Table of Contents
Definition / general | Case reports | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Arora K. Adenocarcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/prostatesemca.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Very rare, must confirm microscopically
- Primary tumors should be localized primarily to seminal vesicle; must rule out invasion from prostate (do PSA / PAP), rectum or other sites
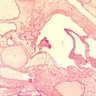
- Usually a papillary adenocarcinoma resembling architecture of normal seminal vesicle
- Resembles prostatic duct adenocarcinoma Gleason patterns 3 or 4 or mucinous (colloid) carcinoma
- Usually unresectable and patients die within 2 years
- Adenocarcinoma: very rare, must rule out prostate primary; often mucin producing, ulcerates through skin of scrotum
Case reports
- 67 year old man with neuroendocrine carcinoma (Int J Urol 2012;19:370)
- 87 year old man (Hum Pathol 1987;18:200)
- Disseminated disease with occult primary discovered at autopsy (Int J Surg Pathol 2011;19:401)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
Differential diagnosis
- Bladder adenocarcinoma: CA125-
- Bladder urothelial carcinoma: CK20+, CA125-
- Prostatic adenocarcinoma: PSA+, PAP+, CA125-
- Rectal adenocarcinoma: CA125-, CK7 neg, CK20+