Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Case reports | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Tanakchi S, Aly FZ. IgG4 related sialoadenitis . PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/salivaryglandsIgG4sialoadenitis.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Presents as painless, bilateral enlargement of lacrimal and salivary glands with mild secretory dysfunction
- IgG4 related disease is now recognized as systemic disorder, characterized by high serum IgG4, marked infiltration of IgG4 positive plasma cells and severe fibrosis
- Diagnosis depends on histologic appearance, elevated ratio of IgG4/IgG, variable elevated serum IgG4 levels
- Submandibular gland biopsy is more useful than labial salivary gland biopsy
- Corticosteroids and rituximab (by targeting peripheral CD20 positive plasma cells) appear to be effective for IgG4 related diseases
Terminology
- Previously called Mikulicz disease and Mikulicz syndrome, but these terms are considered ambiguous and outdated by some sources
Case reports
- 54 year old man with IgG4 related sclerosing disease in lacrimal and submandibular glands (Korean J Ophthalmol 2012;26:216)
- 76 year old man with IgG4 related Mikulicz disease (Ocul Immunol Inflamm 2015;23:173)
Gross description
- Solid, gray-white areas and occasional cysts
Microscopic (histologic) description
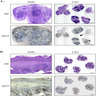
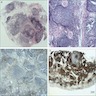
- Lymphoplasmacytic infiltration with lymphoid follicles surrounding solid epithelial nests (epimyoepithelial islands)
- Also scattered histiocytes and dendritic cells
- Excess hyaline basement membrane material deposited between cells
- Mild acinar destruction, lymphoepithelial lesions, monocytoid B cells
- Fibrosis has a characteristic irregular whorled pattern, termed "storiform fibrosis"
- Multiple germinal center formation in granular tissue
Microscopic (histologic) images
Differential diagnosis
- Sjögren syndrome: no association with IgG4, female predominance, presence of SS-A and SS-B antibodies, severe acinar destruction