Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Sample pathology report | Sample cytopathology report | Differential diagnosis | Differential diagnosis in cytology | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Maleki Z. Lymphoepithelial cyst. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/salivaryglandsb9lymphoepithelialcyst.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Unilocular cysts that involve the parotid gland
- Frequently but not always HIV related
- Can be associated with autoimmune disease (e.g., Sjögren syndrome) (Int J Surg Pathol 2009;17:421)
Essential features
- Well defined cysts on imaging (Laryngoscope 2007;117:106)
- Simple cyst lined by low stratified squamous epithelium surrounded by polymorphous lymphocytes with prominent germinal centers (Diagn Cytopathol 2012;40:684)
Terminology
- Salivary type lymphoepithelial cyst
- HIV associated cystic lymphoid hyperplasia (Laryngoscope 2007;117:106)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: K11.8 - other diseases of salivary glands
Epidemiology
- HIV
- Autoimmune disease (e.g., Sjögren syndrome)
Sites
- Almost all arise in parotid gland
- Very rare in submandibular gland
Pathophysiology
- Sporadic lymphoepithelial cyst may result from cystic dilation of ducts within intraparotid or periparotid lymph node or branchial cleft remnants
- HIV associated lymphoepithelial cyst likely forms due to hyperplasia of intra-salivary gland lymph nodes and associated ductal obstruction (J Int Assoc Provid AIDS Care 2017;16:120)
- Sjögren syndrome associated lymphoepithelial cysts arise secondary to infiltration of B cells into the ductal epithelium and their expansion within the striated ducts and subsequent basal ductal cell hyperplasia (Nat Rev Rheumatol 2021;17:333)
Etiology
- Cystic dilation of the salivary gland ducts
- HIV associated
- Autoimmune disease (e.g., Sjögren syndrome) associated
Clinical features
- Presents as a painless unilocular mass near or within the salivary gland
- Sporadic and autoimmune related cysts are generally unilateral
- HIV associated cysts can be bilateral, with an overall incidence of 3 - 5% in HIV patients
Diagnosis
- Unilateral, painless cystic salivary gland mass
- Unilateral or bilateral painless cystic salivary gland mass in HIV patients, with or without cervical lymphadenopathy
Radiology description
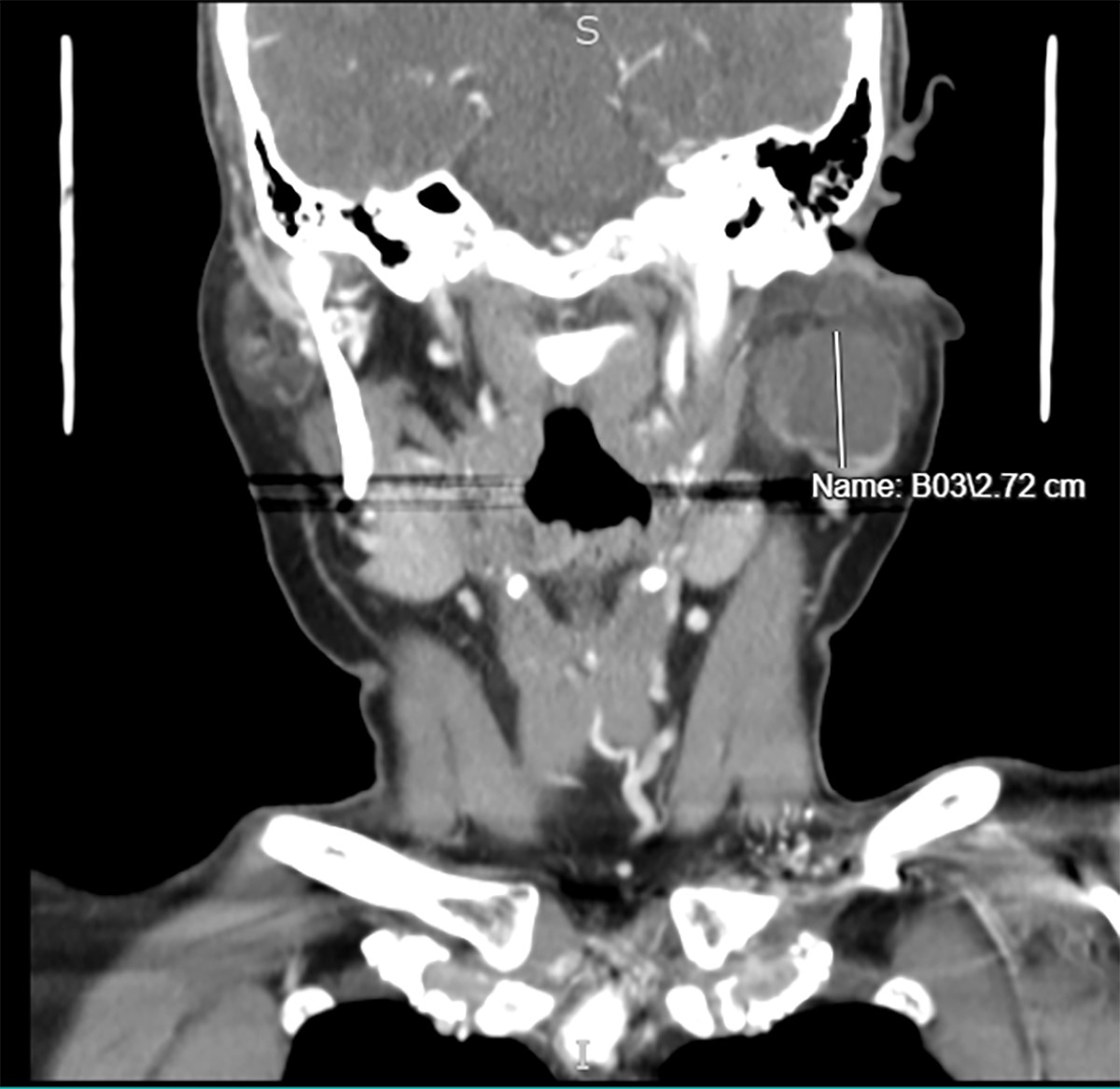
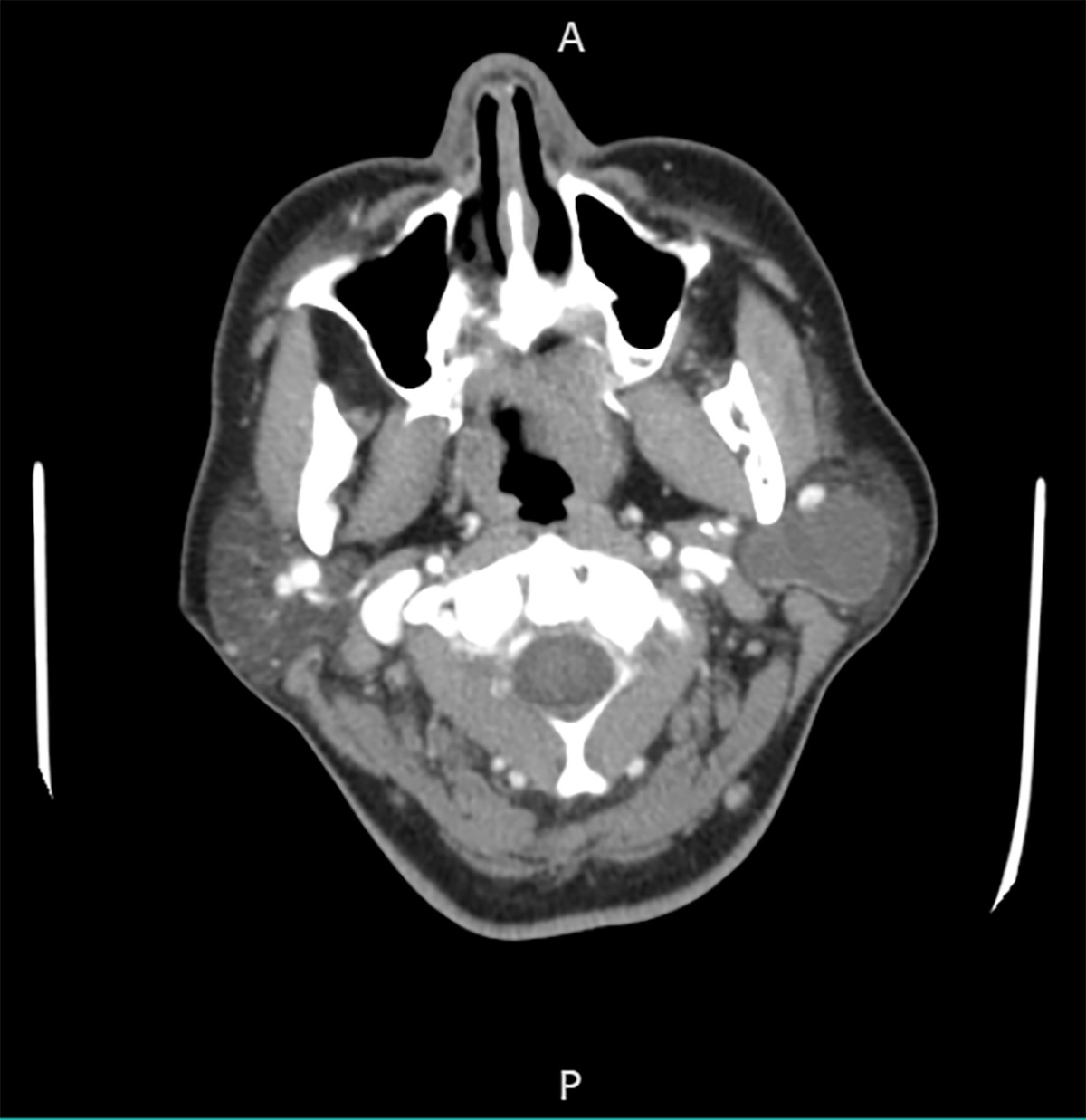
- Well defined, thin, smooth walled unilocular cystic mass (Int J Surg Case Rep 2017;41:383)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Excellent prognosis
- Low to null recurrence rate for all types of salivary gland lymphoepithelial cysts (J Surg Case Rep 2020;2020:rjaa300)
Case reports
- 32 year old woman presented with painless swelling of the left side of the neck for 8 months (J Pharm Bioallied Sci 2014;6:S185)
- 35 year old man with a soft, nontender swelling of the left parotid gland for 9 - 10 months (J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2018;22:S91)
- 37 year old woman with a history of HIV and Hodgkin lymphoma presented with right sided facial swelling for 4 days; 47 year old man with a history of HIV / AIDS and Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) infection presented with right sided jaw mass for 2 months (J Int Assoc Provid AIDS Care 2017;16:120)
Treatment
- Conservative therapy, with institution of highly active antiretroviral therapy medication in HIV related cases (HIV AIDS (Auckl) 2012;4:81)
- Surgical treatment not indicated for HIV associated lymphoepithelial cysts unless there is doubt about the diagnosis or there are cosmetic considerations (Head Neck 2018;40:1073)
- Repeated fine needle aspiration and drainage, sclerotherapy, radiotherapy, surgery (Head Neck 2018;40:1073)
Gross description
- Cystic structure containing a serous clear watery straw colored fluid with smooth and glistening inner lining
Frozen section description
- Benign lymphoepithelial cyst
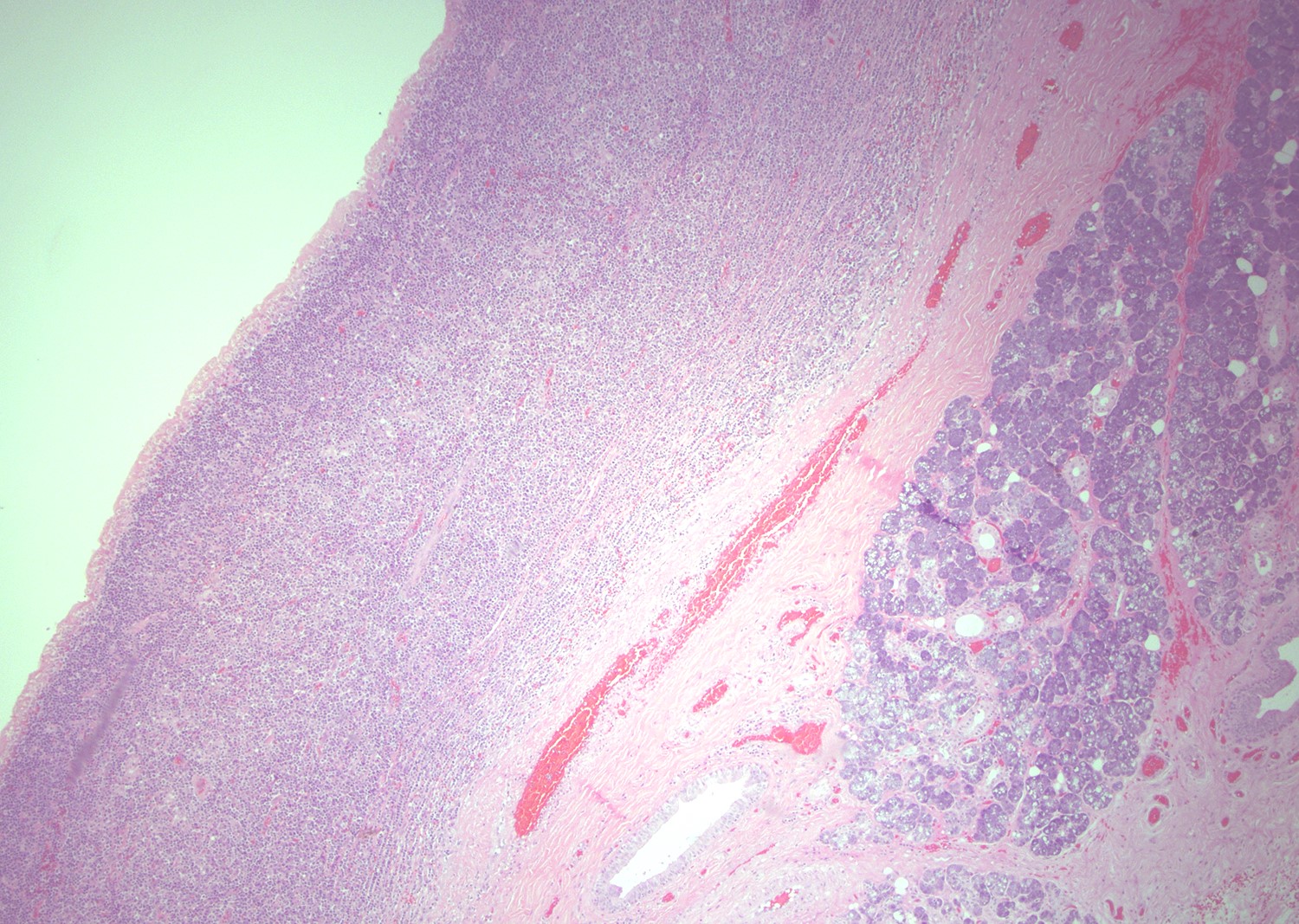
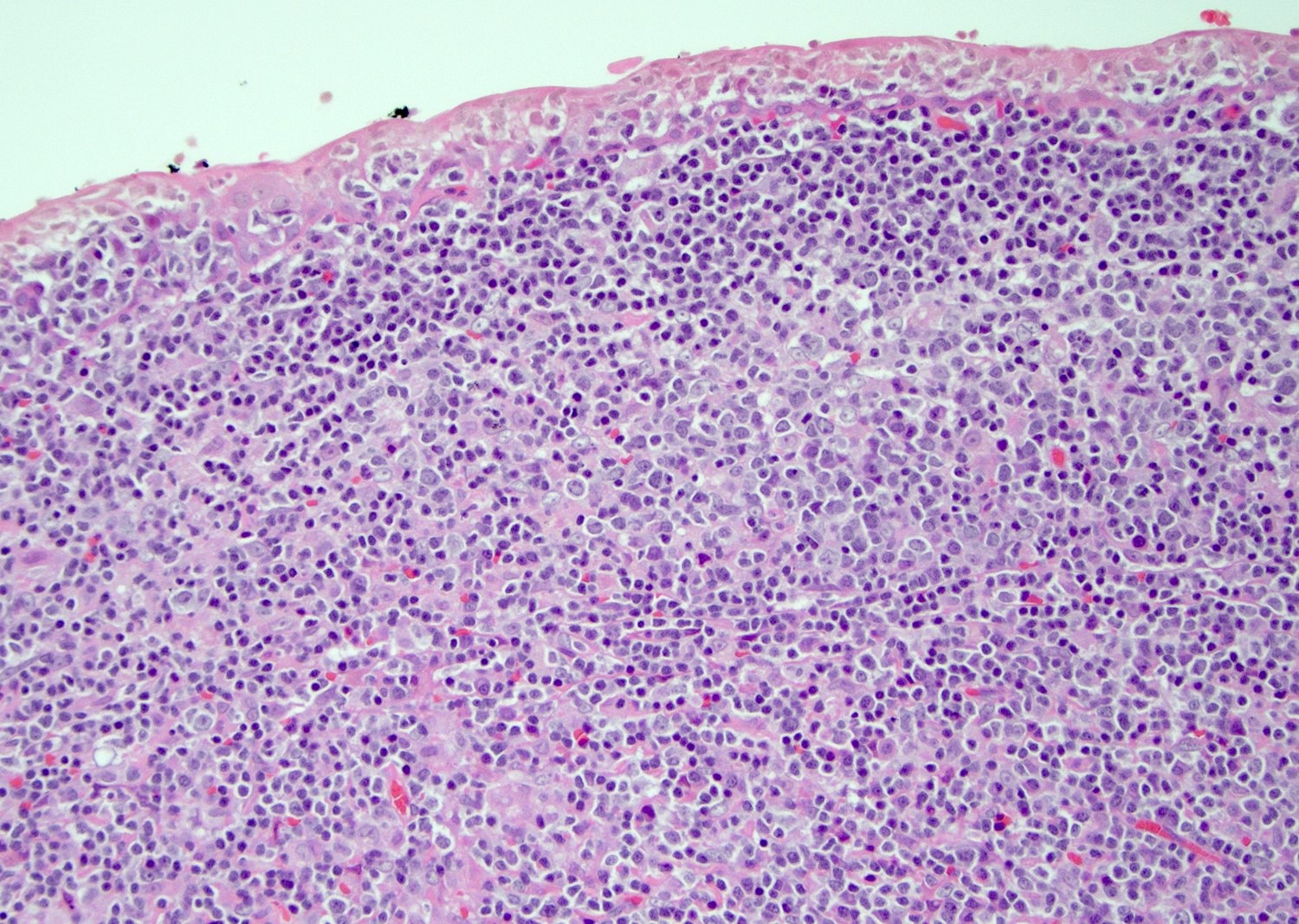
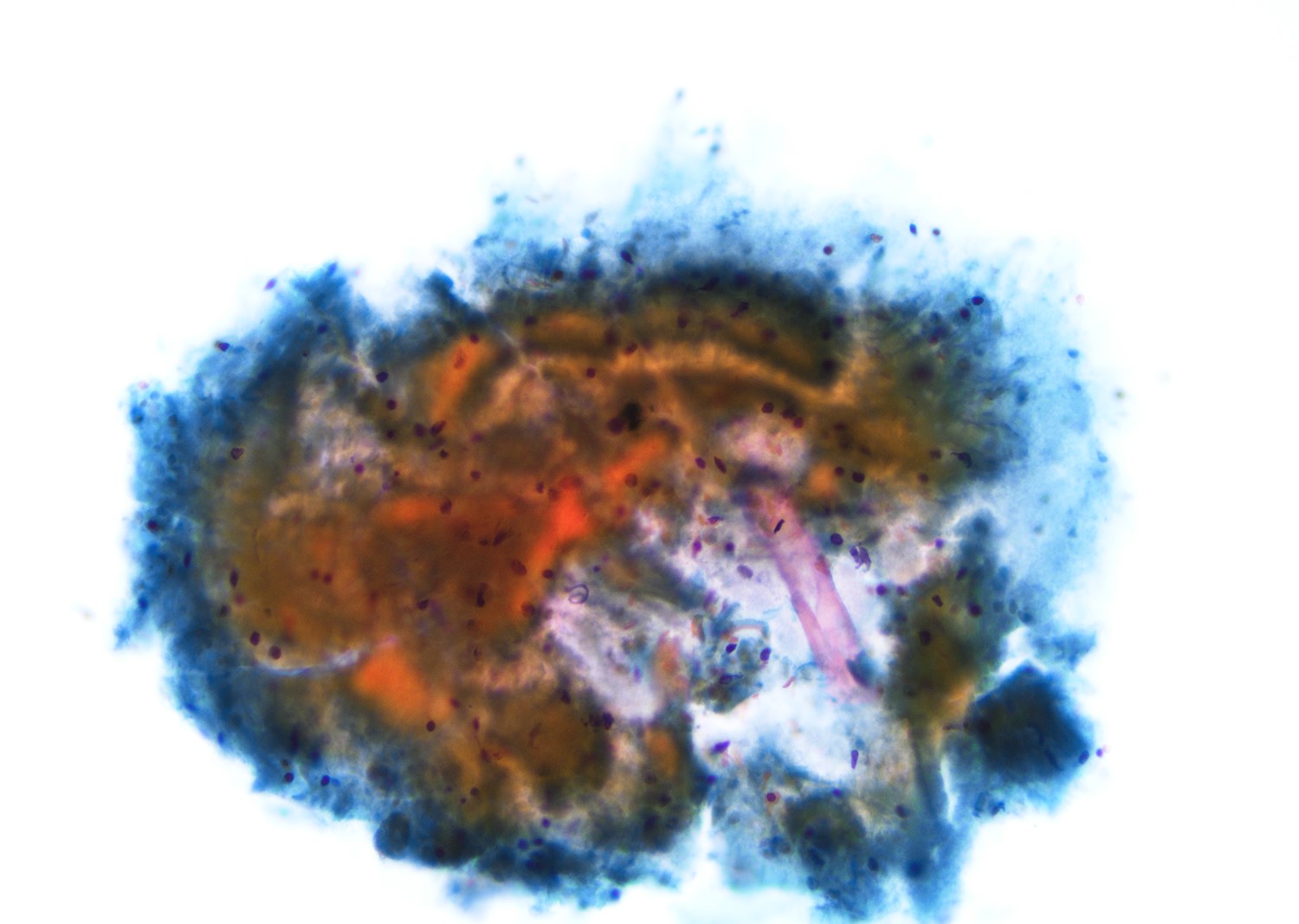
Microscopic (histologic) description
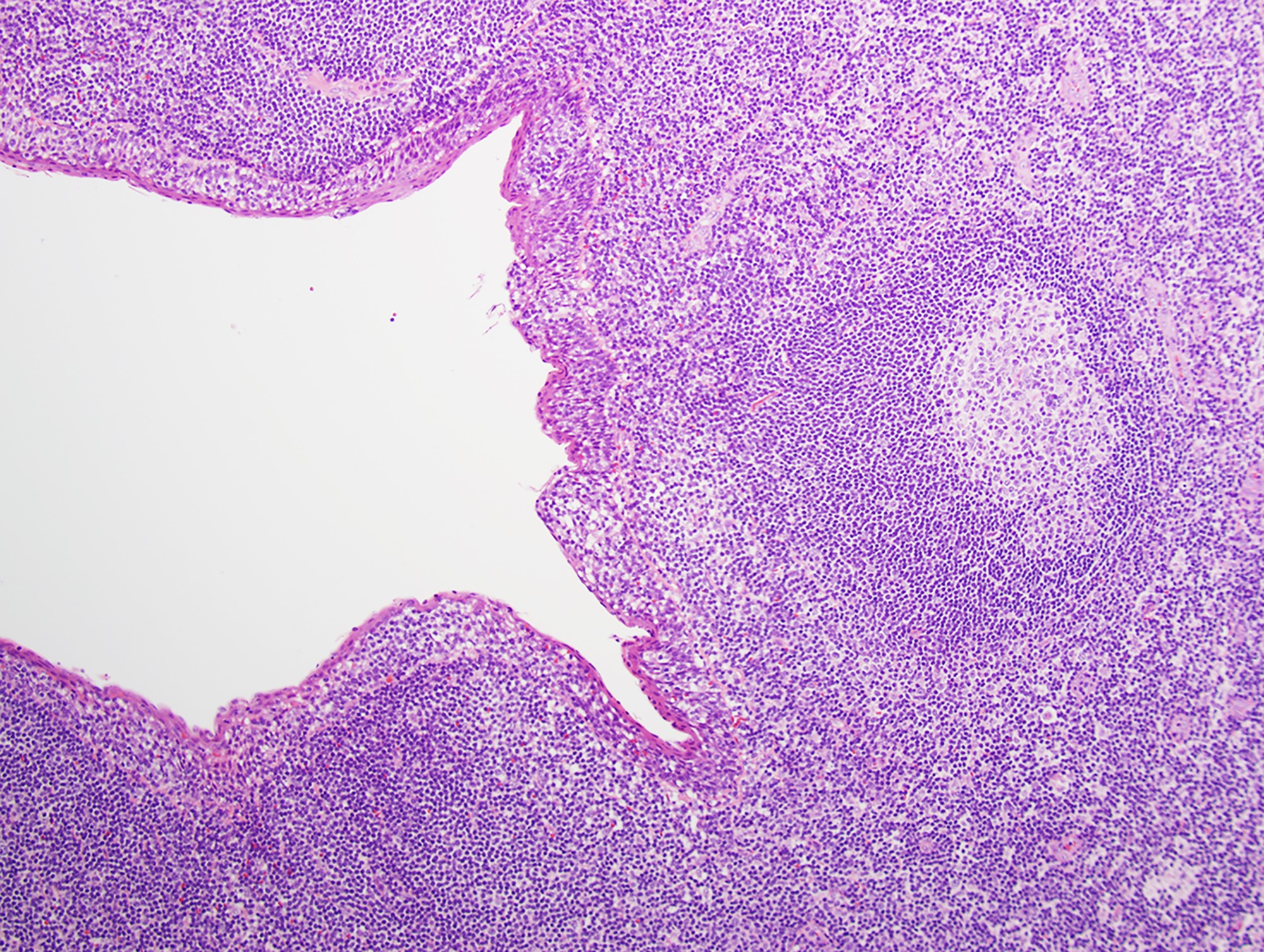
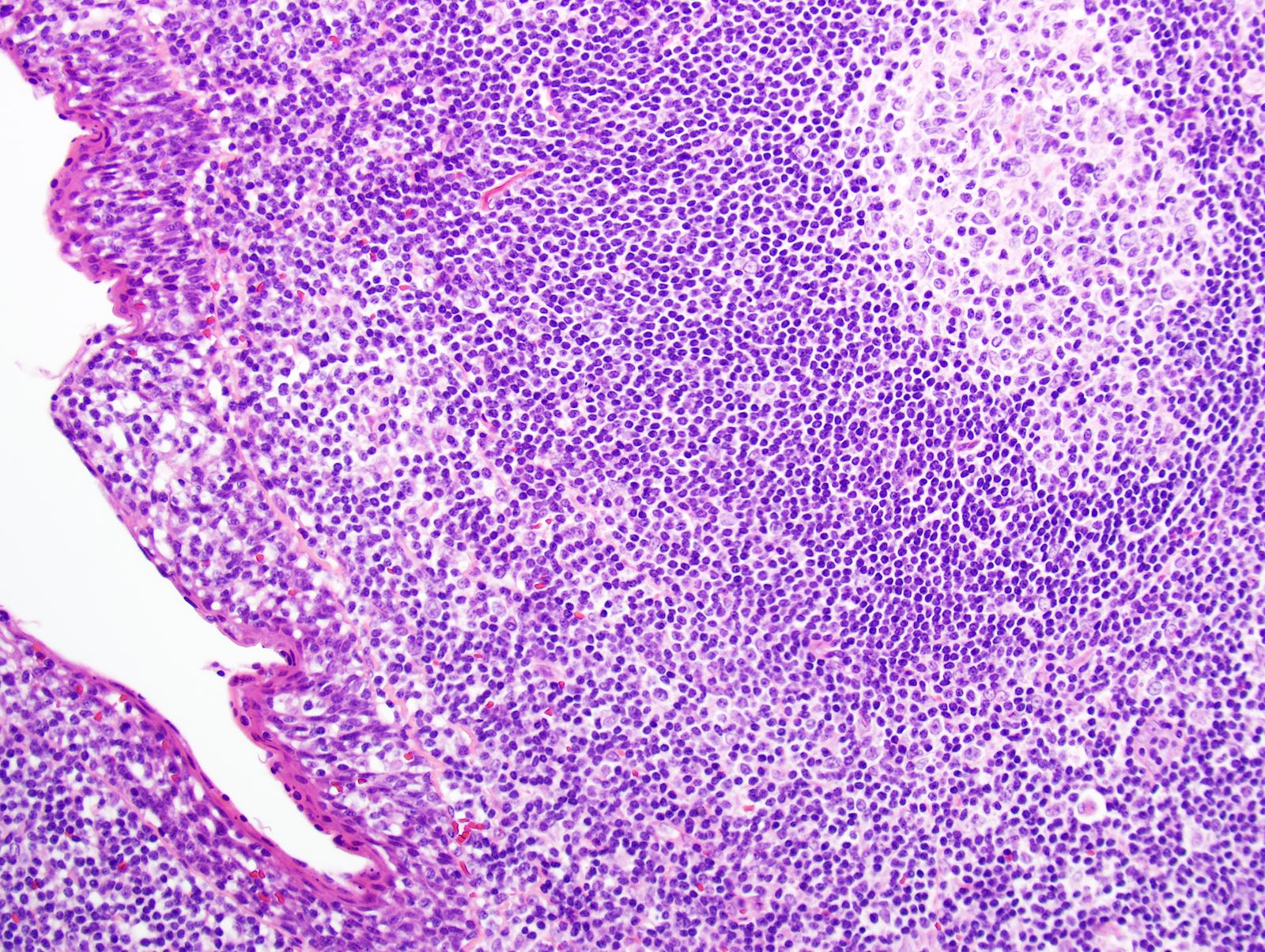
- Most cases show a unilocular cyst with a thin stratified squamous lining
- Ciliated, cuboidal or columnar epithelial lining is seen in rare cases
- Epithelium is surrounded by dense polymorphous lymphoid tissue with germinal centers and sinusoidal spaces
- Lymphocytes frequently permeate the epithelial cyst lining cells
Microscopic (histologic) images
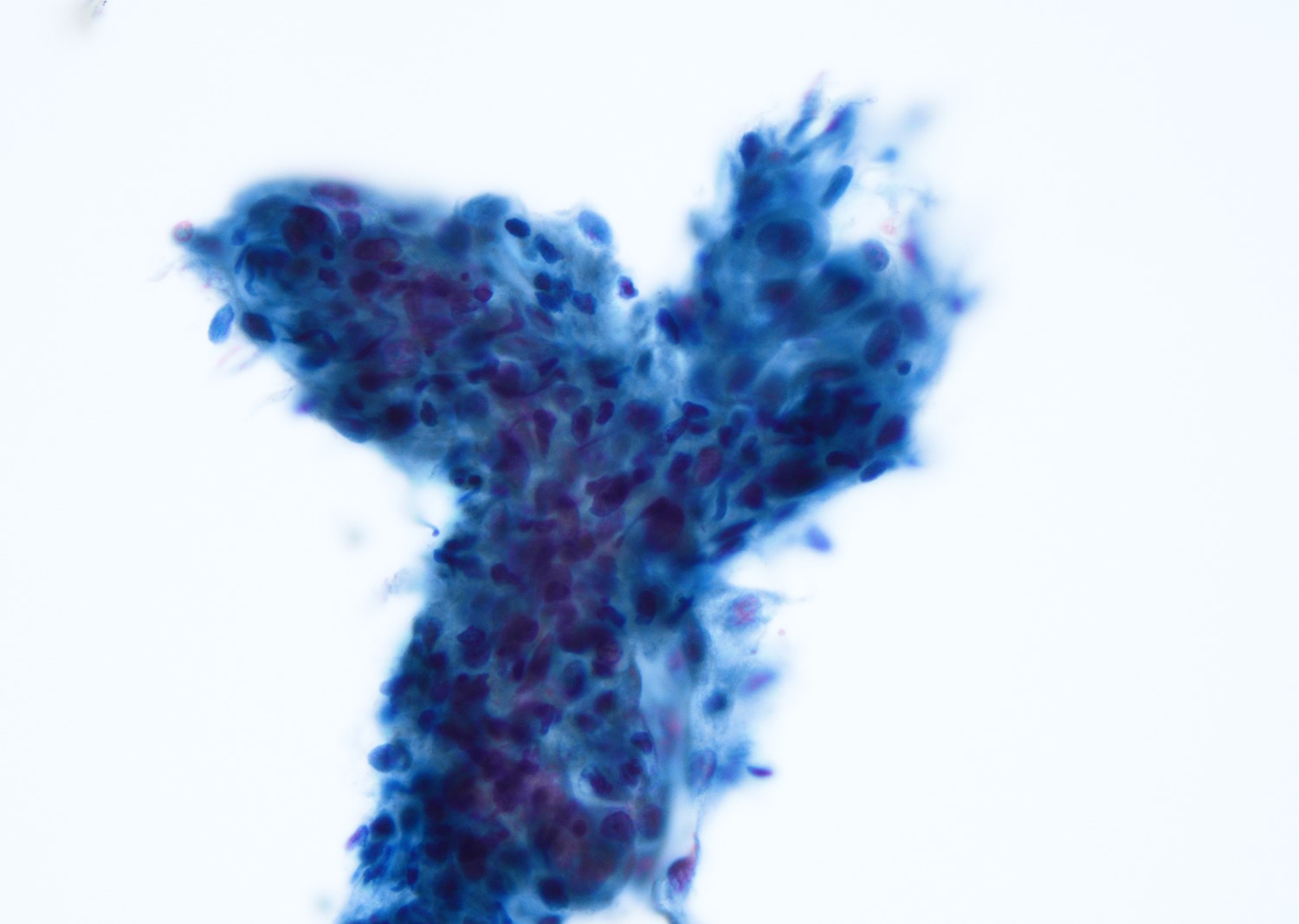
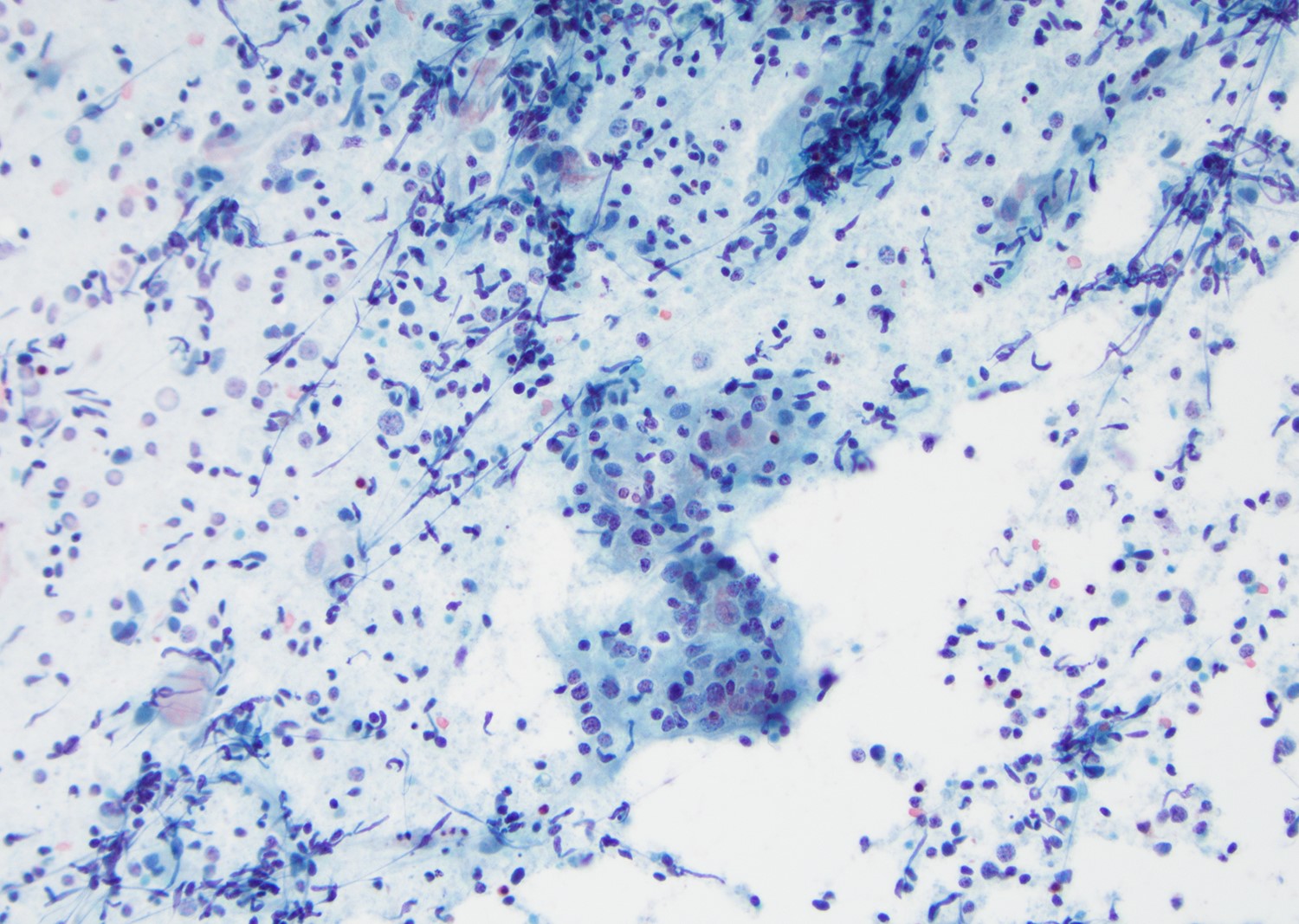
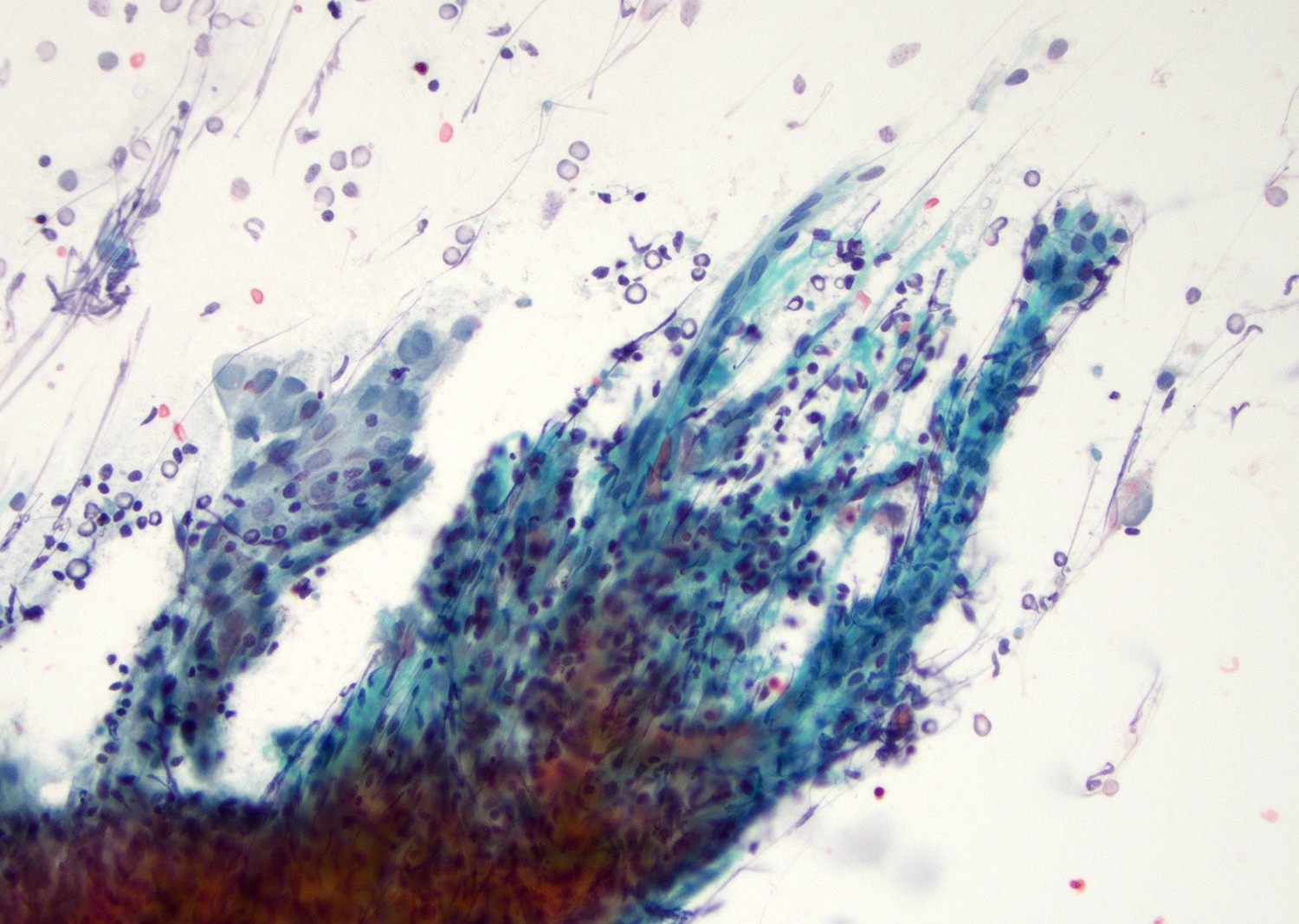
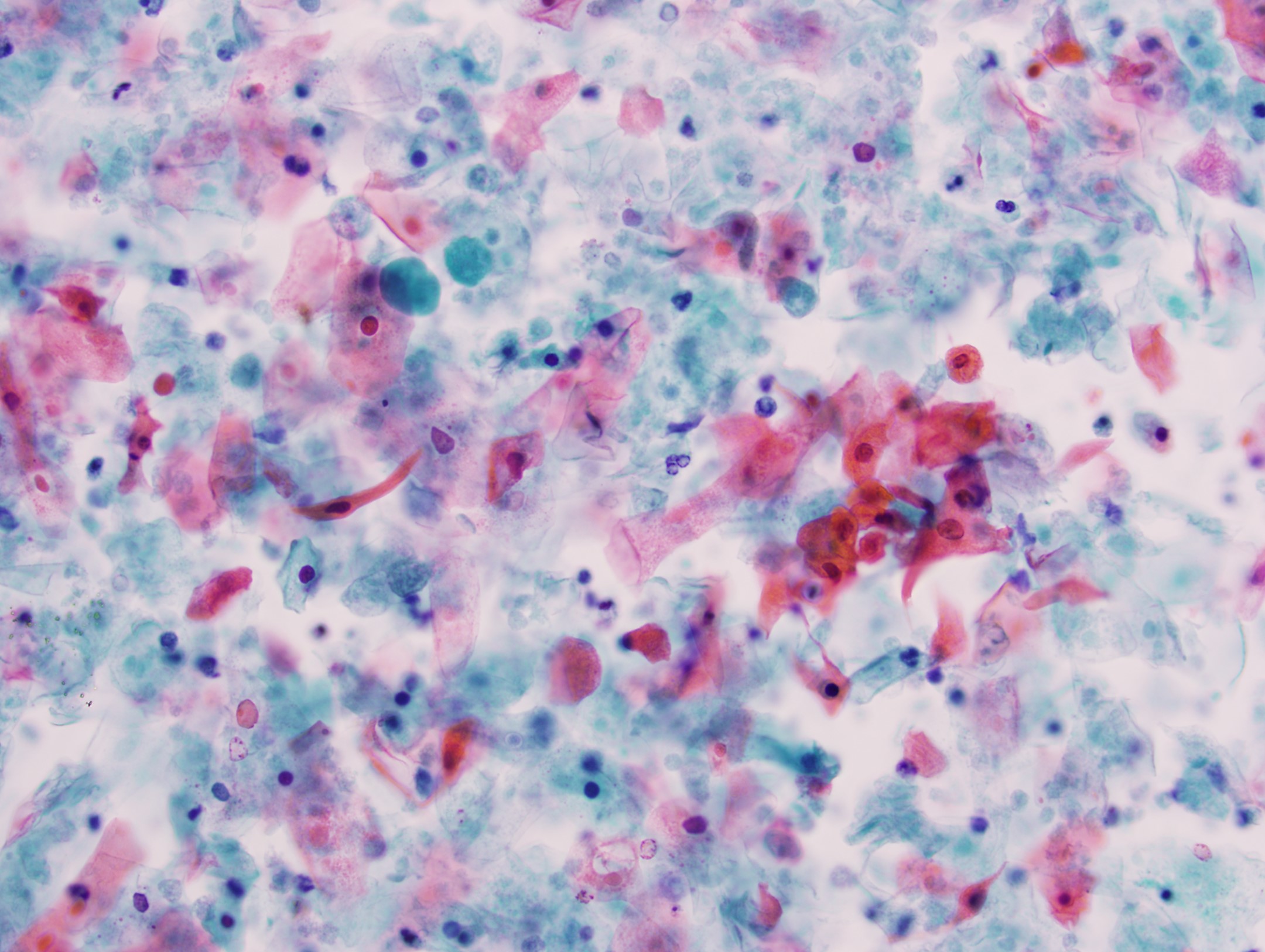
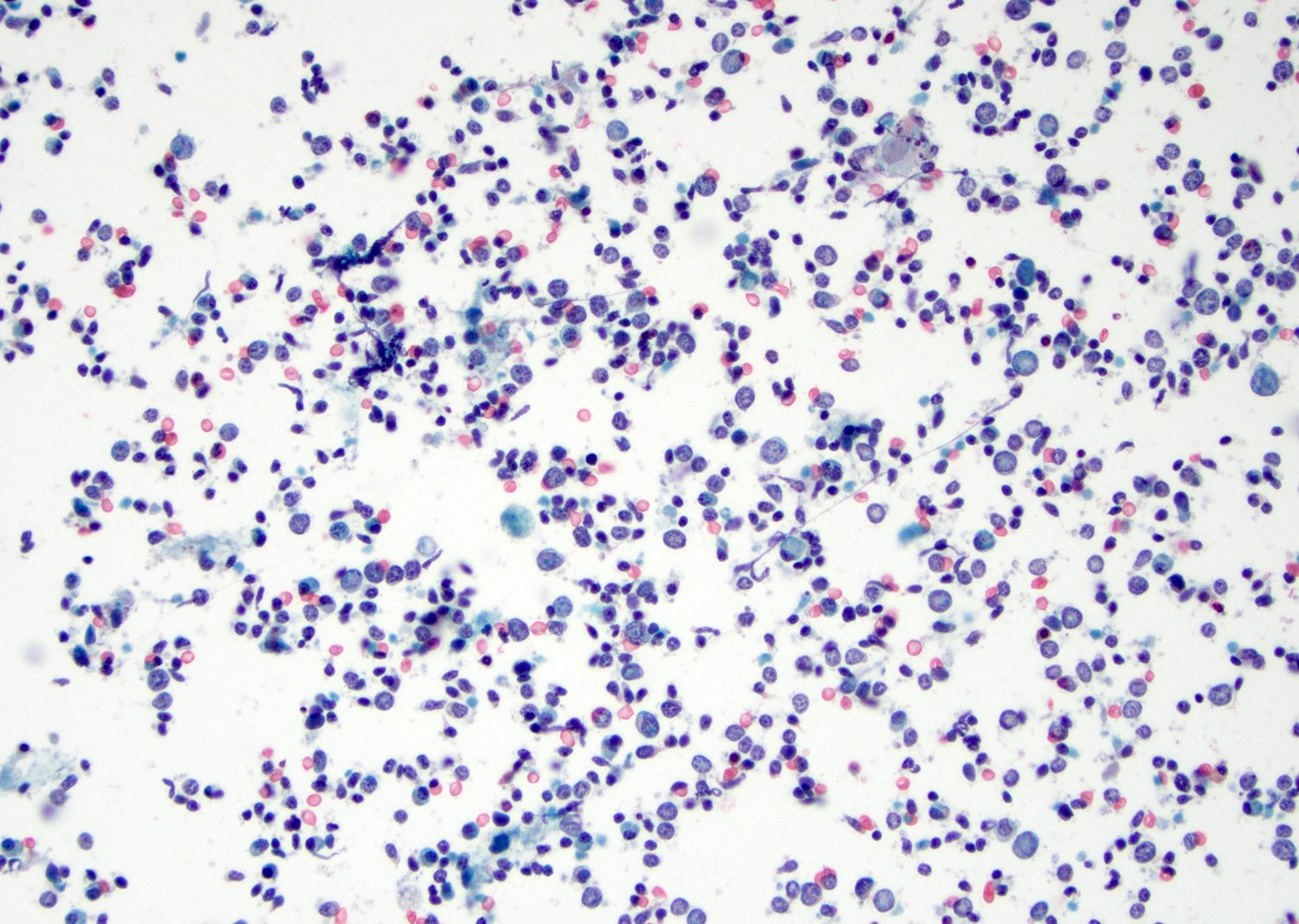
Cytology description
- Mature nucleated squamous cells with variable reactive atypia, anuclear cells and squamous epithelium (Int J Surg Case Rep 2017;41:383, Diagn Cytopathol 2012;40:684)
- Polymorphous lymphocytes and aggregates of epithelioid histiocytes
- Proteinaceous background
- Variable presence of acute inflammation, and bland appearing mucinous ductal cells and ciliated columnar cells
- Scant cellularity, abundant proteinaceous background, lack of squamous cells and epithelial cells, marked atypia of epithelial cells, abundance of lymphocytes pose diagnostic challenges
Cytology images
Positive stains
- AE1 / AE3 in squamous or ciliated columnar cells (Int J Surg Pathol 2021;29:78)
- Numerous intrafollicular CD8+ lymphocytes in HIV associated lymphoepithelial cysts (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 2019;128:52)
Sample pathology report
- Parotid mass, right, resection:
- Benign lymphoepithelial cyst with reactive follicular hyperplasia
Sample cytopathology report
- Parotid, left, fine needle aspiration:
- Fragments of squamous epithelium, lymphocytes and cyst content (see comment)
- Comment: The differential diagnosis includes benign lymphoepithelial cyst, cystic lymphoid hyperplasia, lymphoepithelial sialadenitis, benign cyst with lymph node sampling or a Warthin tumor.
- Recommend: Clinical and radiographic correlation.
Differential diagnosis
- Branchial cleft cyst:
- May have a sinus tract or stalk, infrequently associated with parotid tissue
- Extranodal marginal zone lymphoma:
- Monoclonal lymphoid population with centrocytic or monocytoid appearance
- Retention cyst:
- Mucinous cystic contents without extensive surrounding chronic inflammations
- Warthin tumor:
- Areas of classic bilayered oncocytic epithelium, although occasional squamous metaplasia can be seen
- Cystic metastasis of squamous cell carcinoma:
- Increased cytologic atypia and expansile growth of squamous epithelium
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma with tumor associated lymphoid proliferation:
- More complex epithelial proliferation with intermixed squamoid, mucinous and intermediate cells
Differential diagnosis in cytology
- Mucocele:
- Abundant mucinous content
- Reactive lymph node:
- Polymorphous lymphocytes and aggregates of epithelioid histiocytes
- Warthin tumor:
- Polymorphous lymphocytes and fragments of oncocytic epithelium
- Squamous cell carcinoma:
- Abundant pleomorphic squamous cells with marked atypia, pleomorphism, nuclear enlargement and hyperchromasia
- Low grade mucoepidermoid carcinoma:
- Fragments of malignant epithelial cells and scattered squamous cells in a background of abundant mucin
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2