Table of Contents
Definition / general | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Arora K. Signet ring-like cell adenocarcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/prostatesignet.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- < 50 cases identified in English language literature (Mayo Clin Proc 2010;85:1130)
- Highly malignant
Treatment
- Similar to traditional adenocarcinoma - hormonal therapy, radiation, surgery
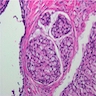
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Solid, acinar, single-line patterns
- Primarily composed of tumor cells with signet ring cell pattern (at least 25%) due to intracellular accumulation of mucin compressing the nucleus into a crescent shape
Positive stains
- PSA (variable in some studies), AE1/AE3, CAM 5.2, Ki-67 (mean 8%), PAS-diastase, mucicarmine (50%), Alcian blue (60%), α-methylacyl coenzyme A racemase (P504S) and cytokeratin 5/6
Negative stains
- Bcl2 (rare cells positive), CEA (80%)
Electron microscopy description
- Intracytoplasmic lumina lined by microvilli
Differential diagnosis
- Artifactual changes in lymphocytes post-TURP: no classic adenocarcinoma, CD45+, negative for mucin, PSA, PAP (Am J Surg Pathol 1986;10:795)
- Benign signet ring cell change: no classic adenocarcinoma, negative for mucin, PSA, PAP (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:1066)
- GI primary: much more common; no typical prostatic adenocarcinoma, positive GI workup (abdominal CT, colonoscopy, esophagogastroduodenoscopy); PSA-, PAP-
- Mucinous carcinoma with signet ring cells: > 25% of tumor is extracellular mucin and < 25% of tumor cells feature signet ring cells
Additional references