Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Epidemiology | Diagrams / tables | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Sample pathology report | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Iczkowski KA. Gleason grading. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/prostategrading.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- In 1966, Dr. Donald Gleason devised grades of 1 - 5 based on glandular architecture and microscopic appearance using a 4x - 10x objective eyepiece that were shown to predict an outcome in prostate cancer (Cancer Chemother Rep 1966;50:125)
Terminology
- Gleason score is the sum of the 2 most prevalent Gleason grades: primary and secondary, designated according to separate rules for biopsy and prostatectomy
- If only 1 pattern is present, the primary and secondary patterns are given the same grade (ex: 3+3=6)
- Systematic needle biopsy sets contain cores from different anatomically designated sites
- Gleason score should be assigned separately for each anatomically designated site
- Highest score may serve as a basis to determine treatment
- Additional reporting of a global (case level) Gleason score is optional and global scoring may show a marginal benefit over using highest score according to Trpkov et al. (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:e87, Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1522)
- Any glands showing perineural invasion must be excluded in assigning Gleason grading because perineural invasion distorts gland morphology such that Gleason 3 glands resemble Gleason 4
- Grading rules:
- Recommendations are based on 3 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) grading consensus conferences:
- 2005 (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:1228, J Urol 2010;183:433)
- 2014 and 2019 (Nice, France) (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:e87)
- Consensus of the GU Pathology Society that is nearly identical (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2021;145:461)
- Minor variances are highlighted (Am J Surg Pathol 2021;45:1007)
- Some specimens may show a pattern that is the third most prevalent; this is called a minor pattern
- Recommendations are based on 3 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) grading consensus conferences:
- In radical prostatectomy:
- Gleason score should be based on the primary and secondary patterns; if a minor pattern constitutes < 5%, the pattern should be mentioned as a minor (tertiary) pattern; any higher grade minor pattern ≥ 5% should be incorporated into the Gleason score and ISUP group as the secondary pattern (2019 consensus) (Eur Urol 2018;73:674)
- Ex: Gleason pattern 3=96% and pattern 4=4%, Gleason score=3+3=6 with minor (tertiary) 4
- Ex: Gleason pattern 3=95% and pattern 4=5%, Gleason score=3+4=7
- In needle biopsy:
- Most prevalent pattern is graded as primary and any amount of a worst pattern is graded as secondary
- Ex: Gleason pattern 3=96% and pattern 4=4%, Gleason score=3+4=7
- Ex: Gleason pattern 3=95% and pattern 4=5%, Gleason score=3+4=7
- For multiparametric MRI targeted biopsies:
- Gleason scores should be given for the aggregate of cores from each individual biopsy site but not for each core (2019 consensus)
- This method of reporting is by research by Gordetsky et al. (Hum Pathol 2018;76:68)
- Benign histologic changes (chronic inflammation, acute inflammation, atrophy) should be reported in high suspicion lesions (PI-RADS 4 and 5) that are negative for cancer (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:e87)
Epidemiology
- In 2014, the ISUP and World Health Organization adopted a simplified patient centric grading system composed of 5 prognostic grade groups as proposed in 2013 based on data and subsequently validated by biochemical recurrence hazard ratios on cases from 5 large academic centers (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:244, Prostate 2016;76:427, BJU Int 2013;111:753, Eur Urol 2016;69:428)
- Grade groups are as follows:
- Gleason score 3+3=6
- Gleason score 3+4=7
- Gleason score 4+3=7
- Gleason score 8 (4+4=8, 3+5=8, 5+3=8)
- Gleason score ≥ 9 (4+5=9, 5+4=9, 5+5=10)
- Note that Gleason grades 1 and 2 are no longer recommended for use, since those patterns of cancer have an outcome no different from grade 3; moreover, pure grade 3 cancer almost never metastasizes and is reasonable to treat by active surveillance, which has sparked speculation about whether it should even be labeled cancer (Oncology (Williston Park) 2014;28:22, Curr Opin Urol 2015;25:238)
- Divisions of Gleason score 3+4=7 from 4+3=7 and of 8 from 9-10, which had often been bundled together for prognostic and research purposes, are supported by studies showing significantly different outcomes (J Clin Oncol 2009;27:3459, World J Urol 2014;32:1067, J Urol 2015;194:91)
- Percentage of grade 4 or 5, when heterogeneous grades are present, should be mentioned in all specimens, although biopsy and prostatectomy have different rules for scoring (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:e87)
- Grade group 4 is heterogeneous as it includes 4+4=8, 3+5=8 and 5+3=8, with recent data showing no or minimal long term outcome difference when present as the highest score in biopsy sampling; instead, the presence or absence of cribriform growth of cancer was a significant prognosticator (J Urol 2016;196:1076)
- If tumor is minimal on biopsy (≤ 1 mm), Gleason score does not predict tumor stage and this can be noted on the report (ex: in a minimal focus with pattern 4, rather than doubling to 4+4=8, tumor can be designated on the report as too small for scoring) (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:1634)
- Targeted biopsies detect a higher percentage of pattern 4 than systemic ones and are less likely to be upgraded on prostatectomy (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2019;143:86)
Diagrams / tables
| Evolution of grading of special prostate cancer patterns | |||
| Histologic pattern | 2005 consensus | 2014 consensus | 2019 consensus |
| Branched / undulating glands | Include as Gleason 3 | ||
| Cribriform (under Gleason scheme: mostly 3, sometimes 4) | 4 but can be 3 if much larger than benign gland, round and has loose cells | Always 4 | Always 4 and presence or absence should be specified for 3+4, 4+3 or 4+4 |
| Glomeruloid variant | No consensus, 3 versus 4 | Always 4 | -- |
| Mucinous variant | No consensus, some favored 4 | Depends on growth pattern regardless of mucin; could be 3, 4 or 5 | -- |
| Small cell (pure) | Do not grade | -- | -- |
| Intraductal, pure form | -- | Do not grade | Do not grade |
| Intraductal, associated with invasive cancer | -- | -- | Include in estimating the percentage of grade 4, instead of keeping it separate |
| Ductal | 4+4=8 | -- | -- |
| Adenoid cystic / basal cell carcinoma | -- | Do not grade | Do not grade |
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Discontinued Gleason grades 1 and 2
- It was agreed at the 2014 consensus conference that Gleason grades 1 and 2 should be discontinued because grade 1 or 2 cancer in needle biopsy does not predict better prostatectomy findings than grade 3 and these grades show marked interpathologist variability
- Gleason score of 1+1=2 was originally described as single, separate, closely packed, uniform round glands arranged in a circumscribed nodule with pushing borders; many of such cases would, with the benefit of today's immunostains, be referred to as atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH or adenosis)
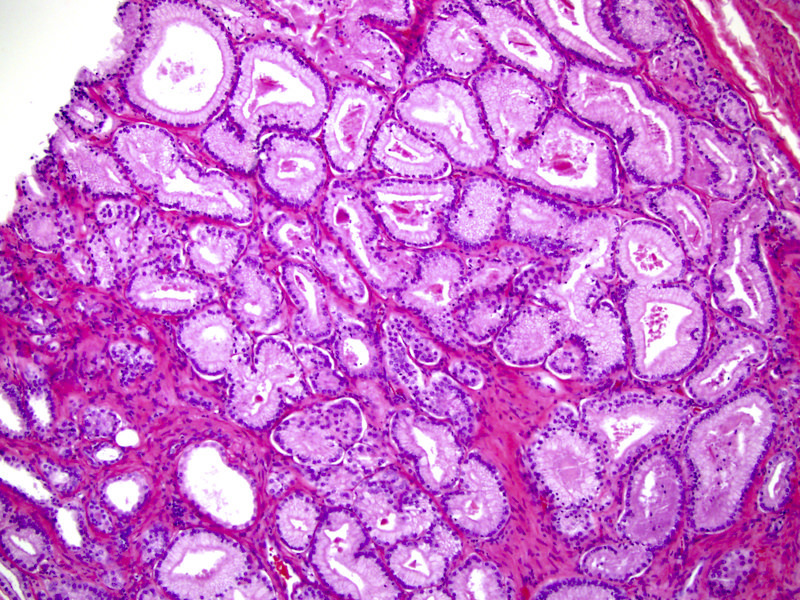
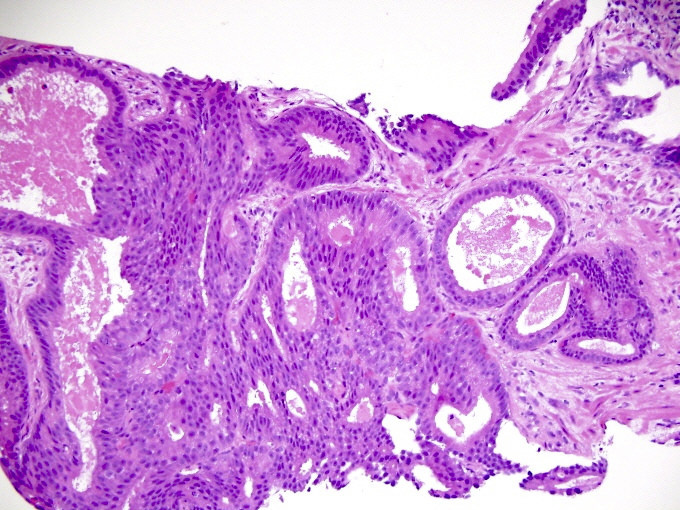
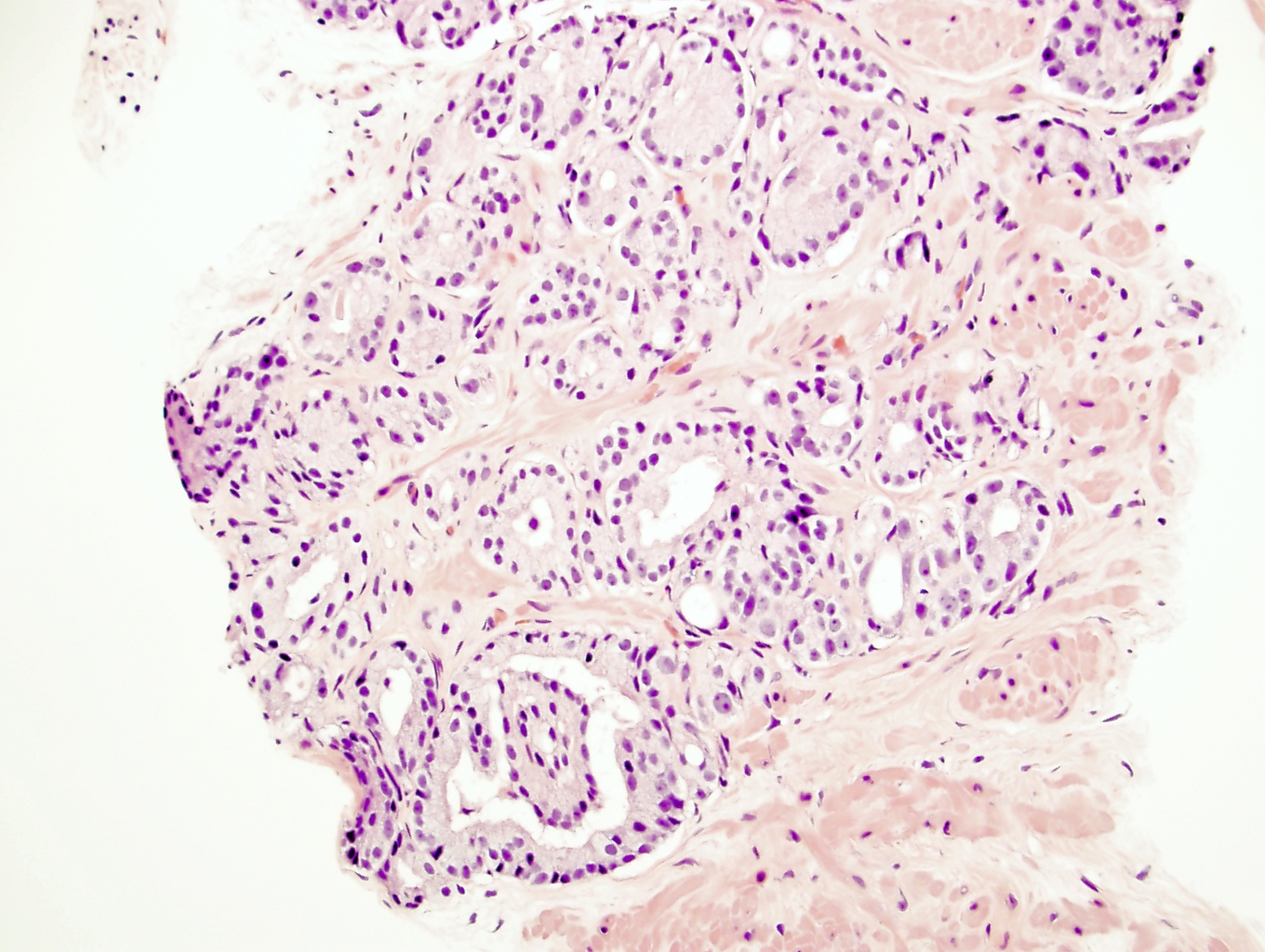
- Gleason grade 3
- Single, separate glands
- May be either minute or large and cyst-like; glands have an irregularly separated, ragged, poorly defined edge, looser than a nodule and are infiltrative
- Key feature is retention of at least a wisp of stroma intervening between neighboring glands
- Tangentially cut glands may appear as if they are poorly formed but should not get graded as a 4 unless poorly formed and fused glands persist on several levels (J Urol 2011;186:465)
- Patterns of Gleason grade 3 prostatic adenocarcinoma:
- Most common pattern is well formed, relatively uniform glands infiltrating between benign glands; glands may be angulated or compressed, separated by > 1 gland diameter
- Small glands with pinpoint lumina, glands still separate
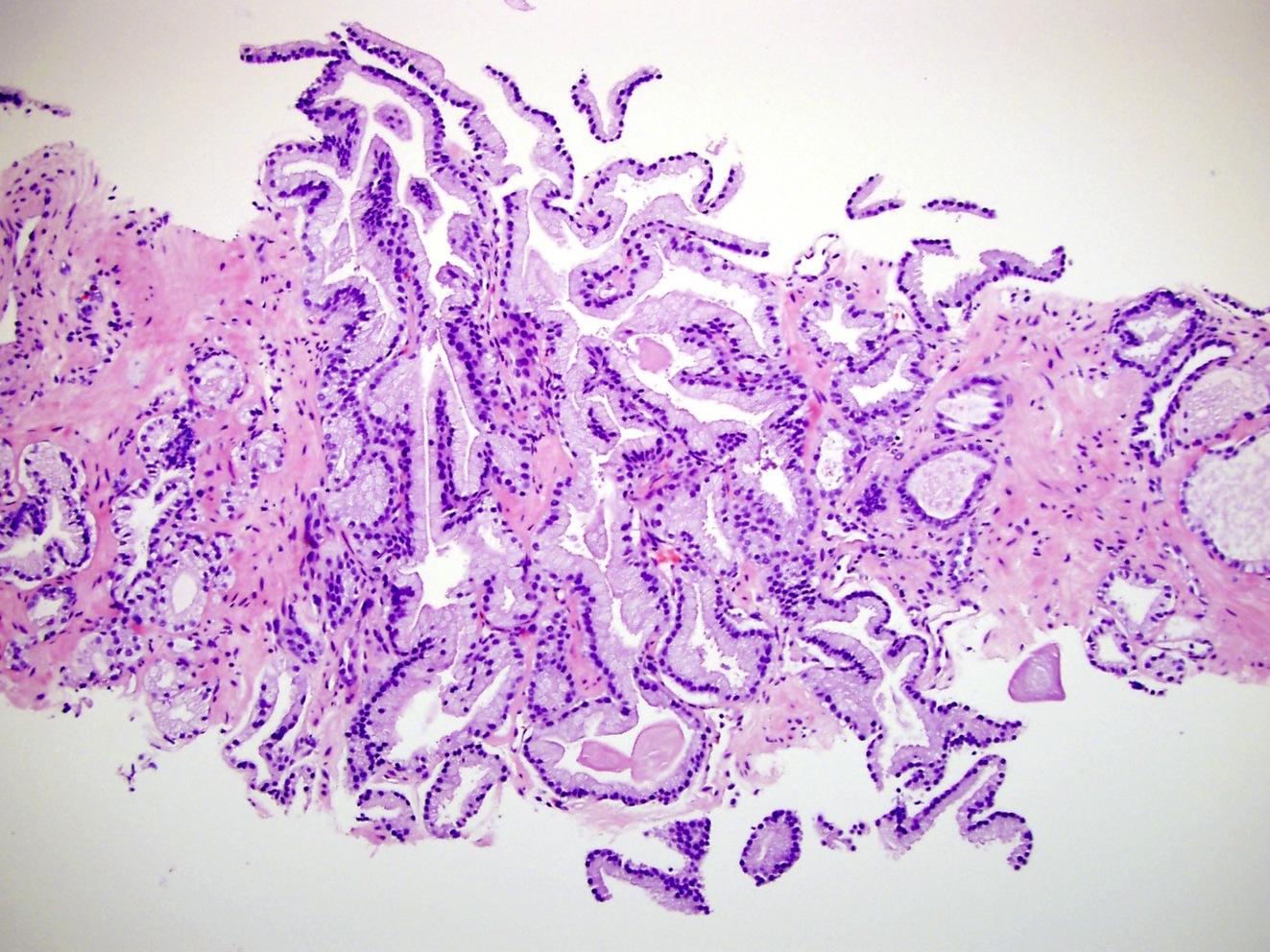
- Medium sized glands with undulating luminal contours or large glands or branching
- Large glands with a pseudoatrophic appearance
- Cribriform cancer no longer qualifies as Gleason 3, even if the glands are similar in size to normal glands (J Urol 2010;183:433)
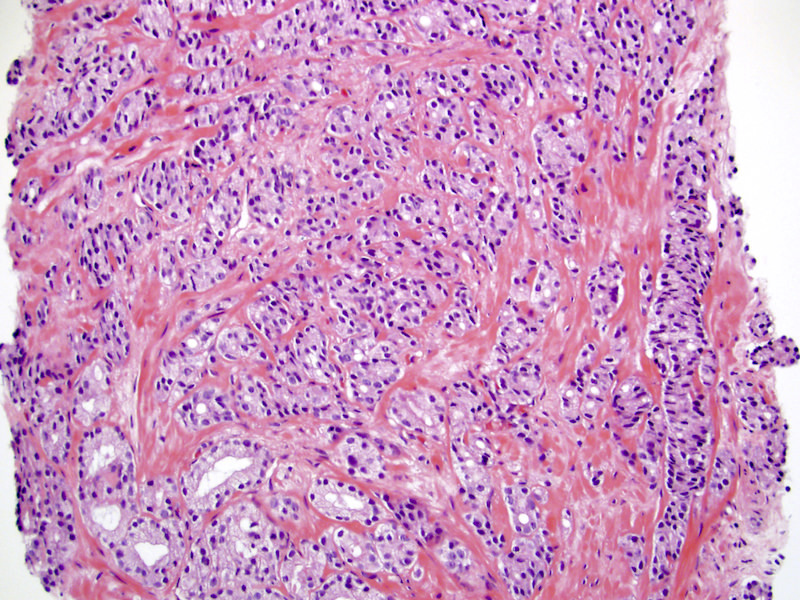
- Gleason grade 4
- Key finding is coalescent or fused glands with > 1 lumen and absence of intervening stroma between adjacent glands
- Patterns of Gleason grade 4 prostatic adenocarcinoma:
- Most common is small acinar structures, some with well formed lumina, fusing into cords or chains; may be undergraded as Gleason 3
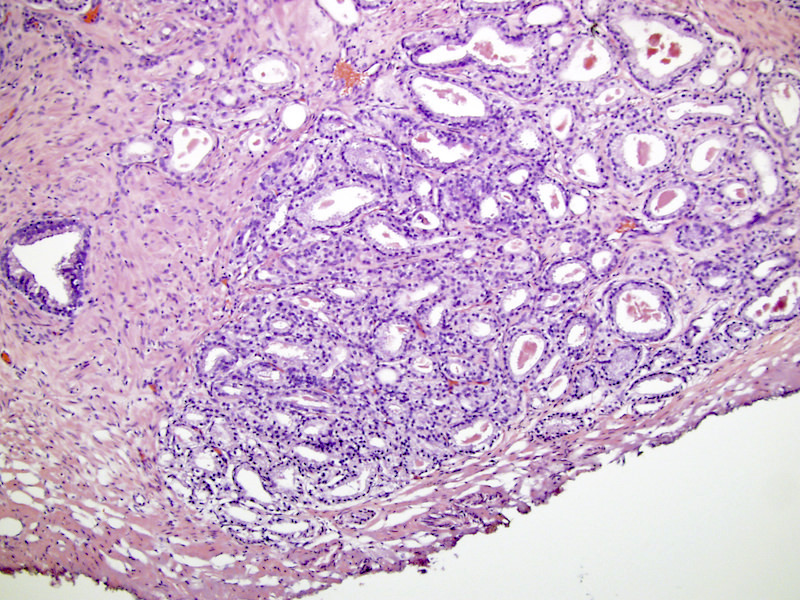
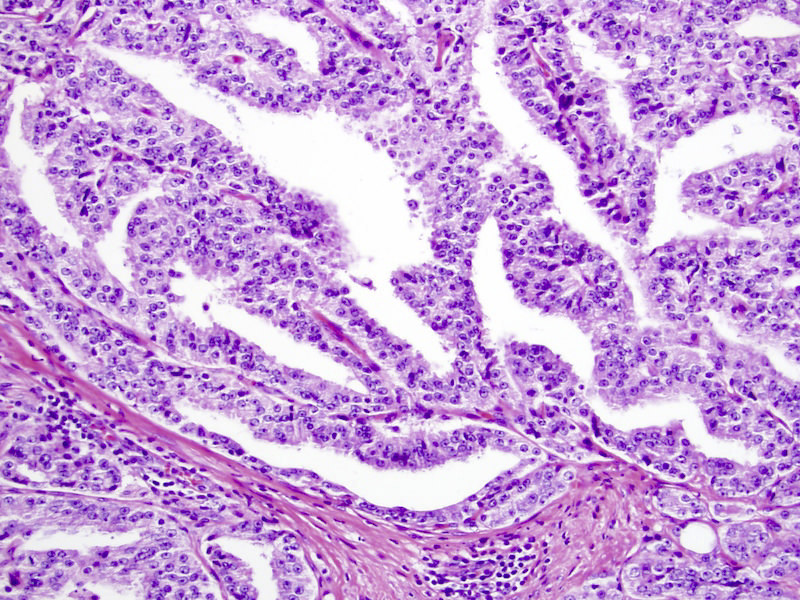
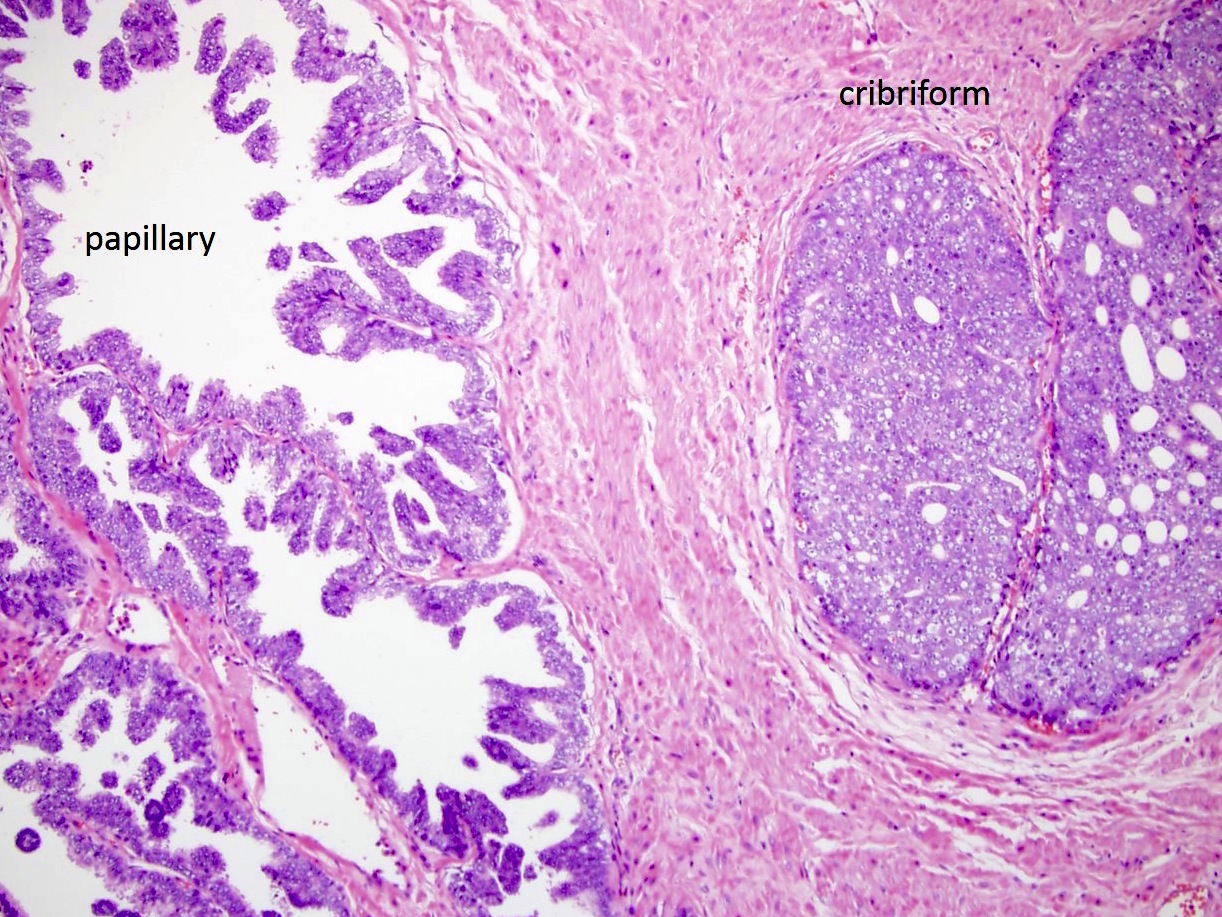
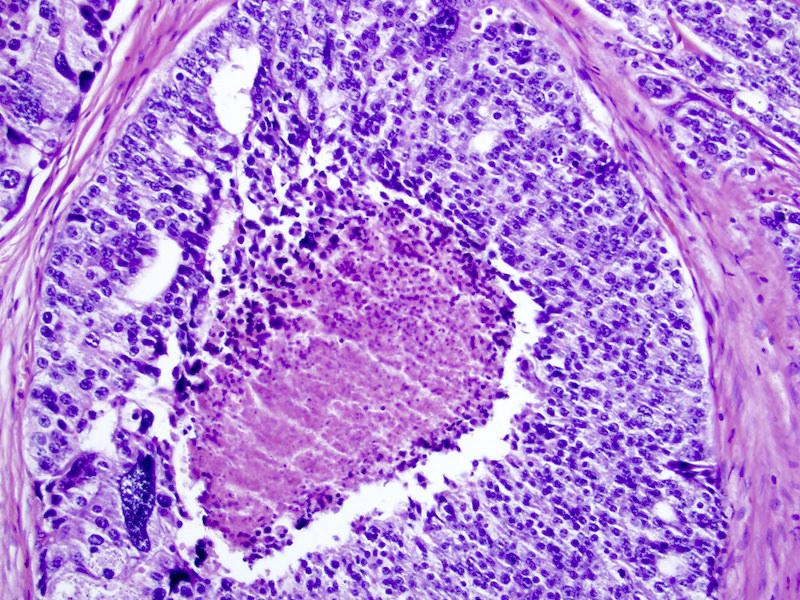
- Cribriform (often merging with papillary, see Microscopic (histologic) images) by consensus has a confluent sheet of contiguous malignant epithelial cells with multiple glandular lumina that are easily visible at low power (objective magnification 10x); there should be no intervening stroma or mucin separating individual or fused glandular structures (Ann Diagn Pathol 2021;52:151733, Am J Surg Pathol 2021;45:1118)
- Nodule of a cribriform gland should be larger than normal prostate gland
- Large nodules of cribriform Gleason 4 lack supporting stroma and tend to fragment
- Thus, fragments of cribriform glands on needle biopsy represent Gleason 4
- Hypernephroid pattern, with nests of clear cells resembling renal cell carcinoma; small, hyperchromatic nuclei; fusion of acini into more solid sheets with the appearance of back to back glands without intervening stroma
- Intraductal carcinoma, when admixed with invasive carcinoma, should be counted as Gleason 4 and not counted separately for quantitation purposes (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:e87)
- Its presence and significance should be mentioned
- This emphasizes the adverse influence which has a unique phenotype of certain driver mutations as shown by Khani et al. (J Pathol 2019;249:79)
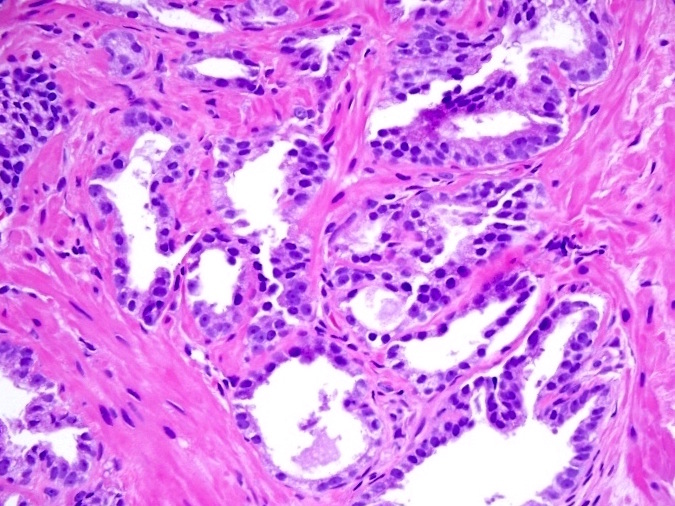
- Glomeruloid pattern (2014 consensus), a rare small cribriform variant, contains a tuft of cells that is mostly detached from its surrounding duct space except for a single point of attachment (see Microscopic (histologic) images)
- Research and 2014 consensus support grading all cribriform cancer as Gleason 4 because the presence and amount of cribriform cancer carries a distinctly adverse prognosis for recurrence and for death from cancer (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1855, Am J Clin Pathol 2011;136:98, Mod Pathol 2015;28:457, Adv Anat Pathol 2018;25:31, Surg Pathol Clinics 2018;11:687)
- Its presence or absence in Gleason 4 cancer should be commented on (J Urol 2016;196:1076)
- Note: patients with Gleason 8 at biopsy may have Gleason 7 at prostatectomy due to unsampled Gleason 3
- Note: basal cell markers are crucial in distinguishing cribriform high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, cribriform intraductal carcinoma and invasive cribriform carcinoma
- Rarely, pure intraductal carcinoma occurs in biopsy specimens
- Rare in totally embedded prostatectomies as shown by Robinson (J Urol 2010;184:1328)
- In its pure form it should not be graded (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:e87)
- Diagnosis of intraductal carcinoma has modest reproducibility (Ann Diagn Pathol 2014;18:333, Virchows Arch 2019;474:525)
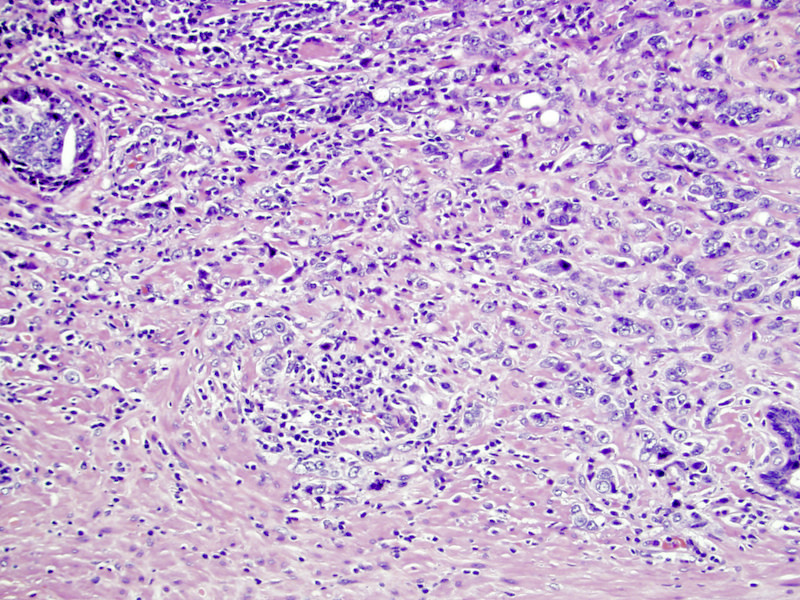
- Gleason grade 5
- Grade 5 has 2 patterns:
- Comedonecrosis: central necrosis with intraluminal necrotic cells or karyorrhexis within papillary / cribriform spaces; caution should be exercised since many such foci have demonstrable basal cells, making them intraductal carcinoma instead; thus, immunostaining is recommended if this would alter the grade group (Histopathology 2019;74:1081, Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1036)
- Single cells, possibly forming cords, possibly with vacuoles (signet ring cells) but without glandular lumens; this pattern may mimic lymphocytes at low power
- Gleason 5 pattern has moderately good reproducibility, although certain patterns are more problematic (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1242)
- Gleason 5 cancer is often missed or underdiagnosed on needle biopsy (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2011;4:468, Urology 2012;79:178)
- Presence of Gleason grade 5 in prostate biopsy specimens predicts higher rates of metastasis and death compared with Gleason 4+4=8 cancer and even the smallest amounts of 5 predict outcome after prostatectomy (J Urol 2015;194:91, World J Urol 2014;32:1067, Eur Urol 2018;73:674)
- Grade 5 has 2 patterns:
Microscopic (histologic) images
Virtual slides
Sample pathology report
- Prostate, left lateral, prostate needle core biopsy:
- Prostatic adenocarcinoma, Gleason score 4+3=7 (Grade group 3) involving 2 of 4 cores and 30% of the tissue (40%, 2 mm and 20%, 4 mm) (60% of the tumor is Gleason pattern 4, not cribriform)
- Prostate, radical prostatectomy:
- Prostatic adenocarcinoma, Gleason score 3+3=6 with tertiary 4 (Grade group 1) (Gleason pattern 3=96% and pattern 4=4%) (see synoptic report)
Board review style question #1
Per the 2019 ISUP consensus conference, a prostate biopsy report for high grade cancer must include
- A case level global Gleason score
- A grade if the entire cancer focus consists of perineural invasion
- Both a primary and secondary grade for tumor measuring less than 1 mm
- For Gleason grade 4, a mention of whether or not cribriform / large gland pattern is present
- Gleason grades 1 and 2, if present
Board review style answer #1
D. For Gleason grade 4, a mention of whether or not cribriform / large gland pattern is present. By consensus, the presence of cribriform carcinoma should be reported. Gleason grades 1 and 2 are discontinued. Grading is not recommended for perineural invasion because perineural invasion distorts gland morphology (grade 3 looks like 4). For tumor that is 1 mm or less, only 1 grade needs to be assigned, avoiding doubling Gleason 4 to 4+4=8, which would be misleading if cancer in other cores is mostly Gleason 3. A case level global score is optional.
Comment Here
Reference: Gleason grading
Comment Here
Reference: Gleason grading
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2
B. Entirely Gleason 4 cancer. The tumor consists entirely of ragged and fused glands. Discrete, round to angulated gland spaces, separated by stroma, diagnostic of Gleason 3 are not present. Single cells without glandular lumen formation, diagnostic of Gleason 5 are not present.
Comment Here
Reference: Gleason grading
Comment Here
Reference: Gleason grading