Table of Contents
Definition / general | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Arora K. Foamy gland adenocarcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/prostatefoamy.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
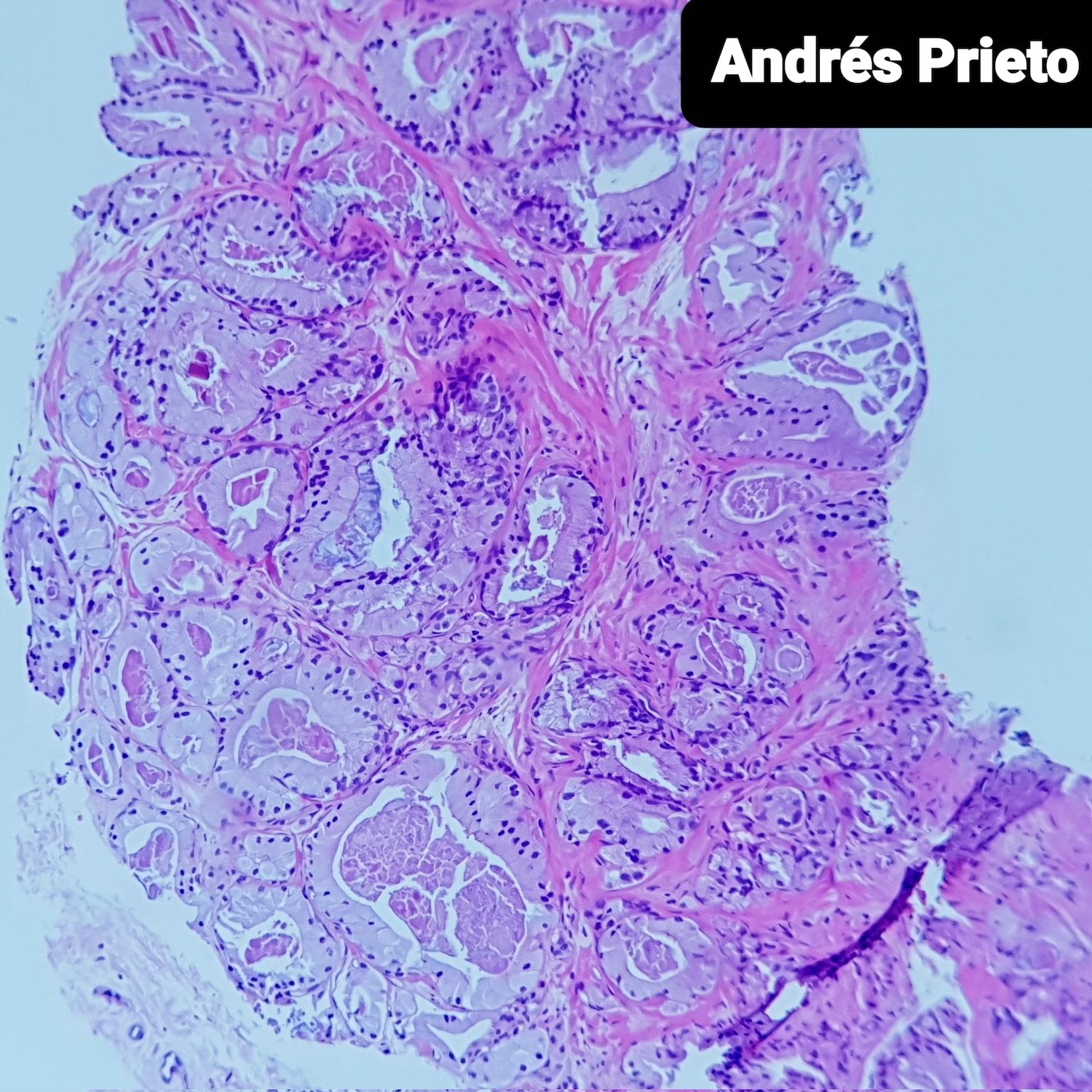
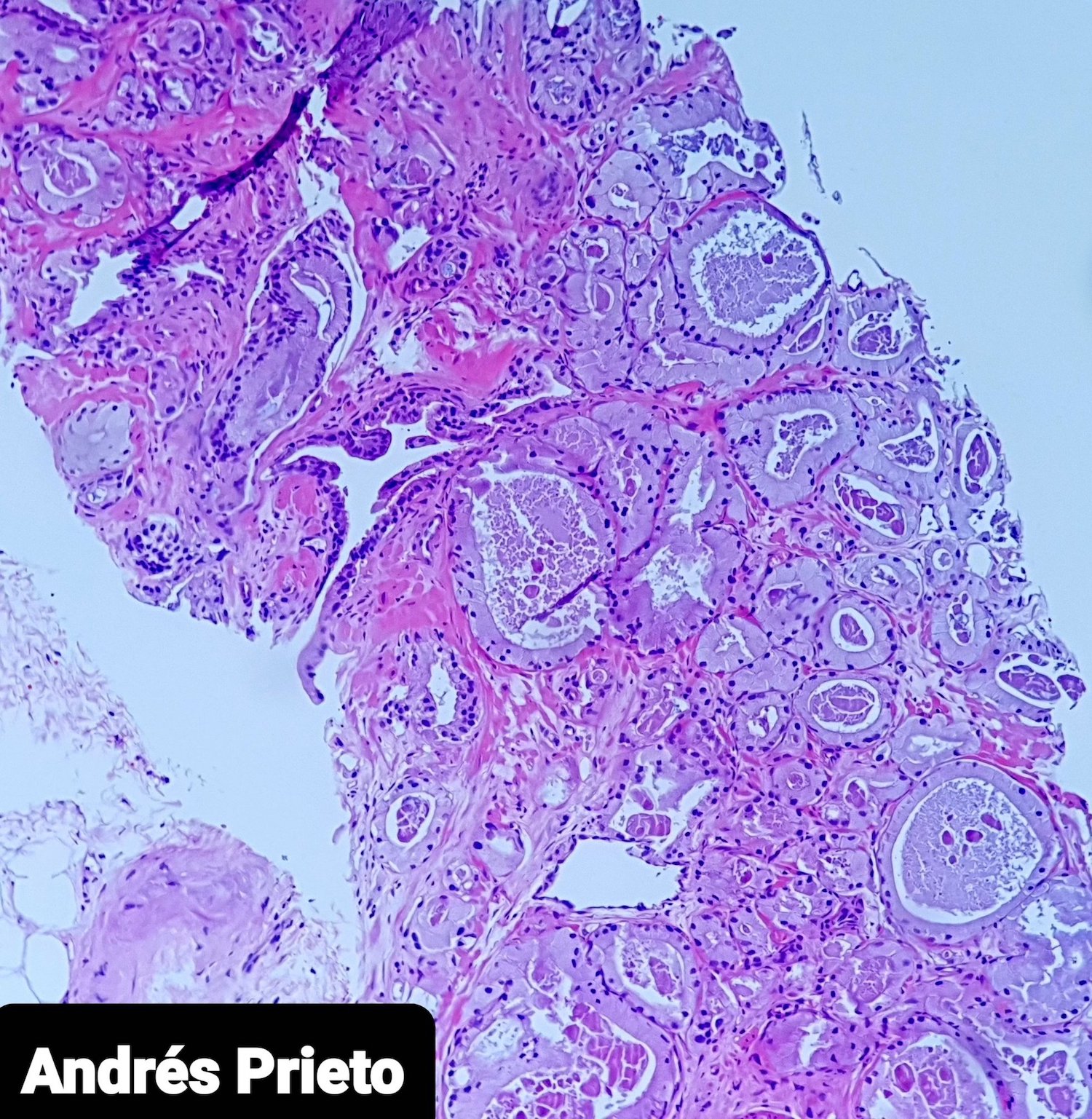
- Rare variant with abundant foamy cytoplasm and minimal cytologic atypia (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:618, Am J Surg Pathol 1996;20:419, Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:616)
- Usually large volume, bilateral, extraprostatic extension
- Foamy appearance due to intracytoplasmic vesicles, not lipid or neutral mucin
- Aggressive behavior despite its benign histologic appearance
Microscopic (histologic) description
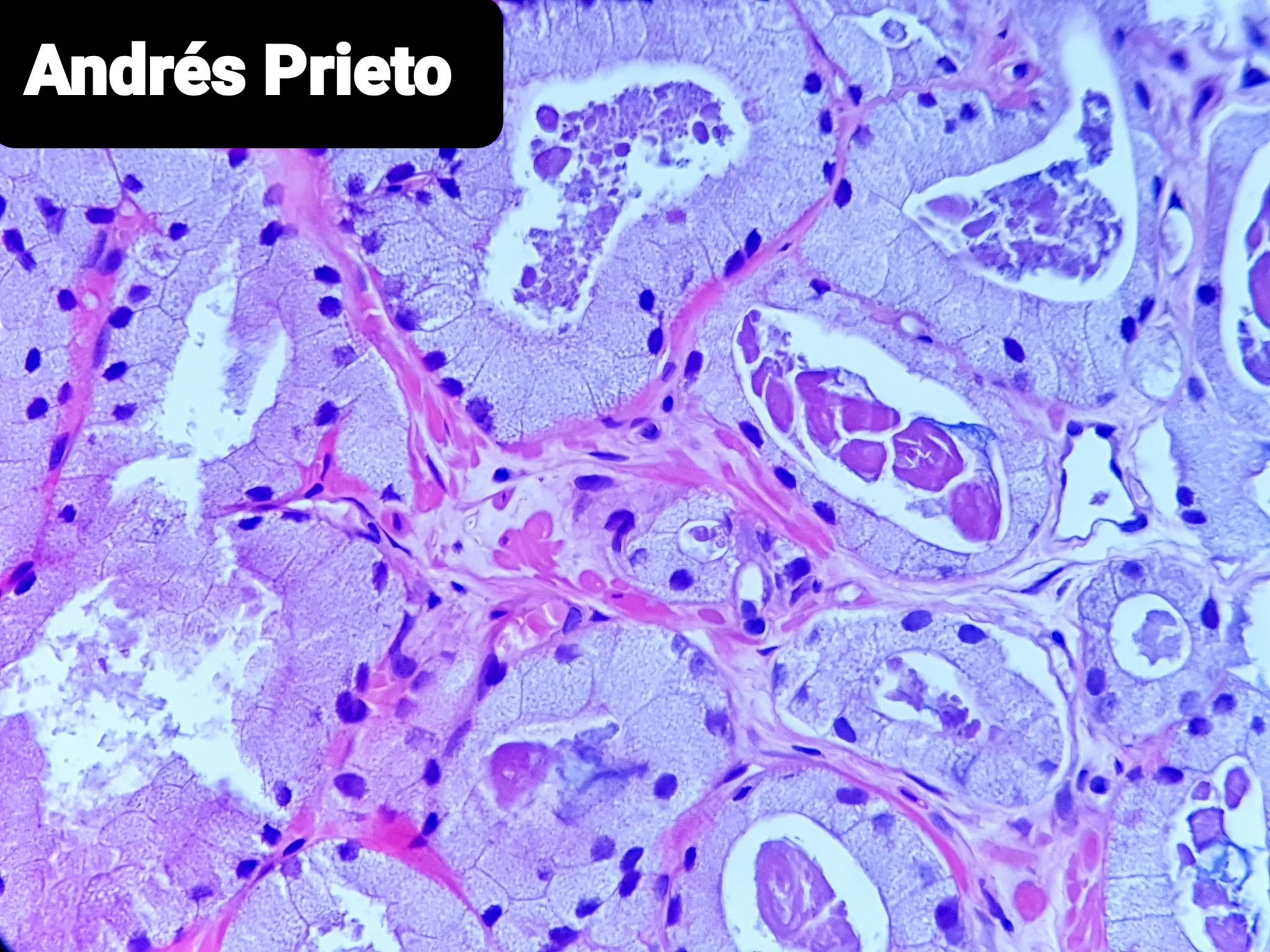
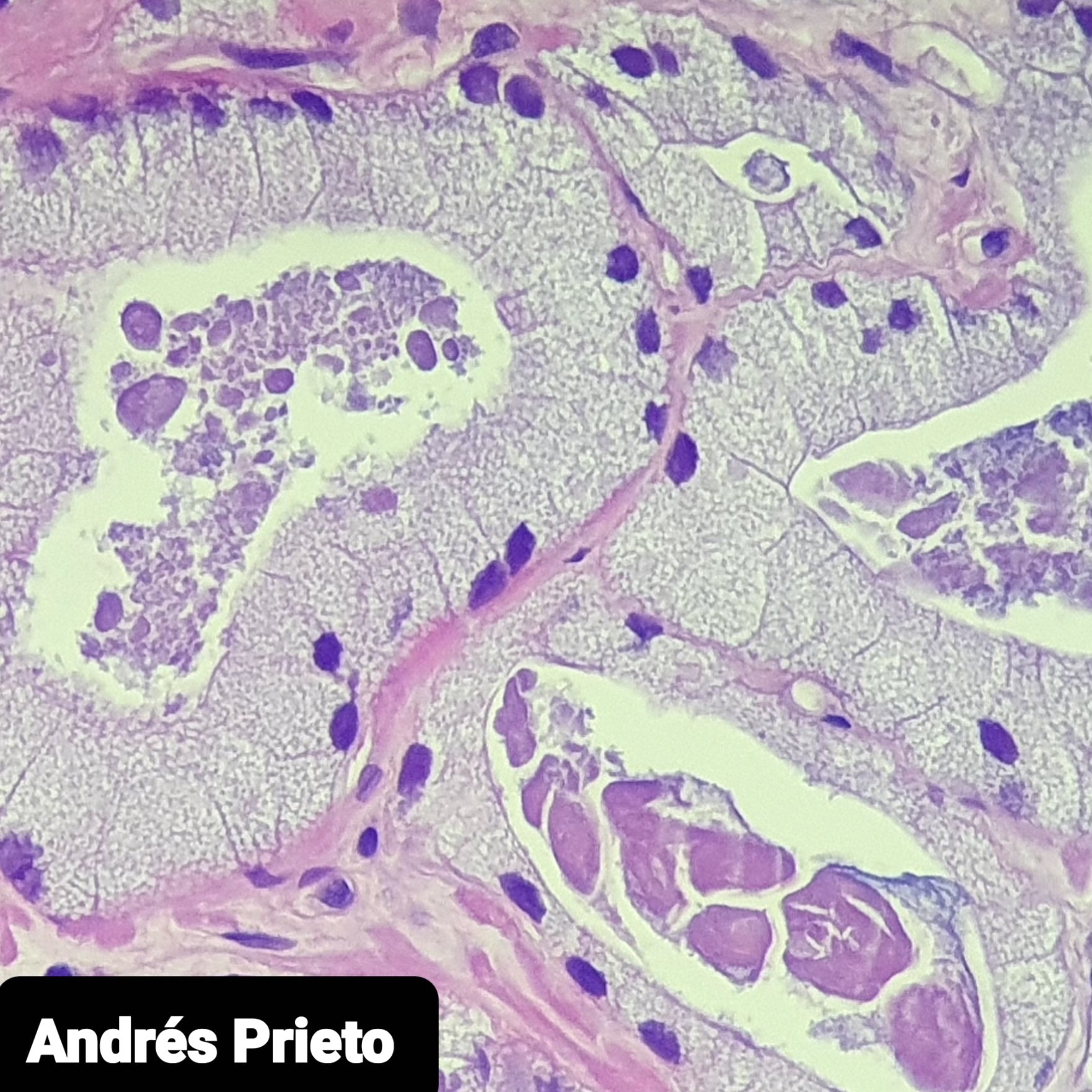
- Abundant xanthomatous cytoplasm, small hyperchromatic nuclei, minimal / no atypia, pink luminal secretions
- Hyperchromatic nuclei may make nucleoli difficult to see
- Cytoplasm differs between malignant and benign glands
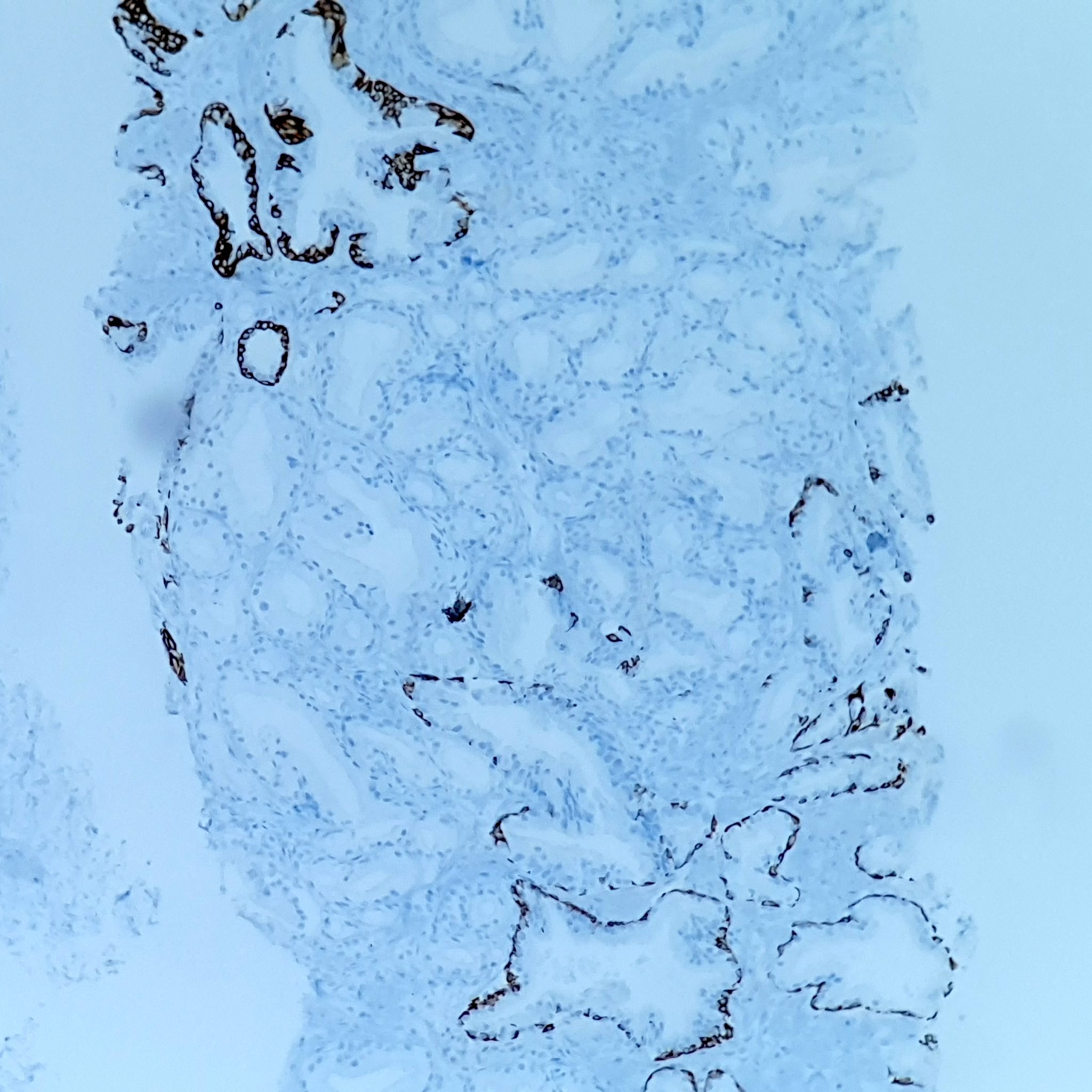
- No obvious basal layer compared to normal glands
- Foamy morphology comprises most of cancer
- Usually Gleason score 3+3=6, occasionally Gleason 7 or higher (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:583)
- Needle biopsies may have only a few atypical foamy glands (Ann Diagn Pathol 2008;12:349)
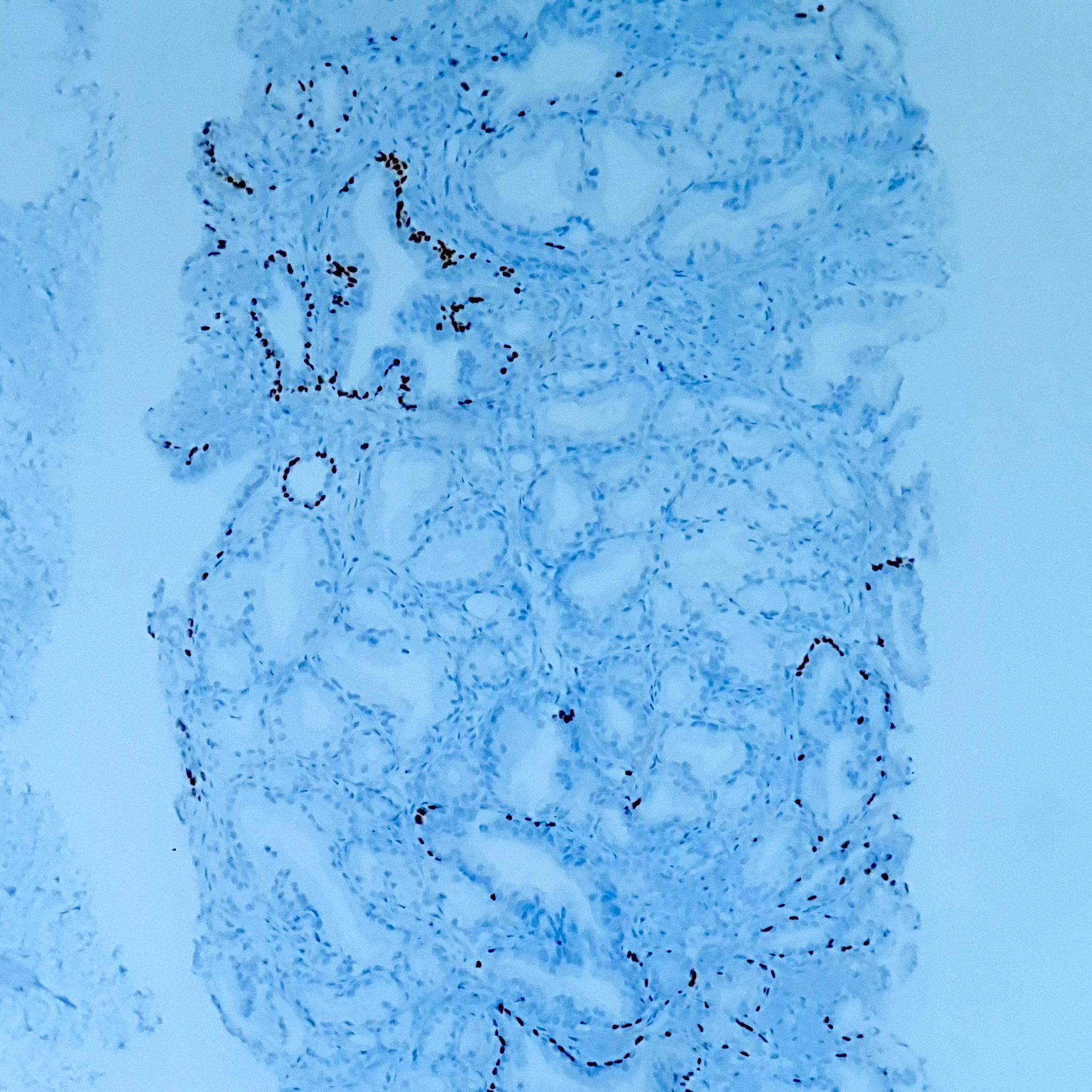
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Colloidal iron
- Alcian blue
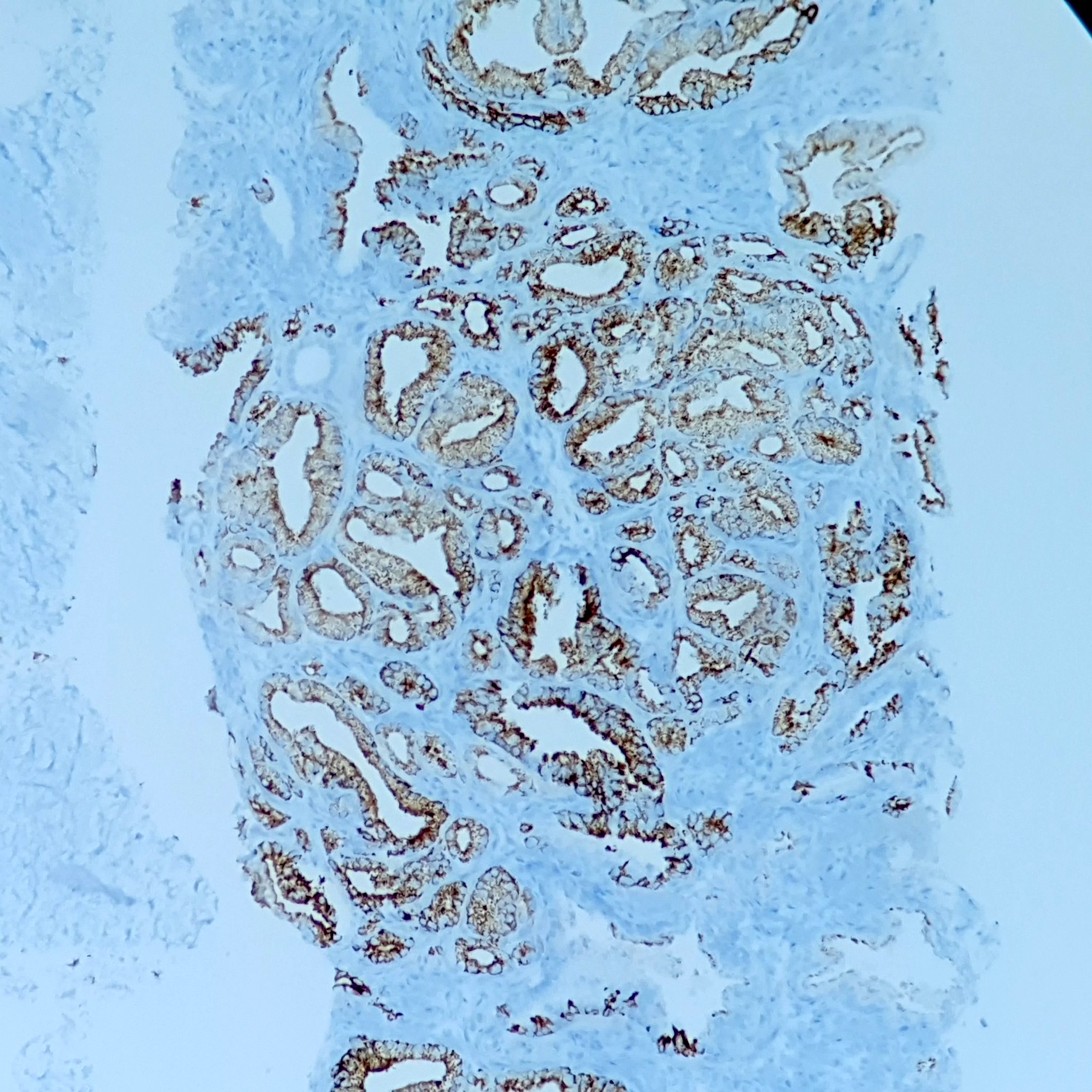
- P504S (Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:772)
Negative stains
- Mucicarmine
- PAS
- Lipid
Electron microscopy description
- Intracytoplasmic vesicles
- Polyribosomes
Differential diagnosis
- Clear cell cribriform hyperplasia: basal cells readily identified
- Cowper's glands: ducts often embedded in skeletal muscle
- Gleason hypernephroid pattern 4: cytoplasm is optically clear but not foamy
- Mucinous metaplasia: focal, cells positive for mucicarmine, PAS