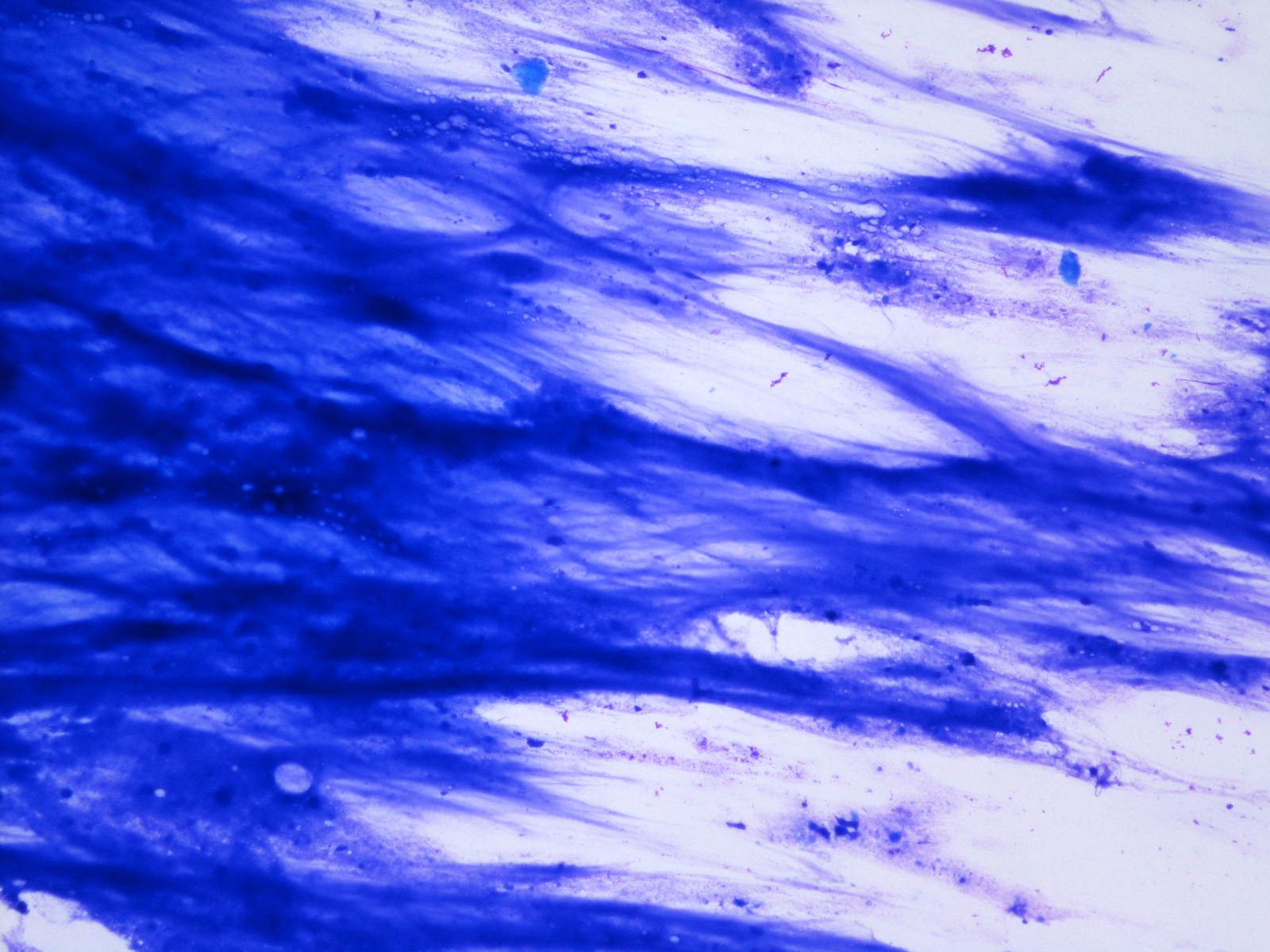
- Poorly prepared slides with artifacts (e.g., air drying, obscuring blood and poor staining) that preclude the evaluation of the cellular component
- Normal nonneoplastic salivary gland elements in the setting of a clinically or radiologically defined mass
- Nonmucinous cyst fluid without an epithelial component
Terminology
- Nondiagnostic
- Nondiagnostic, cystic fluid only for nonmucinous cyst fluid without an epithelial component
Etiology
- Palpation guidance without ultrasound, inadequate sampling determined by rapid on site evaluation and lesions with cystic, vascular or diffuse nature are significantly associated with nondiagnostic results (Cancer Cytopathol 2022;130:609)
Treatment
- Clinical / radiologic follow up only (56%), direct surgery (19%) and repeat FNA (19%) (Cancer Cytopathol 2022;130:609)
Cytology description
- FNA with < 60 lesional cells, although specific criteria have not been established
- Poorly prepared slides with artifacts (e.g., air drying, obscuring blood and poor staining) that preclude the evaluation of the cellular component
- Normal nonneoplastic salivary gland elements in the setting of a clinically or radiologically defined mass
- Nonmucinous cyst fluid without an epithelial component
- Exclusion criteria
- FNA with scant cellularity but significant cytologic atypia → at least atypia of undetermined significance (AUS)
- Mucinous cyst fluid contents without an epithelial component → atypia of undetermined significance
- Abundant inflammatory cells without an epithelial component → nonneoplastic
- Acellular FNA with a matrix component suggestive of a pleomorphic adenoma → neoplasm: benign
- Reference: Faquin: The Milan System for Reporting Salivary Gland Cytopathology, 1st Edition, 2018
Cytology images
Sample pathology report
- Parotid gland, right, fine needle aspiration:
- Nondiagnostic (see comment)
- Comment: Insufficient cellularity for diagnosis.
- Submandibular gland, left, fine needle aspiration:
- Nondiagnostic (see comment)
- Nonneoplastic benign salivary gland elements only
- Comment: The finding of nonneoplastic salivary gland elements only does not explain the presence of a clinically or radiologically defined mass. Repeat fine needle aspiration under radiologic guidance is recommended if clinically indicated.
- Parotid gland, left, fine needle aspiration:
- Nondiagnostic (see comment)
- Comment: Cystic fluid only.
Board review style question #1
A 45 year old woman presents with a 2.8 cm right parotid nodule. Ultrasound demonstrates a well defined nodule with heterogeneous echogenicity. Fine needle aspiration is performed. What is the best diagnosis according to the Milan System for Reporting Salivary Gland Cytopathology (MSRSGC)?
- Atypia of undetermined significance
- Benign neoplasm, pleomorphic adenoma
- Nondiagnostic
- Nonneoplastic
Board review style answer #1
C. Nondiagnostic. The presence of normal nonneoplastic salivary gland acinar cells only in the setting of a clinically and radiologically defined mass should be diagnosed as nondiagnostic. The FNA sample is not considered representative of the lesion detected on clinical and radiologic examination. Repeat FNA under radiologic guidance is recommended if clinically indicated.
Comment Here
Reference: Nondiagnostic
Comment Here
Reference: Nondiagnostic
Board review style question #2
A 38 year old man presents with a 3.0 cm right parotid mass. Ultrasound demonstrates a mixed solid and cystic tumor. Fine needle aspiration is performed. What is the best diagnosis according to the Milan System for Reporting Salivary Gland Cytopathology (MSRSGC)?
- Atypia of undetermined significance, mucinous cystic lesion
- Malignant, low grade mucoepidermoid carcinoma
- Nondiagnostic, cyst fluid only
- Nonneoplastic, compatible with mucocele
Board review style answer #2
A. Atypia of undetermined significance, mucinous cystic lesion. This FNA contains abundant mucin without any epithelial cells. The differential diagnosis includes a benign mucinous cyst; however, a low grade mucoepidermoid carcinoma cannot be excluded. Based on the MSRSGC, the most appropriate diagnosis would be atypia of undetermined significance. Clinical and radiological correlations are needed. Aspiration of a residual mass, if present, may help to achieve a more specific diagnosis.
Comment Here
Reference: Nondiagnostic
Comment Here
Reference: Nondiagnostic