Salivary glands
General
Staging-major salivary glands
Editor-in-Chief: Debra L. Zynger, M.D.
Last author update: 29 October 2019
Last staff update: 3 July 2024
Copyright: 2003-2025, PathologyOutlines.com, Inc.
PubMed Search:
Staging major salivary glands
Page views in 2024: 2,908
Page views in 2025 to date: 849
Cite this page: Magliocca K. Staging-major salivary glands. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/salivaryglandsTNM.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Staging of definitive resections for primary salivary gland carcinoma and neuroendocrine carcinoma of the parotid, submandibular or sublingual gland should use this system
- On occasion it may be difficult to distinguish a sublingual salivary gland primary with certainty from a salivary gland tumor arising from minor salivary glands in the anterior floor of mouth
ICD coding
- C07.9: Parotid gland
- C08.0: Submandibular gland
- C08.1: Sublingual gland
- C08.8: Overlapping lesion of major salivary glands
- C08.9: Major salivary gland, NOS
Primary tumor (pT)
- pTX: Primary tumor cannot be assessed
- pT0: No evidence of primary tumor
- pTis: Carcinoma in situ
- pT1: Tumor ≤ 2 cm without extraparenchymal extension
- pT2: Tumor > 2 cm but ≤ 4 cm without extraparenchymal extension
- pT3: Tumor > 4 cm or tumor with extraparenchymal extension
- pT4a: Tumor of any size invading skin, mandible, ear canal or facial nerve
- pT4b: Tumor of any size invading skull base or pterygoid plates or encases carotid artery
Notes:
- Extraparenchymal extension is clinical or macroscopic evidence of invasion of soft tissues
- Microscopic evidence alone does not constitute extraparenchymal extension for classification purposes
Regional lymph nodes (pN)
- pNX: Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed
- pN0: No regional lymph node metastasis
- pN1: Metastasis in a single ipsilateral lymph node ≤ 3 cm without extranodal extension
- pN2a: Single ipsilateral lymph node metastasis ≤ 3 cm with extranodal extension or > 3 cm but ≤ 6 cm without extranodal extension
- pN2b: Metastasis in multiple ipsilateral lymph nodes ≤ 6 cm without extranodal extension
- pN2c: Metastasis in bilateral or contralateral lymph node(s) ≤ 6 cm without extranodal extension
- pN3a: Metastasis in a lymph node > 6 cm without extranodal extension
- pN3b: Extranodal extension in a single ipsilateral lymph node > 3 cm or single contralateral node or multiple nodes with metastases, any with extranodal extension
Notes:
- A selective neck dissection will include 10+ lymph nodes and a comprehensive neck dissection (radical or modified radical neck dissection) will include 15+ lymph nodes
- Negative pathologic examination of a smaller number of nodes still mandates a pN0 designation
- Midline nodes are considered ipsilateral nodes
- Measurement of tumor metastasis:
- Cross sectional diameter of the largest lymph node metastatic deposit (not the lymph node itself) is measured in the gross specimen at the time of macroscopic examination or if necessary, using the histologic slide
- Extranodal extension (ENE):
- AJCC 8th edition introduces the use of ENE in pN categorization
- Must be clearly defined as tumor present within the confines of the lymph node and extending through the lymph node capsule into the surrounding connective tissue, with or without associated stromal reaction
AJCC prognostic stage grouping
| Stage 0:
| Tis
| N0
| M0
|
| Stage I:
| T1
| N0
| M0
|
| Stage II:
| T2
| N0
| M0
|
| Stage III:
| T3
| N0
| M0
|
|
| T0 - 3
| N1
| M0
|
| Stage IVA:
| T4a
| N0 - 1
| M0
|
|
| T0 - 4a
| N2
| M0
|
| Stage IVB:
| Any T
| N3
| M0
|
|
| T4b
| Any N
| M0
|
| Stage IVC:
| Any T
| Any N
| M1
|
Registry data collection variables
- Extranodal extension clinical (present versus absent)
- Extranodal extension pathological (present versus absent)
- Extent of microscopic extranodal extension (distance of extension from the native lymph node capsule to the farthest point of invasion in extranodal tissue)
- Perineural invasion
- Lymphovascular invasion
- p16 / HPV status
- Performance status
- Tobacco use and pack years
- Alcohol use
- Depression diagnosis
Histopathologic type
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma
- Acinic cell carcinoma
- Polymorphous adenocarcinoma
- (Mammary analogue) secretory carcinoma
- Salivary duct carcinoma
- Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma
- Epithelial myoepithelial carcinoma
- (Hyalinizing) clear cell carcinoma
- Adenocarcinoma, not otherwise specified
- Includes cystadenocarcinoma, intestinal type adenocarcinoma and mucinous adenocarcinoma
- Basal cell adenocarcinoma
- Carcinosarcoma
- Intraductal carcinoma
- Lymphoepithelial carcinoma
- Myoepithelial carcinoma
- Oncocytic carcinoma
- Poorly differentiated carcinoma
- Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma
- Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma
- Undifferentiated carcinoma
- Sebaceous adenocarcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma
Notes:
- In this current classification, sialoblastoma is designated as a tumor of uncertain malignant potential
- Metastasizing pleomorphic adenoma has been collapsed under pleomorphic adenoma
- Since the biologic behavior of these still overlaps with the other malignant tumors, these can be reported under "other"
Board review style question #1
Regarding the following parotid gland primary salivary gland adenocarcinoma, which of the pT category criteria in the 8th edition AJCC staging guide is satisfied by the examination of this gross resection specimen photograph?
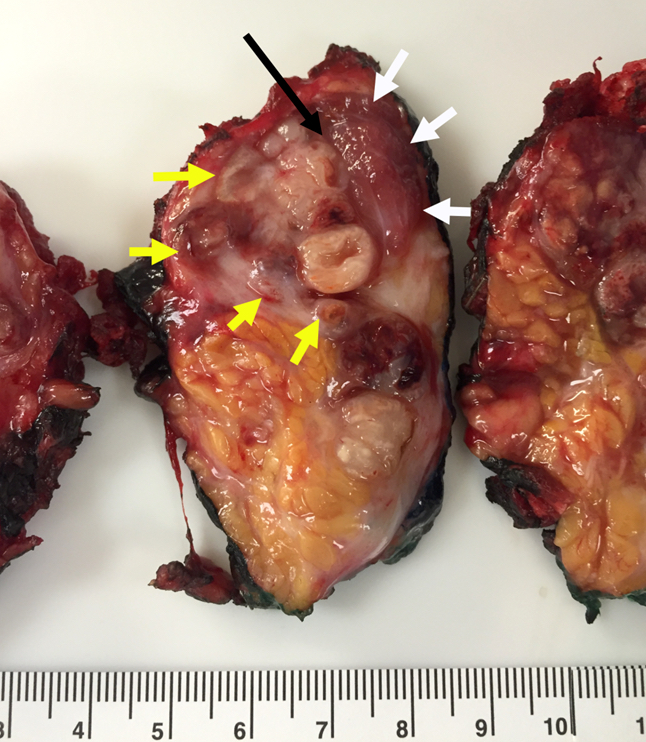
- pT1 by depth of invasion
- pT2 by tumor size
- pT3 by presence of necrosis
- pT3 by extraparenchymal extension
Board review style answer #1
D. pT3 by extraparenchymal extension (white arrows point to border of skeletal muscle, yellow arrows point to border of malignancy, black arrow points to tumor invading skeletal muscle)
Comment Here
Reference:
Staging-major salivary glands

Back to top





